Ferdinand VII of Spain
Ferdinand VII (Spanish: Fernando; 14 October 1784 – 29 September 1833) was the King of Spain during the early- to mid-19th century. He reigned over the Spanish Kingdom in 1808 and again from 1813 to his death in 1833. He was known to his supporters as el Deseado (the Desired) and to his detractors as el Rey Felón (the Felon King).
| Ferdinand VII | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
_-_Prado.jpg.webp) Ferdinand VII in Court Dress by Goya, 1815 | |||||
| King of Spain (more...) | |||||
| 1st reign | 19 March 1808 – 6 May 1808 | ||||
| Predecessor | Charles IV | ||||
| Successor | Joseph I | ||||
| 2nd reign | 11 December 1813 – 29 September 1833 | ||||
| Predecessor | Joseph I | ||||
| Successor | Isabella II | ||||
| Titular Emperor of Mexico (Treaty of Cordoba) | |||||
| Reign | 28 September 1821 – 18 May 1822 | ||||
| Successor | Agustin I | ||||
| Titular King of Chile (1812 Chilean Constitution) | |||||
| Reign | 27 October 1812 – 6 October 1813 | ||||
| Titular King of Cundinamarca (1811 Constitution of Cundinamarca) | |||||
| Reign | 4 April 1811 – 19 September 1812 | ||||
| Titular King of the United Provinces of the Río de La Plata (Provisional Statute of the Superior Government of the United Provinces of Río de la Plata in the Name of the Lord Don Ferdinand VII[1]) | |||||
| Reign | 25 May 1810 - 9 July 1816 | ||||
| Born | 14 October 1784 El Escorial, Spain | ||||
| Died | 29 September 1833 (aged 48) Madrid, Spain | ||||
| Burial | |||||
| Spouses | |||||
| Issue see detail... | Isabella II of Spain Infanta Luisa Fernanda, Duchess of Montpensier | ||||
| |||||
| House | Bourbon | ||||
| Father | Charles IV of Spain | ||||
| Mother | Maria Luisa of Parma | ||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism | ||||
| Signature | 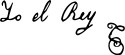 | ||||
Born in Madrid at El Escorial, Ferdinand VII spent his youth as heir apparent to the Spanish throne. Following the 1808 Tumult of Aranjuez, he ascended the throne. That year Napoleon overthrew him; he linked his monarchy to counter-revolution and reactionary policies that produced a deep rift in Spain between his forces on the right and liberals on the left. Back in power in December 1813, he reestablished the absolutist monarchy and rejected the liberal constitution of 1812. A revolt in 1820 led by Rafael del Riego forced him to restore the constitution thus beginning the Liberal Triennium: a three-year period of liberal rule. In 1823 the Congress of Verona authorized a successful French intervention restoring him to absolute power for the second time. He suppressed the liberal press from 1814 to 1833, jailing many of its editors and writers.
Under his rule, Spain lost nearly all of its American possessions, and the country entered into a large-scale civil war upon his death. His political legacy has remained contested since his passing, with most historians regarding him as incompetent, despotic, and short-sighted.[2][3]
Early life

Ferdinand was the eldest surviving son of Charles IV of Spain and Maria Luisa of Parma. Ferdinand was born in the palace of El Escorial near Madrid. In his youth Ferdinand occupied the position of an heir apparent who was excluded from all share in government by his parents and their favourite advisor and Prime Minister, Manuel Godoy.[4] National discontent with the government produced a rebellion in 1805.[4] In October 1807, Ferdinand was arrested for his complicity in the El Escorial Conspiracy in which the rebels aimed at securing foreign support from the French Emperor Napoleon.[4] When the conspiracy was discovered, Ferdinand submitted to his parents.
Abdication and restoration

Following a popular riot at Aranjuez Charles IV abdicated in March 1808.[4] Ferdinand ascended the throne and turned to Napoleon for support. He abdicated on 6 May 1808 and thereafter Napoleon kept Ferdinand under guard in France for six years at the Château de Valençay.[5] Historian Charles Oman records that the choice of Valençay was a practical joke by Napoleon on his former foreign minister Talleyrand, the owner of the château, for his lack of interest in Spanish affairs.[6]
While the upper echelons of the Spanish government accepted his abdication and Napoleon's choice of his brother Joseph Bonaparte as king of Spain, the Spanish people did not. Uprisings broke out throughout the country, marking the beginning of the Peninsular War. Provincial juntas were established to control regions in opposition to the new French king. After the Battle of Bailén proved that the Spanish could resist the French, the Council of Castile reversed itself and declared null and void the abdications of Bayonne on 11 August 1808. On 24 August, Ferdinand VII was proclaimed king of Spain again, and negotiations between the council and the provincial juntas for the establishment of a Supreme Central Junta were completed. Subsequently, on 14 January 1809, the British government acknowledged Ferdinand VII as king of Spain.[7]
Five years later after experiencing serious setbacks on many fronts, Napoleon agreed to acknowledge Ferdinand VII as king of Spain on 11 December 1813 and signed the Treaty of Valençay, so that the king could return to Spain. The Spanish people, blaming the policies of the Francophiles (afrancesados) for causing the Napoleonic occupation and the Peninsular War by allying Spain too closely to France, at first welcomed Fernando. Ferdinand soon found that in the intervening years a new world had been born of foreign invasion and domestic revolution.[4] In his name Spain fought for its independence and in his name as well juntas had governed Spanish America. Spain was no longer the absolute monarchy he had relinquished six years earlier. Instead he was now asked to rule under the liberal Constitution of 1812. Before being allowed to enter Spanish soil, Ferdinand had to guarantee the liberals that he would govern on the basis of the Constitution, but, only gave lukewarm indications he would do so.[8]
On 24 March the French handed him over to the Spanish Army in Girona, and thus began his procession towards Madrid.[9] During this process and in the following months, he was encouraged by conservatives and the Church hierarchy to reject the Constitution. On 4 May he ordered its abolition and on 10 May had the liberal leaders responsible for the Constitution arrested. Ferdinand justified his actions by claiming that the Constitution had been made by a Cortes illegally assembled in his absence, without his consent and without the traditional form. (It had met as a unicameral body, instead of in three chambers representing the three estates: the clergy, the nobility and the cities.) Ferdinand initially promised to convene a traditional Cortes, but never did so, thereby reasserting the Bourbon doctrine that sovereign authority resided in his person only.[4]
Meanwhile, the wars of independence had broken out in the Americas, and although many of the republican rebels were divided and royalist sentiment was strong in many areas, the Manila galleons and the Spanish treasure fleets – tax revenues from the Spanish Empire – were interrupted. Spain was all but bankrupt.
Ferdinand's restored autocracy was guided by a small camarilla of his favorites, although his government seemed unstable. Whimsical and ferocious by turns, he changed his ministers every few months. "The king," wrote Friedrich von Gentz in 1814, "himself enters the houses of his prime ministers, arrests them, and hands them over to their cruel enemies;" and again, on 14 January 1815, "the king has so debased himself that he has become no more than the leading police agent and prison warden of his country."[4]
The king did recognize the efforts of foreign powers on his behalf. As the head of the Spanish Order of the Golden Fleece, Ferdinand made the Duke of Wellington, head of the British forces on the peninsula, the first Protestant member of the order.
During the aftermath of the Mexican War of Independence, the general of the Army of the Three Guarantees, Agustin de Iturbide, and Jefe Superior Juan O'Donojú, signed the Treaty of Cordoba, which concluded the war of independence and established the Mexican Empire. They intended to offer the Mexican Imperial Crown to Ferdinand VII, in which he would rule in personal union, but unfortunately, he decreed that it was "void" and stated that no European could accede to the Mexican throne.[10]
Revolt

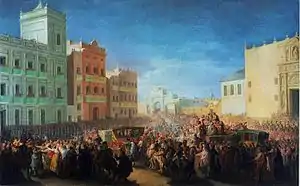
In 1820 a revolt broke out in favor of the Constitution of 1812, beginning with a mutiny of the troops under Col. Rafael del Riego. The king was quickly taken prisoner. Ferdinand had restored the Jesuits upon his return, but now they had become identified with repression and absolutism among the liberals, who attacked them: twenty-five Jesuits were slain in Madrid in 1822. For the rest of the 19th century, expulsions and reinstatements of the Jesuits would continue to be the hallmarks of liberal and authoritarian political regimes, respectively.
At the beginning of 1823, as a result of the Congress of Verona, the French invaded Spain, "invoking the God of St. Louis, for the sake of preserving the throne of Spain to a descendant of Henry IV, and of reconciling that fine kingdom with Europe." When in May the revolutionary party carried Ferdinand to Cádiz, he continued to make promises of amendment until he was free.[4]
When Ferdinand was freed after the Battle of Trocadero and the fall of Cádiz, reprisals followed. The Count of Artois made known his protest against Ferdinand's actions by refusing the Spanish decorations Ferdinand offered him for his military services.[4]
During his last years Ferdinand's political appointments became more stable.[4] The last ten years of reign (sometimes referred to as the Ominous Decade) saw the restoration of absolutism, the re-establishment of traditional university programs and the suppression of any opposition, both of the Liberal Party and of the reactionary revolt (known as "War of the Agraviados") which broke out in 1827 in Catalonia and other regions.
Death and succession crisis
As Ferdinand lay dying, his new wife Maria Christina of Bourbon-Two Sicilies had him set aside the Salic Law which would have made his brother Don Carlos heir to the throne instead of any female. Ferdinand was thus succeeded by his infant daughter Isabella II. Carlos revolted and said he was the legitimate king. Needing support, Maria Christina (as Regent for her daughter Isabella) turned to the liberals. She issued a decree of amnesty on 23 October 1833. Liberals who had been in exile returned and dominated Spanish politics for decades, and the Carlist Wars resulted.[11][12]
Marriages

Ferdinand VII was married four times. In 1802, he married his first cousin Princess Maria Antonia of Naples and Sicily (1784–1806), daughter of Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies and Marie Caroline of Austria. There were no children, because her two pregnancies (in 1804 and 1805) both ended in miscarriages.
In 1816, Ferdinand married his niece Maria Isabel of Portugal (1797–1818), daughter of his older sister Carlota Joaquina and John VI of Portugal. She bore him two daughters, the first of whom lived only five months and the second of whom was stillborn.
In 20 October 1819, in Madrid, Ferdinand married Princess Maria Josepha Amalia of Saxony (1803–1829), daughter of Maximilian, Prince of Saxony, and Caroline of Parma. No children were born from this marriage.
Lastly, on 27 May 1829, Ferdinand married another niece, Maria Christina of the Two Sicilies (1806–1878), daughter of his younger sister Maria Isabella of Spain and Francis I of the Two Sicilies. She bore him two surviving daughters, the older of whom succeeded Ferdinand upon his death.
Issue
| Name | Birth | Death | Burial | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| By Maria Isabel of Portugal (1797–1818) | ||||
| Infanta María Luisa Isabel | 21 August 1817 Madrid | 9 January 1818 Madrid | El Escorial | |
| Infanta María Luisa Isabel | 26 December 1818 Madrid | El Escorial | Stillborn; Maria Isabel died as a result of her birth. | |
| By Maria Christina of the Two Sicilies (1806–1878) | ||||
| Infanta María Isabel Luisa | 10 October 1830 Madrid | 10 April 1904 Paris | El Escorial | Princess of Asturias 1830–1833, Queen of Spain 1833–1868. Married Francis, Duke of Cádiz, had issue. |
| Infanta María Luisa Fernanda | 30 January 1832 Madrid | 2 February 1897 Seville | El Escorial | Married Antoine, Duke of Montpensier, had issue. |
Honours
 Spain:
Spain:
- Knight of the Golden Fleece, 14 October 1784[13]
- Grand Cross of the Order of Charles III, 1784[14]
- Founder and Grand Master of the Military Order of St. Ferdinand, 31 August 1811
- Founder and Grand Master of the Military Order of St. Hermengild, 28 November 1814
- Founder and Grand Master of the Order of Isabella the Catholic, 24 March 1815[15]
.svg.png.webp) Kingdom of Portugal: Grand Cross of the Sash of the Three Orders, 1796[16][17]
Kingdom of Portugal: Grand Cross of the Sash of the Three Orders, 1796[16][17]- France:
.svg.png.webp) Kingdom of Prussia: Knight of the Black Eagle, 3 June 1814[20]
Kingdom of Prussia: Knight of the Black Eagle, 3 June 1814[20] United Kingdom: Knight of the Garter, 10 August 1814[21]
United Kingdom: Knight of the Garter, 10 August 1814[21] Russian Empire:[22]
Russian Empire:[22]
- Knight of St. Andrew, 23 May 1815
- Knight of St. Alexander Nevsky, 23 May 1815
 Denmark: Knight of the Elephant, 29 August 1818[23]
Denmark: Knight of the Elephant, 29 August 1818[23] Austrian Empire: Grand Cross of St. Stephen, 1825[24]
Austrian Empire: Grand Cross of St. Stephen, 1825[24].svg.png.webp) Two Sicilies:[25]
Two Sicilies:[25]
Ancestry
| Ancestors of Ferdinand VII of Spain[26] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- http://www.cedesyc.com.ar/todalahistoria/Estatutoprovicional1810.htm
- Royal Splendor in the Enlightenment: Charles IV of Spain, Patron and Collector. Meadows Museum, SMU. 2010. ISBN 9788471204394.
- Sevilla, Fred (1997). Francisco Balagtas and the Roots of Filipino Nationalism: Life and Times of the Great Filipino Poet and His Legacy of Literary Excellence and Political Activism. Trademark Publishing Corporation.
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. 10 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 267–268.
- Carr, pp 79–85
- Oman, Charles (1902). A History of the Peninsular War. 1. Oxford: Clarendon Press. p. 56.
- Carr, pp 85–90
- Carr, pp 105–119
- Artola, Miguel. La España de Fernando VII. Madrid, Espasa, 1999, 405. ISBN 84-239-9742-1
- "¿Por qué firmaron Iturbide y O'Donojú los Tratados de Córdoba?". www.milenio.com. Retrieved 4 February 2019.
- A. W. Ward; G.P. Gooch (1970). The Cambridge History of British Foreign Policy 1783-1919 (reprint ed.). CUP. pp. 186–87.
- John Van der Kiste (2011). Divided Kingdom: The Spanish Monarchy from Isabel to Juan Carlos. History Press Limited. pp. 6–9. ISBN 9780752470832.
- "Caballeros Existentes en la Insignie Orden del Toison de Oro", Calendario Manual y Guía de Forasteros en Madrid (in Spanish): 40, 1796, retrieved 17 March 2020
- "Caballeros Grandes Cruces Existentes en la Real y Distinguida Orden Española de Carlos Tercero", Calendario Manual y Guía de Forasteros en Madrid (in Spanish): 42, 1796, retrieved 17 March 2020
- "Caballeros Grandes Cruces Existentes en la Real Orden Americana de Isabel la Catolica", Calendario Manual y Guía de Forasteros en Madrid (in Spanish): 52, 1819, retrieved 17 March 2020
- Trigueiros, António Miguel (1999), D. João VI e o seu Tempo (PDF) (in Portuguese), Ajuda National Palace, Lisbon: Portuguese Commission on Discoveries, p. 232, archived from the original (PDF) on 29 October 2013, retrieved 10 May 2020
- Bragança, José Vicente de (2014), A Banda de Grã-Cruz das Três Ordens Militares (in Portuguese), Encontro Europeu de Associações de Falerística, p. 26
- M. & B. Wattel. (2009). Les Grand'Croix de la Légion d'honneur de 1805 à nos jours. Titulaires français et étrangers. Paris: Archives & Culture. p. 446. ISBN 978-2-35077-135-9.
- Teulet, Alexandre (1863). "Liste chronologique des chevaliers de l'ordre du Saint-Esprit depuis son origine jusqu'à son extinction (1578-1830)" [Chronological List of Knights of the Order of the Holy Spirit from its origin to its extinction (1578-1830)]. Annuaire-bulletin de la Société de l'Histoire de France (in French) (2): 113. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- Liste der Ritter des Königlich Preußischen Hohen Ordens vom Schwarzen Adler (1851), "Von Seiner Majestät dem Könige Friedrich Wilhelm III. ernannte Ritter" p. 17
- Shaw, Wm. A. (1906) The Knights of England, I, London, p. 51
- Almanach de la cour: pour l'année ... 1817. l'Académie Imp. des Sciences. 1817. pp. 62, 76.
- Johann Heinrich Friedrich Berlien (1846). Der Elephanten-Orden und seine Ritter: eine historische Abhandlung über die ersten Spuren dieses Ordens und dessen fernere Entwicklung bis zu seiner gegenwärtigen Gestalt, und nächstdem ein Material zur Personalhistorie, nach den Quellen des Königlichen Geheimen-Staatsarchivs und des Königlichen Ordenskapitelsarchivs zu Kopenhagen. Gedruckt in der Berlingschen Officin. pp. 155-156.
- "A Szent István Rend tagjai" Archived 22 December 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- Almanacco della real casa e corte. 1825. pp. 118, 121.
- Genealogie ascendante jusqu'au quatrieme degre inclusivement de tous les Rois et Princes de maisons souveraines de l'Europe actuellement vivans [Genealogy up to the fourth degree inclusive of all the Kings and Princes of sovereign houses of Europe currently living] (in French). Bourdeaux: Frederic Guillaume Birnstiel. 1768. pp. 9, 96.
Works cited
- Carr, Raymond. Spain, 1808–1975 (1982)
- Payne, Stanley G. History of Spain and Portugal: v. 2 (1973) pp 415–36
Further reading
- Clarke, Henry Butler. Modern Spain, 1815–1898 (1906) pp 1–92; old but full of factual detail online
- Fehrenbach, Charles Wentz. "Moderados and Exaltados: The Liberal Opposition to Ferdinand VII, 1814–1823". Hispanic American Historical Review (1970): 52–69. in JSTOR
- Woodward, Margaret L. "The Spanish Army and the Loss of America, 1810–1824". Hispanic American Historical Review (1968): 586–607. in JSTOR
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ferdinand VII of Spain. |
- Historiaantiqua. Fernando VII at Historia Antiqua (in Spanish)
Ferdinand VII of Spain Cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty Born: 14 October 1784 Died: 29 September 1833 | ||
| Regnal titles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Charles IV |
King of Spain 1808 |
Succeeded by Joseph |
| Preceded by Joseph |
King of Spain 1813–1833 |
Succeeded by Isabella II |
| Spanish nobility | ||
| Preceded by Charles (IV) |
Prince of Asturias 1788–1808 |
Vacant Title next held by Isabella (II) |




