Foreign trade of South Africa
Since the end of apartheid foreign trade in South Africa has increased, following the lifting of several sanctions and boycotts which were imposed as a means of ending apartheid.
| Part of a series on |
| World trade |
|---|
 |
South Africa is the second largest producer of gold[1] and is the world's largest producer of chrome, manganese, platinum, vanadium and vermiculite, the second largest producer of ilmenite, palladium, rutile and zirconium.[2] It is also the world's third largest coal exporter.[3] Although, mining only accounts for 3% of the GDP, down from around 14% in the 1980s.[4] South Africa also has a large agricultural sector and is a net exporter of farming products.
Principal international trading partners of South Africa—besides other African countries—include Germany, the United States, China, Japan, the United Kingdom and Spain.[5] Chief exports include corn, diamonds, fruits, gold, metals and minerals, sugar, and wool. Machinery and transportation equipment make up more than one-third of the value of the country's imports. Other imports include chemicals, manufactured goods, and lots more, mainly found in other hot country mainly Spanish countries.
History
During apartheid, South Africa's foreign trade and investment were affected by sanctions and boycotts by other countries ideologically opposed to apartheid. In 1970, the United Nations Security Council, adopted resolution 282 imposing a voluntary arms embargo upon South Africa, and which was extended by subsequent resolutions 418 and 591, declaring the embargo mandatory. In 1978, South Africa was prohibited loans from the Export-Import Bank of the United States which was later followed by a prohibition on IMF loans in 1983. An oil embargo was imposed by OPEC in 1983 which was strengthened by Iran in 1979.

Imports and exports
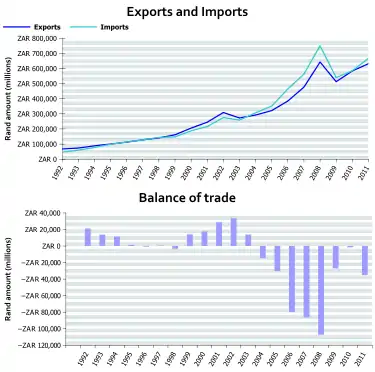
South Africa's main export trading partners are the European Union, the United States, Japan. China's share in exports is increasing, and has risen from 1.7% in 1994 to nearly 11% in 2007.
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
African trade
Almost 90% of South Africa's exports to the rest of Africa go to the SADC economies. In 2018, South Africa exported and imported goods to and from the rest of Africa to the value of US$25 billion and US$11.5 billion, respectively. Intra-Africa exports account for 26% of South Africa's total exports and imports for 12% of total imports for 2018. South African exports to the rest of Africa are predominantly of value-added goods. In terms of South Africa's total trade (exports + imports) with the rest of the continent; Namibia (13%), Botswana (12%), Nigeria (12%) and Mozambique (12%) are South Africa's main African trading partners.[8]
Trade agreements
The following includes a list of existing trade agreements signed by South Africa.
- The African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA)
 EU: Trade Agreement between the European Union (EU) and South Africa
EU: Trade Agreement between the European Union (EU) and South Africa- The Southern African Development Community (SADC) Trade Agreement
- The Generalized System of Preferences
 Zimbabwe: Trade Agreement between Zimbabwe and South Africa
Zimbabwe: Trade Agreement between Zimbabwe and South Africa- Trade Agreement between Southern African Customs Union (SACU) and European Free Trade Association (EFTA) states
- Rules of Origin Guides / Trade Agreements
- Approved Exporter (SAEU, SACU EFTA)
Currently UAE is also one of the most important trade partners with African buyers/importers.
- US-Southern African Customs Union Free Trade Agreement: (US-SAUC; incl.
 South Africa,
South Africa,  Botswana,
Botswana,  Lesotho,
Lesotho,  Eswatini, and
Eswatini, and  Namibia; on hold since 2006 due to US demands on intellectual property rights, government procurement rights and investment)
Namibia; on hold since 2006 due to US demands on intellectual property rights, government procurement rights and investment) - Cape to Cairo free trade area: In June 2011, South Africa and 25 other heads of state in Africa began negotiating the establishment of a free trade area (FTA) which would extend trade concessions beyond the Southern Africa Development Community, opening a trade pathway along the east coast of Africa to Egypt.[9][10] The FTA would include about half of Africa's countries but would not include the Economic Community of West African States.
References
- "Ghana beats South Africa to continent's gold production crown | Automation & AI | Mining Global". www.miningglobal.com. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- Mineral Commodity summaries
- South Africa looks bright
- South Africa, Jobless growth – The Economist
- "South Africa". The World Factbook. CIA.
- "South African EXPORT by Codes". Department of Trade and Industry. 2012. Archived from the original on 14 April 2012. Retrieved 3 April 2012.
- "Rand/US$ exchange value in July 2011". Retrieved 4 April 2012.
- Tralac Center (June 2018). "South Africa: Intra-Africa trade and tariff profile". Tralac. Retrieved 23 October 2019.
- "SA hosts 26 heads of state for 'Cape to Cairo' free trade area". Independent Online. 10 June 2011. Retrieved 10 June 2011.
- "Free trade zone envisioned from Egypt to South Africa, Angola across to Madagascar". The Washington Post. 10 June 2011. Retrieved 10 June 2011.
https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/south-africa/