Boconó Fault
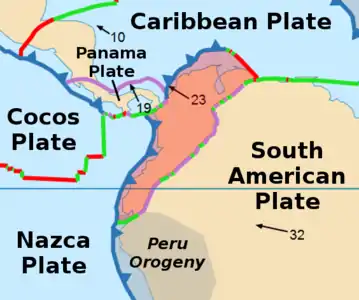
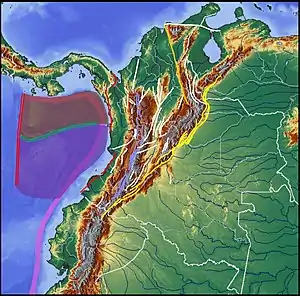
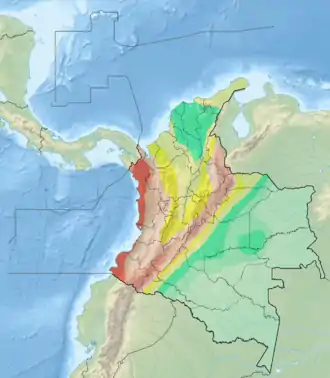
The Boconó Fault is a complex of geological faults located in the Eastern Ranges of northeastern Colombia and the Mérida Andes of northwestern Venezuela. The fault has a NE-SW orientation; it is a strike-slip fault and has a dextral relative movement.[1] It extends over a length of 500 kilometres (310 mi). The fault, with a slip rate ranging from 4.3 to 6.1 millimetres (0.17 to 0.24 in) per year, has been active since the Early Holocene and earthquakes of 1610 and 1894 are associated with it.[2]
| Boconó Fault | |
|---|---|
| Falla Boconó | |
.jpg.webp) Location of the fault in Venezuela | |
| Etymology | Boconó, Trujillo |
| Location | Northern South America |
| Coordinates | 9°15′N 70°16′W |
| Country | |
| Region | Andean |
| State | Norte de Santander, Santander Mérida, Táchira |
| Cities | Cúcuta |
| Characteristics | |
| Range | Mérida Andes, Eastern Ranges |
| Part of | Boconó-San Sebastián-El Pilar Fault System |
| Length | 500 km (310 mi) |
| Strike | NE-SW |
| Displacement | 4.3–6.1 mm (0.17–0.24 in)/yr |
| Tectonics | |
| Plate | South American |
| Status | Active |
| Earthquakes | 1610, 1894 |
| Type | Strike-slip fault |
| Movement | Dextral |
| Age | Holocene |
| Orogeny | Andean |
References
- Audemard et al., 2006
- Audemard, 1997
Bibliography
- Audemard M., Franck A.; Singer P., André; Soulas, Jean-Pierre (2006). "Quaternary faults and stress regime of Venezuela" (PDF). Revista de la Asociación Geológica Argentina. Asociación Geológica Argentina. 61 (4): 480–491. Retrieved 2017-06-22.
- Audemard Mennessier, Franck A. (1997). "Holocene and historical earthquakes on the Boconó fault system, Southern Venezuelan Andes: Trench confirmation". Journal of Geodynamics. 24 (1–4): 155–167. doi:10.1016/S0264-3707(96)00037-3. Retrieved 2017-06-22.
Further reading
- Paris, Gabriel; Machette, Michael N.; Dart, Richard L.; Haller, Kathleen M. (2000). Map and Database of Quaternary Faults and Folds in Colombia and its Offshore Regions (PDF). USGS. pp. 1–66. Retrieved 2017-06-20.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.