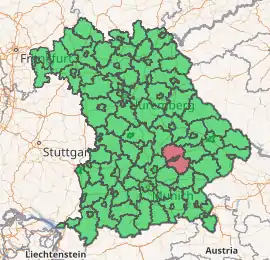
Landshut (district)
Landshut is a Landkreis (district) in Bavaria, Germany. It is bounded by (from the north and clockwise) the districts of Kelheim, Straubing-Bogen, Dingolfing-Landau, Rottal-Inn, Mühldorf, Erding and Freising. The city of Landshut is enclosed by, but does not belong to the district. It is nonetheless its administrative seat.
Landshut | |
|---|---|
| |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Bavaria |
| Adm. region | Lower Bavaria |
| Capital | Landshut |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,348 km2 (520 sq mi) |
| Population (31 December 2019)[1] | |
| • Total | 159,895 |
| • Density | 120/km2 (310/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Vehicle registration | LA |
| Website | landkreis-landshut.de |
History
The city of Landshut was founded in 1204 by the ruling Wittelsbach family of Bavaria. Since then the region has always been a part of Bavaria. Heinrich Himmler attended Landshut Grammar School, He would go on to become Reichsführer-SS of the Schutzstaffel in Nazi Germany and one of the organizers of the Holocaust. The present district was established in 1972 by merging the former districts of Landshut, Rottenburg and Vilsbiburg and adding some municipalities of surrounding districts.
Geography
The district comprises plain countryside on both banks of the Isar river.
Economy
Many residents work at the Dingolfing BMW (formerly Glas) car plant which expanded massively during the 1970s. Others commute daily to Munich, which is about 46 miles (74 km) to the southwest.
The first research nuclear power plant at Niederaichbach was torn down and returned to greenfield status in 1995. Two other nuclear reactors, known as Isar I and Isar II, in the Essenbach district remain operational: nuclear power generation remains a significant local employer.
Coat of arms
 |
The coat of arms displays:
|
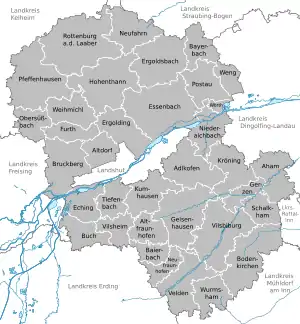
Towns and municipalities
| Towns | Municipalities | |
|---|---|---|
References
- "Tabellenblatt "Daten 2", Statistischer Bericht A1200C 202041 Einwohnerzahlen der Gemeinden, Kreise und Regierungsbezirke". Bayerisches Landesamt für Statistik und Datenverarbeitung (in German). July 2020.