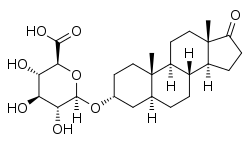
Androsterone glucuronide
Androsterone glucuronide (ADT-G) is a major circulating and urinary metabolite of testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT).[1] It accounts for 93% of total androgen glucuronides in women.[1] ADT-G is formed from androsterone by UDP-glucuronosyltransferases, with the major enzymes being UGT2B15 and UGT2B17.[1] It is a marker of acne in women while androstanediol glucuronide is a marker of hirsutism (excess hair growth) in women.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S,3S,4S,5R,6R)-6-[[(3R,5S,8R,9S,10S,13S,14S)-10,13-Dimethyl-17-oxo-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-tetradecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl]oxy]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
ADT-G; 5α-Androstan-3α-ol-17-one 3-glucuronide; 17-Oxo-5α-androstan-3α-yl β-D-glucopyranosiduronic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H38O8 | |
| Molar mass | 466.571 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB02829
- Jerome F. Strauss, III; Robert L. Barbieri (13 September 2013). Yen and Jaffe's Reproductive Endocrinology. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 837–. ISBN 978-1-4557-2758-2.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.