13th (film)
13th is a 2016 American documentary film by director Ava DuVernay. The film explores the "intersection of race, justice, and mass incarceration in the United States;"[3] it is titled after the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, adopted in 1865, which abolished slavery throughout the United States and ended involuntary servitude except as a punishment for conviction of a crime.
| 13th | |
|---|---|
.png.webp) Digital release poster | |
| Directed by | Ava DuVernay |
| Produced by |
|
| Written by |
|
| Music by | Jason Moran |
| Cinematography |
|
| Edited by | Spencer Averick |
Production company | Kandoo Films |
| Distributed by | Netflix |
Release date |
|
Running time | 100 minutes |
| Country | United States |
| Language | English |
| Budget | $1 million[1] |
| Box office | $566 (UK only)[2] |
| Part of a series on |
| Slavery |
|---|
 |
DuVernay contends that slavery has been perpetuated since the end of the American Civil War through criminalizing behavior and enabling police to arrest poor freedmen and force them to work for the state under convict leasing; suppression of African Americans by disenfranchisement, lynchings, and Jim Crow; politicians declaring a war on drugs that weighs more heavily on minority communities and, by the late 20th century, mass incarceration affecting communities of color, especially American descendants of slavery, in the United States. She examines the prison-industrial complex and the emerging detention-industrial complex, discussing how much money is being made by corporations from such incarcerations.
13th garnered acclaim from a number of film critics. It was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature at the 89th Academy Awards, and won the Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Documentary or Nonfiction Special at the 69th Primetime Emmy Awards.[4]
It experienced a surge in viewership by 4,665 percent in June 2020 during the George Floyd protests.[5]
Synopsis
The film begins with an audio clip of President Barack Obama stating that the US had 5 percent of the world's population but 25 percent of the world's prisoners. This film features several activists, academics, political figures from both major US political parties, and public figures, such as Angela Davis, Bryan Stevenson, Michelle Alexander, Jelani Cobb, Van Jones, Newt Gingrich, Cory Booker, Henry Louis Gates Jr., and others.[6]
It explores the economic history of slavery and post-Civil War racist legislation and practices that replaced it. DuVernay contends as "systems of racial control" and forced labor from the years after the abolition of slavery to the present. Southern states criminalized minor offenses, arresting freedmen and forcing them to work when they could not pay fines; institutionalizing this approach as convict leasing (which created an incentive to criminalize more behavior). She contends they disenfranchised most black people across the South at the turn of the 20th century, excluding them from the political system (including juries), at the same time that lynching of black people by white mobs reached a peak. In addition, Jim Crow legislation was passed by Democrats, to legalize segregation and suppress minorities, forcing them into second-class status. Following the passage of civil rights legislation in the 1960s that restored civil rights, the film notes the Republican Party's appeal to southern white conservatives, including the claim to be the party to fight the war on crime and war on drugs, which began to include mandatory, lengthy sentencing. A new wave of minority suppression began, reaching African Americans and others in the northern, mid-western and western cities where many had migrated in earlier decades. After their presidential candidates lost to Republicans, Democratic politicians such as Bill Clinton joined the war on drugs.
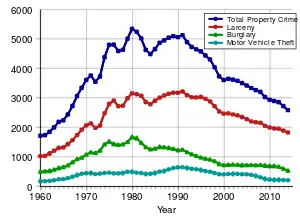
As a result, from the early 1970s to the present, the rate of incarceration and the number of people in prisons has climbed dramatically in the United States, while at the same time the rate of crime in the United States has continued to decline since the late 20th century. As late as the 2016 presidential election, the eventual winner Donald Trump worked to generate fear of crime, claiming high rates in New York City, for instance, which was not true according to the documentary. The documentary states that crime was lower overall than it had been in decades, but that Republican candidates raised it to generate fear. Private prison contractors entered the market to satisfy demand as arrests and sentences increased, forming an independent group with its own economic incentives to criminalize minor activities and lengthen sentences in order to keep prisons full. Politicians and businessmen in rural areas encouraged construction of prisons to supply local jobs, and they also allegedly have had incentives to keep prisons full.
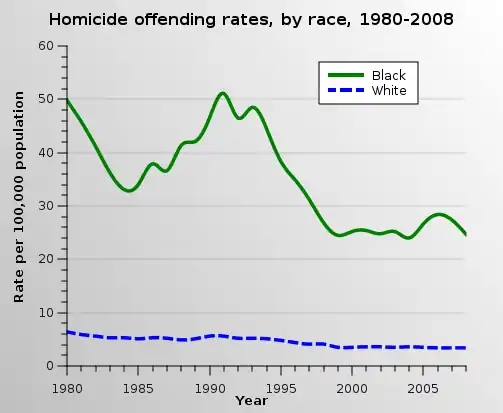
The federal Bureau of Prisons announced in 2016 its intention to stop contracting with private providers for prison services. According to the film, the "over-incarceration" of adults has severely damaged generations of black and minority families and their children.
The film explores the role of the American Legislative Exchange Council, backed by corporations, that has provided Republican state and federal legislators with draft legislation to support the prison-industrial complex. It contends that only after some of the relationships were revealed did corporations like Walmart and others receive criticism and drop out of the organization.
The film explores the demonization of minority poor through these decades putatively to serve political ends, contributing to fears of minorities by whites and to problems of police brutality against minority communities. In the 21st century, the regularity of fatal police shootings of unarmed minorities in apparently minor confrontations has been demonstrated by videos taken by bystanders and by the increasing use of cameras in police cars or worn by officers; DuVernay ends the film with graphic videos of fatal shootings of black people by police, what Manohla Dargis describes as, after the previous discussion, having the effect of "a piercing, keening cry."[3]
Production
The film was written by Ava DuVernay, who wrote and directed Selma (2014), and Spencer Averick. Averick also edited the film. Produced and filmed in secrecy, 13th was revealed only after it was announced as the opening film for the 2016 New York Film Festival, the first documentary ever to open the festival.[8][9]
Release
The film was released on October 7, 2016, on Netflix.[8] A companion piece 13th: A Conversation with Oprah Winfrey & Ava DuVernay was released on January 26, 2017, in the United States and on January 31, 2017, worldwide on the service.[10] On April 17, 2020, Netflix released the film for free on YouTube.[11]
Reception
Critical response
On Rotten Tomatoes, the film has an approval rating of 97% based on 102 reviews, with an average rating of 8.77/10. The site's critical consensus reads, "13th strikes at the heart of America's tangled racial history, offering observations as incendiary as they are calmly controlled."[12] On Metacritic, the film has a score of 83 out of 100, based on reviews from 29 critics, indicating "universal acclaim".[13]
Manohla Dargis of The New York Times praised what she called the power of DuVernay's film and its meticulous marshaling of facts. She said, summarizing the film, "The United States did not just criminalize a select group of black people. It criminalized black people as a whole, a process that, in addition to destroying untold lives, effectively transferred the guilt for slavery from the people who perpetuated it to the very people who suffered through it."[3] Peter Travers of Rolling Stone awarded the film four stars and named it one of the best films of 2016.[14]
Viewership
On a panel about the future of film for The New York Times on June 23, 2019, DuVernay said:
I'm told by the system that [a theatrical release] is what matters, but then people aren't seeing your movies. Take the number of people who saw 'Selma,' a Christmas release with an Oscar campaign about Dr. Martin Luther King. Well, more than a quadruple amount of people saw '13th,' about the prison-industrial complex. If I'm telling these stories to reach a mass audience, then really, nothing else matters.[15]
In 2020, the film saw a surge in viewership by 4,665 percent during the George Floyd protests.[5]
Accolades
The film was nominated for dozens of awards, winning best documentary at the British Academy Film Awards and the Primetime Emmy Awards, a Peabody Award for excellence, and receiving a nomination for the Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature. DuVernay received a Primetime Emmy Award for her writing, and was nominated for directing. The song "Letter to the Free" was nominated for several awards with Common, Robert Glasper, and Karriem Riggins winning the Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Original Music and Lyrics.
| Award | Category | Recipients | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Academy Awards | Best Documentary Feature | Ava DuVernay, Spencer Averick & Howard Barish | Nominated |
| ACE Eddie Awards | Best Edited Documentary Feature | Spencer Averick | Nominated |
| African-American Film Critics Association Awards | Best Documentary | 13th | Won |
| Alliance of Women Film Journalists' EDA Awards | Best Documentary | 13th | Won |
| Best Woman Director | Ava DuVernay | Won | |
| Outstanding Achievement by a Woman in the Film Industry | Ava DuVernay | Won | |
| Austin Film Critics Association Awards | Best Documentary | 13th | Nominated |
| Black Reel Awards | Best Film | 13th | Nominated |
| Best Feature Documentary | 13th | Won | |
| Best Original or Adapted Song | "Letter to the Free" – Common | Nominated | |
| British Academy Film Awards | Best Documentary | Ava DuVernay, Spencer Averick & Howard Barish | Won |
| Cinema Audio Society | Outstanding Achievement in Sound Mixing for a Motion Picture – Documentary | Jeffrey Perkins | Nominated |
| Critics' Choice Documentary Awards | Best Documentary Feature | 13th | Nominated |
| Best Documentary (TV/Streaming) | 13th | Won | |
| Best Director (TV/Streaming) | Ava DuVernay | Won | |
| Best Political Documentary | 13th | Won | |
| Best Song in a Documentary | "Letter to the Free" | Nominated | |
| Dallas–Fort Worth Film Critics Association Awards | Best Documentary | 13th | Runner-up |
| Detroit Film Critics Society Awards | Best Documentary | 13th | Nominated |
| Hollywood Music in Media Awards | Best Original Song – Documentary | "Letter to the Free" | Nominated |
| Houston Film Critics Society Awards | Best Documentary Feature | 13th | Nominated |
| Independent Spirit Awards | Best Documentary Feature | 13th | Nominated |
| MTV Movie & TV Awards | Best Documentary | 13th | Won |
| NAACP Image Awards | Outstanding Documentary (Film) | 13th | Won |
| National Society of Film Critics Awards | Best Non-Fiction Film | 13th | 3rd Place |
| New York Film Critics Online Awards | Best Documentary | 13th | Won |
| Online Film Critics Society Awards | Best Documentary Film | 13th | Nominated |
| Peabody Awards | Excellence | Forward Movement LLC and Kandoo Films | Won |
| Phoenix Film Critics Society Awards | Best Documentary | 13th | Nominated |
| Primetime Emmy Awards | Outstanding Documentary or Nonfiction Special | 13th | Won |
| Outstanding Directing for Nonfiction Programming | Ava DuVernay | Nominated | |
| Outstanding Writing for Nonfiction Programming | Ava DuVernay and Spencer Averick | Won | |
| Outstanding Cinematography for a Nonfiction Program | Hans Charles, Kira Kelly | Nominated | |
| Outstanding Original Music and Lyrics | Common, Robert Glasper and Karriem Riggins for "Letter to the Free" | Won | |
| Outstanding Picture Editing for a Nonfiction Program | Spencer Averick | Nominated | |
| Outstanding Sound Editing for Nonfiction Programming (Single or Multi-Camera) | Tim Boggs, Alex Lee, Julie Pierce and Lise Richardson | Nominated | |
| Outstanding Sound Mixing for a Nonfiction Program (Single or Multi-Camera) | Jeffrey Perkins | Nominated | |
| Satellite Awards | Best Documentary Film | 13th | Won |
| San Francisco Film Critics Circle Awards | Best Documentary Film | 13th | Nominated |
| Vancouver Film Critics Circle Awards | Best Documentary | 13th | Nominated |
| Washington D.C. Area Film Critics Association | Best Documentary | 13th | Won |
| Women Film Critics Circle Awards | Best Movie by a Woman | 13th | Won |
| Best Woman Storyteller (Screenwriting Award) | Ava DuVernay | Won | |
| Best Documentary By or About Women | 13th | Won | |
| Courage in Filmmaking | Ava DuVernay | Won |
See also
References
- "13th (2016)". The Wrap. Retrieved May 29, 2017.
- "13th". Box Office Mojo. Retrieved February 20, 2017.
- Manohla Dargis, "Review: '13TH,' the Journey From Shackles to Prison Bars", The New York Times, September 29, 2016. Retrieved February 20, 2017
- "Oscar Nominations". The Oscars. Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences. Archived from the original on January 10, 2013. Retrieved January 24, 2017.
- Nolan, Emma (June 17, 2020). "'13th' Netflix Documentary Viewers Surge by 4,665 Percent in Three Weeks".
- Smith, Nigel M. (September 26, 2016). "The 13th: inside Ava DuVernay's Netflix prison documentary on racial inequality". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved February 16, 2017.
- Cooper, Alexia D.; Smith, Erica L. (November 16, 2011). Homicide Trends in the United States, 1980-2008 (Report). Bureau of Justice Statistics. p. 11. NCJ 236018. Archived from the original on March 30, 2018.
- Lockett, Dee (July 19, 2016). "Ava DuVernay's The 13th Will Be the First Documentary to Ever Open the New York Film Festival". Vulture.
- Cox, Gordon (July 19, 2016). "2016 New York Film Festival to Open With Ava DuVernay Documentary 'The 13th'". Variety.
- Calvario, Liz. "13TH: A Conversation with Oprah Winfrey & Ava DuVernay Clip". IndieWire. Retrieved April 24, 2017.
- "13TH | FULL FEATURE | Netflix". YouTube. April 17, 2020. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- "13th (2016)". Rotten Tomatoes. Retrieved October 28, 2020.
- "13th reviews". Metacritic. Retrieved October 28, 2020.
- "20 Best Movies of 2016". Rolling Stone. Retrieved March 20, 2017.
- "Film: Forecasting the Future of the Movie Business, The New York Times , Arts & Leisure section, June 23, 2019, p. 12-13"
External links
- 13th on Netflix
- 13th at IMDb
- 13th at Rotten Tomatoes
- 13th at Metacritic
- 13th on Facebook