Total carbon
Total carbon (TC) is an analytical measurement for carbon content. This measurement is commonly found in environmental and pharmaceutical analysis.
| Part of a series on the |
| Carbon cycle |
|---|
 |
Carbon types
A variety of different terms are used to identify the different types of carbon present at different levels of detail.
.svg.png.webp)
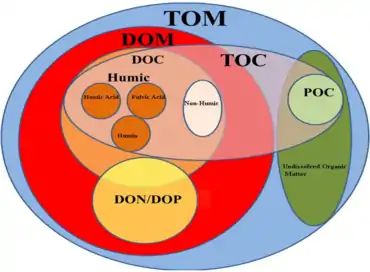
Relationship between carbon types
- Total carbon (TC) – all the carbon in the sample, including both inorganic and organic carbon
- Total inorganic carbon (TIC) – often referred to as inorganic carbon (IC), carbonate, bicarbonate, and dissolved carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Total organic carbon (TOC) – material derived from decaying vegetation, bacterial growth, and metabolic activities of living organisms or chemicals.
- Volatile organic compounds (VOC) – also referred to as purgeable organic carbon (POC); organic carbon that has been removed from a neutral, or acidified sample by purging with an inert gas. These are usually determined by purge and trap gas chromatography–mass spectrometry.
- Non-purgeable organic carbon (NPOC) – commonly referred to as TOC; organic carbon remaining in an acidified sample after purging the sample with gas.
- Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) – organic carbon remaining in a sample after filtering the sample, typically using a 0.45 micrometer filter.
- Suspended organic carbon – also called particulate organic carbon (POC); the carbon in particulate form that is too large to pass through a filter.
References
- Schumacher, B. A. (2002). "Methods for the Determination of Total Organic Carbon (TOC) in Soils and Sediments" Ecological Risk Assessment Support Center. US. Environmental Protection Agency 23p.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.