European driving licence
The European driving licence is a driving licence which replaced the various driving licence styles formerly in use in the member states of the European Economic Area (EEA). The licence is currently issued by all of the EEA member states; all 27 EU member states and three EFTA member states; Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway. It is credit card-style with a photograph and a microchip. They were introduced to replace the 110 different plastic and paper driving licences of the 300 million drivers in the EEA. The main objective of the licence is to reduce the risk of fraud.
| European driving licence | |
|---|---|
| Issued by | |
| First issued | 29 July 1991 |
| Purpose | Access to unified driving licence in any of the EEA member states |
| Valid in | The European Economic Area |
| Eligibility | EEA residency |

A driving licence issued by a member state of the EEA is recognised throughout the EEA and can be used as long as it is valid, the driver is old enough to drive a vehicle of the equivalent category, and the licence is not suspended or restricted and has not been revoked in the issuing country. If the holder of an EEA driving licence moves to another EEA country, the licence can be exchanged for a driving licence from the new EEA country. However, as all EEA driving licences are recognised throughout the EEA, it is usually not necessary to exchange it.[1]
The exception is for those holding EEA driving licences issued in exchange for a non‑EEA licence. When holding a converted licence, one should not assume the licence can be exchanged when moving to another EEA country. This only applies when permanently relocating to a different EEA country. As a tourist, an EEA-licence issued in exchange of a non-EEA licence is recognised throughout the EEA.[1]
History
1980–1996
The first step to a European driving licence was taken on 4 December 1980, when the Council of Ministers adopted Council Directive 80/1263/EEC on the introduction of a Community driving licence, which established a Community model national licence that guaranteed the mutual recognition by the Member States of national licences. It also established the practice of exchange of licences by holders moving from one Member State to another.
1996–2013
| European Union directive | |
 | |
| Title | Council Directive on driving licences |
|---|---|
| Made by | Council of the European Union |
| Made under | Art. 75 TEC |
| Journal reference | L237, pp 1–24 |
| History | |
| Date made | 29 July 1991 |
| Came into force | 24 August 1991 |
| Implementation date | 1 July 1996 |
| Other legislation | |
| Replaces | Directive 80/1263/EEC |
| Replaced by | Directive 2006/126/EC |
| Repealed | |
On 29 July 1991, the Council of Ministers adopted the Council of the European Union Directive 91/439/EEC on driving licences. The directive required EU Member States to adopt laws implementing the directive before 1 July 1994, which took effect on 1 July 1996. Directive 80/1263/EEC was repealed on the same date. Directive 91/439/EEC specified the European Union driving licence until its repeal on 19 January 2013.
Provisions
The Council of the European Union Directive 91/439/EEC harmonised the categories of driving licences among the Member States and established two Community driving licence models, one paper version and one plastic card version. It furthermore established an obligatory test of knowledge (theory) and a test of skills and behaviour (practical) which had to be successfully passed before an individual is offered a driving licence. It also required an applicant to meet the minimum standards of physical and mental fitness to drive. The directive specified the minimum ages for driving different types of vehicles, and established progressive access in categories A, C, and D, from light vehicles to larger or more powerful vehicles. The directive stipulated that it is mandatory to have the normal residence in the Member State issuing the licence.[2]
Amendments
The Directive was substantially amended by nine directives and two acts of accession. The plastic card version of the Community licence model, for example, was added to the Directive by Council Directive 96/47/EC of 23 July 1996.[3]
Since 2013
| European Union directive | |
| Text with EEA relevance | |
 | |
| Title | Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council on driving licences (Recast) |
|---|---|
| Made by | European Parliament & Council |
| Made under | Art. 71 TEC |
| Journal reference | L403, pp. 18–60 |
| History | |
| Date made | 30 December 2006 |
| Came into force | 19 January 2007 |
| Implementation date | 19 January 2013 |
| Other legislation | |
| Replaces | Directive 91/439/EEC |
| Current legislation | |
In March 2006, the Council of Ministers adopted a Directive proposed by the European Commission to create a single European driving licence to replace the 110 different models in existence throughout the EU/EEA at the time.[4][5] The European Parliament adopted the Directive in December 2006.[6] Directive 2006/126/EEC was published in the Official Journal of the European Union on 30 December 2006.[7] Its provisions took effect on 19 January 2013; Directive 91/439/EEC was then concurrently repealed.
Provisions
The licence is a credit-card-style, single plastic-coated document, very difficult to counterfeit. The document is renewable every 10 or 15 years depending on the member state. Several member states have the option to include a microchip containing information about the card holder on the card.
Some categories like C and D are issued for five years only. After expiration, a medical check-up is necessary in order to renew the licence for another five years.
EEA relevance
The provisions of Directive 2006/126/EC mention that it has European Economic Area (EEA) relevance, meaning that its provisions apply to all 28 EU member states, as well as Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway, through incorporation into the agreement on the EEA.[8] The Directive was incorporated into the EEA agreement through Decision of the EEA Joint committee No 29/2008 of 14 March 2008 amending Annex XIII (Transport) to the EEA Agreement,[9] with some adaptions. For instance shall, according to the Decision, the distinguishing sign of the EFTA State issuing the licence be encircled by the ellipse referred to in Article 37 of the U.N Vienna Convention on Road Traffic, instead of being printed in negative in a blue rectangle encircled by twelve yellow stars (the European flag).[9]
Although Switzerland is a member state of EFTA, it is not a contracting party of EEA Agreement. Switzerland is instead linked to the EU by a series of bilateral agreements and has generally adopted much of the harmonised EU legislation with regard to driving licences. Switzerland has used the EU system of vehicle categories since the 2000s, and Swiss driving licences are EEA-style credit-card licences.
Implementation
The directive stipulated that all 31 EEA members states must have adopted laws implementing the directive no later than 19 January 2011. Those laws took effect in all EEA members states on 19 January 2013. All licences issued before that date will become invalid by 2033.
Brexit
The UK left the EU on 1 February 2020, starting a transition period terminating on 31 December 2020 in accordance with the withdrawal agreement.[10] EU law continued to apply to the UK during the transition period and UK driving licences were valid in the EU and, EU driving licences were valid in the UK until 31 December 2020. UK licence holders living in the EU were advised to switch their UK driving licence for a local one before the transition period ended.[11][12][13] The EU flag was removed from UK driving licences when the transition period ended.[14]
From 1 January 2021, UK driving licence holders are still able to use their driving licence to drive in the EU for short visits, although with some exceptions.[15][16] International Driving Permits, governed by treaties such as the Geneva Convention on Road Traffic and Vienna Convention on Road Traffic, as well as arrangements within the Common Travel Area facilitates driving possibilities between the UK and the EU/EEA countries in those cases. Depending on which convention the country in question has ratified, a 1949 IDP (Geneva Convention) might be required in some EEA countries, and a 1968 IDP (Vienna Convention) in other EEA countries. However, none of the EEA countries currently require IDPs for visitors staying shorter than 12 months.[13]
Standard data field labelling
To help users of different languages to understand what each of the data fields on the licence contains, they are labelled with a number. A legend is usually supplied on the reverse of the card in the issuing authority's language.
- surname
- given name[a]
- date of birth, place of birth[d]
- a) date of issue, b) date of expiry, c) issuing authority, d) personal number[b]
- licence number
- photograph of holder
- signature of holder
- Address[c]
- licence categories
- first issuing date of the category
- expiry date of the category
- restrictions (number coded)
- space reserved for the possible entry by the host Member State of information essential for administering the licence[17] (barcode (personal number))
- space reserved for the possible entry by the Member State which issues the licence of information essential for administering the licence or related to road safety (optional).
Notes
- aThough the EU directive states this to be other names, local variations may occur
- bThe addition of the personal number is a local variation. 4(d) is optional and should be a number other than the one listed under number 5
- cThe address is optional and not implemented by all countries
- dNorway[18] and Sweden:[19] a hyphen (-) is shown in lieu of place of birth.
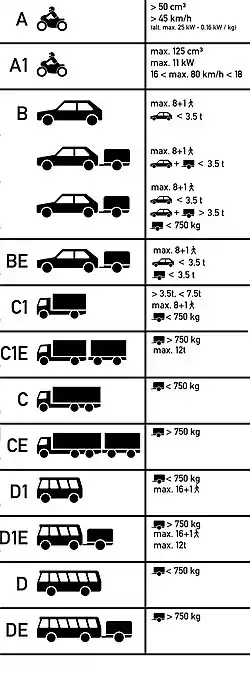
Categories valid in all EEA member states
| Class | Description | Age of acquisition | Requires | Includes | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mopeds | ||||||
| AM | Two-wheel vehicles or three-wheel vehicles with a maximum design speed of not more than 45 kilometres per hour (28 mph) and with a cylinder capacity not exceeding 50 cubic centimetres (3.1 cu in). | 16 years (15 years in Austria, Denmark, Finland, Czech Republic, Slovenia, Spain and Sweden, 14 years in Estonia, Latvia, France, Italy, Poland, and Hungary). | Until 19 January 2013 this class was called "M" in Bulgaria, Finland, Germany, Iceland, Ireland, and Norway. | |||
| Motorcycles | ||||||
| A1 | Motorcycles with a cylinder capacity not exceeding 125 cubic centimetres (7.6 cu in) and a power not exceeding 11 kilowatts (15 hp); and motor tricycles with a power not exceeding 15 kilowatts (20 hp). | 16 years. (17 years in the UK, 18 years in Denmark, Greece, Belgium, and the Netherlands). | AM, (also T in Finland) | B licence holders in Czech Republic (only motorcycles with automatic transmission), Greece (with addition of Code 121, thus only Greek licenses), Italy, Latvia, Malta (after a training of 10 hours), Slovakia (after two years and only motorcycles with automatic transmission), Spain (after three years), Poland (after three years), Portugal (at least 25 years old or additional licence for mopeds), and Belgium (after two years) are allowed to drive motorcycles not exceeding 125 cubic centimetres (7.6 cu in) within the respective countries. In Austria (after five years, training of 6 hours), France (after two years, a training of 7 hours), Germany (after 5 years, training of 9x1,5 hours) and Luxembourg (after two years, training of 7 hours), a practical training without exam is needed for B licence holders. | ||
| A2 | Motorcycles of a power not exceeding 35 kilowatts (47 hp) and with a power/weight ratio not exceeding 0.2 kilowatts per kilogram (0.12 hp/lb) and not derived from a vehicle of more than double its power. | 18 years. (19 years in the UK, 20 years in Denmark, Greece, and the Netherlands). | A1, AM, (also T in Finland) | Replaced class "A" on 19 January 2013 in Malta.[22] | ||
| A | Any motorcycle or motor tricycle not in category A1/A2 | 20 years. (21 years in the UK, 22 years in Denmark, Greece, and the Netherlands). However, access to the driving of motorcycles of this category shall be subject to a minimum of two years' experience on motorcycles under an A2 licence. This requirement as to previous experience may be waived if the candidate is at least 24 years old. | A2, A1, AM, (also T in Finland) | B licence holders who are at least 21 years of age are allowed to drive motor tricycles (including three-wheeled motorcycles with a power exceeding 15 kilowatts (20 hp) in the following countries: France, Germany, Austria, Czech Republic, Finland, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Spain and Poland (after three years of B licence). In France, a practical training (at least 7 hours) without an exam is needed for B licence holders who want to drive motor tricycles only, and this option is available only after at least two years of B licence. In the Netherlands it's allowed to drive from the age of at least 18, and if you had your driving licence B before 19 January 2013.[23] Replaced class "A+" on 19 January 2013 in Malta.[24] | ||
| Motor vehicles | ||||||
| B | Motor vehicles with a maximum authorised mass (MAM) not exceeding 3,500 kilograms (7,700 lb) and designed and constructed for the carriage of no more than eight passengers in addition to the driver; motor vehicles in this category may be combined with a trailer having a maximum authorised mass which does not exceed 750 kilograms (1,650 lb). You can also tow heavier trailers if the total MAM of the vehicle and trailer isn't more than 3,500 kilograms (7,700 lb).
The limit in the first condition is: 3,500 kilograms (7,700 lb) + 750 kilograms (1,650 lb)= 4,250 kilograms (9,370 lb). The limit for in the second condition is: 2,500 kilograms (5,500 lb) + 1,000 kilograms (2,200 lb)= 3,500 kilograms (7,700 lb). |
18 years (17 years in the UK, Ireland and Hungary) [25] Iceland, Germany, and Netherlands (under supervision, from age of 18 without supervision). | 17 in Austria after 3000 km of driving under supervision. | AM (some countries), S, (F and G in Croatia). In some countries, holders of a B driver licence are also entitled (sometimes with special conditions) to ride motorcycles <= 125 centimetres (49 in) and power <= 11 kilowatts (15 hp) and ratio power/weight <= 0.1 kilowatts per kilogram (0.061 hp/lb) | Does not include S in Norway. | |
| BE | Without prejudice to the provisions of type-approval rules for the vehicles concerned, a combination of vehicles consisting of a tractor vehicle in category B and any number of trailers or semi-trailer wheres the maximum authorised mass of the trailer(s) or semi-trailer(s) do not exceed 3,500 kilograms (7,700 lb). | 18 years (17 years in the UK and Ireland). | B | Includes T in Norway and Poland. | ||
| B1 | Heavy quadricycles | 16 years | AM | This class is optional, i.e. it is not implemented by all countries. | ||
| Large goods vehicle | ||||||
| C1 | Large goods vehicle with a maximum authorised mass of not more than 7.5 tonnes (7.4 long tons; 8.3 short tons); with or without a trailer with a maximum mass of less than 750 kilograms (1,650 lb). | 18 years | B | |||
| C1E | Combinations of vehicles where the tractor vehicle is in category C1 and its trailer(s) or semi-trailer(s) have a maximum authorised mass of over 750 kilograms (1,650 lb), and the combined mass of the tractor vehicle and trailer(s) do not exceed 12,000 kilograms (26,000 lb). | 18 years | C1 | BE | ||
| C | Large goods vehicle with a maximum authorised mass of more than 3.5 tonnes (3.4 long tons; 3.9 short tons) mass and not more than 8 + 1 seats (lorry); with a trailer with a maximum mass of 750 kilograms (1,650 lb). | 21 years (18 years in Sweden, Finland, UK and Ireland; 18 years in Germany for non-commercial use only except for apprenticeship as professional driver; 18 years in Belgium for professional drivers) | B for 1 year, not including restricted licence | C1 | ||
| CE | Other combinations of vehicles and trailers which with combined maximum authorised mass of more than 750 kilograms (1,650 lb). | 21 years (18 years in Belgium for professional drivers) | C | BE, C1E, T | ||
| Buses | ||||||
| D1 | Light buses with a maximum of 16 + 1 seats, maximum length of 8 metres (26 ft). | 21 years (18 years in Belgium for professional drivers) | B | Motor vehicles designed and constructed for the carriage of no more than 16 passengers in addition to the driver.; motor vehicles in this category may be combined with a trailer having a maximum authorised mass not exceeding 750 kilograms (1,650 lb). | ||
| D1E | Combinations of vehicles where the tractor vehicle is in category D1 and its trailer(s) or semi-trailer(s) have a maximum authorised mass of over 750 kilograms (1,650 lb), and the combined mass of the tractor vehicle and trailer(s) do not exceed 12,000 kilograms (26,000 lb). | 21 years (18 years in Belgium for professional drivers) | D1 | |||
| D | Vehicles with more than 8 + 1 seats (buses). | 24 years (21 years in Ireland; 21 years in Belgium for professional drivers) | B (C for 2 years in Bulgaria) | D1 | Motor vehicles designed and constructed for the carriage of more than eight passengers in addition to the driver; motor vehicles which may be driven with a category D licence may be combined with a trailer having a maximum authorised mass which does not exceed 750 kilograms (1,650 lb). Includes articulated buses (at least in the UK and in Germany).[26] | |
| DE | Combinations of vehicles where the tractor vehicle is in category D and its trailer has a maximum authorised mass of over 750 kilograms (1,650 lb). | 24 years (21 years in Ireland; 21 years in Belgium for professional drivers) | D | D1E | ||
National categories in EEA member states
There are other national categories for tractors, large motorcycles, motorised wheel boats, motor tricycles (modern voiturettes, Category B1 or S), and military categories such as for driving tanks. National categories mean they are not harmonised and only valid within the issuing country. The tables below are general descriptions that do not include full details of regulations.
Austria
| Class | Description | Age minimum | Valid in |
|---|---|---|---|
| F | Tractor | 16 | Austria |
Belgium
| Class | Description | Age minimum | Included in |
|---|---|---|---|
| G | Agricultural vehicles | 16 | Licences B, B+E, C1, C1+E, C or C+E
(only for agricultural vehicles with the same maximum authorised mass as the vehicles you have a licence for) |
Bulgaria
In 2013 the driving licence category Tтб was phased out and incorporated into the D category. Trolleybus drivers are now required to possess a D category driving licence and to complete additional training on a trolleybus. Entitlement to drive a trolleybus is specified on the driving licence by a code 103.
| Class | Description | Age minimum | Valid in |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tкт | Tractor | 16 | Bulgaria |
| Tтб | Trolleybus | 24 | |
| Tтм | Tram | 24 | |
Croatia
| Class | Description | Age minimum | Valid in |
|---|---|---|---|
| F | Tractor – with or without a trailer | 16 | Croatia |
| G | Heavy equipment | 16 | |
| H | Tram | 21 | |
Czech Republic
| Class | Description | Age minimum | Valid in |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | Tractor | 17 | Czech Republic |
Denmark
| Class | Description | Age minimum | Valid in |
|---|---|---|---|
| LK | Small moped | Denmark | |
| TM | Tractor | 16 | |
Germany
| Class | Description | Age minimum | Valid in |
|---|---|---|---|
| BF17 | Begleitetes Fahren (accompanied driving) – BF17 licensed driver must be accompanied by B-licence holder age 30+ | 17 | Germany, Austria[27] |
| L | Tractor not exceeding 40 km/h by design (with trailer attached: max. 25 km/h) | 16 | Germany |
| T | Tractor | 16 | |
Hungary
| Class | Description | Age minimum | Valid in |
|---|---|---|---|
| M | Moped | 14 | Hungary |
| K | Two-wheel tractor | 16 | |
| T | Tractor – with maximum 2 trailer | 16 | |
| TR | Trolleybus | 20 | |
| V | Tram | 20 | |
Ireland
| Class | Description | Age minimum | Valid in |
|---|---|---|---|
| W | Work Vehicle – includes land tractors with or without a trailer | 16 | Ireland |
Latvia
| Class | Description | Valid in |
|---|---|---|
| TRAM | Tram | Latvia |
| TROL | Trolleybus | |
Norway
| Class | Description | Age minimum | Valid in |
|---|---|---|---|
| S | Snowmobile | 16 | Norway |
| T | Tractor | 16 | |
Poland
| Class | Description | Age minimum | Valid in |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | Tractor | 16 | Poland |
Slovenia
| Class | Description | Age minimum | Valid in |
|---|---|---|---|
| F | Tractor | 16 | Slovenia |
Gallery
| Country | Code | Driving licence in accordance with
Directive 80/1263/EEC or 91/439/EEC |
Driving licence in accordance with Directive 2006/126/EC
(Issued since 19 January 2013 (in Croatia since 1 July 2013)) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Austria | A |  |  |
| Belgium | B | .jpg.webp)
|

|
| Bulgaria | BG | ||
| Croatia | HR |   |   |
| Cyprus | CY | ||
| Czech Republic | CZ | ||
| Denmark | DK | 
|
Link to image |
| Estonia | EST | ||
| Finland | FIN |  
| |
| France | F |  |  |
| Germany | D |   |   |
| Greece | GR |  | |
| Hungary | H | ||
| Iceland | IS |  | |
| Ireland | IRL |  | |
| Italy | I | _back.jpg.webp) _front.jpg.webp) | .jpg.webp) .jpg.webp) |
| Latvia | LV | ||
| Liechtenstein | FL | ||
| Lithuania | LT | ||
| Luxembourg | L | ||
| Malta | M | ||
| Netherlands | NL | Link to image | |
| Norway | N |  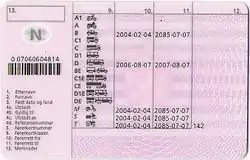 | Link to image |
| Poland | PL | 
|
 |
| Portugal | P | ||
| Romania | RO | 
| |
| Slovakia | SK | ||
| Slovenia | SLO | ||
| Spain | E |  | |
| Sweden | S | Link to image |
See also
Notes
- The legal acquis is marked as EEA-relevant by the EU, and is incorporated into the EEA Agreement (by Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway).
References
- "Driving licence recognition and validity". Europa.eu. Retrieved 27 December 2018.
- European Commission website – Transport: driving licence Archived 7 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- "Consolidated version of Directive 91/439/EEC as of 18 July 2008". europa.eu.
- "Klartecken för EU-körkort". Svenska Dagbladet. Archived from the original on 11 October 2006. Retrieved 27 March 2006.
- "EU backs European driving licence". BBC News. 27 March 2006. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- "EU announces plans for European driving license". Workpermit.com. 18 December 2006.
- "DIRECTIVE 2006/126/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL". Official Journal of the European Union.
- "32016L1106 – European Free Trade Association – European Free Trade Association". Efta.int.
- https://www.efta.int/media/documents/legal-texts/eea/other-legal-documents/adopted-joint-committee-decisions/2008%20-%20English/029-2008.pdf
- Asa Bennett (27 January 2020). "How will the Brexit transition period work?". Telegraph.
- Ó Scannáil, Mícheál (23 December 2019). "Explainer: Why Irish citizens are advised to ditch their British driving licence ahead of Brexit". Independent. Ireland. Retrieved 1 December 2019.
- "Driving in the EU from 1 January 2021: UK licence holders living in the EU". GOV.UK. Retrieved 30 January 2020.
- https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-47459859
- https://www.whatdotheyknow.com/request/630879/response/1500846/attach/4/FOIR%208148%20Declan%20Hayden.pdf?cookie_passthrough=1
- "Brexit: What are the rules on driving in the EU after transition?". BBC News. 27 December 2020. Retrieved 29 December 2020.
- "Visit Europe from 1 January 2021". GOV.UK. Retrieved 29 December 2020.
- Directive 2006/126/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 December 2006 on driving licences
- "Nytt norsk førerkort : fra 19. januar 2013" (PDF). Vegvesen.no. Retrieved 27 December 2018.
- "Föreskrifter om ändring i Transportstyrelsens föreskrifter (TSFS 2012:60) om körkortets utformning och innehåll" (PDF). Transportstyrelsen.se. Retrieved 27 December 2018.
- "DIRECTIVE 2006/126/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL" (PDF). Official Journal of the European Union.
- "Press Release: Changes to the Minimum Ages and Test Requirements to obtain a Driving Licence". Transport Malta.
- "Wanneer mag ik op een trike rijden?".
- "Press Release: Changes to the Minimum Ages and Test Requirements to obtain a Driving Licence". Transport Malta.
- "Kørekort til 17-årige (Ledsagerordningen)". Sikkertrafik.dk.
- "INF30 – Requirements for towing trailers in Great Britain – GOV.UK" (PDF). Web.archive.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 October 2013.
- "Ist Begleitetes Fahren mit 17 im Ausland erlaubt?". Focus.de.
- "Polisen.ax – Körkort". Polisen.ax.
External links
- "EU announces plans for European driving license". Workpermit.com. 18 December 2006. Retrieved 27 December 2018.
- "EU driving licence coming in 2013". News.bbc.co.uk. 14 December 2006. Retrieved 27 December 2018.
- "Vehicles you can drive". Gov.uk. Retrieved 27 December 2018.
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)


