Trichomonasvirus
Trichomonasvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Totiviridae. The protozoan parasite Trichomonas vaginalis serves as the natural host. There are currently four species in this genus, including the type species Trichomonas vaginalis virus 1.[1][2]
| Trichomonasvirus | |
|---|---|
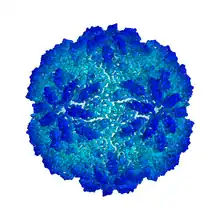 | |
| Cryo-EM image of protein surface of Trichomonas vaginalis virus 1 | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Duplornaviricota |
| Class: | Chrymotiviricetes |
| Order: | Ghabrivirales |
| Family: | Totiviridae |
| Genus: | Trichomonasvirus |
| Type species | |
| Trichomonas vaginalis virus 1 | |
Taxonomy
Group: dsRNA
- Family: Totiviridae
- Genus: Trichomonasvirus
- Trichomonas vaginalis virus 1
- Trichomonas vaginalis virus 2
- Trichomonas vaginalis virus 3
- Trichomonas vaginalis virus 4
Structure
Viruses in Trichomonasvirus are non-enveloped, with icosahedral geometries, and T=2 symmetry. The diameter is around 36 nm. Genomes are linear and non-segmented, around 4.6-4.9kb in length. The genome has 2 open reading frames.[1]
| Genus | Structure | Symmetry | Capsid | Genomic arrangement | Genomic segmentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trichomonasvirus | Icosahedral | T=2 | Non-enveloped | Linear |
Life cycle
Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment to host receptors, which mediates endocytosis. Replication follows the double-stranded RNA virus replication model. Double-stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. Protozoan parasite trichomonas vaginalis serve as the natural host.[1]
| Genus | Host details | Tissue tropism | Entry details | Release details | Replication site | Assembly site | Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trichomonasvirus | Protozoa | Endocytosis | Unknown | Unknown | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Unknown |
References
- "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Retrieved 13 August 2015.
- ICTV. "Virus Taxonomy: 2014 Release". Retrieved 13 August 2015.