Jennifer Doudna
Jennifer Anne Doudna ForMemRS (/daʊdnə/;[2] born February 19, 1964)[3] is an American biochemist known for her pioneering work in CRISPR gene editing, for which she was awarded the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry along with Emmanuelle Charpentier.[4][5] She is the Li Ka Shing Chancellor's Chair Professor in the Department of Chemistry and the Department of Molecular and Cell Biology at the University of California, Berkeley. She has been an investigator with the Howard Hughes Medical Institute since 1997.[6]
| External video | |
|---|---|
 | |
Doudna grew up in Hilo, Hawaii. Graduated from Pomona College in 1985, she earned a Ph.D. from Harvard Medical School in 1989. Apart from her professorship at U C Berkeley, she is also president and chair of the board of the Innovative Genomics Institute, a faculty scientist at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, a senior investigator at the Gladstone Institutes, and an adjunct professor of cellular and molecular pharmacology at the University of California, San Francisco.[7][8][9][10][11][1]
Doudna has been a leading figure in what is referred to as the "CRISPR revolution" for her fundamental work and leadership in developing CRISPR-mediated genome editing.[12]
In 2012, Doudna and Emmanuelle Charpentier were the first to propose that CRISPR-Cas9 (enzymes from bacteria that control microbial immunity) could be used for programmable editing of genomes,[12][13] which is now considered one of the most significant discoveries in the history of biology.[14]
Doudna has made fundamental contributions in biochemistry and genetics and received many prestigious awards and fellowships, including the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, with Charpentier, "for the development of a method for genome editing,"[5][4] the 2000 Alan T. Waterman Award for her research on the structure as determined by X-ray crystallography of a ribozyme,[15] and the 2015 Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences for CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing technology, with Charpentier.[16] She has been a co-recipient of the Gruber Prize in Genetics (2015),[17] the Tang Prize (2016),[18] the Canada Gairdner International Award (2016),[19] and the Japan Prize (2017).[20]
Outside the scientific community, she has been named one of the Time 100 most influential people in 2015 (with Charpentier),[21] and she was listed as a runner-up for Time Person of the Year in 2016 alongside other CRISPR researchers.[22] In 2017 she was the lead author of A Crack in Creation: Gene Editing and the Unthinkable Power to Control Evolution,[12] a rare case of the first-person account of a major scientific breakthrough, aimed at the general public, published shortly after the discovery.[23]
Early life and education
Jennifer Doudna was born February 19, 1964, in Washington, D.C., as the daughter of Dorothy Jane (Williams) and Martin Kirk Doudna.[3][24] Her father received his Ph.D. in English literature from the University of Michigan, and her mother, a stay-at-home parent, held a master's degree in education.[12][13] When Doudna was seven years old, the family moved to Hawaii so her father could accept a teaching position in American literature at the University of Hawaii at Hilo.[12][13] Doudna's mother earned a second master's degree in Asian history from the university and taught history at a local community college.[12][13] Growing up in Hilo, Hawaii, Doudna was fascinated by the environmental beauty of the island and its exotic flora and fauna. Nature built her sense of curiosity and her desire to understand the underlying biological mechanisms of life.[12][13] This was coupled with the atmosphere of intellectual pursuit that her parents encouraged at home. Her father enjoyed reading about science and filled the home with many books on popular science.[12][13] When Doudna was in the sixth grade, he gave her a copy of James Watson's 1968 book on the discovery of the structure of DNA, The Double Helix, which was a major inspiration.[25] Doudna also developed her interest in science and mathematics in school.[12][25] While she attended Hilo High School, Doudna's interest in science was nurtured by her 10th-grade chemistry teacher, Ms. Jeanette Wong, whom she has routinely cited as a significant influence in sparking her nascent scientific curiosity.[25][26][27][28] A visiting lecturer on cancer cells further encouraged her pursuit of science as a career choice.[25] She spent a summer working in the University of Hawaii at Hilo lab of noted mycologist Don Hemmes and graduated from Hilo High School in 1981.[29]
Doudna was an undergraduate student at Pomona College in Claremont, California, where she studied biochemistry.[12][13] During her freshman year, while taking a course in general chemistry, she questioned her own ability to pursue a career in science, and considered switching her major to French as a sophomore.[10][12] However, her French teacher suggested she stick with science.[12][10] Chemistry professors Fred Grieman and Corwin Hansch at Pomona had a major impact on her.[10] She started her first scientific research in the lab of professor Sharon Panasenko.[10] She earned her Bachelor of Arts degree in Biochemistry in 1985.[10][30] She chose Harvard Medical School for her doctoral study and earned a Ph.D. in Biological Chemistry and Molecular Pharmacology in 1989.[6][31] Her Ph.D. dissertation was on a system that increased the efficiency of a self-replicating catalytic RNA[16] and was supervised by Jack W. Szostak.[16]
Career and research
After her PhD, she held research fellowships in molecular biology at the Massachusetts General Hospital and in genetics at Harvard Medical School.[6] From 1991 to 1994, she was Lucille P. Markey Postdoctoral Scholar in Biomedical Science at the University of Colorado Boulder, where she worked with Thomas Cech.[6]
Research on ribozyme structure and function
Early in her scientific career, Doudna worked to uncover the structure and biological function of RNA enzymes or ribozymes.[10] While in the Szostak lab, Doudna re-engineered the self-splicing Tetrahymena Group I catalytic intron into a true catalytic ribozyme that copied RNA templates.[10] Her focus was on engineering ribozymes and understanding their underlying mechanisms; however, she came to realize that not being able to see the molecular mechanisms of ribozymes was a major problem. Doudna went to the lab of Thomas Cech at the University of Colorado Boulder to crystallize and determine the three-dimensional structure of a ribozyme for the first time, so ribozyme structure could be compared with that of enzymes, the catalytic proteins.[10] She started this project at the Cech lab in 1991 and finished it at Yale University in 1996.[16] Doudna joined Yale's Department of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry as an assistant professor in 1994.[6]
X-ray diffraction-based structure of active site of a ribozyme at Yale

At Yale, Doudna's group was able to crystallize and solve the three-dimensional structure of the catalytic core of the Tetrahymena Group I ribozyme.[10] They showed that a core of five magnesium ions clustered in one region of the P4-P6 domain of the ribozyme, forming a hydrophobic core around which the rest of the structure could fold. [10] This is analogous, but chemically distinct from, the way proteins typically have a core of hydrophobic amino acids. [10] Her group has crystallized other ribozymes,[16] including the Hepatitis Delta Virus ribozyme.[10] This initial work to solve large RNA structures led to further structural studies on an internal ribosome entry site(IRES) and protein-RNA complexes such as the Signal Recognition Particle.[10]
Doudna was promoted to the position of Henry Ford II Professor of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry at Yale in 2000. In 2000–2001, she was Robert Burns Woodward Visiting Professor of Chemistry at Harvard University.[6]
Move to UC Berkeley

In 2002, she accepted a faculty position at the University of California, Berkeley, as a Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, joining her husband Jamie Cate who was a professor there.[16] Doudna also gained access to the synchrotron at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory for her experiments with high powered x-ray diffraction.[16]
In 2009, she took a leave of absence from Berkeley to work at Genentech to lead discovery research.[32] She left Genentech after two months and returned to Berkeley and cancelled all her obligations to study CRISPR.[32]
As of 2020, Doudna was located at the University of California, Berkeley, where she directs the Innovative Genomics Institute (a joint center of UC Berkeley and the University of California, San Francisco), holds the Li Ka Shing Chancellor's Professorship in Biomedicine and Health, and is the chair of the Chancellor's Advisor Committee on Biology.[6] Her lab now focuses on obtaining a mechanistic understanding of biological processes involving RNA.[16] This work is divided into three major areas, the CRISPR system, RNA interference, and translational control via MicroRNAs.[16]
CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing discovery
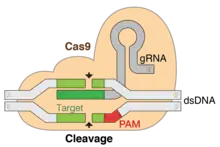
Doudna was introduced to CRISPR by Jillian Banfield who had found Doudna by way of a Google search, having typed "RNAi and UC Berkeley" into her browser, and Doudna’s name came up at the top of the list.[33][34] In 2012, Doudna and her colleagues made a new discovery that reduces the time and work needed to edit genomic DNA.[22][35] Their discovery relies on a protein named Cas9 found in the Streptococcus bacterial "CRISPR" immune system that cooperates with guide RNA and works like scissors. The protein attacks its prey, the DNA of viruses, and slices it up, preventing it from infecting the bacterium.[13] This system was discovered by Francisco Mojica, but she and Emmanuelle Charpentier showed for the first time that they could use different RNAs to program it to cut and edit different DNAs.[13]
As CRISPR becomes increasingly used to edit multicellular organisms, Doudna continues to be called upon to serve as a thought-leader on the ethics of changing an organism's function using CRISPR technology.[36] Their discovery has since been further developed by many research groups[16] for applications ranging from fundamental cell biology, plant, and animal research to treatments for diseases including sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, Huntington's disease, and HIV.[12][22] Doudna and several other leading biologists called for a worldwide moratorium on any clinical application of gene editing using CRISPR.[37] [38] Doudna supports the usage of CRISPR in somatic gene editing, gene alterations which do not get passed to the next generation, but not germline gene editing.[39]
The CRISPR system created a new straightforward way to edit DNA and there was a rush to patent the technique.[12] Doudna and UC Berkeley collaborators applied for a patent and so did a group at the Broad Institute affiliated with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Harvard.[40] Zhang at the Broad Institute had shown that CRISPR-Cas9 could edit genes in cultured human cells a few months after Doudna and Charpentier published their method.[22] Before the UC Berkeley patent application was decided, a patent was granted to the Broad investigators and UC Berkeley filed a lawsuit against the decision.[40] In 2017, the court decided in favor of the Broad Institute, who claimed that they had initiated the research earliest and had first applied it to human cell engineering thus supporting editing in human cells with evidence but that the UC Berkeley group had only suggested this application.[40] UC Berkeley appealed on grounds that they had clearly discussed and spelled out how to do the application the Broad had pursued.[41] In September 2018, the appeals court decided in favor of the Broad Institute's patent.[42] Meanwhile, UC Berkeley and co-applicants' patent to cover the general technique was also granted.[43] To further cloud the issue, in Europe the claim of the Broad Institute, to have initiated the research first, was disallowed.[44] The rejection was due to a procedural flaw in the application involving a different set of personnel listed in the lawsuit and the patent application, leading to speculation that the UC Berkeley group would prevail in Europe.[44] Doudna has co-founded Caribou, a company to commercialize CRISPR technology.[45] She is also a cofounder of Scribe Therapeutics which pioneered CasX, a more compact, next-generation Cas9 which can efficiently cut DNA.[46]
In addition to the CRISPR breakthrough, Doudna has discovered that the hepatitis C virus utilizes an unusual strategy to synthesize viral proteins.[47] This work could lead to new drugs to stop infections without causing harm to the tissues of the body.[47]
Mammoth Biosciences
In 2017, Doudna co-founded Mammoth Biosciences,[48] a San Francisco-based bioengineering tech startup. Initial funding raised $23 million,[49] with a series B round of funding in 2020 raising $45 million.[50] The business is focused on improving access to bio sensing tests which address "challenges across healthcare, agriculture, environmental monitoring, biodefense, and more."[51]
COVID-19 response
As executive director of the Innovative Genomics Institute (IGI) at UC Berkeley, Doudna is leading a COVID-19 testing center. This center processes more than 1,000 patient samples per day.[52] Mammoth Biosciences announced a peer-reviewed validation of a rapid, CRISPR-based point of need COVID-19 diagnostic which is faster and less expensive than qRT-PCR based tests.[53]
Personal life
As a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Colorado Doudna met Jamie Cate, then a graduate student; they worked together on the project to crystallize and determine the structure of the Tetrahymena Group I intron P4-P6 catalytic region. They married when she was teaching at Yale, and they both accepted faculty positions at UC Berkeley and moved there together. Cate is currently a UC Berkeley professor and works on gene-editing yeast to increase their cellulose fermentation for biofuel production. Doudna and Cate have a son born in 2003 who "likes computers and math."[13]
Awards and honors
Doudna was a Searle Scholar and received the 1996 Beckman Young Investigators Award.[54][55] In 2000, she was awarded the Alan T. Waterman Award, the National Science Foundation's highest honor that annually recognizes an outstanding researcher under the age of 35, for her structure determination of a ribozyme.[15] In 2001, she received the Eli Lilly Award in Biological Chemistry of the American Chemical Society.[6]
In 2015, together with Emmanuelle Charpentier, she received the Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences for her contributions to CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing technology.[56] In 2016, together with Charpentier, Feng Zhang, Philippe Horvath and Rodolphe Barrangou, she received the Canada Gairdner International Award.[19] Also in 2016, she received the Heineken Prize for Biochemistry and Biophysics.[57] She has also been a co-recipient of the Gruber Prize in Genetics (2015),[58] the Tang Prize (2016),[59] the Japan Prize (2017) and the Albany Medical Center Prize (2017).[60] In 2018, Doudna was awarded the NAS Award in Chemical Sciences,[61] the Pearl Meister Greengard Prize from the Rockefeller University,[62] and a Medal of Honor from the American Cancer Society.[63] In 2019 she received the Harvey Prize of the Technion/Israel for the year 2018 (jointly with Emmanuelle Charpentier and Feng Zhang)[64] and the LUI Che Woo Prize in the category of Welfare Betterment.[65] In 2020, she received the Wolf Prize in Medicine (jointly with Emmanuelle Charpentier).[66] Also in 2020, Doudna and Charpentier were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry "for the development of a method for genome editing."[5][4]
She was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 2002,[10] the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 2003, the National Academy of Medicine in 2010 and the National Academy of Inventors in 2014.[6] She was elected a Foreign Member of the Royal Society (ForMemRS) in 2016.[67] In 2017, Doudna was awarded the Golden Plate Award[68] of the American Academy of Achievement.[69] In 2020, she was awarded a Guggenheim Fellowship.[70]
References
- Jennifer Doudna publications indexed by Google Scholar

- "Jennifer Doudna – American biochemist". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved November 13, 2015.
- Wu, Katherine J.; Zimmer, Carl; Peltier, Elian (October 7, 2020). "Nobel Prize in Chemistry Awarded to 2 Scientists for Work on Genome Editing". The New York Times. Retrieved October 7, 2020.
- "Press release: The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2020". nobelprize.org. Nobel Foundation. October 7, 2020. Retrieved October 7, 2020.
- "Curriculum Vitae (Jennifer A. Doudna)" (PDF). Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. Retrieved October 24, 2017.
- "UC Berkeley's Jennifer Doudna wins 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry". University of California, Berkeley. Retrieved October 10, 2020.
- Langelier, Julie (September 5, 2018). "Jennifer Doudna Opens Laboratory at the Gladstone Institutes". Gladstone Institutes.
- "Interview with Jennifer Doudna (recorded in 2004)". National Academy of Sciences. Archived from the original on December 18, 2015. Retrieved November 8, 2017.
- Marino, M. (2004). "Biography of Jennifer A. Doudna". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 101 (49): 16987–9. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10116987M. doi:10.1073/pnas.0408147101. PMC 535403. PMID 15574498.
- Jennifer Doudna's publications indexed by the Scopus bibliographic database. (subscription required)
- Jennifer A. Doudna and Samuel H. Sternberg. A Crack in Creation: Gene Editing and the Unthinkable Power to Control Evolution. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 2017.
- Russell, Sabin (December 8, 2014). "Cracking the Code: Jennifer Doudna and Her Amazing Molecular Scissors". Cal Alumni Association. Retrieved November 10, 2017.
- Pollack, Andrew (May 11, 2015). "Jennifer Doudna, a Pioneer Who Helped Simplify Genome Editing". The New York Times. Retrieved May 12, 2015.
- "Alan T. Waterman Award Recipients, 1976 – present". National Science Foundation. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- "Laureates: Jennifer A. Doudna". breakthroughprize.org. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- "2015 Genetics Prize: Jennifer Doudna". The Gruber Foundation. Retrieved October 24, 2017.
- "Laureates: Biopharmaceutical Science (2016)". Tang Prize Foundation. Retrieved November 1, 2017.
- "Jennifer Doudna". Canada Gairdner Foundation. Retrieved November 2, 2017.
- "Laureates of the Japan Prize: Jennifer A. Doudna, Ph.D." The Japan Prize Foundation. Retrieved November 1, 2017.
- King, Mary-Claire. "Time 100 Most Influential People: Emmanuelle Charpentier & Jennifer Doudna". Time. April 16. 2015. Web. December 25, 2016.
- Park, Alice. "The CRISPR Pioneers: Their Breakthrough Work Could Change the World." Time. N.d. 2016. Web. December 25, 2016.
- "A Crack in Creation review – Jennifer Doudna, Crispr and a great scientific breakthrough". Retrieved October 8, 2020.
- Who's who in the West. 1999. ISBN 9780837909240.
- Mukhopadyay, Rajendrani. "On the same wavelength". American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Retrieved October 24, 2017.
- Cataluna, Lee. "Remembering The Hilo Teacher Who Inspired A Nobel Prize Winner". Honolulu Civil Beat. Retrieved October 22, 2020.
- "Big Questions, Big Answers". SBGrid Consortium. Retrieved October 22, 2020.
- "2018 Kavli Prize in Nanoscience: A Conversation with Jennifer Doudna, Emmanuelle Charpentier and Virginijus Šikšnys". The Kavli Prize. Retrieved October 22, 2020.
- "Genome editing pioneer and Hilo High graduate Jennifer Doudna speaks at UH Hilo about her discovery: CRISPR technology". UH Hilo Stories. Retrieved October 7, 2020.
- Engineer, Anushe (October 7, 2020). "Pomona College alumna wins Nobel Prize in Chemistry". The Student Life. Retrieved October 8, 2020.
- Doudna, Jennifer Anne (1989). Towards the Design of an RNA Replicase (Ph.D. thesis). Harvard University. OCLC 23230360. ProQuest 303754572.
- "A DAY WITH JENNIFER DOUDNA: TRYING TO KEEP UP WITH ONE OF THE WORLD'S MOST SOUGHT-AFTER SCIENTISTS". March 8, 2020.
- Jill Banfield: How a curious Google search led me to Jennifer Doudna, Jill Banfield (Berkeley News, published Oct 7, 2020)
- Jennifer Doudna's First Reactions to 2020 Nobel Prize Win (published Oct 7, 2020 to the UC Berkeley channel on YouTube)
- Jinek, M.; Chylinski, K.; Fonfara, I.; Hauer, M.; Doudna, J. A.; Charpentier, E. (2012). "A Programmable Dual-RNA-Guided DNA Endonuclease in Adaptive Bacterial Immunity". Science. 337 (6096): 816–821. Bibcode:2012Sci...337..816J. doi:10.1126/science.1225829. PMC 6286148. PMID 22745249.
- "CRISPR co-inventor Jennifer Doudna talks ethics and biological frontiers". January 25, 2019.
- "Scientists Seek Ban on Method of Editing the Human Genome". March 19, 2015.
- Baltimore D, Berg P, Botchan M, Carroll D, Charo RA, Church G, Corn JE, Daley GQ, Doudna JA, Fenner M, Greely HT, Jinek M, Martin SG, Penhoet E, Puck J, Sternberg SH, Weissman JS, Yamamoto KR (April 2015). "A prudent path forward for genomic engineering and germline gene modification". Science. 348 (6230): 36–38. Bibcode:2015Sci...348...36B. doi:10.1126/science.aab1028. PMC 4394183. PMID 25791083.
- "CRISPR's co-developer on the revolutionary gene-editing technology's past — and its future". February 28, 2020.
- Netburn, Deborah (February 15, 2017). "UC Berkeley suffers big loss in CRISPR patent fight: What's next for the gene-editing technology?". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved September 2, 2018.
- Decker and Cortez, Susan and Michelle (April 28, 2018). "This court battle will decide who will make a fortune from gene-editing technique". Bloomberg. Retrieved September 2, 2018.
- Jeff Akst, (2018) "The higher court's decision to uphold the ruling of the Patent Trial and Appeal Board essentially ends the intellectual property battle in theUS" The Scientist, September 10, 2018.
- Paganelli, Jennifer (June 19, 2018). "CRISPR Therapeutics, Intellia Therapeutics, and Caribou Biosciences announce grant of US patent for CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing". Caribou Biosciences, Inc. Retrieved September 2, 2018.
- Servick, Kelly (January 18, 2018). "Broad Institute takes a hit in European CRISPR patent struggle". Science. Retrieved September 2, 2018.
- "Caribou Biosciences, Inc". Bloomberg business. Retrieved September 2, 2018.
- "A day with Jennifer Doudna: Trying to keep up with one of the world's most sought-after scientists". Chemical & Engineering News. Retrieved May 2, 2020.
- "Jennifer A. Doudna, Ph.D." HHMI. Retrieved August 26, 2012.
- "Mammoth Biosciences". Crunchbase. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- "Mammoth Biosciences Closes on Series A Worth $23 Million". BioSpace. August 1, 2019. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- "Mammoth Biosciences Raises $45 Million to Build Next Generation CRISPR Products For Therapeutics and Diagnostics". BioSpace. January 30, 2020. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- "Mammoth Biosciences | About Us". Mammoth Biosciences. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- "CRISPR pioneer Doudna opens COVID-19 testing lab – BioNews". www.bionews.org.uk. Retrieved May 2, 2020.
- Release, Press (April 21, 2020). "Mammoth Biosciences Announces Peer-Reviewed Validation Of Its Rapid, CRISPR-Based COVID-19 Diagnostic". SynBioBeta. Retrieved May 2, 2020.
- "Beckman Young Investigators Award Recipients". Arnold and Mabel Beckman Foundation. Retrieved November 6, 2017.
- "Jennifer A. Doudna". Arnold and Mabel Beckman Foundation. Retrieved August 1, 2018.
- "Jennifer Doudna". Breakthrough Prize. Retrieved September 13, 2018.
- "Jennifer Doudna". The Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences. Retrieved November 6, 2017.
- "2015 Genetics Prize: Jennifer Doudna". The Gruber Foundation. Retrieved October 24, 2017.
- "Laureates: Biopharmaceutical Science (2016)". Tang Prize Foundation. Retrieved November 1, 2017.
- "Gene Editing Pioneers Selected to Receive America's Most Distinguished Prize in Medicine". Albany Medical Center. Retrieved November 1, 2017.
- "National Academy of Sciences Awards". National Academy of Sciences. Retrieved September 13, 2018.
- "Jennifer Doudna To Receive 2018 Pearl Meister Greengard Prize". Rockefeller University. Retrieved September 13, 2018.
- Sanders, Robert (October 18, 2018). "Doudna receives Medal of Honor from American Cancer Society". Berkeley News. Retrieved March 16, 2019.
- Harvey Prize 2018
- "LUI Che Woo Prize Reveals 2019 Laureates – Furthering Its Mission to Enrich World Civilisation". luiprize.org. Retrieved November 12, 2019.
- Wolf Prize 2020
- Anon (2016). "Professor Jennifer Doudna ForMemRS". London: Royal Society. One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from the royalsociety.org website where:
“All text published under the heading 'Biography' on Fellow profile pages is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.” --"Royal Society Terms, conditions and policies". Retrieved March 9, 2016.
- "Golden Plate Awardees of the American Academy of Achievement". achievement.org. American Academy of Achievement.
- "Jennifer A. Doudna, Ph.D. Biography and Interview". achievement.org. American Academy of Achievement.
- "Guggenheim Fellowship in 2020".
External links
- "Jennifer Doudna (UC Berkeley / HHMI): Genome Engineering with CRISPR-Cas9". YouTube. iBiology Science Stories. March 23, 2015.
- "Jennifer Doudna: CRISPR Basics". YouTube. Innovative Genomics Institute – IGI. November 4, 2017.
- "Into the Future with CRISPR Technology with Jennifer Doudna". YouTube. University of California Television (UCTV). October 26, 2019.
- "How CRISPR lets us edit our DNA". TED talk by Jennifer Doudna on YouTube
- Jennifer A. Doudna on Nobelprize.org




