Asmat–Mombum languages
The Asmat–Muli Strait languages are a branch of the Trans–New Guinea languages spoken along the southern coast of Indonesian New Guinea, established by Timothy Usher and Edgar Suter.[1]
| Asmat–Muli Strait | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | New Guinea |
| Linguistic classification | Trans–New Guinea
|
| Subdivisions | |
| Glottolog | None |
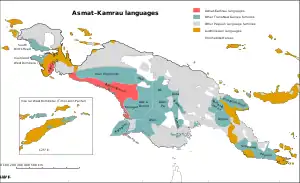 Map: The Asmat-Muli Strait languages of New Guinea
The Asmat–Kamrau Bay languages
The Muli Strait languages
Other Trans–New Guinea languages
Other Papuan languages
Austronesian languages
Uninhabited | |
Protoforms of basic vocabulary include *moi 'water', *iafVnV 'ear', *uase 'name', *awoɣ 'breast'.[1]
Subdivision
Asmat–Muli Strait consists of two primary subgroups:[2]
- Asmat–Kamrau
- Muli Strait (or Mombum, Komolom)
Proto-language
Phonology
Proto-Asmat–Muli Strait is reconstructed with 12 consonants and 5 vowels:[1]
*m *n *p *t *k *(m)b *(n)d *(ŋ)g *s *w *ɾ *j
Vowels are *a *e *i *o *u.
Basic vocabulary
Some lexical reconstructions by Usher (2020) are:[1]
gloss Proto-Asmat-Muli Proto-Asmat-Kamrau Proto-Muli Strait head/hair *gVɸV *uɸu *ɣo̝p, *ɣo̝w ear *iaɸVnV *iaɸ[a/o]ne *ie̝pær nose/tip *mVnVgV *m[e/a]n[e] *mæne̝ɣ tooth/sharp *sisV *sisV *-sir blood *[i/e]sV *ese *ir breast *awVgV *awo *abuɣ louse *amV *amo *am dog *iuwuɾi *juwuɾi *i[u]bui pig *[o/u]ɸV *oɸo *up egg *[o]k[a] *oka sun *jau[a] *jawu *zaua water *mVi *moi *mo̝i name *uase *uwase *ur eat *nV *nV *no̝ku
References
- New Guinea World, Asmat – Muli Strait
- Usher, Timothy; Suter, Edgar (2020). "The Asmat-Muli Languages of Southwestern New Guinea" (PDF). Language & Linguistics in Melanesia. Port Moresby: Journal of the Linguistic Society of Papua New Guinea. 38. ISSN 0023-1959.
External links
- Timothy Usher & Edgar Suter, New Guinea World, Proto–Asmat – Muli Strait
- Asmat-Kamrau Bay. New Guinea World.
- Asmat-Kamoro. New Guinea World.
- Asmat. New Guinea World.
- Kamrau Bay. New Guinea World.
- Muli Strait. New Guinea World.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.