Glendale, Arizona
Glendale (/ˈɡlɛndeɪl/) is a city in Maricopa County, Arizona, United States, located about nine miles (14 km) northwest from Downtown Phoenix. According to the 2019 U.S. Census estimates, the population of the city is 252,381.[4]
Glendale, Arizona | |
|---|---|
 Downtown Glendale, Arizona, as viewed from the intersection of Glendale Ave. and 58th Ave. | |
 Seal | |
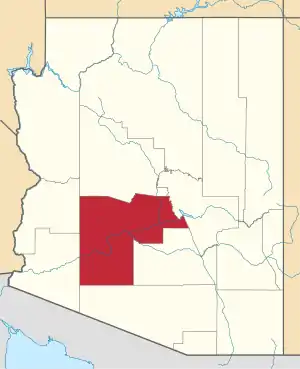
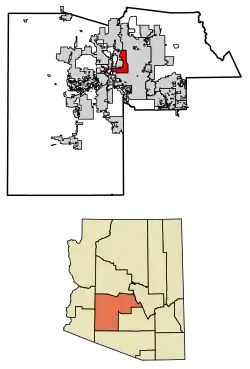 Location of Glendale in Maricopa County, Arizona | |
 Glendale, Arizona Location in the United States  Glendale, Arizona Glendale, Arizona (the United States)  Glendale, Arizona Glendale, Arizona (North America) | |
| Coordinates: 33°32′19″N 112°11′11″W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | Maricopa |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Jerry Weiers (Non-Partisan) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 61.99 sq mi (160.56 km2) |
| • Land | 61.59 sq mi (159.52 km2) |
| • Water | 0.40 sq mi (1.04 km2) |
| Elevation | 1,152 ft (351 m) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 226,721 |
| • Estimate (2019)[4] | 252,381 |
| • Rank | US: 89th |
| • Density | 4,097.63/sq mi (1,582.10/km2) |
| Demonym(s) | Glendalian |
| Time zone | UTC−7 (MST (no DST)) |
| ZIP code | 85301-85318 |
| Area code(s) | 623 and 602 |
| FIPS code | 04-27820 |
| Website | www |
History
In the late 1800s what is now known as Glendale, Arizona, was all desert. William John Murphy, a native of New Hartford, New York, who resided in the town of Flagstaff in what was then known as the territory of Arizona, was in charge of building a 40-mile-long (64 km) Arizona Canal from Granite Reef to New River for the Arizona Canal Company. In 1885, he completed the canal, which would bring water to the desert land.[5] Murphy was deep in debt, since he had agreed to be paid in Arizona Canal Company stock and bonds and land instead of cash.[6]

In 1887, Murphy formed the Arizona Improvement Company. His objective was to sell the land and water rights south of the canal. Murphy raised capital from out of state sources in order to meet payroll and construction expenses.[6] Murphy decided to refer to this land as "Glendale". In order to develop and interest potential investors and settlers in this new town, Murphy decided to provide a better way of access from Phoenix to Glendale and ending in the town of Peoria by building an 18-mile-long (29 km) diagonal road which he named Grand Avenue.
In 1891, Burgess Hadsell worked with Murphy to bring 70 Brethren and River Brethren families to Glendale to form a temperance colony. Soon settlers, attracted by the town's ban on alcoholic beverages, continued to arrive. In 1895, Murphy platted the original town site and amended the plat to include a town park and some business lots. It was bounded by Lamar Road on the south, 55th Avenue on the east, Myrtle Avenue on the north, and 59th Avenue on the west.[7] The construction of a railroad from Prescott to Phoenix was made possible with an exchange of the right-of-way made by Murphy along Grand Avenue.[5] The railroad allowed Glendale settlers to transport goods to the north and easily receive building materials.
The construction and commercial applications of the Beet Sugar Factory in 1906, also contributed to the growth of Glendale. Though the operations of the factory only lasted until 1913, it played an important role in the increase of immigrant and migrant settlers in the city.[8]
Geography
Glendale is located at 33°32′19″N 112°11′11″W (33.538654, −112.186261).[9]
Climate
| Climate data for Phoenix Int'l, Arizona (1981–2010 normals,[lower-alpha 1] extremes 1895–present)[lower-alpha 2] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 88 (31) |
92 (33) |
100 (38) |
105 (41) |
114 (46) |
122 (50) |
121 (49) |
117 (47) |
116 (47) |
107 (42) |
99 (37) |
87 (31) |
122 (50) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 78.7 (25.9) |
82.8 (28.2) |
90.0 (32.2) |
98.6 (37.0) |
105.9 (41.1) |
112.5 (44.7) |
114.4 (45.8) |
112.5 (44.7) |
108.6 (42.6) |
100.1 (37.8) |
88.1 (31.2) |
77.1 (25.1) |
115.2 (46.2) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 67.2 (19.6) |
70.7 (21.5) |
76.9 (24.9) |
85.2 (29.6) |
94.8 (34.9) |
103.9 (39.9) |
106.1 (41.2) |
104.4 (40.2) |
99.8 (37.7) |
88.5 (31.4) |
75.5 (24.2) |
66.0 (18.9) |
86.6 (30.3) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 45.6 (7.6) |
48.7 (9.3) |
53.5 (11.9) |
60.2 (15.7) |
69.4 (20.8) |
77.7 (25.4) |
83.5 (28.6) |
82.7 (28.2) |
76.9 (24.9) |
64.8 (18.2) |
52.7 (11.5) |
44.8 (7.1) |
63.4 (17.4) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 36.2 (2.3) |
39.4 (4.1) |
43.2 (6.2) |
49.5 (9.7) |
58.0 (14.4) |
68.4 (20.2) |
73.7 (23.2) |
73.7 (23.2) |
67.1 (19.5) |
53.6 (12.0) |
40.8 (4.9) |
34.6 (1.4) |
33.5 (0.8) |
| Record low °F (°C) | 16 (−9) |
24 (−4) |
25 (−4) |
35 (2) |
39 (4) |
49 (9) |
63 (17) |
58 (14) |
47 (8) |
34 (1) |
27 (−3) |
22 (−6) |
16 (−9) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.91 (23) |
0.92 (23) |
0.99 (25) |
0.28 (7.1) |
0.11 (2.8) |
0.02 (0.51) |
1.05 (27) |
1.00 (25) |
0.64 (16) |
0.58 (15) |
0.65 (17) |
0.88 (22) |
8.03 (204) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 4.1 | 4.4 | 3.9 | 1.7 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 4.2 | 5.0 | 2.8 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 3.9 | 36.6 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 50.9 | 44.4 | 39.3 | 27.8 | 21.9 | 19.4 | 31.6 | 36.2 | 35.6 | 36.9 | 43.8 | 51.8 | 36.6 |
| Average dew point °F (°C) | 32.4 (0.2) |
32.2 (0.1) |
32.9 (0.5) |
31.6 (−0.2) |
34.3 (1.3) |
39.0 (3.9) |
56.1 (13.4) |
58.3 (14.6) |
52.3 (11.3) |
43.0 (6.1) |
35.8 (2.1) |
33.1 (0.6) |
40.1 (4.5) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 256.0 | 257.2 | 318.4 | 353.6 | 401.0 | 407.8 | 378.5 | 360.8 | 328.6 | 308.9 | 256.0 | 244.8 | 3,871.6 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 81 | 84 | 86 | 90 | 93 | 95 | 86 | 87 | 89 | 88 | 82 | 79 | 87 |
| Source: NOAA (relative humidity and sun 1961–1990)[10][11][12], Weather.com[13] | |||||||||||||
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 55.8 square miles (145 km2), of which, 55.7 square miles (144 km2) of it is land and 0.1 square miles (0.26 km2) of it (0.13%) is water.
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1910 | 1,000 | — | |
| 1920 | 2,737 | 173.7% | |
| 1930 | 3,665 | 33.9% | |
| 1940 | 4,855 | 32.5% | |
| 1950 | 8,179 | 68.5% | |
| 1960 | 15,893 | 94.3% | |
| 1970 | 36,228 | 127.9% | |
| 1980 | 97,172 | 168.2% | |
| 1990 | 147,864 | 52.2% | |
| 2000 | 218,812 | 48.0% | |
| 2010 | 226,721 | 3.6% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 252,381 | [4] | 11.3% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[14] | |||
As of the census of 2010, there were 226,710 people, 79,114 households, and 54,721 families residing in the city. The population density was 3,929.5 people per square mile (1,517.3/km2). There were 79,667 housing units at an average density of 1,430.7 per square mile (552.4/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 75.54% White, 6% Black or African American, 1.7% Native American, 3.9% Asian, 0.2% Pacific Islander, 16.95% from other races, and 4.0% from two or more races. 35.5% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
There were 79,114 households, out of which 39.9% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 53.5% were married couples living together, 12.8% had a female householder with no husband present, and 28.2% were non-families. 21.3% of all households were made up of individuals, and 5.8% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.85 and the average family size was 3.33.
In the city, the population was spread out, with 30.1% under the age of 18, 10.8% from 18 to 24, 31.9% from 25 to 44, 19.9% from 45 to 64, and 7.4% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 31 years. For every 100 females, there were 99.6 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 97.1 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $45,015, and the median income for a family was $51,162. Males had a median income of $35,901 versus $27,736 for females. The per capita income for the city was $19,124. About 8.8% of families and 11.9% of the population were below the poverty line, including 15.3% of those under age 18 and 9.5% of those age 65 or over.
Notable attractions


- Adobe Mountain Desert Park
- Glendale Chocolate Festival (every February)[15]
- Glendale Folk & Heritage Festival[16]
- Glendale Glitters (every December)[15]
- Glendale Jazz and Blues Festival[15]
- Historic Manistee Ranch
- Historic Sahuaro Ranch
- Cerreta Candy Co. factory tour[17]
- Downtown Glendale featuring antique shops and restaurants
- Deer Valley Rock Art Center
- State Farm Stadium
- Gila River Arena
- Brelby Theatre Company
- Spotlight Youth Theatre
- Elsie McCarthy Sensory Garden
- Westgate Entertainment District
Sports

.jpg.webp)
Glendale is the site of two major sports venues: State Farm Stadium and Gila River Arena. Both venues are part of the Glendale Sports and Entertainment District development plan, meant to spur growth in the sparsely inhabited Yucca district. Both venues are owned by the City of Glendale.
State Farm Stadium has been the home field of the Arizona Cardinals in the National Football League since 2006, and the annual Fiesta Bowl college football game since 2007. Both the Cardinals and bowl game moved from Sun Devil Stadium on the Arizona State University campus in Tempe. Since opening, the facility has brought two Super Bowls, three college football national championship games, the NCAA Men's Basketball Final Four, WrestleMania XXVI and International Champions Cup soccer to Glendale. Designed by architect Peter Eisenman, the stadium was featured on The History Channel TV series, Modern Marvels because of its roll-out natural grass field.
Gila River Arena (formerly Glendale Arena, then Jobing.com Arena) and Westgate City Center is adjacent to State Farm Stadium, and is the home of the Arizona Coyotes of the National Hockey League (NHL). It was also the home of the now defunct Arizona Sting of the National Lacrosse League (NLL). The inaugural Street League Skateboarding event was held in the summer of 2010 in Glendale at the Gila River Arena. This street skateboarding competition returns to Glendale annually.
In 2009, the Los Angeles Dodgers and the Chicago White Sox of Major League Baseball began to share the new Camelback Ranch-Glendale spring training complex and stadium in Glendale owned and operated by the City of Glendale.
Education

There are a number of higher education campuses in Glendale. Glendale Community College and Glendale Community College North, just across the border in northwestern Phoenix, are members of the Maricopa County Community College District. Arizona State University’s Thunderbird School of Global Management was founded in Glendale at Thunderbird Field after World War II and recently relocated its campus to the downtown location of ASU after joining the university as an independent unit dedicated to international business education. West campus is just across the border from Glendale in west Phoenix. Midwestern University is a graduate college of medicine located in Glendale.
Many school districts serve the city of Glendale.
The following school districts serve the city:
- Unified school districts
- Deer Valley Unified School District
- Dysart Unified School District
- Peoria Unified School District (headquartered in Glendale)[18]
- High school districts
- Glendale Union High School District
- Phoenix Union High School District
- Tolleson Union High School District
- Elementary school districts
- Alhambra Elementary School District
- Glendale Elementary School District
- Pendergast Elementary School District
- Washington Elementary School District
Grace Lutheran School is a Pre-K-8 Christian school of the Wisconsin Evangelical Lutheran Synod (WELS) in Glendale.[19]
Our Lady of Perpetual Help Catholic School is a Pre-K-8 Catholic school of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Phoenix in Glendale.[20]
Transportation
The city of Glendale has a roughly average percentage of households without a car. In 2015, 8.4 percent of Glendale households lacked a car, and increased slightly to 9 percent in 2016. The national average was 8.7 percent in 2016. Glendale averaged 1.72 cars per household in 2016, compared to a national average of 1.8.[21]

Top employers
| # | Employer | # of Employees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Luke Air Force Base | 5,100 |
| 2 | Banner Health | 3,000 |
| 3 | Arrowhead Town Center | 2,650 |
| 4 | Walmart | 2,175 |
| 5 | Glendale Union High School District | 1,974 |
| 6 | Glendale Community College | 1,948 |
| 7 | The City of Glendale | 1,693 |
| 8 | Deer Valley Unified School District | 1,594 |
| 9 | Glendale Elementary School District | 1,400 |
| 10 | Tanger Outlets | 1,200 |
Notable people
- Prince Amukamara – professional football player
- Eddie Bonine – professional baseball player
- Elijah Burke – professional wrestler
- Danny Cruz – professional soccer player
- Nick Evans – professional baseball player
- Trent Franks – former United States congressman
- Lauren Froderman – winner of So You Think You Can Dance (Season 7)
- Jennie Garth – actress
- Job for a Cowboy – death metal band formed in Glendale in 2003
- Paul LoDuca – professional baseball player
- Craig Mabbitt – lead vocalist of band Escape The Fate
- Michael McDowell – NASCAR driver
- Evan Mecham – Arizona governor
- Lou Novikoff – professional baseball player
- Sterling Ridge – Arizona legislator
- Marty Robbins – Grammy-winning country musician and auto racer
- Nate Ruess – lead singer of Fun
- Tage Thompson - NHL player for the Buffalo Sabres
- Jason Zumwalt – actor
Culture
Arizona's Antique Capital
Glendale bills itself as "Arizona's Antique Capital", with support for its claim from both Sunset magazine (2004) and a 1998 article in USA Today. Glendale is home to the popular Arrowhead Towne Center mall in the northwest part of the city. Glendale also is home to Midwestern University, metropolitan Phoenix's first medical school. It used to also host a major post-graduate international business school: the Thunderbird School of Global Management, until Arizona State University bought the school[23] and moved it to ASU's Downtown and West campuses.[24] The site is now home to Arizona Christian University.[25]
An extension of Valley Metro Rail service is planned to serve the city, opening in 2026,[26] reprising a role played by the Phoenix Street Railway between 1911 and 1926.
Historic buildings
There are numerous properties in the city of Glendale which are considered to be historical and have been included either in the National Register of Historic Places[27] or the listings of the Glendale Arizona Historical Society. At the end of the article are some of these properties with a short description of the same.
- Historical Glendale, Arizona
(NRHP = National Register of Historic Places)[27]
(GAHS=Glendale Arizona Historical Society-listed)
 Beet Sugar Factory Building, built in 1906 (NRHP)
Beet Sugar Factory Building, built in 1906 (NRHP) Main mansion of the Manistee Ranch, built in 1897 (NRHP)
Main mansion of the Manistee Ranch, built in 1897 (NRHP) Main mansion in Sahuaro Ranch, built in 1886 (NRHP)
Main mansion in Sahuaro Ranch, built in 1886 (NRHP) First National Bank of Glendale, built in 1906 (NRHP)
First National Bank of Glendale, built in 1906 (NRHP) E.C. Bunch House, built in 1898 (NRHP)
E.C. Bunch House, built in 1898 (NRHP) George O'Dowdy Rental Cottage, built in 1926 (NRHP)
George O'Dowdy Rental Cottage, built in 1926 (NRHP) Glendale Woman's Club, structure built in 1912 (NRHP)
Glendale Woman's Club, structure built in 1912 (NRHP) Jonas McNair House, built in 1897 (NRHP)
Jonas McNair House, built in 1897 (NRHP) C.H. Tinker House, built 1913 (NRHP)
C.H. Tinker House, built 1913 (NRHP) Glendale Grammar School One-Room Class Building, built in 1920 (NRHP)
Glendale Grammar School One-Room Class Building, built in 1920 (NRHP) Glendale High School Auditorium, built 1939 (NRHP)
Glendale High School Auditorium, built 1939 (NRHP) Santa Fe Railroad Depot, built in 1895. The building serves as the offices of BNSF-MOW (Burlington Northern Santa Fe – Maintenance of Way) (GAHS)
Santa Fe Railroad Depot, built in 1895. The building serves as the offices of BNSF-MOW (Burlington Northern Santa Fe – Maintenance of Way) (GAHS) Murphy Park. The turn of the century town clock (pictured) was dedicated in 1987 to the memory of Thelma Renick Heatwole (1912–1991), who covered life in the Glendale community for more than 40 years as a newspaper reporter. The park is located at 58th & Glendale Avenues and has a public library.
Murphy Park. The turn of the century town clock (pictured) was dedicated in 1987 to the memory of Thelma Renick Heatwole (1912–1991), who covered life in the Glendale community for more than 40 years as a newspaper reporter. The park is located at 58th & Glendale Avenues and has a public library. The Forney House, built in 1893, is the second oldest house in Glendale, Arizona. It is located at 7534 North 61st Avenue. The oldest house in Glendale is the Adobe house located in Saguaro Ranch.
The Forney House, built in 1893, is the second oldest house in Glendale, Arizona. It is located at 7534 North 61st Avenue. The oldest house in Glendale is the Adobe house located in Saguaro Ranch. The historic William John Murphy House was built in 1895 and is located at 7514 N. Central Ave. in Phoenix, Arizona. Even though the house is not located in Glendale, it served as the residence of William J. Murphy who created the Arizona Improvement Company in 1887 and bought land in areas that would eventually become the towns of Peoria and Glendale. The house is listed as historic by the Phoenix Historic Property Register.
The historic William John Murphy House was built in 1895 and is located at 7514 N. Central Ave. in Phoenix, Arizona. Even though the house is not located in Glendale, it served as the residence of William J. Murphy who created the Arizona Improvement Company in 1887 and bought land in areas that would eventually become the towns of Peoria and Glendale. The house is listed as historic by the Phoenix Historic Property Register.
Catlin Court Historic District
Thunderbird 1 Army Air Field
 The historic Thunderbird Control Tower was built in 1941 and served as the Air Control Tower and Officers' quarters during the operation of the Thunderbird 1 Army Air Field, in Glendale. There American, British, Canadian and Chinese pilots trained during WWII. The air field was deactivated in 1945 and is now occupied by Arizona Christian University which is located southeast of the intersection of West Greenway Road & North 59th Avenue in Glendale, Arizona
The historic Thunderbird Control Tower was built in 1941 and served as the Air Control Tower and Officers' quarters during the operation of the Thunderbird 1 Army Air Field, in Glendale. There American, British, Canadian and Chinese pilots trained during WWII. The air field was deactivated in 1945 and is now occupied by Arizona Christian University which is located southeast of the intersection of West Greenway Road & North 59th Avenue in Glendale, Arizona Different view of the historic Thunderbird Control Tower. The tower and officer quarters were built in 1941 and served the Thunderbird 1 Army Air Field, in Glendale during WW II
Different view of the historic Thunderbird Control Tower. The tower and officer quarters were built in 1941 and served the Thunderbird 1 Army Air Field, in Glendale during WW II The historic Thunderbird 1 Army Air Field Airplane Hangar was built in 1941
The historic Thunderbird 1 Army Air Field Airplane Hangar was built in 1941
See also
Notes
- Mean monthly maxima and minima (i.e. the highest and lowest temperature readings during an entire month or year) calculated based on data at said location from 1981 to 2010.
- Official records for Phoenix kept at downtown August 1895 to September 1953, and at Sky Harbor Int'l since October 1953. For more information see ThreadEx.
References
- "2019 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 30, 2020.
- "Glendale". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 18, 2012.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved May 21, 2020.
- "William J. Murphy Historical Marker". www.hmdb.org.
- "WaterHistory.org". www.waterhistory.org.
- "Glendale City Center Master Plan" (PDF). glendaleaz.com.
- "Beet Sugar Factory History, Glendale, Arizona". molokane.org.
- "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. February 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2011.
- "NowData - NOAA Online Weather Data". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved November 6, 2020.
- "Station Name: AZ Phoenix Sky Harbor INTL AP". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved July 18, 2020.
- "WMO Climate Normals for PHOENIX/SKY HARBOR INTL, AZ 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved July 18, 2020.
- "Monthly Averages for Phoenix, AZ – Temperature and Precipitation". The Weather Channel. Retrieved May 7, 2009.
- "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2016.
- "Glendale, AZ - Events and Festivals". www.glendaleaz.com.
- Hwang, Kellie. "3/23-24: Glendale Folk & Heritage Festival". azcentral.com.
- "The Sweetest Tour in Glendale, Arizona". TripSavvy.
- "District Overview" Archived July 30, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- "School". Grace Evangelical Lutheran Church.
- "School". Our Lady of Perpetual Help Catholic School.
- "Car Ownership in U.S. Cities Data and Map". Governing. Retrieved May 4, 2018.
- "Top 10 largest employers in Glendale". AZCentral.com.
- Ryman, Russ Wiles, and Anne. "ASU finalizes agreement to integrate Thunderbird school". The Arizona Republic. Retrieved September 7, 2020.
- "Academic programs". ASU Students. December 2, 2014. Retrieved September 7, 2020.
- Fifield, Jen. "5 things to know about Arizona Christian University's move to Glendale". The Arizona Republic. Retrieved September 7, 2020.
- "Providing Public Transportation Alternatives for the Greater Phoenix Metro Area | Valley Metro |". Archived from the original on May 18, 2011.
- "National Register of Historical Places - ARIZONA (AZ), Maricopa County". nationalregisterofhistoricplaces.com.
- "Interactive City Directory: Glendale, Arizona". sister-cities.org. Archived from the original on August 13, 2017.