Ascension Island
Ascension Island is an isolated volcanic island, 7°56′ south of the Equator in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is about 1,000 miles (1,600 km) from the coast of Africa and 1,400 miles (2,300 km) from the coast of Brazil. It is governed as part of the British Overseas Territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha,[2] of which the main island, Saint Helena, is around 800 miles (1,300 km) to the southeast. The territory also includes the sparsely populated Tristan da Cunha archipelago, 2,300 miles (3,700 km) to the south, about halfway to the Antarctic Circle.
Ascension Island | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: "God Save the Queen" | |
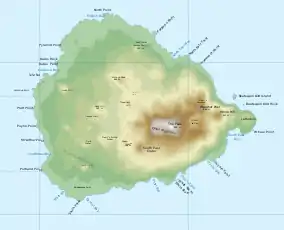 Topographic map of Ascension Island | |
.svg.png.webp) Location of Ascension Island in the southern Atlantic Ocean | |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| British settlement | 1815 |
| Part of UK Overseas Territory of Saint Helena, Ascension Island and Tristan da Cunha | 12 September 1922 |
| Current constitution | 1 September 2009 |
| Capital and largest settlement | Georgetown 7°56′S 14°25′W |
| Official languages | English |
| Government | Devolved locally governing dependency under a constitutional monarchy |
• Monarch | Elizabeth II |
• Governor | Philip Rushbrook |
| Sean Burns | |
| Legislature | Island Council |
| Government of the United Kingdom | |
• Minister | Tariq Ahmad |
| Area | |
• Total | 88 km2 (34 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 2,818 ft (859 m) |
| Population | |
• 2016 census | 806[1] |
| Currency | Saint Helena pound (£) (SHP) |
| Time zone | UTC±00:00 (GMT) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +247 |
| UK postcode | ASCN 1ZZ |
| ISO 3166 code | SH-AC |
| Internet TLD | .ac |
Named after the day of its recorded discovery, Ascension of Jesus, Ascension Island was an important safe haven and coaling station to both mariners and commercial airliners back in the days of international air travel by flying boats.
During World War II, it was an important naval and air station, especially providing antisubmarine warfare bases in the Battle of the Atlantic.[3] Ascension Island was garrisoned by the British Admiralty from 22 October 1815 to 1922.
The island is the location of RAF Ascension Island, which is a Royal Air Force station, a European Space Agency rocket tracking station, an Anglo-American signals intelligence facility and the BBC World Service Atlantic Relay Station. The island was used extensively as a staging point by the British military during the Falklands War. Ascension Island hosts one of four ground antennas that assist in the operation of the Global Positioning System (GPS) navigational system (others are on Kwajalein Island, Diego Garcia, and Cape Canaveral). NASA operates a Meter Class Autonomous Telescope (MCAT) on Ascension Island for tracking orbital debris, which is potentially hazardous to operating spacecraft and astronauts, at a facility called the John Africano NASA/AFRL Orbital Debris Observatory.[4]
History

Discovery
In 1501, the Portuguese navigator João da Nova sighted the island on Ascension Day (which fell on 21 May that year) and named it Ilha da Ascensão after this feast day.[5] Dry and barren, the island had little appeal for passing ships except for collecting fresh meat, and was not claimed for the Portuguese Crown. Mariners could hunt for the numerous seabirds and the enormous female green turtles that laid their eggs on the sandy beaches. The Portuguese also introduced goats as a potential source of meat for future mariners.
In February 1701, HMS Roebuck, commanded by William Dampier, sank in the common anchoring spot in Clarence Bay to the northwest of the island. Sixty men survived for two months until they were rescued. Almost certainly, after a few days they found the strong water spring in the high interior of the island, in what is now called Breakneck Valley (there is a much smaller water source, lower on the mountain, which was named Dampier's Drip by people who probably misinterpreted Dampier's story).[6]
It is possible that the island was sometimes used[7] as an open prison for criminal mariners, although there is only one documented case of such an exile, a Dutch ship's officer, Leendert Hasenbosch, set ashore at Clarence Bay as a punishment for sodomy in May 1725.[8] British mariners found the Dutchman's tent, belongings and diary in January 1726; the man's remains were not found. His diary was published in translation in London later that same year, under the title Sodomy Punish'd.[9]
Organised settlement
Organised settlement of Ascension Island began in 1815, when the British garrisoned it as a precaution after imprisoning Napoleon on Saint Helena to the southeast.[5] On 22 October the Cruizer-class brig-sloops Zenobia and Peruvian claimed the island for King George III. The Royal Navy designated the island as a stone frigate, HMS Ascension, with the classification of "Sloop of War of the smaller class".[10]

The location of the island made it a useful stopping-point for ships and communications. The Royal Navy used the island as a victualling station for ships, particularly those of the West Africa Squadron working against the slave trade.[11] A garrison of Royal Marines was based at Ascension from 1823 and Colonel Edward Nicolls became the first commandant.[12]
Botany
In 1836 the second Beagle voyage visited Ascension. Charles Darwin described it as an arid treeless island, with nothing growing near the coast. Sparse vegetation inland supported "about six hundred sheep, many goats, a few cows & horses," large numbers of guineafowl imported from the Cape Verde islands, rats, mice, and land crabs; he agreed with the saying attributed to the people of St Helena that "We know we live on a rock, but the poor people at Ascension live on a cinder." He noted the care taken to sustain "houses, gardens & fields placed near the summit of the central mountain," and cisterns at roadsides to provide drinking water. The springs were carefully managed, "so that a single drop of water may not be lost: indeed the whole island may be compared to a huge ship kept in first-rate order." In commenting on this, he noted René Primevère Lesson's remark "that the English nation alone would have thought of making the island of Ascension a productive spot; any other people would have held it as a mere fortress in the ocean."[13]
In 1843, botanist and explorer Joseph Hooker visited the island. Four years later, Hooker, with much encouragement from Darwin, advised the Royal Navy that with the help of Kew Gardens, they should institute a long-term plan of shipping trees to Ascension. The planted trees would capture more rain and improve the soil, allowing the barren island to become a garden. So, from 1850 and continuing year on year, ships came with an assortment of plants from botanical gardens in Argentina, Europe and South Africa. By the late 1870s Norfolk pines, eucalyptus, bamboo, and banana trees grew in profusion at the highest point of the island, Green Mountain, creating a tropical cloud forest.[14]
Astronomical observation
Beginning in July 1877, the astronomer Sir David Gill and his wife Isobel spent six months on Ascension Island. This was to take advantage of the near approach of Mars occurring that year. Based on Johannes Kepler's laws of planetary motion, Gill conceived that in pioneering the use of a heliometer he would be able to accurately measure the transit of Mars on his own, rather than in combination with many observers simultaneously recording the position of the planet as had been the technique during the time. This is because a heliometer is a telescope that uses a split image to measure the angular separation of celestial bodies. In observing this from near the equator a greater observable distance would be visible, hence a temporary observatory being decided upon for Ascension.[15]
Although originally based in Georgetown, the pair found the evenings to be too cloudy to make observations of the night sky due to Georgetown being located downwind of orthographic cloud emanating from Green Mountain.[15] Isobel quickly endeavoured to find an area less affected by the evening cloud and trekked for several miles over lava fields to find a new location. Having found an area on the south west of the island seemingly less affected, they then had to determine how to move 20 tons of delicate observational equipment to the new location. Fortunately a small clear beach was located nearby which was used for landing the equipment by sea. This was later named Mars Bay, a name which it carries to this day and which has since been designated a Nature Reserve.[16] The couple then spent several months camped out at the bay making their observations, assisted by a krooman and a marine.
All of the effort was ultimately a success producing a solar distance of 93.08 ± 0.16 million miles, not far off the modern day measurement of 92.9558. As a result of his work on the solar parallax David Gill went on to be appointed Royal Astronomer at the Cape of Good Hope.[17]
Early government
Between 1872 and 1889, the permanent population of the island was listed as HMS Flora (Tender), under the orders of the Commander-in-Chief, Cape of Good Hope. HMS Flora (1844) had been the guardship at Ascension from 1865 to 1872 before being ordered south to become the Simonstown depot ship. Five ratings died while on a recreational boat trip in 1879.[18]
In 1899, the Eastern Telegraph Company installed the first underwater cable from the island, connecting the UK with its colonies in South Africa.[5] In 1922, letters patent made Ascension a dependency of Saint Helena.[5] The island was managed by the head of the Eastern Telegraph Company on the island until 1964 when the British Government appointed an Administrator to represent the Governor of Saint Helena on Ascension.[5]
World War II

The Island was under direct control of the Board of Admiralty until 1923.[19]
During World War II, to supply and augment extensive amphibious aircraft antisubmarine patrol operations ongoing from the early days of the war, the United States built an airbase on Ascension Island, known as "Wideawake",[5] after a nearby colony of sooty terns (locally called 'wideawake' birds because of their loud, distinctive constant (day-and-night) cawing chatter).[20] The airbase, which was under construction by the 38th Combat Engineer Battalion of the Army Corps of Engineers, was unexpectedly visited by two British Fairey Swordfish torpedo planes on 15 June 1942. According to one of the pilots, Peter Jinks, the planes were fired upon before being recognised as allies. The Swordfish had to land on the unfinished airstrip, thus becoming the first aircraft to land on Ascension Island proper—which had long served as an anti-submarine warfare base for Consolidated PBY Catalina flying boats. The event was commemorated with a postage stamp 15 June 1982.
The airfield was used by the US military as a stopping point for American aircraft crossing the Atlantic Ocean on the way to theatres of operation in Europe and Africa. American bombers based at Wideawake were engaged in the Laconia incident.
The only local military action during World War II occurred on 9 December 1941. At around mid-day, the German submarine U-124 approached Georgetown on the surface with the intention of sinking any ships at anchor or shelling the cable station. Fort Bedford, a two-gun shore battery at Cross Hill, above Georgetown, fired on the submarine. The guns scored no hits but the U-boat submerged and retreated. The battery remains largely intact to this day, together with its guns, BL 5.5 inch Mark I naval guns removed from HMS Hood during a refit in Malta in 1938.
The airbase fell into disuse following the American departure at the end of World War II.
Later military involvement
With the Space Race and the Cold War, the Americans returned in 1956.[5] Wideawake Airfield expanded in the mid-1960s. The runway, with its strange hump, was extended, widened, and improved to allow its use by large aircraft, and later to act as an emergency runway for the Space Shuttle, although the Shuttle never had to use it.[5] At the time, it was the world's longest airport runway.[20] The United States Space Force uses the island as part of its Eastern Range.[21] NASA established a tracking station on the island in 1967, which it operated for more than 20 years before closing it down in 1990.[5]
Ascension was the shore terminal for the furthest down range installation of the Atlantic Missile Impact Location System (MILS), an acoustic system for locating splashdown of test nose cones.[22] The MILS hydrophones that were located in the SOFAR channel for broad area coverage have played a significant role in long range acoustic transmission studies and incidents. The island's location makes it a first point of Atlantic reception for acoustics from the other oceans. As an example the Ascension hydrophones received and the site processed signals generated near Heard Island in the Indian Ocean some 9,200 km (5,700 mi; 5,000 nmi) from the Ascension arrays and passing around Africa.[23][24] The Ascension array was one of those involved in the Vela incident acoustic signal in which there were correlated acoustic arrivals with the time and estimated location of the double flash detected by the Vela satellite.[25]
A joint Government Communications Headquarters and National Security Agency signals intercept station was also established on Ascension during the Cold War.[26][27] The island retains a role in space exploration: the European Space Agency now operates an Ariane monitoring facility there.[5] The BBC Atlantic Relay Station was installed in 1966 for short-wave broadcasts to Africa and South America.
In 1982 the British task force used Ascension Island as a staging post during the Falklands War. The Royal Air Force deployed a fleet of Avro Vulcan bombers and Handley Page Victor tankers at the airfield. Vulcans launched the opening shots of the British offensive from Ascension in Operation Black Buck. The RAF also used the base to supply the task force. Because of the increase in air traffic during the war, Wideawake, with up to 400 movements of all types each day, was one of the busiest airfields in the world for a short period.[28] The Royal Navy's fleet stopped at Ascension for refuelling on the way. Following the war, the British retained an increased presence on the island, establishing RAF Ascension Island, and providing a refuelling stop for the regular airlink between RAF Brize Norton in Oxfordshire, and RAF Mount Pleasant in the Falkland Islands.
Twenty-first century
As of 2004, it was reported that the Composite Signals Organisation, an arm of GCHQ, continued to operate a signals interception facility at Cat Hill on Ascension.[29] As of 2007 NASA continued to list Ascension Island as a "downrange site" used for range safety instrumentation.[30] In particular, the Post-Detect Telemetry System used to acquire launch vehicle telemetry includes a station on Ascension.[31]
In 2008 British diplomats at the United Nations Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf (UN CLCS), requested sovereignty over 200,000 km2 (77,220 sq mi) of submarine territory around the island. This would enable exploration into new reserves of oil, gas and minerals, though none are thought to exist.[32]
The 2009 Constitution order ended Ascension's status as a dependency of St Helena and provided for one Governor of the combined Overseas Territory of St Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha.[33]
In 2016, the United States Department of Energy started operating a mobile climate research facility on the island. It is operated by the Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Climate Research Facility (ARM) near the South East Crater, south of the Green Mountain summit. The field campaign requires the mobile facility to be operational for about 17 months until October 2017.[34]
The island hosts one of four dedicated ground antennas that assist in the operation of the Global Positioning System (GPS) navigation system (the others are on Diego Garcia (British Indian Ocean Territory), Kwajalein (Marshall Islands), and at Cape Canaveral, Florida (US)).[35] NASA and the Air Force Research Laboratory operate a Meter-Class Autonomous Telescope (MCAT) on Ascension as part of the deep space surveillance system for tracking orbital debris, which can be a hazard to spacecraft and astronauts.[35][36]
Geography

The main island has an area of approximately 88 km2. A volcanic peak rising from 100 km (62 mi) west of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, much of the island is a wasteland of lava flows and cinder cones; forty-four distinct dormant craters have been identified.[11]
Geology
Ascension is a geologically young formation, the tip of an undersea volcano which rose above the waves only a million years ago. Although volcanic activity is mainly associated with the Mid-Atlantic Ridge plate boundary 80 km to the west, Ascension also displays some features which are commonly attributed to "hotspot" volcanism. Such volcanism is typically assumed to arise from a deep mantle thermal plume from the core-mantle boundary. Alternatively it may result from minor deformations of the oceanic crust that cause extension and permit magma to rise passively up from the asthenosphere. Ascension last erupted about 500 years ago.[37] Due to the low rainfall and geologically recent eruptions, its soil consists mostly of clinker.[20]
The island consists of a wide range of alkaline rocks atypical for oceanic islands, ranging from basalt through trachyandesite and trachyte to rhyolite.[38][39]

Climate
Ascension has a hot desert climate (BWh, according to the Köppen climate classification). The temperatures at the coast average from 22.7 to 27.8 °C (72.9 to 82.0 °F), and about 5 to 6 °C (9 to 11 °F) cooler at the highest point. Rain showers may occur at any time during the year, but tend to be heavier between June and September. Although the island is in the tropical zone, average annual rainfall is very low. The cause of this might be the relatively low temperature of the ocean water, as the Benguela Current and South Equatorial Current flow northward west of Africa. These currents bring cooling effects around the eastern South Atlantic Ocean. Tropical cyclones also occur only rarely in the South Atlantic Ocean which might be caused by the same phenomenon, and by strong vertical wind shear.[40][41][42]
| Climate data for Georgetown, Ascension Island | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 31.7 (89.1) |
31.7 (89.1) |
31.7 (89.1) |
32.2 (90.0) |
31.7 (89.1) |
30.6 (87.1) |
30.6 (87.1) |
28.9 (84.0) |
28.9 (84.0) |
28.9 (84.0) |
30.0 (86.0) |
30.6 (87.1) |
32.2 (90.0) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 28.3 (82.9) |
29.4 (84.9) |
30.0 (86.0) |
30.0 (86.0) |
28.9 (84.0) |
27.8 (82.0) |
27.2 (81.0) |
26.1 (79.0) |
26.1 (79.0) |
26.1 (79.0) |
26.7 (80.1) |
27.2 (81.0) |
27.8 (82.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 22.8 (73.0) |
23.9 (75.0) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.4 (75.9) |
23.9 (75.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
22.2 (72.0) |
21.1 (70.0) |
21.1 (70.0) |
21.1 (70.0) |
22.2 (72.0) |
22.6 (72.7) |
22.7 (72.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 18.9 (66.0) |
20.0 (68.0) |
21.1 (70.0) |
20.6 (69.1) |
19.4 (66.9) |
19.4 (66.9) |
19.4 (66.9) |
18.3 (64.9) |
17.2 (63.0) |
18.3 (64.9) |
17.8 (64.0) |
17.8 (64.0) |
17.2 (63.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 8 (0.3) |
10 (0.4) |
38 (1.5) |
30 (1.2) |
10 (0.4) |
15 (0.6) |
13 (0.5) |
10 (0.4) |
10 (0.4) |
13 (0.5) |
8 (0.3) |
8 (0.3) |
173 (6.8) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.3 mm) | 7 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 8 | 8 | 94 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 74 | 73 | 73 | 73 | 70 | 69 | 69 | 70 | 73 | 73 | 72 | 73 | 72 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 229 | 224 | 276 | 267 | 264 | 260 | 239 | 217 | 165 | 161 | 159 | 198 | 2,659 |
| Source 1: Deutscher Wetterdienst[43] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Danish Meteorological Institute[44] | |||||||||||||
Ecology
Flora

The endemic flora includes plants like Pteris adscensionis, Asplenium ascensionis, Euphorbia origanoides as well as the extinct species Oldenlandia adscensionis, Sporobolus durus and Dryopteris ascensionis. Anogramma ascensionis (Ascension Island parsley fern) was thought to have become extinct due to habitat loss, until four plants were found on the island in 2010. Over 60 specimens were then successfully cultivated.[45] Portuguese explorers released goats in the 1500s which ate many species to extinction. The later introduction of rabbits, sheep, rats and donkeys, and over 200 imported species further marginalised the original flora.[46]
By 1843 the island was barren with few plants. However, due to the introduction of species by the British, Ascension Island's Green Mountain is now one of the few large-scale planned forests, and is gradually growing with each year. Its highest point is at 859 m.[11] Non-indigenous plants teem there, and the crown of Green Mountain is a lush halo of bamboo. Flanking one side is a large stand of tall Norfolk pine, trees planted by British mariners, which were to have been used as replacement masts for sailing ships. In June 2005 the first National Park on Ascension Island, the Green Mountain National Park, was opened.
Prosopis juliflora, a type of mesquite known as Mexican thorn, was introduced by BBC engineers to bind the dry top soil when they arrived in 1966 to construct a shortwave relay station. It has thrived on the barren lava of the island – an estimated 38,000 bushes existed by 2016. Its spread has been destructive to other species, and current encroachment on the edges of beaches threatens those that use this space, such as the green turtle. Its hardy taproots can extend to 30 metres deep. Local authorities are considering means of controlling or eradicating it.[20][47]
Fauna

A variety of mammals have been introduced: donkeys, sheep, cats and rats among others. Reptiles consist of two species of lizards. Endemic insect species include the minute, wingless Psocopteran Troglotroctes ashmoleorum, that has been found in caves and between lava blocks.[48] In summer, flies are known to be a problem. The largest native land animal is the land crab Johngarthia lagostoma (formerly Gecarcinus lagostoma).[49] Offshore, there is a variety of open-ocean fish, including sharks, wahoo, tuna, bonito, barracuda, marlin, blackfish and sailfish. The protected green turtle is perhaps the most notable of the endemic fauna, coming ashore to lay their eggs on the beaches from November to May. Turtles were regularly harvested until 1930, when the practice was banned. By 1970 the turtle population had begun to rebound.[20] From the 1970s, when records began, to 2014, green turtle nesting increased by 500%, resulting in some 24,000 nests being laid on the island's main beaches each year.[50]
On land are found such non-native birds such as canaries, francolins, mynas, sparrows, and waxbills. Sooty terns or "wideawake birds" nest in great seashore lava "fairs". Other seabirds include some types of boobies, petrels, and tropicbirds (named boatswain, pronounced BO-sun birds, by the inhabitants of the island), white tern, brown noddy, black noddy and Ascension frigatebird. The Ascension crake became extinct around the beginning of the nineteenth century.[47]

Off the east coast of Ascension is the islet of Boatswain Bird Island. It is a haven for sea birds providing refuge from the rats, cats and people that came to Ascension Island from Europe and Africa. Following a successful campaign headed by the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds, the main island was in 2006 declared free of feral cats, and sea birds are now once again nesting on Ascension Island.[51]
Bird life

After cats were introduced to Ascension Island in 1815, large seabird breeding colonies were quickly wiped out everywhere except in small cat-inaccessible areas, such as on the offshore Boatswain Bird Island. Following a two-year campaign, feral cats were eradicated by 2009 and seabirds began to recolonise the main island.[52]
Ascension Island, including fourteen inshore stacks and marine habitat extending out for 3 nautical miles (5.6 km; 3.5 mi) from the coastline, has been identified as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International as a breeding site for seabirds. Birds for which the IBA is significant include red-billed tropicbirds, Ascension frigatebirds (an endemic breeder), sooty terns and black noddies.[53] The island was formerly home to the endemic Ascension crake, but the species has been extinct since the early nineteenth century.
Marine Protected Area
In January 2016 the UK Government announced that an area around Ascension Island was to become a huge marine reserve, to protect its varied and unique ecosystem, including some of the largest marlin in the world, large populations of green turtle, and the island's own species of frigate bird.[54]
On 22 August 2019 the Ascension Island Government announced the designation of 100% of Ascension's Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) as a Marine Protected Area (MPA). The EEZ covers an area of over 440,000 square km, making it one of the largest in the world. Within the MPA it is proposed that commercial fishing and mineral extraction will be prohibited. Legislation is now being brought forward and development of a management plan is underway. These will be put into place subject to confirmation that the ongoing costs of management, monitoring and enforcement have been provided by the UK government.[55]
Government
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Ascension Island |
Ascension had formed part of a British overseas territory together with Saint Helena and Tristan da Cunha.[11] and was governed by St Helena, until it achieved its own Constitution.
Although being legally and economically separate from Saint Helena and Tristan da Cunha, for efficiency purposes, the three territories share some administrative resources. Executive authority is vested in Elizabeth II,[11] who is represented by the Governor of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. The Governor resides in Jamestown, Saint Helena, and an Administrator is appointed to represent the Governor on Ascension Island.
Island Council

As a result of changes in the constitutional arrangements for Ascension Island, a unicameral Legislative Council with advisory powers was introduced in 2002. The first Island Council of seven members was elected, and took office on 1 November 2002. This council was dissolved by order of the Governor of Saint Helena on 24 October 2005, and a new election was held on 16 November 2005. 697 electors chose among ten candidates contesting the seven seats.[56]
Six of the seven members resigned in January 2007 in the belief that they were "assisting to legitimise a democracy that doesn't really exist on Ascension Island".[57] A memorandum sent by a group of Ascension Island residents suggests that the handling of economic development, taxation and representation led to the dispute and that all six councillors resigned (five of them at once). The memorandum states, "The elected Council has been used to legitimise an illegitimate system that has never been a true democracy and, it seems, was never intended to be."[58] The counter-argument was that, as the island has no indigenous population whatsoever, it is in an unusual political position. Consequently, a general election was called, but by the close of nominations, there were only two candidates.[58] The election was abandoned, and the governor suspended the Island Council for 12 months. It was stated that an election would take place in April 2008 but following consultations this was extended to October.[59] Eventually, candidates were elected to form a new Island Council, which was sworn in on 27 October 2008.[60][61]
On 26 September 2019 a general election of the Island Council was held. This followed the dissolution of the previous Council on 1 September 2019, in accordance with the Island Government (Ascension) Ordinance 2008. Seven candidates ran for five available Councillor positions, with electors being permitted to cast up to five votes each. Of 518 registered electors 150 electors cast 498 votes. The five successful Councillors were sworn in on 26 September 2019.[62]
Laws
Ascension Island has its own local system of law, much of which is based on the laws of Saint Helena and some parts of English law with modifications.[11] The Island Council advises on new or revised laws. Where local legislation does not exist, Saint Helena law may be used where appropriate and suitable for local adaptation, or specific Ascension Island law is enacted. Employment legislation is a mixture of contract law and the Workmen's Protection Ordinance, which guarantees a contract, and obliges employers to provide free accommodation, medical cover, food (or a food allowance), and travel.
The Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Constitution Order 2009 was made by HM the Queen and the Privy Council on 8 July and came into operation in September 2009.[11] The new constitution replaced the 1988 version and among other changes limited the Governor's powers, included a Bill of Rights, established independence of the judiciary and the public service, and designated the Governor of St Helena as, concurrently, the Governor for Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. It ended the "dependency" status of Ascension and Tristan da Cunha on Saint Helena that had been in place, for administrative convenience, since 1922.[63]
Relationship to St Helena
Although the first Island Council was elected in 2002, between 1922 and 2009 Ascension was a dependency of St Helena with an appointed Administrator representing the UK Government on the island under the purview of the Governor of St Helena.
Whilst the Ascension Island Government is distinct from the St Helena Government, the Governor of St Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha serves as head of both of these. The executive authority of Ascension is exercised on behalf of Her Majesty by the Governor, either directly or through the Administrator of Ascension and other officers subordinate to the Governor.[64] In practice the Administrator is the head of the Ascension Island Government and is responsible for the day-to-day running of the Government.
In 2019, the UK House of Commons Foreign Affairs Select Committee published its report Global Britain and the British Overseas Territories: Resetting the relationship, following an investigation into the relationship between the UK and the Overseas Territories. The report recommended that Ascension and Tristan da Cunha be recognised as Overseas Territories in their own right (paragraph 48 / recommendation 8):
The Committee notes that the Overseas Territory of St. Helena includes the separate and distinct territories of Ascension Island and Tristan da Cunha. These are both inhabited territories with a population that is not directly connected to St. Helena and have their own identities, elected governments and flags. Therefore, Ascension Island and Tristan da Cunha should be treated with equality as British Overseas Territories in their own right and the FCO should change their status to this effect. However, this change should not necessarily imply that the practice of St. Helena, Ascension Island and Tristan da Cunha sharing the same Governor should come to an end.[65]
To date the UK Government has not responded to the committee's recommendation.
Demographics

In the February 2016 census, 806 people were recorded living on Ascension Island, 556 from Saint Helena (nicknamed the "Saints")[66] and 250 people of other nationalities.[1] RAF Ascension Island is made up of 17 staff. There has never been an indigenous population on the island.[67]
There are five settlements:
- Georgetown (the main civilian settlement and capital of the island)
- Two Boats (a civilian village, with its school)
- Cat Hill (the United States's main base on the island)
- Traveller's Hill (Royal Air Force base)
- Wideawake Airfield (with the Royal Air Force station).
Additionally, there are some cottages on Green Mountain, occasionally occupied by visitors, and the Residency, the official residence of the Administrator.
To enter Ascension Island, individuals need the Administrator's written permission. There are no permanent residents. A contract of employment is a requirement to stay on the island,[66] though short term visits by tourists are possible with prior approval. The British government has confirmed that there is no "right of abode" on Ascension Island.[68] As the local newspaper The Islander reported at the time,[69][70] it was raised by some former Council members and four expatriate employees that whilst it was agreed there was no right of abode, the authorities had previously indicated it would consider changing the law to allow the rights of abode and property purchase, but decided not to do so.[71]
Culture
There are Scouting and Guiding groups on Saint Helena and Ascension Island. Scouting was established on Ascension Island in November 1973,[72] having been established on St Helena island in 1912.
The Islander has been published since 1971. It is available online.[73]
Economy

The main economic activity on the island is centred on the military bases at Wideawake Airfield, and the BBC World Service's Atlantic Relay station. The Ministry of Defence estate and facilities are managed by the infrastructure support provider Interserve Defence. Serco runs the airport services and Sodexo provides catering and domestic facilities. A former feature of Ascension was a 70,000-tonne tanker permanently moored offshore that was operated by Maersk as a bulk fuel facility. In December 2002, this was replaced by an on-shore Petroleum Supply Depot under military management, with fuel still being delivered by a chartered tanker, Maersk Rapier, which operates on an MOD resupply contract for both Ascension and the Falkland Islands every two months. Fuel for the island is transferred via a floating hose, which is connected to the on-shore depot at the island's pier head and to the ship at anchor.
The main export items are Ascension Island postage stamps, first issued in 1922, and, since 2010, commemorative coins (which are legal tender but non-circulating) and commercial fishing licences for long-line tuna fishing vessels operating to ICCAT quotas.
A secondary export is the international internet domain code .ac, which small UK educational colleges and science museums are favouring due to its similarity to .ac.uk, the domain code reserved for well-established UK educational institutions. In December 2013, The Pirate Bay (one of the most well-known file piracy websites in the world) moved to .ac following the seizure of their .sx website.
Tourism and related industries

Until 2002, tourism was virtually non-existent because of the inaccessibility of the island to transport, the absence of guest accommodation and the need for a sponsor. Limited air travel has, however, been made available in recent years to the public by the RAF, and the Georgetown Obsidian Hotel and a number of guest cottages have been opened. All visitors are required to obtain an entry permit before travelling. Sport fishing is the main attraction for many of the visitors. The island also boasts what is sometimes called the worst golf course in the world.[74][75]
Communications
The island hosts many communications and relay stations, exploiting its mid-Atlantic position. Both the BBC and Cable & Wireless Worldwide (owned by Vodafone since 2012)[76] have communications posts there. The European Space Agency (ESA) also has a tracking station on the island that tracks the Ariane 5 and the Soyuz rockets shortly after their launch from Kourou in French Guiana.
Ascension has one local radio station and one relayed from St. Helena. It also receives broadcasts from the British Forces Broadcasting Service and television services for the US military.[11]
Ascension Island has the international calling code +247 and, from 1 June 2015 has five digit numbers (the old four-digit number prefixed by the digit "6" and "4" for mobile telephones).[77]
The island provided a base for a NASA communications dish during the space race in the mid-twentieth century.[20] The island was chosen due to its central location in the Atlantic. Sites were chosen due to their proximity to orbital paths—generally along the Equator.
Banking and currency
The Bank of St. Helena has a branch on the island; it holds an account with the UK's Lloyds Bank for the purposes of conducting money transfers with the rest of the world.[78] The currency on Ascension Island is the Saint Helena pound. Tristan da Cunha however uses the pound sterling rather than the Saint Helena pound. The coins of the Saint Helena pound specify that they are for use on both Saint Helena and Ascension Island, but with no mention of Tristan da Cunha, whereas the banknotes only say “Government of St. Helena”. There are also distinct commemorative coins for Ascension island. For more information on currency in the wider region, see Pound sterling in the South Atlantic and the Antarctic.
Education
Two Boats School is the only school on the island and provides education to all children aged 3–16.
Transport

In 2003 the British and US governments signed the Wideawake agreement designed to allow a limited number of non-scheduled civilian aircraft to land on Ascension Island, under responsibility of the British government.[79][80]
Poor runway conditions at RAF Ascension Island led in April 2017 to the cancellation of twice-weekly flights from there to the UK (RAF Brize Norton) and to the Falkland Islands (RAF Mount Pleasant). An Airbus A330 aircraft operated by AirTanker Services on behalf of the Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom) carried out those flights, called the South Atlantic Air Bridge, although a limited number of commercial passenger tickets were available. Those flights now travel via Cape Verde.[81] AW Ship Management arranged for civilians to board RAF flights to and from RAF Ascension Island and RAF Brize Norton. Previously AW Ship Management had a package deal where passengers could travel in one direction on the RAF flights and in the other on the RMS St Helena, which travelled between Ascension, Saint Helena, and Cape Town, South Africa until the opening of St Helena Airport to passenger flights.[82][83]
While A330s are for now unable to land at the airport, the United States military uses Air Transport International flying 757 "combi" jets to maintain a twice monthly flight between the island and Patrick Space Force Base in Florida for the use of its personnel only, while the (MV Ascension) supply ship regularly services US facilities.
A mixture of A400 and C17 planes land at Ascension every three weeks to supply the RAF operation and deliver mail.[81]
There is no taxi service on the island and most visitors requiring transport hire a car. There are around 40 kilometres (25 mi) of roads on the island, all hard-surfaced,[11] along with many unsurfaced paths and trails. Some of the road surfacing used was surplus tarmac from a previous airstrip construction operation.[66] Traffic drives on the left.[66]
Currently the cargo vessel M/V Helena, under AW Shipping Management, takes a limited number of passengers[84] between Cape Town and St Helena and Ascension on its voyages.[85]
Following the retirement of the RMS St Helena in 2018 the South African airline SA Airlink has operated an inter-island Air service between St Helena and Ascension once a month. This is operated as a charter service extension on the regular Johannesburg to St Helena route with an overnight turnaround on Ascension.[86][87]
As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic and South African government response, the SA Airlink air service was suspended in April 2020. Since this time Ascension, along with its sister island of St Helena, has been intermittently supplied by a Titan operated charter service originating in the UK. [88][89]
See also
References
- "Census 2016 – summary report" (PDF). St Helena Government. June 2016. p. 9. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 October 2016. Retrieved 23 January 2017.
- "The St Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Constitution Order 2009". Archived from the original on 12 March 2010. Retrieved 26 September 2009.
- Victory at Sea (Series title), Volume-10 "Beneath the Southern Cross" 1952 production of NBC, (Disc 2 of DVD collection reproduction ca. 2007-2008)
- Garcia, Mark (11 August 2016). "Searching for "Space Junk" in Paradise". Archived from the original on 15 August 2016. Retrieved 14 August 2016.
- "Ascension History". mysterra.org. Mysterra Magazine. Archived from the original on 27 October 2010. Retrieved 3 January 2011.
- Duff Hart-Davis, Ascension, the story of a South Atlantic island.
- see Carl Friedrich Behrens, Reise durch die Sued-Laender und um die Welt (1737), p. 250, who wrote that various criminal mariners had been exiled to the island; also in Alex Ritsema A Dutch Castaway on Ascension Island in 1725 (2010), pp. 26, 115-117.
- Alex., Ritsema (2010). A Dutch castaway on Ascension Island in 1725. Alex Ritsema. pp. 48–56. ISBN 9781446189863.
- Sodomy Punish'd, as well as two other translations of the diary are available at "The MAN and other families". Retrieved 23 June 2019.
- https://www.ascension.gov.ac/section/history
- "Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 3 January 2011.
- Admiralty, Great Britain (December 1919). "Other Senior Naval Officers or Officers in Charge at Ports Abroad". Navy List. London England: HM Stationery Office. p. 700.
- Keynes 2001, pp. 431–432
- "Charles Darwin's ecological experiment on Ascension isle". BBC News. 1 September 2010. Archived from the original on 1 September 2010. Retrieved 1 September 2010.
Wilkinson, David M. (2003). "The parable of Green Mountain: Ascension Island, ecosystem construction and ecological fitting". Journal of Biogeography. 31: 1–4. doi:10.1046/j.0305-0270.2003.01010.x. S2CID 59332510. - "Six Months in Ascension". American Scientist. 6 February 2017. Retrieved 1 October 2019.
- "National Protected Areas Ordinance" (PDF).
- "Sir David Gill | Scottish astronomer". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 1 October 2019.
- "Answers," The Mariner's Mirror, Vol. 87, Issue 3, 2001, 337.
- Blethen Levy, Dianne A. (2017). "Saint Helena, Ascension, Tristan da Cunha. The Maritime Heritage Project. Sea Captains, Ships, Merchant Marines, Merchandise, Migrations". www.maritimeheritage.org. California United States: Maritime Heritage. Retrieved 19 October 2018.
- "BBC News, The island where nothing makes sense, 19 April 2016". BBC News. 19 April 2016. Archived from the original on 20 February 2018. Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- https://www.stripes.com/news/us/space-force-units-are-already-operating-worldwide-and-experts-expect-more-to-pop-up-soon-1.641654
- Cone, Bruce E. (1 July 1976). The United States Air Force Eastern Test Range — Range Instrumentation Handbook (PDF). Patrick Air Force Base, Florida: Eastern Test Range, Directorate of Range Operations. p. 1-1. Retrieved 12 September 2020.
- Munk, Walter H.; Spindel, Robert C.; Baggeroer, Arthur; Birdsall, Theodore G. (20 May 1994). "The Heard Island Feasibility Test" (PDF). Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. Acoustical Society of America. 96 (4): 2330–2342. doi:10.1121/1.410105. Retrieved 26 September 2020.
- NOAA AOML (February 1993). Reception At Ascension Island, South Atlantic, of the Transmissions From The Heard Island Feasibility Test (NOAA Technical Memorandum ERL AOML-73) (PDF) (Report). Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory. Retrieved 12 September 2020.
- De Geer, Lars-Erik; Wright, Christopher (22 September 2019). "From Sheep to Sound Waves, the Data Confirms a Nuclear Test". Foreign Policy (FP). Washington, DC: FP Group, Graham Holdings Company. Retrieved 23 September 2020.CS1 maint: date and year (link)
- Aldrich, Richard (2010). GCHQ: The Uncensored Story of Britain's Most Secret Intelligence Agency. London: HarperPress. ISBN 9780007357123.
- Bamford, James (2008). Body Of Secrets. New York: Random House. p. 168. ISBN 9781407009209.
- "Part 19. Ascension Island - Stepping Stone to Victory". Naval History. Archived from the original on 12 December 2016. Retrieved 17 October 2017.
- "Settlers wanted for a quiet life. No rush". The Telegraph. 5 April 2004. Archived from the original on 1 March 2016. Retrieved 4 March 2013.
- "NASA Range Safety Program – 2007 Annual Report" (PDF). NASA. p. 60. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 September 2008. Retrieved 7 August 2008.
- "NASA Range Safety Program – 2007 Annual Report" (PDF). NASA. p. 62. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 September 2008. Retrieved 7 August 2008.
- Lewis, Paul (28 August 2008). "Ascension Island. Barren, 4,044 miles (6,508 km) from Land's End, but ours says the FO". The Guardian. London. p. 1. Archived from the original on 31 August 2008. Retrieved 28 August 2008.
- "2009 Constitution Order" (PDF).
- "ARM - Field Campaign - LASIC: Layered Atlantic Smoke Interactions with Clouds". www.arm.gov. Archived from the original on 7 July 2016. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- "Africa :: Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha — The World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov. Retrieved 18 December 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - Lederer, S. M.; Stansbery, E. G.; Cowardin, H. M.; Hickson, P. (2019). The NASA Meter Class Autonomous Telescope: Ascension Island (PDF) (Report). NASA. Retrieved 13 December 2020.
- Preece, Katie; Mark, Darren F.; Barclay, Jenni; Cohen, Benjamin E.; Chamberlain, Katy J.; Jowitt, Claire; Vye-Brown, Charlotte; Brown, Richard J.; Hamilton, Scott (1 December 2018). "Bridging the gap: 40Ar/39Ar dating of volcanic eruptions from the 'Age of Discovery'" (PDF). Geology. 46 (12): 1035–1038. Bibcode:2018Geo....46.1035P. doi:10.1130/G45415.1. ISSN 0091-7613.
- "The geology of Ascension Island". Ascension Island Volcanology. 25 October 2017. Archived from the original on 5 January 2018. Retrieved 5 January 2018.
- Chamberlain, K. J.; Barclay, J.; Preece, K. J.; Brown, R. J.; Davidson, J. P. (2019). "Lower Crustal Heterogeneity and Fractional Crystallization Control Evolution of Small-volume Magma Batches at Ocean Island Volcanoes (Ascension Island, South Atlantic)" (PDF). Journal of Petrology. 60 (8): 1489–1522. doi:10.1093/petrology/egz037.
- "The South Equatorial Current System". oceancurrents.rsmas.miami.edu. Archived from the original on 5 May 2016. Retrieved 27 April 2016.
- "The Benguela Current". oceancurrents.rsmas.miami.edu. Archived from the original on 7 May 2016. Retrieved 27 April 2016.
- "TCFAQ G6) Why doesn't the South Atlantic Ocean experience tropical". www.aoml.noaa.gov. Archived from the original on 27 March 2015. Retrieved 28 April 2016.
- "Klimatafel von Georgetown (Flugh.), Insel Ascension / Südatlantik / Großbritannien" (PDF). Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure. Retrieved 4 November 2016.
- "STATIONSNUMMER 61902" (PDF). Ministry of Energy, Utilities and Climate. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 4 November 2016.
- Gill, Victoria (24 June 2010). "Experts rediscover plant presumed extinct for 60 years". BBC News. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 19 July 2010.
- "native flora" (PDF).
- "Bermuda Conference, Procedure Point 5b" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 June 2007. Retrieved 4 April 2007.
- Lienhard, 1996, Psocoptères nouveaux ou peu connus de quelques îles atlantiques (Canaries, Madère, Açores, Ascension) et de l'Afrique du Nord (Insecta: Psocoptera), Boletim do Museu Municipal do Funchal (Historia Natural) 48(267)
- Richard G. Hartnoll; Annette C. Broderick; Brendan J. Godley; Kate E. Saunders (2009). "Population structure of the land crab Johngarthia lagostoma on Ascension Island" (PDF). Journal of Crustacean Biology. 29 (1): 57–61. doi:10.1651/08-2992.1. S2CID 83991276. Archived from the original (pdf]) on 3 June 2011.
- "Scientists: Number of Green Turtles Increases More than 500%". 2 August 2014. Archived from the original on 8 August 2014. Retrieved 3 August 2014.
- Jorge. "Stray pets". Retrieved 3 January 2016.
- Ratcliffe, Norman; et al. (January 2010). "The eradication of feral cats from Ascension Island and its subsequent recolonization by seabirds" (PDF). Cambridge.org. Fauna & Flora International. pp. 20–22. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 November 2018. Retrieved 6 November 2018.
- "Ascension Island: mainland and stacks". Important Bird Areas factsheet. BirdLife International. 2012. Archived from the original on 30 June 2007. Retrieved 25 October 2012.
- Harrabin, Roger (3 January 2016). "Ascension Island to become marine reserve". BBC News. BBC. Archived from the original on 3 January 2016. Retrieved 3 January 2016.
- Bain, Alasdair. "Large-scale Marine Protected Area designated by Ascension Island Government – Ascension Island Government". Retrieved 1 October 2019.
- Juanita Brock, Ascension: Ascension Island Votes for Councillors Archived 16 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- "Ascension Island News for October 2015 from The Islander Newspaper". Archived from the original on 22 April 2016. Retrieved 3 January 2016.
- "Letter and submission from Residents of the Ascension Island". publications.parliament.uk. 12 October 2007. Archived from the original on 3 October 2017. Retrieved 3 October 2017.
- "Ascension Island Council". Archived from the original on 10 February 2008. Retrieved 3 February 2008.
- Ascension : Councillors Response to Article - Ascension Island – Why should we bother?
- "Ascension : Ascension Island Council Election - 2008". Archived from the original on 20 November 2018. Retrieved 3 October 2017.
- "Island Council Election Results – Ascension Island Government". Archived from the original on 18 December 2019. Retrieved 18 December 2019.
- "Ascension Island News for October 2015 from The Islander Newspaper". Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 3 January 2016.
- "The St Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Constitution Order 2009".
- "Global Britain and the British Overseas Territories: Resetting the relationship".
- "Ascension Population". mysterra.org. Mysterra Magazine. Archived from the original on 8 November 2010. Retrieved 3 January 2011.
- "The Island". 17 December 2012. Archived from the original on 2 February 2018. Retrieved 5 February 2018.
- "CONSTITUTION OF ST HELENA, ASCENSION AND TRISTAN DA CUNHA DRAFT FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION OF 25 June 2008". Archived from the original on 25 September 2008. Retrieved 3 June 2009.
- "FOREIGN AFFAIRS COMMITTEE — SELECT COMMITTEE ANNOUNCEMENT (4 July 2008)". Archived from the original on 31 May 2011. Retrieved 3 June 2009.
- "Letter's To FCO From Cyril Leo". Archived from the original on 31 May 2011. Retrieved 3 June 2009.
- "Ascension workers know the reality, says administrator". 16 September 2013. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 26 November 2017.
- The Ascension Island Newspaper November 1998
- "News from Ascension Island". The Islander. Archived from the original on 17 August 2019.
- "Travel news, photos, flight status, trip booking and more". MSN Travel. Archived from the original on 4 July 2014. Retrieved 3 January 2016.
- Ella Morton. "Ascension Island: Home of Lava Fields, a False Forest, and the World's Worst Golf Course". Slate. Slate. Archived from the original on 29 May 2018. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 29 June 2013. Retrieved 2 July 2013.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "International Telecommunication Union Directory" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 July 2015. Retrieved 2 July 2015.
- "the Bank of St. Helena". Archived from the original on 15 July 2011. Retrieved 16 February 2010.
- "AGREEMENT BETWEEN THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED KINGDOM OF GREAT BRITAIN AND NORTHERN IRELAND AND THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA CONCERNING THE USE OF WIDEAWAKE AIRFIELD ON ASCENSION ISLAND BY CIVIL AIRCRAFT NOT ENGAGED IN SCHEDULED INTERNATIONAL AIR SERVICES." Archived 3 November 2010 at WebCite 1 October 2003. United Nations Treaty Collection, Volume 2270, I-40420. Retrieved 10 August 2010.
- "Information for Aviators" Ascension Island Government. Retrieved 10 August 2010.
- Leithead, Alastair (4 July 2017). "Ascension: The increasingly unreachable island". BBC News. Archived from the original on 25 February 2018. Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- "RMS St Helena Brochure" (PDF). AW Ship Management. p. 18. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- "RAF Flights Fly with the RAF and meet the RMS en route". AW Ship Management. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- https://www.telegraph.co.uk/travel/lists/cabins-on-cargo-ships/
- "Passengers". St Helena Shipping. AW Shipping Management. Retrieved 6 January 2020. - see Routes and Prices
- Government, St Helena. "Air services to St Helena and Ascension". St helena government.
- "Air Services to St Helena and Ascention Island" (PDF). sainthelena.gov.sh. February 2018. Retrieved 16 January 2021.
- "Titan Airways take medical staff and supplies to St Helena". Titan Airways. 21 April 2020. Retrieved 16 January 2021.
- "Further St Helena Charter Flights Confirmed – Ascension Island Government". Retrieved 16 January 2021.
- Keynes, Richard (2001), Charles Darwin's Beagle Diary, Cambridge University Press, archived from the original on 18 September 2010, retrieved 19 September 2010
Bibliography
- Duff Hart-Davis, Ascension, the story of a South Atlantic island, p. 15
- Mitchell, David F. 2010. Ascension Island and the Second World War. Ascension Island: Ascension Island Heritage Society.
- Correspondent's diary: Ascension Island | The Economist
- Official Ascension Island Government site
- Global Volcanism Program: Ascension Island
- Sanders, Sarah, Important Bird Areas in the United Kingdom Overseas Territories; priority sites for conservation (RSPB, 2006)
- Stonehouse, Bernard. (1960). Wideawake Island. The Story of the BOU Centenary Expedition to Ascension. Hutchinson: London
- Duff Hart-Davis, The Spectator 17 October 2015, "The Stone Frigate Sails On", p. 16.
External links
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Ascension. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ascension Island. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Ascension. |
News and Government
History and Geography
Associated Organisations
- Rocket launches from Ascension
- Detailed description of the BBC Atlantic Relay Station
- Army Ornithological Society Ascension Island Research
- The Status and Location of the Military Installations of the Member States of the European Union and Their Potential Role for the European Security and Defence Policy (ESDP). Brussels: European Parliament, 2009. 25 pp.

.JPG.webp)