List of participants to Paris Peace Conference, 1919–1920
The Paris Peace Conference, 1919–1920 gathered over 30 nations at the Quai d'Orsay in Paris, France, to shape the future after World War I. The Russian SFSR was not invited to attend, having already concluded a peace treaty with the Central Powers in the spring of 1918. The Central Powers - Austria-Hungary, Germany, Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire - were not allowed to attend the conference until after the details of all the peace treaties had been elaborated and agreed upon. The main result of the conference was the Treaty of Versailles with Germany.
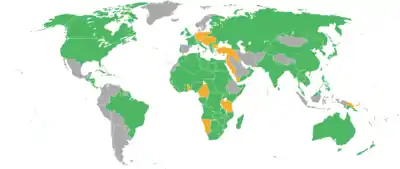
Signing delegations

This list shows all nations and delegations who signed the Treaty of Versailles. All plenipotentiaries signed the treaty, except where indicated otherwise.[1]
- Non-signatory
Other national representatives

Despite not signing the treaties, other delegations were sent to the Paris Peace Conferences, some uninvited, in order to represent their national interests.
| Nation | Representatives | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Faisal Lawrence of Arabia | Faisal, later King of Iraq, advocated for an independent Arab state. T.E. Lawrence acted as the delegation's translator.[2][3] | |
| Avetis Aharonyan Hamo Ohanjanyan Armen Garo | ||
| Alimardan Topchubashev | ||
| Anton Łuckievič | Attempted to gain international recognition of the independence of Belarus. | |
| Jaan Poska Nikolai Köstner Jaan Tõnisson Ants Piip Karl Robert Pusta Mihkel Martna Eduard Laaman Joakim Puhk | Attempted to gain recognition of the independence of Estonia.[4][5] | |
| Nikolay Chkheidze Irakli Tsereteli Zurab Avalishvili | ||
| Seán T. O'Kelly | The unrecognized Irish Republic sent representatives in hope the republic declared at the Easter Rising in 1916 would be recognised, but they were ignored.[6][7] | |
| Attempted to gain recognition of the independence of Latvia.[4][8] | ||
| Augustinas Voldemaras Antanas Smetona | Attempted to gain recognition of the independence of Lithuania.[4][9] | |
| Nicholas I of Montenegro | The unification of Serbia and Montenegro on 18th Novem-ber 1918 was contested by the exiled king of Montenegro. Despite Italian support, Montenegro was denied an official seat at the Peace Conferences, and the unification of Serbia and Montenegro was recognised.[10] | |
| William F. Lloyd | [11] | |
| Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus | ||
| Kim Kyu-sik | Representing the Provisional Government of the Republic of Korea, in-exile in China.[12] | |
| Sergey Sazonov | The Allied Powers refused to recognise the Bolshevik government of Russia, and instead invited representatives of the Russian Provincial Council (chaired by Prince Lvov), the successor to the Russian Constituent Assembly and the political arm of the Russian White movement.[13][14] | |
| M. Bucquet | [15] | |
| Sālote Tupou III | ||
| Ho Chi Minh | Ho Chi Minh petitioned the conference, seeking self determination and independence for the Vietnamese people.[16][17] |
Non-national representatives

Other non-national or pan-national delegations were in Paris, hoping to petition the allies on issues relating to their causes.
| Group | Major People | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1st Pan-African Congress | W. E. B. Du Bois Ida Gibbs | Held in February 1919 in order to petition the allies on African issues. |
| Inter-Allied Women's Conference | Marguerite de Witt-Schlumberger | Convened and met from 10 February to 10 April 1919. |
| Zionists | 117 Zionist representativeness attended the conference, lobbying for the establishment of a Jewish state in Palestine. |
Oversights
The Principality of Andorra was not invited to attend, due to an 'oversight'. The issue of Andorra being at war was eventually resolved on September 24, 1958, when a peace treaty was signed.[18]
References
- . 1919 – via Wikisource.
- "The Middle Eastern Prince Who Tried to Change the Treaty of Versailles". The Saturday Evening Post. 2019-06-28. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- "Story Map Journal". www.arcgis.com. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- Trapans, Jan Arveds (1994). "THE WEST AND THE RECOGNITION OF THE BALTIC STATES: 1919 AND 1991. A STUDY OF THE POLITICS OF THE MAJOR POWERS". Journal of Baltic Studies. 25 (2): 153–173. ISSN 0162-9778.
- "Estonian Ministry of Foreign Affairs / Välisministeerium". www.facebook.com. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- Gannon, Darragh. "January 1919: the Irish Republic, the League of Nations and a new world order". The Conversation. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- "Ireland and the Paris Peace Conference: How Sinn Féin Waged a Diplomatic War". IrishCentral.com. 2017-02-03. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- Bražūne, Alda. "THE ROLE OF FRANCE IN THE FOREIGN POLICY OF LATVIA, 1921-1933" (PDF). Retrieved 2020-10-09.
- "The state of Lithuania placing itself on the international stage in 1918–1924". valstybingumas.lt. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- Pećinar. "The Paris Peace Conference — Contemporary Balkans' perspective" (PDF). Retrieved 2020-10-09.
- "William F. Lloyd". memim.com. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- "Wilson Center Digital Archive". digitalarchive.wilsoncenter.org. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- "First World War.com - Who's Who - Sergei Sazonov". www.firstworldwar.com. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- Department Of State. The Office of Electronic Information, Bureau of Public Affairs (2007-08-01). "The Paris Peace Conference and the Treaty of Versailles". 2001-2009.state.gov. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- "The Project Gutenberg eBook of THE INSIDE STORY OF THE PEACE CONFERENCE, by Dr. E.J. Dillon". www.gutenberg.org. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- "Ho Chi Minh seeks Vietnamese independence (1919)". alphahistory.com. Retrieved 2020-10-09.
- Bria, Maggie (2017-03-30). "What Did the 1919 Paris Peace Conference Have to Do with the Vietnam War?". Bria Historica. Retrieved 2020-10-09.
- Reich, Herb (2012). Lies They Teach in School: Exposing the Myths Behind 250 Commonly Believed Fallacies. New York: Skyhorse Publication, Inc. p. 52. ISBN 1616085967.