Barron County, Wisconsin
Barron County is a county located in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. As of the 2010 census, the population was 45,870.[1] Its county seat is Barron.[2] The county was created in 1859 and later organized in 1874.[3]
Barron County | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Wisconsin | |
 Wisconsin's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 45°25′N 91°51′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1874 |
| Named for | Henry D. Barron |
| Seat | Barron |
| Largest city | Rice Lake |
| Area | |
| • Total | 890 sq mi (2,300 km2) |
| • Land | 863 sq mi (2,240 km2) |
| • Water | 27 sq mi (70 km2) 3.0% |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 45,870 |
| • Estimate (2019) | 45,244 |
| • Density | 52/sq mi (20/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Congressional district | 7th |
| Website | www |
History
The county was created in 1859[4] as Dallas County (named after Vice President George M. Dallas), with the county seat located at Barron. It was renamed Barron County on March 4, 1869. The county took the name Barron in honor of Wisconsin lawyer and politician Henry D. Barron, who served as circuit judge of the Eleventh Judicial Circuit.[5][6] Barron County was organized in 1874.[3] In the late 1800s and early 1900s a community of Russian immigrants moved to Barron County.[7]
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 890 square miles (2,300 km2), of which 863 square miles (2,240 km2) is land and 27 square miles (70 km2) (3.0%) is water.[8]
Adjacent counties
- Washburn County – north
- Sawyer County – northeast
- Rusk County – east
- Chippewa County – southeast
- Dunn County – south
- St. Croix County – southwest
- Polk County – west
- Burnett County – northwest
Major highways

 U.S. Highway 8
U.S. Highway 8 U.S. Highway 53
U.S. Highway 53 U.S. Highway 63
U.S. Highway 63 Highway 25 (Wisconsin)
Highway 25 (Wisconsin) Highway 48 (Wisconsin)
Highway 48 (Wisconsin)
Airports
- KRPD - Rice Lake Regional Airport serves Barron County.
- KUBE - Cumberland Municipal Airport is located three miles south of Cumberland.
- Y23 - Chetek Municipal–Southworth Airport also serves the county and surrounding communities.
- 9Y7 - Barron Municipal Airport enhances county service.
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1860 | 13 | — | |
| 1870 | 538 | 4,038.5% | |
| 1880 | 7,024 | 1,205.6% | |
| 1890 | 15,416 | 119.5% | |
| 1900 | 23,677 | 53.6% | |
| 1910 | 29,114 | 23.0% | |
| 1920 | 34,281 | 17.7% | |
| 1930 | 34,301 | 0.1% | |
| 1940 | 34,289 | 0.0% | |
| 1950 | 34,703 | 1.2% | |
| 1960 | 34,270 | −1.2% | |
| 1970 | 33,955 | −0.9% | |
| 1980 | 38,730 | 14.1% | |
| 1990 | 40,750 | 5.2% | |
| 2000 | 44,963 | 10.3% | |
| 2010 | 45,870 | 2.0% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 45,244 | [9] | −1.4% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[10] 1790–1960[11] 1900–1990[12] 1990–2000[13] 2010–2019[1] | |||
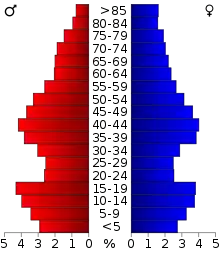
As of the census[14] of 2000, there were 44,963 people, 17,851 households, and 12,352 families residing in the county. The population density was 52 people per square mile (20/km2). There were 20,969 housing units at an average density of 24 per square mile (9/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 97.69% White, 0.14% Black or African American, 0.81% Native American, 0.32% Asian, 0.04% Pacific Islander, 0.32% from other races, and 0.69% from two or more races. 0.96% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 34.4% were of German, 21.8% Norwegian and 5.3% Irish ancestry.
There were 17,851 households, out of which 31.30% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 56.90% were married couples living together, 8.20% had a female householder with no husband present, and 30.80% were non-families. 25.40% of all households were made up of individuals, and 12.20% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.48 and the average family size was 2.97.
In the county, the population was spread out, with 25.30% under the age of 18, 8.10% from 18 to 24, 26.80% from 25 to 44, 23.40% from 45 to 64, and 16.40% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 39 years. For every 100 females there were 98.20 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 96.00 males.
In 2017, there were 504 births, giving a general fertility rate of 70.6 births per 1000 women aged 15–44, the 15th highest rate out of all 72 Wisconsin counties.[15] Additionally, there were fewer than five reported induced abortions performed on women of Barron County residence in 2017.[16]
Communities
Cities
- Barron (county seat)
- Chetek
- Cumberland
- Rice Lake
Villages
- Almena
- Cameron
- Dallas
- Haugen
- New Auburn (mostly in Chippewa County)
- Prairie Farm
- Turtle Lake (partly in Polk County)
Towns
Census-designated place
Politics
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 62.4% 15,797 | 36.3% 9,188 | 1.3% 328 |
| 2016 | 60.1% 13,614 | 34.8% 7,889 | 5.2% 1,168 |
| 2012 | 50.4% 11,443 | 48.0% 10,890 | 1.6% 359 |
| 2008 | 45.7% 10,457 | 52.8% 12,078 | 1.5% 351 |
| 2004 | 50.3% 12,030 | 48.9% 11,696 | 0.9% 211 |
| 2000 | 49.5% 9,848 | 44.9% 8,928 | 5.7% 1,128 |
| 1996 | 35.8% 6,158 | 46.7% 8,025 | 17.5% 3,008 |
| 1992 | 32.5% 6,572 | 39.9% 8,063 | 27.7% 5,595 |
| 1988 | 48.5% 8,527 | 50.9% 8,951 | 0.5% 92 |
| 1984 | 53.9% 9,587 | 45.4% 8,061 | 0.7% 124 |
| 1980 | 47.1% 8,791 | 46.3% 8,654 | 6.6% 1,240 |
| 1976 | 45.1% 7,393 | 53.0% 8,678 | 1.9% 311 |
| 1972 | 59.9% 8,418 | 38.3% 5,376 | 1.8% 251 |
| 1968 | 55.4% 7,526 | 38.1% 5,183 | 6.5% 880 |
| 1964 | 40.6% 5,701 | 59.3% 8,332 | 0.2% 23 |
| 1960 | 57.1% 8,640 | 42.7% 6,464 | 0.3% 41 |
| 1956 | 61.1% 8,634 | 38.4% 5,419 | 0.5% 73 |
| 1952 | 66.8% 10,013 | 32.7% 4,902 | 0.4% 66 |
| 1948 | 45.9% 5,516 | 51.2% 6,148 | 2.9% 352 |
| 1944 | 55.7% 7,137 | 43.6% 5,585 | 0.8% 101 |
| 1940 | 54.9% 7,806 | 43.5% 6,183 | 1.7% 238 |
| 1936 | 37.9% 5,067 | 55.6% 7,419 | 6.5% 869 |
| 1932 | 32.9% 3,852 | 63.4% 7,413 | 3.7% 436 |
| 1928 | 72.0% 8,455 | 27.1% 3,185 | 0.9% 106 |
| 1924 | 29.4% 2,703 | 4.1% 377 | 66.5% 6,100 |
| 1920 | 84.2% 6,887 | 9.1% 742 | 6.7% 547 |
| 1916 | 55.0% 2,746 | 37.3% 1,863 | 7.8% 388 |
| 1912 | 35.6% 1,414 | 26.8% 1,065 | 37.6% 1,491[18] |
| 1908 | 66.5% 3,247 | 25.9% 1,266 | 7.6% 373 |
| 1904 | 78.3% 3,575 | 13.7% 625 | 8.0% 366 |
| 1900 | 72.8% 2,950 | 23.3% 943 | 4.0% 161 |
| 1896 | 64.7% 2,772 | 30.9% 1,324 | 4.3% 186 |
| 1892 | 57.4% 1,818 | 24.2% 767 | 18.4% 584 |
References
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 6, 2011. Retrieved January 17, 2014.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on July 12, 2012. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- "Wisconsin: Individual County Chronologies". Wisconsin Atlas of Historical County Boundaries. The Newberry Library. 2007. Retrieved August 12, 2015.
- Wisconsin Legislative Reference Bureau (comp.) State of Wisconsin 1991-1992 Blue Book. Madison: Author, 1991, p. 731.
- Dictionary of Wisconsin History (Wisconsin Historical Society)
- "Here's How Iron Got Its Name". The Rhinelander Daily News. June 16, 1932. p. 2. Retrieved August 24, 2014 – via Newspapers.com.

- https://www.wisconsinhistory.org/Records/Article/CS1855
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Retrieved August 2, 2015.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved March 26, 2020.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 2, 2015.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved August 2, 2015.
- Forstall, Richard L., ed. (March 27, 1995). "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 2, 2015.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. April 2, 2001. Retrieved August 2, 2015.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved May 14, 2011.
- "Annual Wisconsin Birth and Infant Mortality Report, 2017 P-01161-19 (June 2019): Detailed Tables". Archived from the original on 2019-06-19. Retrieved 2019-06-20.
- Reported Induced Abortions in Wisconsin, Office of Health Informatics, Division of Public Health, Wisconsin Department of Health Services. Section: Trend Information, 2013-2017, Table 18, pages 17-18
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved November 9, 2020.
- The leading "other" candidate, Progressive Theodore Roosevelt, received 968 votes, while Socialist candidate Eugene Debs received 265 votes, Prohibition candidate Eugene Chafin received 253 votes, and Independent candidate Arthur Reimer received 5 votes.
Further reading
- Curtiss-Wedge, Franklin. (comp.) History of Barron County Wisconsin. Minneapolis: H. C. Cooper Jr., 1922.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Barron County, Wisconsin. |
- Barron County website
- Barron County map from the Wisconsin Department of Transportation
