Torquay
Torquay (/tɔːrˈkiː/ tor-KEE) is a seaside town in Devon, England, part of the unitary authority area of Torbay. It lies 18 miles (29 km) south of the county town of Exeter and 28 miles (45 km) east-north-east of Plymouth, on the north of Tor Bay, adjoining the neighbouring town of Paignton on the west of the bay and across from the fishing port of Brixham.
| Torquay | |
|---|---|
 View across Torquay Harbour | |
 Torquay Location within Devon | |
| Population | 65,245 (2011)[1] |
| OS grid reference | SX915655 |
| Unitary authority | |
| Ceremonial county | |
| Region | |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | TORQUAY |
| Postcode district | TQ1, TQ2 |
| Dialling code | 01803 |
| Police | Devon and Cornwall |
| Fire | Devon and Somerset |
| Ambulance | South Western |
| UK Parliament | |
The town's economy, like Brixham's, was initially based upon fishing and agriculture, but in the early 19th century it began to develop into a fashionable seaside resort, initially frequented by members of the Royal Navy during the Napoleonic Wars while the Royal Navy anchored in the bay. Later, as the town's fame spread, it was popular with Victorian society. Renowned for its mild climate, the town earned the nickname the English Riviera.
The writer Agatha Christie was born in the town and lived at Ashfield in Torquay during her early years. There is an "Agatha Christie Mile", a tour with plaques dedicated to her life and work.[2]
The poet Elizabeth Barrett Browning lived in the town from 1837 to 1841 on the recommendation of her doctor in an attempt to cure her of a disease which is thought likely to have been tuberculosis. Her former home now forms part of the Regina Hotel in Vaughan Parade.
Toponymy
Torquay's name originates in its being the quay of the ancient village of Torre. In turn, Torre takes its name from the tor, the extensively quarried remains of which can be seen by the town's Lymington Road thus giving this the original name of Torrequay, then Torkay, Torkey and Tor Quay before joining the words together to Torquay.[3]
History
The area comprising modern Torquay has been inhabited since Paleolithic times. Hand axes found in Kents Cavern have been dated as 40,000 years old,[4] and a maxilla fragment, known as Kents Cavern 4, may be the oldest example of a modern human in Europe, dating back to 37,000–40,000 years ago.[5][6]

Roman soldiers are known to have visited Torquay during the period when Britain was a part of the Roman Empire, leaving offerings at a curious rock formation in Kents Cavern, known as "The Face". No evidence has been found of Roman settlement in the town.
The first major building in Torquay was Torre Abbey, a Premonstratensian monastery founded in 1196.[7][5] Torquay remained a minor settlement until the Napoleonic wars, when Torbay was used as a sheltered anchorage by the Channel Fleet, and relatives of officers often visited Torquay. The mild climate (for the UK) attracted many visitors who considered the town a convalescence retreat where they could recover from illness away from the cold and cloudy winters of more northerly or easterly locations. The population of Torquay grew rapidly from 838 in 1801, to 11,474 in 1851.

The second phase in the expansion of Torquay began when Torre railway station was opened on 18 December 1848. The improved transport connections resulted in rapid growth at the expense of nearby towns not on Isambard Kingdom Brunel's railways. The more central Torquay railway station was opened on 2 August 1859 with views of the sea from the platforms. After the growth of the preceding decades, Torquay was granted borough status in 1872. Previously regarded as a convalescence retreat, Torquay began to encourage summer visitors, and 1902, saw the first advertising campaign to market Torquay to summer tourists.
Torquay Tramways operated electric street trams from 1907. They were initially powered by the unusual Dolter stud-contact electrification so as not to disfigure the town with overhead wires, but in 1911, was converted to more conventional overhead-line supply. The line was extended into Paignton in 1911 but the network was closed in 1934.[8]
The Royal National Lifeboat Institution's Torquay Lifeboat Station was at the Ladies Bathing Cove from 1876 until 1923. A second lifeboat was kept at the harbour from 1917 until 1928.[9] Torquay was regarded as a "Spa Town" after the Marine Spa was built on Beacon Hill near the harbour. Originally called the "Bath Saloons complex", it had an open air tide-filled swimming bath. The complex was opened in 1853 after Beacon Hill headland was dynamited to make space for it. Charles Dickens was said to have made readings there. In the 1900s, a ballroom and a new sea water-filled swimming pool were built. The Marine Spa provided various therapies such as seaweed baths, needle, douche showers, hot and cold water baths and electric shock treatment. Bands such as Ivy Benson and Ted Heath played at Marine Spa ballroom. Four stone arches that were part of the Marine Spa are still visible on the outside of the harbour wall.
During World War I, military hospitals were sited in Torquay – many survivors from the Battle of Gallipoli recuperated in the town – and it was used as a troop staging area. In September 1915, King George V and Queen Mary visited. After the war, the Great Western Railway launched an advertising campaign to attract tourists, and this helped the town grow to a major south coast resort.

During World War II Torquay was regarded as safer than the towns of South East England, and played host to evacuees from the London area, the town did, however, suffer minor bomb damage during the war, mainly from planes dumping excess loads after participating in the Plymouth Blitz. The last air raid on Torquay took place on 29 May 1944, shortly before the D-Day landings in June and, in the months leading up to D-Day, thousands of US Army personnel arrived with the 3204th Quartermaster Service Company billeted in Chelston and Cockington. During Operation Overlord more than 23,000 men of the American 4th Infantry Division departed Torquay for Utah Beach. The loading ramps used by the American army are still visible in front of the Regina Hotel on Vaughan Parade, a plaque giving details.
The water sport events of the 1948 Summer Olympic Games were held in Torquay, and the Olympic flame brought from London to Torre Abbey Gardens.[10] Although it did not host any Olympic events for the 2012 Summer Olympics, with the sailing taking place in Weymouth, Torbay looked to host teams as a preparation camp and the flame passed through once more on its route around the UK.

After World War II several private high-rise blocks of flats were constructed above the Rock Walk cliffs and harbour, giving the area a Monte Carlo feel. In 1971, after a tragedy, the Marine Spa was demolished to make way for the ill-fated Coral Island leisure complex. This was characterised by its concrete arches on its uppermost floor and sunbathing decks like those of a cruise liner. The site featured a hexagonal outdoor plunge pool surrounded by sunbathing terraces leading down to Beacon Cove beach. Inside the building were several lounges, a restaurant and a nightclub within the arches of the ancient swimming bath. All levels were served by a hydraulic passenger lift. Coral Island opened in 1977, and closed in 1988. The complex was demolished in 1997, 20 years after its construction. The site remained derelict until 2002 when the Living Coasts coastal zoo was built there.
Torquay also boasted rehabilitation facilities for the blind at America Lodge, which was owned by the RNIB for a number of decades. Like many RNIB properties, this was sold off in the 1990s and the building is subdivided into private apartments.
In the late 1980s, Fleet Street was rebuilt as the Fleet Walk shopping centre which has street-level shops and an upper-level shopping deck. The long, curved building which follows the street is magnolia-coloured and in mock Victorian style. In the late 1990s and early 2000s new pubs and night clubs opened around the harbour, leading to an increase in binge drinking,[11] however in recent years a better police presence and responsible drinks promotions have improved the situation.[12] Since World War II, the nature of tourism in the United Kingdom has changed significantly. Increasing wealth has meant that holidays abroad are now commonplace. Coastal towns are now more popular for short stays as part of a touring holiday. Recently, Torquay has seen an increase in foreign visitors and is a major destination for foreign exchange students who come to the town to learn English in summer schools.
Areas around Torquay have also been affected by either refurbishments or closure. For instance, the Rock Walk located on the town's seafront was refurbished through a £3 million funding project,[13] resulting in its reopening on 3 October 2010, as part of the Royal Terrace Gardens festival.[14] In 2013, the Torquay Pavilion was closed after a loss in funding and attempts to reopen it under new funding are ongoing.[15]
Governance
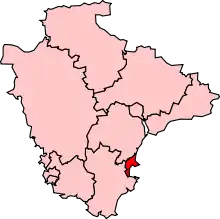
Torquay is part and the Administrative HQ of Torbay, created in 1968 as a county borough with Torquay being the county town [16] before returning to a two-tier system of local government under Devon County Council in 1974, from the amalgamation of the Boroughs of Torquay, Paignton and Brixham. Historically part of the county of Devon, Torbay was made a unitary authority on 1 April 1998, making it responsible for its own affairs. For local elections, the district is divided into 11 wards, 7 of them in Torquay. The main council offices are at Torquay Town Hall, built c. 1911.[17]
Torbay Council is headed by Mayor Gordon Oliver (Conservative). Mayor Oliver is the second directly elected mayor, with the first being Mayor Nick Bye, who served from November 2005 till May 2011.
Torquay (along with part of Paignton) is in the Torbay parliamentary constituency, created in 1974; previous to that, it was in its own eponymous constituency. The constituency elects one Member of Parliament, since 2015 Kevin Foster of the Conservatives. Torquay, the rest of South West England, and Gibraltar was in the South West England constituency of the European Parliament until 31 January 2020.
Geography

Torquay is situated on the southwestern coast of England, forming one-third of Torbay, on the western side of the bay. It has a mild microclimate, receiving among the longest hours of sunlight per day in the south-west of the United Kingdom, with winters that tend to be mild and wet. The record low temperature of −8.9C was recorded in 1940, and again in 1947. A record high temperature of 31.5C was recorded on 14 July 2013, at 5:30 pm,[19]
The town is made up of a number of small settlements that amalgamated into the town of Torquay. The town's historic core consists of Tormohun (also historically known as Tormoham),[20] Wellswood, The Warberries, Upton and Ellacombe and is based upon what was once the holdings of the Palk family. In 1900, Chelston and Livermead, part of the Cockington estate owned by the Mallocks, were annexed by the town and this was followed by the absorption of the former borough of St Marychurch. In this period St Marychurch covered Plainmoor, Watcombe, Babbacombe and Kingskerswell.[21] In 1928, the Mallocks' last holdings in Cockington were integrated into the town borders. Torquay expanded throughout the century leading to the development of Shiphay, Hele Village, Barton and since the 1990s, The Willows and since 2010, onwards Edginswell and into Kingskerswell giving the town its current layout as well as Maidencombe up to the Gabwell's.
Wellswood and the Lincombes were built up by wealthy Victorians who, influenced by their travels around the Mediterranean, built large villas with Italianate features and towers. There are many pine trees, Bay bushes and trees (Laurus nobilis), various palm tree species and Phormiums. Cabbage trees or "Torbay Palms" are a notable feature of the area; the trees were introduced into the area from New Zealand in 1820, and since then have flourished. The vegetation gives Torquay a look of a more exotic climate than its high latitude cool oceanic location.
The main beaches of Torquay are Oddicombe Beach, Meadfoot Beach, Maidencombe, Watcombe, Babbacombe Beach, Anstey's Cove, Redgate, Torre Abbey Sands, Corbyn Sands and Institute Beach and Hollacombe Beach.[22] The first two of these held European Blue Flag status in 2012.[23]
The Sticklepath fault line, which runs across Devon from Bideford Bay to Torquay,[24] is one of many geological faults criss-crossing Torbay; the Babbacombe Cliff Railway takes advantage of one of these fault lines.[25]
Transport

Torquay has two railway stations. Torquay railway station is situated near the sea, close to Torre Abbey Sands. Torre railway station is situated a little inland adjacent to the road leading to Newton Abbot. Not all trains stop at Torre. As of 2013, there were plans for station improvements at Torquay and Torre (and at Paignton) and to build a new station at Edginswell.[26]
Torquay is connected to the UK motorway network by the A380, which traces the outskirts of the town as Hellevoetsluis Way and Hamelin Way, leading to the A38 and the M5 at Exeter. The A3022 branches from the A380, leading into Torquay as Riviera Way, to the seafront as Newton Road and then Avenue Road, and then on to Paignton as Torbay Road. The A379 runs past the harbour to Babbacombe and St Marychurch, and then north along the coast to Teignmouth. Work on constructing a new dual carriageway on the outskirts of Torquay near the Kingskerswell end was completed in 2015 with a new junction between the A380 South Devon Highway and Torbay Ring Road. The main bus route operated by Stagecoach Devon passes through Torquay – the "Hop 12" number 12 service between Newton Abbot and Brixham, – while other routes operate within the town.[27]
Religion

For a summary of the 2001 census results on religion, see below, Demographics
Torquay has about 60 churches[28] from a wide variety of Christian denominations. The largest congregations are those of St Matthias (Anglican) and Upton Vale Baptist church. Central Church (Methodist and United Reformed Church) has a notable pierced screen wall facade. St Matthias's Church, Wellswood, was built as a chapel-of-ease to St Mark's, Torwood, in the 1850s and became a parish church in 1880. In the 1970s, the churches of St Mark and Holy Trinity were closed and in 1979, the vicar of St Matthias's became rector of the parish of St Matthias, St Mark and Holy Trinity.[29]
St Saviour's Church and St Michael's Chapel are medieval church buildings, now Anglican. St Saviour's originally had no aisles but a north aisle was added in the 14th century. The tower is at the west end and early medieval in date. Over restoration was carried out both on the exterior and interior in 1849. The monuments include one in early Tudor style to Thomas Cary (d. 1567) and another to Thomas Ridgeway (d. 1604) which includes an alabaster effigy. The Chapel of St Michael is only 36 by 15 ft and its floor is the uneven surface of the rock on which it stands. The roof has a barrel vault and the windows are small. The 19th-century Anglican churches of Torquay include All Saints, Bamfylde Road (1884–90, architect John Loughborough Pearson), St John's, Montpelier Terrace (1861–71, architect George Edmund Street), St Luke's (1863, architect Sir Arthur Blomfield), St Mark's, St Mark's Road (1856–57, architect Anthony Salvin), St Mary Magdalene, Union Street (1846, architect Anthony Salvin), and St Michael, Pimlico (1877, architect Pritchard).[30]
The former St Andrew's Presbyterian church (built in 1862) on Torwood Gardens Road closed in 1951, and after a time as a nightclub, was converted to private residences.[31]
There is also a Christadelphian meeting hall in the town.[32]
There is also an Islamic centre and mosque.[33] A United Hebrew Congregation synagogue was closed in 2000, and the congregation dissolved.[34]
Economy
In 2001, unemployment in Torquay was high at 6.8% – this compared with 3.9% for Devon, and 5.0% for England as a whole.[35]
Many locals were employed in the Pontins holiday centre before it was sold off. Torquay was the home of Suttons Seeds until it relocated to the neighbouring town of Paignton in 1998, and Beverage Brands, the owners of the popular and controversial alcoholic brand WKD, was based in the town until 2011.[36]
Tourism



Torquay has numerous tourist attractions, including Kents Cavern, Britain's most important Stone Age site, which was home to early man for some 40,000 years. The floor is composed of several strata, with remains indicating the prehistoric coexistence there of humans and now-extinct animals. The Rev. J. McEnery explored the cave between 1825 and 1829, and put forth the coexistence theory. The cave was extensively explored from 1865 to 1880 by William Pengelly, who found evidence to support McEnery's hypothesis. The caves have attracted many famous people, among them Agatha Christie,[37] Beatrix Potter, King George V and Haile Selassie who was so impressed with his visit that he gave his guide, Leslie Powe a gold sovereign.
On the seafront between the Rock Walk and the Marina is the Victorian Pavilion (pictured). The adjacent "Friends Fountain" complements the Victorian architecture.
Torquay Museum, the oldest in Devon, was founded in 1844, by The Torquay Natural History Society.[38] The museum contains extensive geology, natural science, archaeology and ethnography collections of international importance, including the oldest fossil evidence of modern man in north-west Europe. The story of the English Riviera Geopark is told through exhibitions about geology, fossils and archaeology including artefacts from Kents Cavern and other local archaeology. The museum has galleries dedicated to diverse topics such as the life of Agatha Christie, ancient Egypt, explorers and ecology. Another gallery displays replica historic farmhouse interiors.[39]
In 1857, the Bath's Saloons complex was built on the promontory overlooking Beacon Cove. This included a ballroom, concert hall and sunlit conservatory and private bathing facilities with, underneath, a large public swimming bath open to the sea. Living Coasts, a coastal zoo owned by Paignton Zoo, was later built on the site of the complex. The stone arches of the public bath were incorporated into the shop at Living Coasts. Development of the site as a marine animal exhibit was first proposed in early 1999 in response to a call from Torbay Council for submissions from interested parties. The project, developed by Kay Elliott architects, included an exhibit to house marine birds, rather than fish, due to the need to avoid duplicating the exhibits at the National Marine Aquarium in Plymouth. The project was subsequently taken on by Paignton Zoo Environmental Park and named Living Coasts. It was announced in June 2020, that due to the COVID-19 pandemic, they were to close permanently.[40]
Other attractions are the Babbacombe Model Village, which opened in 1963; the Babbacombe Theatre which opened in 1939; the Princess Theatre. A large tethered balloon offering aerial views of the town operated for several years until it was destroyed by strong winds in January 2012.[41][42]
From 1875, number of potteries operated in Torquay, making Torquay pottery for both the tourist trade and high-end retail.
Culture
Arts
In the early years of British cinema, Torquay was home to two production companies, Cairns Torquay Films[43] and Torquay And Paignton Photoplay Productions,[44] who in 1920, produced a total of three films between them. Recently, Devon Films, based in Torquay, has established itself as the Bay's latest film production company. The company financed and produced Stepdad in 2007, starring Ricky Tomlinson and Chris Bisson among others; it was entered into the Cannes Film Festival. A new film Snappers set in Torquay itself and shot on location, starred Caroline Quentin,[45] Bruce Jones and other prominent British television actors, and was due to be released in March 2009.[46]
The Princess Theatre, which is by the side of the harbour, is owned by Torbay Council and operated by ATG (Ambassador Theatre Group). It was previously owned by Live Nation Theatres, but they sold their theatres to ATG for 100 million pounds in 2009. With about 1,500 seats, it is Torquay's largest theatre and plays host to touring independent production companies. The Princess Theatre also holds weddings and other functions such as parties and large seminars.[47] TOADS Theatre Company operates the Little Theatre in Meadfoot in the converted St Mark's Church, hosting both the company's own productions and those of visiting societies.[48] Babbacombe Theatre is located on Babbacombe Downs and describes itself as having the longest-running summer season in the country, which lasts nine months.[49]
Torbay Council, along with other local bodies, administrates Creative Torbay, a website for local cultural organisations, creatives and artists to promote their work.[50]
Media
Torquay has two commercial local radio stations: Heart Devon, which broadcasts from studios in Exeter, and The Breeze (formerly known as Palm 105.5), which has its studios in Lymington Road in Torquay. Heart Devon is owned by Global Radio, while The Breeze 10 owned by the London Media Company.
Torquay is also home to the non-profit community radio station Riviera FM which has just completed its second RSL and is in the process of applying for a licence from Ofcom.
BBC Radio Devon is the radio station covering the whole of Devon including Torbay. Torquay is part of the ITV West Country region, which broadcasts local news and some local documentaries. BBC Spotlight provides BBC news. Both TV stations cover the whole of Devon and Cornwall.
The town's local newspaper is called the Herald Express and has been published since 1925, after a merger of two papers. Its catchment area includes towns outside the Bay itself including Newton Abbot and Dartmouth. Torbay also has a monthly community newspaper called the Torbay Times founded locally in 2011.
Past newspapers include the Torquay and Tor General Advertisor and Director, founded in 1839, which in 1853 became The Torquay Directory and South Devon Journal until 1949, finally becoming The South Devon Journal, which closed in 1973.[51]
Sport
Torquay has a long history of holding sailing events and regattas due to the favourable easterly facing nature of the bay and its popularity in the 19th and 20th centuries; this tradition reached its height in 1948 when the water sport events of the 1948 Summer Olympics were held in Torquay, with the Olympic flame being transferred from London to Torre Abbey Gardens to reside throughout the event.[10]
Torquay is represented in Association Football in the National League by Torquay United F.C.. The team plays their home matches at Plainmoor and have never progressed beyond the third tier of the English leagues. Torquay United were promoted from the Conference Premier after winning the play-off final at Wembley in June 2009. However, after a poor Football League Two campaign in the 13/14 season, Torquay United came last and were relegated back to the Conference Premier (now the National League). Torquay were relegated previously in 2007 from the Football League after 80 years of membership and spent two years playing in the Conference Premier; this downfall came just three years after promotion from the league's basement division and ultimately led to a change in ownership of the club to a consortium of local businessmen and fans. Notable former managers of the club include Frank O'Farrell who would later go on to manage Leicester City and Manchester United, David Webb, Cyril Knowles, Neil Warnock and Roy McFarland. Notable former players include Lee Sharpe, Neville Southall, Garry Nelson and Eddie Kelly. The club won a Wembley final in 1991, defeating Blackpool on penalties in the Fourth Division play-off final to win promotion to the Third Division. In doing so, they became the first Football League team to win promotion on penalties.
The town also houses three major football teams from the local non-league scene, including Hele Rovers, Kingskerswell & Chelston and Upton Athletic, all of whom compete in the South Devon League.
Torquay is represented in the sport of rugby union by Torquay Athletic Rugby Football Club, who compete in Tribute Western Counties West, which is six leagues below the Guinness Premiership. Rugby league team Devon Sharks are based in Torquay. They play in the South West Division of the Rugby League Conference.
For athletics Torre Valley North sports field is the summer training base for Torbay Athletic club and Torbay Triathlon Club. Torre Valley North has a 400m grass running track in summer, it also provides a long jump pit and concrete shot put circle, with a pavilion. A variety of track and field sports take place at Torre Valley North including hurdles and high jump. In winter months the Torbay Athletic and Torbay Triathlon club uses the English Riviera Centre. The club organises the annual Torbay Half Marathon which starts in Paignton and the Torbay 5 Bays 10k, which takes place between Paignton and Brixham, superseding the Torquay to Paignton 10k Road Race.
Torquay also hosted the World Snooker European Open 2003 at the Palace Hotel, which was won by Ronnie O'Sullivan, In the same year, the Palace Hotel also hosted the World Snooker Championship Qualifiers. Recently the resort has become popular among the powerboating community and has held various national championships in various classes over the past few years.
Social issues
Politics
From 1974, when it was created until 1997 Torbay constituency was a safe Conservative seat, but Liberal Democrat Adrian Sanders overturned spy writer Rupert Allason's majority by just 12 votes in 1997, widened to 6,708 in 2001.
During the 2005 general election, Conservative leader Michael Howard visited the town. However, Sanders retained the seat with 40.8% of the votes (19,317, down from 23,012 in 2001). A swing of 9.7% away from the Liberal Democrats was split between the Conservatives (with a 4.9% swing), Labour – who gained a substantial increase in their vote as support for Lib Dems in 1997 and 2001 moved back and the United Kingdom Independence Party (UKIP), whose candidate Graham Booth improved on his deposit-losing 2001 performance with a 4.7% increase in his vote.
In 2005, a referendum was held to appoint Torbay's first elected Mayor. In the ensuing election in October 2005, the winning candidate was a former Liberal Parliamentary Candidate, Nicholas Bye, who won the election as a Conservative.
In 2011 Gordon Oliver was elected as Torbay's' new mayor beating the existing Mayor Nicholas Bye. Mr Oliver finished with 12,716 votes and Mr Bye 9,631 after the two made it to the second and final round of counting.
Education
Torquay has a number of primary schools, including St Margarets Primary School in St. Marychurch which has around 329 pupils and is situated on a large site of over 1800 square metres which was formerly a farm.[52]
There are five main secondary schools in the town. Torquay Academy, previously known as Torquay Community School and Audley Park, has had its troubles in the past but since 2001 has come out of Ofsted special measures. The school has recently had a £26million pound rebuild and in December 2010, when reassessed by Ofsted it was told that it had become "A good and improving school". It changed to academy status in September 2001, sponsored by Torquay Boys' Grammar School.
The Spires College (formerly Westlands School) is a combined secondary college and sixth form that takes students of all variations and in 2002 moved to a new building. St Cuthbert Mayne School is a joint Roman Catholic and Church of England secondary school and sixth form.
Torquay's other two state secondary schools are selective. They are Torquay Boys' Grammar School and Torquay Grammar School for Girls which are available only to those that pass the Eleven plus exam and the schools' own standardised test. There are also a number of private schools in the area including the Abbey School.
For further education, students can either go to one of the sixth forms at the previously mentioned The Spires, St Cuthbert's Mayne or Grammar schools, or they can go to South Devon College which is based in Long Road in Paignton on a new campus that fully opened in January 2006.
Crime
| Offences | Total | Rate per 1,000 population | Average rate per 1,000 population in England & Wales |
|---|---|---|---|
| Violence against the Person with injury | 1,125 | ||
| Violence against a Person without Injury | 1,005 | ||
| Sexual Offences | 167 | ||
| Robbery Offences | 60 | ||
| Burglary in a Dwelling | 385 | ||
| Burglary in a Building other than a Dwelling | 496 | ||
| Offences against a Vehicle | 834 | ||
| Drug Offences | 638 | ||
| Fraud and Forgery | 234 | ||
| Criminal Damage | 2,090 | ||
| Other Theft Offences | 2,277 | ||
| Other Offences | 138 | ||
Information taken from 2010 crime figures in Torbay (up to and including 31 December 2010)[53]
Healthcare
Torquay has two hospitals, the NHS-run Torbay Hospital which is situated on Newton Road, Shiphay and the private, non-emergency Mount Stuart Hospital on St. Vincent's Road, Torre.
In English culture
| Notable people born in Torquay | |
|---|---|
| 1821 | Richard Burton, explorer and linguist[54] |
| 1867 | Percy Fawcett, archaeologist and explorer[55] |
| 1890 | Agatha Christie, best-selling crime novelist[37] |
| 1937 | Peter Cook, writer and comedian[56] |
| 1947 | Martin Turner, Wishbone Ash founder[57] |
| 1949 | Roger Deakins, cinematographer[58] |
| 1972 | Miranda Hart, actress and comedian[59] |
| 1983 | Lauren Pope, DJ, model and entrepreneur |
| 1987 | Lily Cole, model and actress |
| 1994 | Georgia Toffolo, TV and media personality |
A number of sketches for the Monty Python's Flying Circus television show (1969–74) were filmed on location in and around both Torquay and neighbouring Paignton. It was while staying in Torquay at the Gleneagles Hotel with the Python team in 1971, that John Cleese found inspiration (and the setting, although not the actual film location) for the popular sitcom Fawlty Towers (1975, 1979).[60] Incidents during the Pythons' stay are said to include the owner, Donald Sinclair, having thrown Eric Idle's suitcase out of a window in case it contained a bomb.[61] Cleese later described the eccentric owner as, "the most wonderfully rude man I have ever met", although Mr. Sinclair's widow has since said her husband was totally misrepresented in the comedy.[62]
In the 1970s, several episodes of the comedy series The Goodies were filmed in and around Torquay. In 1979, the town was again the site of filming, when the Ray Winstone, BAFTA nominated drama That Summer! was both set in and filmed around the town. In 2003, the movie Blackball starring Paul Kaye was set and partly shot there.[63]
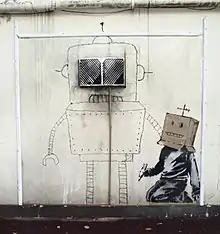
In October 2010, it was reported that Bristol-based artist Banksy had painted a mural on the wall of the Grosvenor Hotel in Belgrave Road. The mural shows a child drawing a robot, and uses the vent of an extractor fan as the head of the robot.[64] The painting was vandalised in May 2011.[65] This mural has now been painted over due to the Grosvenor Hotel being refurbished by the new owners (Richardsons) in 2014.
The Victorian mansion in Torquay where Agatha Christie was born and grew up, Ashfield in Barton Road, was demolished in 1961, to build an estate and extension for South Devon College.[66] A blue plaque was unveiled in 2007, marking the spot.[67][68]
Notable people
- Agatha Christie - English mystery and detective writer
See also
References
- "Census 2011 - Torbay Profile". Torbay Council. 3 July 2013. p. 4. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2014. (Word document)
- "Go on a mystery walk in beautiful Torquay". BBC. Retrieved 18 February 2010.
- Russell, 7–8
- "Early explorers – History & Archaeology". Kents Cavern. Archived from the original on 4 September 2010. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
- John R. Pike, Torquay (Torquay: Torbay Borough Council Printing Services, 1994), 5–6
- Rincon, Paul (27 April 2005). "Jawbone hints at earliest Britons". news.bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 7 November 2006.
- Russell, p. 19
- Crawley, Robert (2007). Torquay Trams. Colaton Raleigh: West Country Historic Omnibus and Transport Trust. pp. 1–3.
- Denton, Tony (2009). Handbook 2009. Shrewsbury: Lifeboat Enthusiasts Society. p. 59.
- Russell, p. 199
- "Blackpool and Torquay hit by alcohol-fuelled violence". The Independent. London. 2 August 2004. Retrieved 25 May 2010.
- Page 12,17,18
- "Choir to rock Rock Walk opening". 29 September 2010. Retrieved 5 December 2019.
- "Royal Terrace Gardens - Enjoy Torbay". Home. Retrieved 5 December 2019.
- Finch, Hannah (17 March 2019). "What's next for Torquay's crumbling Pavilion". devonlive. Retrieved 5 December 2019.
- Torbay County Council Archives 1968-1974
- Historic England. "The Town Hall (1208247)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 11 December 2020.
- Map of Torquay by Torbay Council 2013
- "Torbay's July heatwave is a record-breaker". Torquay Herald Express. 25 July 2013. Archived from the original on 28 July 2013. Retrieved 16 December 2016.
- The National Gazetteer of Great Britain and Ireland (1868), reprinted at Genuki. Retrieved 6 January 2016
- The book of Kingskerswell by Carsewella Local History Group, 2001, inside front cover ISBN 1-84114-236-0
- History of Torbay by Frank Pearce
- "SouthWest". Blue Flag. Archived from the original on 7 June 2012. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
- "The Geology of Devon" (PDF). North Devon AONB Unit. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 December 2012. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
- "Cenozoic". English Riviera Global Geopark. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
- Crowson, Tina (22 May 2013). "Torbay train improvements unveiled". Herald Express. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- "Devon – Timetables". Stagecoach Group. Archived from the original on 2 October 2009. Retrieved 1 November 2006.
- "Index to Torquay Churches". Terry Leaman. Retrieved 29 June 2019.
- "St Matthias Church - church history". St Matthias Church. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- Pevsner, N. (1952) South Devon. Harmondsworth: Penguin; pp. 291–94
- Dixon, Kevin (21 March 2018). "The church that rocked". We Are South Devon. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- "Torquay Christadelphians". Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- "Welcome to Torbay Islamic Centre". Torbayislamiccentre.com. Archived from the original on 8 May 2012.
- "JCR-UK: Torquay United Hebrew Congregation (Synagogue closed), Torbay, Devon". Jewish Communities and Records - United Kingdom. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- Office for National Statistics, "Table CAS021: Economic activity by sex and limiting long-term illness" in United Kingdom Census 2001 (London: Office for National Statistics, 2001)
- "Staff at Beverage Brands in Torquay face losing jobs". BBC News. 11 May 2011. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- Christie, Agatha (1977). An Autobiography. Collins. ISBN 0-00-216012-9.
- "Torquay Museum – About Us". torquaymuseum.org. Retrieved 3 April 2008.
- "See the Museum". Torquay Museum. Retrieved 3 April 2008.
- "Zoo to close due to lockdown impact". BBC News. 15 June 2020. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- "English Riviera: Torquay Hotel, Paignton, Brixham, Holidays, Hotels, Bed & Breakfast, South Devon".
- "Legal fight begins over £50,000 Torquay balloon cash". Torquay Herald Express. 11 July 2013. Archived from the original on 31 December 2013. Retrieved 29 December 2013.
- "Cairns Torquay Films". IMDb. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- "Torquay & Paignton Photoplay Productions". IMDb. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- "TV Star Lined up for Bay Comedy". thisissouthdevon.co.uk. Archived from the original on 29 August 2004. Retrieved 3 April 2008.
- "Devon Films : Creators of Snappers, a British romantic comedy". devonfilms.com. Archived from the original on 4 April 2008. Retrieved 3 April 2008.
- "Princess Theatre : Official Website". livenationtheatres.co.uk. Archived from the original on 1 August 2009. Retrieved 3 April 2008.
- "Little Theatre in Torquay, Devon". toadstheatre.co.uk. Retrieved 3 April 2008.
- "Babbacombe Theatre – Let us entertain you ..." babbacombe-theatre.com. Archived from the original on 4 August 2007. Retrieved 3 April 2008.
- Creative Torbay Retrieved 30 October 2013.
- Devon Library and Information Services (6 May 2005). "Devon newspaper bibliography: Torquay". Devon County council. Archived from the original on 4 December 2008. Retrieved 4 December 2008.
- "School Prospectus" (PDF). St Margarets Primary School. p. 18.
- "Recorded crime datasets". Homeoffice.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 17 January 2013.
- "BBC – Devon – Features – Explorer and word inventor". bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 9 October 2006.
- "Percy (Harrison) Fawcett Biography - Biography.com". The Biography Channel. Archived from the original on 7 August 2007. Retrieved 9 October 2006.
- "Peter Cook (I)". Internet Movie Database Incorporated. Retrieved 9 October 2006.
- "Wishbone Ash – The Band – Past Members". wishboneash.com. Retrieved 8 October 2006.
- "Roger Deakins". Internet Movie Database Incorporated. Retrieved 9 October 2006.
- "Miranda Hart". Internet Movie Database Incorporated. Retrieved 9 October 2006.
- "BBC – Comedy – Fawlty Towers". bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 29 October 2006.
- "Sybil to return to Fawlty Towers". BBC News. 9 August 2006. Retrieved 3 October 2018.
- Savill, Richard (11 May 2002). "My husband was not like Basil". London: Telegraph Media Group. Retrieved 21 January 2007.
- "Blackball (2003)". Internet Movie Database Incorporated. Retrieved 21 January 2007.
- Laing, Jemima (20 October 2010). "Has Banksy left his mark at a Torquay hotel?". BBC News. Retrieved 21 October 2010.
- "'Banksy' art at Grosvenor Hotel in Torquay vandalised". BBC News. 31 May 2011. Retrieved 19 October 2012.
- "Local Studies Education Series - Agatha Christie" (PDF). Torbay Council Library Services. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 December 2013. Retrieved 22 November 2013.
- "Ashfield". The English Riviera. Retrieved 21 November 2013.
- "Agatha Christie (née Miller) writer and playwright 1890-1976. Blue plaque". Open Plaques. Retrieved 22 November 2013.
Sources
- Russell, Percy (1960). A History of Torquay. Torquay: Devonshire Press Limited.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Torquay. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Torquay. |
- – The Geology of Torbay, from a local geologist.