Cousin marriage
A cousin marriage is a marriage where the spouses are cousins (i.e. people with common grandparents or people who share other fairly recent ancestors). The practice was common in earlier times, and continues to be common in some societies today, though in some jurisdictions such marriages are prohibited.[1] Worldwide, more than 10% of marriages are between first or second cousins.[2] Cousin marriage is an important topic in anthropology and alliance theory.[3]
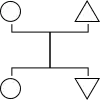
 |
| Part of a series on the |
| Anthropology of kinship |
|---|
 |
|
Social anthropology Cultural anthropology |
In some cultures and communities, cousin marriages are considered ideal and are actively encouraged and expected; in others, they are seen as incestuous and are subject to social stigma and taboo. Cousin marriage was historically practised by indigenous cultures in Australia, North America, South America, and Polynesia. Different religions have ranged from prohibiting up to sixth cousins from marrying (some forms of Hinduism and Catholicism) to freely allowing first cousin marriage (Protestantism, Islam and Judaism).
In some jurisdictions, cousin marriage is legally prohibited: for example, in China, Taiwan, North Korea, South Korea, the Philippines and 24 of the 50 United States.[4][5] The laws of many jurisdictions set out the degree of consanguinity prohibited among sexual relations and marriage parties. Supporters of cousin marriage where it is banned may view the prohibition as discrimination,[6][7] while opponents may appeal to moral or other arguments.[8]
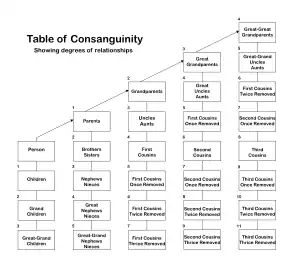
Opinions vary widely as to the merits of the practice. Children of first-cousin marriages have an increased risk of autosomal recessive genetic disorders, and this risk is higher in populations that are already highly ethnically similar.[9] Children of more distantly related cousins have less risk of these disorders, though still higher than the average population.[9] A study indicated that between 1800 and 1965 in Iceland, more children and grandchildren were produced from marriages between third or fourth cousins (people with common great-great- or great-great-great-grandparents) than from other degrees of separation.[10]
History
The prevalence of first-cousin marriage in Western countries has declined since the 19th century.[11][12] In the Middle East and South Asia, cousin marriage is still strongly favoured.[13][14][15]
Cousin marriage has often been practised to keep cultural values intact, preserve family wealth, maintain geographic proximity, keep tradition, strengthen family ties, and maintain family structure or a closer relationship between the wife and her in-laws. Many such marriages are arranged (see also pages on arranged marriage in the Indian subcontinent, arranged marriages in Pakistan, and arranged marriages in Japan).[2][16][17][18][19]
China
Confucius described marriage as "the union of two surnames, in friendship and in love".[20] In ancient China, some evidence indicates in some cases, two clans had a longstanding arrangement wherein they would only marry members of the other clan. Some men also practiced sororate marriage, that is, a marriage to a former wife's sister or a polygynous marriage to both sisters. This would have the effect of eliminating parallel-cousin marriage as an option, but would leave cross-cousin marriage acceptable.[21] In the ancient system of the Erya dating from around the third century BC, the words for the two types of cross cousins were identical, with father's brother's children and mother's sister's children both being distinct.[22] However, whereas it may not have been permissible at that time, marriage with the mother's sister's children also became possible by the third century AD.[23] Eventually, the mother's sister's children and cross cousins shared one set of terms, with only the father's brother's children retaining a separate set.[24] This usage remains today, with biao (表) cousins considered "outside" and paternal tang (堂) cousins being of the same house.[25] In some periods in Chinese history, all cousin marriage was legally prohibited, as law codes dating from the Ming Dynasty attest. However, enforcement proved difficult and by the subsequent Qing Dynasty, the former laws had been restored.[26]
The following is a Chinese poem by Po Chu-yi (A.D. 772–846).[27]
In Ku-feng hsien, in the district of Ch'u chou [Kiangsu] Is a village called Chu Ch'en [the names of the two clans]. There are only two clans there Which have intermarried for many generations.
Anthropologist Francis Hsu described mother's brother's daughter (MBD) as being the most preferred type of Chinese cousin marriage, mother's sister's daughter (MSD) as being tolerated, and father's brother's daughter (FBD) as being disfavored.[28] Some writers report this last form as being nearly incestuous.[29] One proposed explanation is that in FBD marriage, the daughter does not change her surname throughout her life, so the marriage does not result in an extension of the father's kinship ties. In Chinese culture, these patrilineal ties are most important in determining the closeness of a relation.[30] In the case of the MSD marriage, no such ties exist, so consequently this may not even be viewed as cousin marriage. Finally, one reason that MBD marriage is often most common may be the typically greater emotional warmth between a man and his mother's side of the family.[31] Later analyses have found regional variation in these patterns; in some rural areas where cousin marriage is still common, MBD is not preferred but merely acceptable, similar to MSD.[29] By the early to mid-20th century, anthropologists described cross-cousin marriage in China as "still permissible ... but ... generally obsolete" or as "permitted but not encouraged".[26][27]
Middle East
Cousin marriage has been allowed throughout the Middle East for all recorded history.[32] Anthropologists have debated the significance of the practice; some view it as the defining feature of the Middle Eastern kinship system[33] while others note that overall rates of cousin marriage have varied sharply between different Middle Eastern communities.[34] Very little numerical evidence exists of rates of cousin marriage in the past.[35]
Raphael Patai reports that in central Arabia, no relaxation of a man's right to the father's brother's daughter, seems to have taken place in the past hundred years before his 1962 work. Here the girl is not forced to marry her male cousin, but she cannot marry another unless he gives consent.[36] The force of the custom is seen in one case from Jordan when the father arranged for the marriage of his daughter to an outsider without obtaining the consent of her male cousin. When the marriage procession progressed with the bride toward the house of the bridegroom, the male cousin rushed forward, snatched away the girl, and forced her into his own house. This was regarded by all as a lawful marriage.[37] In Iraq, the right of the cousin has also traditionally been followed and a girl breaking the rule without the consent of the male cousin could have ended up murdered by him.[38] The Syrian city of Aleppo during the 19th century featured a rate of cousin marriage among the elite of 24% according to one estimate, a figure that masked widespread variation: some leading families had none or only one cousin marriage, while others had rates approaching 70%. Cousin marriage rates were highest among women, merchant families, and older well-established families.[39]
In-marriage was more frequent in the late pre-Islamic Hijaz than in ancient Egypt. It existed in Medina during Muhammad's time, but at less than today's rates.[40] In Egypt, estimates from the late 19th and early 20th centuries state variously that either 80% of fellahin married first cousins or two-thirds married them if they existed. One source from the 1830s states that cousin marriage was less common in Cairo than in other areas. In traditional Syria-Palestina, if a girl had no paternal male cousin (father's brother's son) or he renounced his right to her, the next in line was traditionally the maternal male cousin (mother's brother's son) and then other relatives. Raphael Patai, however, reported that this custom loosened in the years preceding his 1947 study.[37] In ancient Persia, the Achaemenid kings habitually married their cousins and nieces,[41] while between the 1940s and 1970s, the percentage of Iranian cousin marriages increased from 34 to 44%.[42] Cousin marriage among native Middle Eastern Jews is generally far higher than among the European Ashkenazim, who assimilated European marital practices after the diaspora.[43]
According to anthropologist Ladislav Holý, cousin marriage is not an independent phenomenon, but rather one expression of a wider Middle Eastern preference for agnatic solidarity, or solidarity with one's father's lineage. According to Holý, the oft-quoted reason for cousin marriage of keeping property in the family is, in the Middle Eastern case, just one specific manifestation of keeping intact a family's whole "symbolic capital".[44] Close agnatic marriage has also been seen as a result of the conceptualization of men as responsible for the control of the conduct of women.[45] Honor is another reason for cousin marriage: while the natal family may lose influence over the daughter through marriage to an outsider, marrying her in their kin group allows them to help prevent dishonorable outcomes like either attacks on her or her own unchaste behavior.[46] Pragmatic reasons for the husband, such as warmer relations with his father-in-law, and those for parents of both spouses, like reduced bride price and access to the labor of the daughter's children, also contribute.[47][48] Throughout Middle Eastern history, cousin marriage has been both praised and discouraged by various writers and authorities.[49]
A 2009 study found that many Arab countries display some of the highest rates of consanguineous marriages in the world, and that first cousin marriages which may reach 25–30% of all marriages.[50] In Qatar, Yemen, and UAE, consanguinity rates are increasing in the current generation. Research among Arabs and worldwide has indicated that consanguinity could have an effect on some reproductive health parameters such as postnatal mortality and rates of congenital malformations.[51]
Middle Eastern parallel-cousin marriage
Andrey Korotayev claimed that Islamization was a strong and significant predictor of parallel cousin (father's brother's daughter – FBD) marriage, bint 'amm marriage. He has shown that while a clear functional connection exists between Islam and FBD marriage, the prescription to marry a FBD does not appear to be sufficient to persuade people to actually marry thus, even if the marriage brings with it economic advantages. According to Korotayev, a systematic acceptance of parallel-cousin marriage took place when Islamization occurred together with Arabization.[52]
Africa
Cousin marriage rates from most African nations outside the Middle East are unknown. An estimated 35–50% of all sub-Saharan African populations either prefer or accept cousin marriages.[53] In Nigeria, the most populous country of Africa, the three largest tribes in order of size are the Hausa, Yoruba, and Igbo.[54] The Hausa are overwhelmingly Muslim, though followers of traditional religions do exist. Muslim Hausas practice cousin marriage preferentially, and polygyny is allowed if the husband can support multiple wives.[55] The book Baba of Karo presents one prominent portrayal of Hausa life: according to its English coauthor, it is unknown for Hausa women to be unmarried for any great length of time after around the age of 14.[56] Divorce can be accomplished easily by either the male or the female, but females must then remarry.[57] Even for a man, lacking a spouse is looked down upon.[58] Baba of Karo's first of four marriages was to her second cousin. She recounts in the book that her good friend married the friend's first cross cousin.[59]
The Yoruba people are 50% Muslim, 40% Christian, and 10% adherent of their own indigenous religious traditions.[60] A 1974 study analyzed Yoruba marriages in the town Oka Akoko, finding that among a sample of highly polygynous marriages having an average of about three wives, 51% of all pairings were consanguineous. These included not only cousin marriages, but also uncle-niece unions. Reportedly, it is a custom that in such marriages at least one spouse must be a relative, and generally such spouses were the preferred or favorite wives in the marriage and gave birth to more children. However, this was not a general study of Yoruba, but only of highly polygynous Yoruba residing in Oka Akoko.[61]
The Igbo people of southeastern Nigeria, who are predominantly Christian, strictly practice non-consanguineal marriages, where kinfolks and cousins are not allowed to marry or have intimacy. Consequently, men and women are forbidden to marry within their recent patrilineage and matrilineage. Before the advent of Christianity through colonization, the Igbos had always frowned upon and specifically prohibited consanguineal marriages, both the parallel and cross-cousin types, which are considered incestuous and cursed. Arranged marriages, albeit in great decline, was also done to consciously prevent accidental consanguineal and bad marriages, such that the impending in-laws were aware of each other's family histories. Currently, like in the old days, before courtship commences, thorough enquiries are made by both families to not only ascertain character traits, but to also ensure their children are not related by blood. Traditionally, parents closely monitor whom their children relate intimately to avoid having them commit incest. Proactively, it is customary for parents to groom their children to know their immediate cousins and, when opportune, their distant cousins. They encourage their adult children to disclose their love interests for consanguineal screening.[62]
In Ethiopia, most of the population was historically rigidly opposed to cousin marriage, and could consider up to third cousins the equivalent of brother and sister, with marriage at least ostensibly prohibited out to sixth cousins.[63] They also took affinal prohibitions very seriously. The prospect of a man marrying a former wife's "sister" was seen as incest, and conversely for a woman and her former husband's "brother".[64] Though Muslims make up over a third of the Ethiopian population, and Islam has been present in the country since the time of Muhammad, cross-cousin marriage is very rare among most Ethiopian Muslims.[65] In contrast to the Nigerian situation, in Ethiopia, Islam cannot be identified with particular tribal groups and is found across most of them, and conversions between religions are comparatively common.[66] The Afar practice a form of cousin marriage called absuma that is arranged at birth and can be forced.[67]
Europe
Roman civil law prohibited marriages within four degrees of consanguinity.[68] This was calculated by counting up from one prospective partner to the common ancestor, then down to the other prospective partner.[69] Early Medieval Europe continued the late Roman ban on cousin marriage. Under the law of the Catholic Church, couples were also forbidden to marry if they were within four degrees of consanguinity.[70] In the 9th century, the church raised the number of prohibited degrees to seven and changed the method by which they were calculated.[71] Eventually, the nobility became too interrelated to marry easily as the local pool of unrelated prospective spouses became smaller; increasingly, large payments to the church were required for exemptions ("dispensations"), or retrospective legitimizations of children.[72]
In 1215, the Fourth Lateran Council reduced the number of prohibited degrees of consanguinity from seven back to four.[73][74] The method of calculating prohibited degrees was changed also.[75] Instead of the former practice of counting up to the common ancestor then down to the proposed spouse, the new law computed consanguinity by counting back to the common ancestor.[75] In the Roman Catholic Church, unknowingly marrying a closely consanguineous blood relative was grounds for a declaration of nullity, but during the 11th and 12th centuries, dispensations were granted with increasing frequency due to the thousands of persons encompassed in the prohibition at seven degrees and the hardships this posed for finding potential spouses.[76] After 1215, the general rule was that while fourth cousins could marry without dispensation, the need for dispensations was reduced.[76]
For example, the marriage of Louis XIV of France and Maria Theresa of Spain was a first-cousin marriage on both sides.[77] It began to fall out of favor in the 19th century as women became socially mobile. Only Austria, Hungary, and Spain banned cousin marriage throughout the 19th century, with dispensations being available from the government in the last two countries.[78] First-cousin marriage in England in 1875 was estimated by George Darwin to be 3.5% for the middle classes and 4.5% for the nobility, though this had declined to under 1% during the 20th century.[79] Queen Victoria and Prince Albert were a preeminent example.[80][81]
The 19th-century academic debate on cousin marriage developed differently in Europe and America. The writings of Scottish deputy commissioner for lunacy Arthur Mitchell claiming that cousin marriage had injurious effects on offspring were largely contradicted by researchers such as Alan Huth and George Darwin.[82][83] In fact, Mitchell's own data did not support his hypotheses and he later speculated that the dangers of consanguinity might be partly overcome by proper living. Later studies by George Darwin found results that resemble those estimated today. His father, Charles Darwin, who did marry his first cousin, had initially speculated that cousin marriage might pose serious risks, but perhaps in response to his son's work, these thoughts were omitted from a later version of the book they published. When a question about cousin marriage was eventually considered in 1871 for the census, according to George Darwin, it was rejected on the grounds that the idle curiosity of philosophers was not to be satisfied.[84] In Southern Italy, cousin marriage was a common practice within regions such as Calabria and Sicily where first cousin marriage in the previous century was close to 50% of all marriages.[85] Cousin marriage to third cousins was allowed and considered favourably in Greece.[86]
Ancient Europe
Cousin marriage were legal in ancient Rome from the Second Punic War (218–201 BC), until it was banned by the Christian emperor Theodosius I in 381 in the West, and until after the death of Justinian (565) in the East,[87][88] but the proportion of such marriages is not clear. Anthropologist Jack Goody said that cousin marriage was a typical pattern in Rome, based on the marriage of four children of Emperor Constantine to their first cousins and on writings by Plutarch and Livy indicating the proscription of cousin marriage in the early Republic.[89] Professors Brent Shaw and Richard Saller, however, counter in their more comprehensive treatment that cousin marriages were never habitual or preferred in the western empire: for example, in one set of six stemmata (genealogies) of Roman aristocrats in the two centuries after Octavian, out of 33 marriages, none was between first or second cousins. Such marriages carried no social stigma in the late Republic and early Empire. They cite the example of Cicero attacking Mark Antony not on the grounds of cousin marriage, but instead on grounds of Antony's divorce.
Shaw and Saller propose in their thesis of low cousin marriage rates that as families from different regions were incorporated into the imperial Roman nobility, exogamy was necessary to accommodate them and to avoid destabilizing the Roman social structure. Their data from tombstones further indicate that in most of the western empire, parallel-cousin marriages were not widely practiced among commoners, either. Spain and Noricum were exceptions to this rule, but even there, the rates did not rise above 10%.[90] They further point out that since property belonging to the nobility was typically fragmented, keeping current assets in the family offered no advantage, compared with acquiring it by intermarriage. Jack Goody claimed that early Christian marriage rules forced a marked change from earlier norms to deny heirs to the wealthy and thus to increase the chance that those with wealth would will their property to the Church. Shaw and Saller, however, believe that the estates of aristocrats without heirs had previously been claimed by the emperor, and that the Church merely replaced the emperor. Their view is that the Christian injunctions against cousin marriage were due more to ideology than to any conscious desire to acquire wealth.[90]
For some prominent examples of cousin marriages in ancient Rome, such as the marriage of Octavian's daughter to his sister's son, see the Julio-Claudian family tree. Marcus Aurelius also married his maternal first cousin Faustina the Younger, and they had 13 children. Cousin marriage was more frequent in ancient Greece, and marriages between uncle and niece were also permitted there.[3] One example is King Leonidas I of Sparta, who married his half-niece. A Greek woman who became epikleros, or heiress with no brothers, was obliged to marry her father's nearest male kin if she had not yet married and given birth to a male heir. First in line would be either her father's brothers or their sons, followed by her father's sisters' sons.[91]
Early medieval
According to Goody, cousin marriage was allowed in the newly Christian and presumably also pre-Christian Ireland, where an heiress was also obligated to marry a paternal cousin. From the seventh century, the Irish Church only recognized four degrees of prohibited kinship, and civil law fewer. This persisted until after the Norman conquests in the 11th century and the synod at Cashel in 1101.[92] In contrast, contemporary English law was based on official Catholic policy, and Anglo-Norman clergy often became disgusted with the Irish "law of fornication".[93] Ironically, within less than a hundred years of the Anglo-Norman Invasion of Ireland the Catholic Church reformed Canon Law on cousin marriage at the Fourth Lateran Council, with the effect bringing the Catholic Church's teaching back into alignment with the Irish Church and the original Christian Church's teachings. The Catholic Churches' teachings had proved unworkable in practice as they required people to know, and not marry, all relations back as far as their common Great Great Great Great Great Grandparents (i.e. as far as their sixth cousins) or else purchase a dispensation from the church.[94] Finally, Edward Westermarck states that marriage among the ancient Teutons was apparently prohibited only in the ascending and descending lines and among siblings.[95]
United States
Anthropologist Martin Ottenheimer argues that marriage prohibitions were introduced to maintain the social order, uphold religious morality, and safeguard the creation of fit offspring.[96] Writers such as Noah Webster (1758–1843) and ministers like Philip Milledoler (1775–1852) and Joshua McIlvaine helped lay the groundwork for such viewpoints well before 1860. This led to a gradual shift in concern from affinal unions, like those between a man and his deceased wife's sister, to consanguineous unions. By the 1870s, Lewis Henry Morgan (1818–1881) was writing about "the advantages of marriages between unrelated persons" and the necessity of avoiding "the evils of consanguine marriage", avoidance of which would "increase the vigor of the stock". To many, Morgan included, cousin marriage, and more specifically parallel-cousin marriage, was a remnant of a more primitive stage of human social organization.[97] Morgan himself had married his cousin in 1853.[98]
In 1846, Massachusetts Governor George N. Briggs appointed a commission to study mentally handicapped people (termed "idiots") in the state. This study implicated cousin marriage as responsible for idiocy. Within the next two decades, numerous reports (e.g., one from the Kentucky Deaf and Dumb Asylum) appeared with similar conclusions: that cousin marriage sometimes resulted in deafness, blindness, and idiocy. Perhaps most important was the report of physician Samuel Merrifield Bemiss for the American Medical Association, which concluded cousin inbreeding does lead to the "physical and mental depravation of the offspring". Despite being contradicted by other studies like those of George Darwin and Alan Huth in England and Robert Newman in New York, the report's conclusions were widely accepted.[99]
These developments led to 13 states and territories passing cousin marriage prohibitions by the 1880s. Though contemporaneous, the eugenics movement did not play much of a direct role in the bans. George Louis Arner in 1908 considered the ban a clumsy and ineffective method of eugenics, which he thought would eventually be replaced by more refined techniques. By the 1920s, the number of bans had doubled.[7] Since that time, Kentucky (1943) and Texas have banned first-cousin marriage and since 1985, Maine has mandated genetic counseling for marrying cousins to minimize risk to any of serious health defect to their children. The National Conference of Commissioners on Uniform State Laws unanimously recommended in 1970 that all such laws should be repealed, but no state has dropped its prohibition.[5][16][100]
Legal status
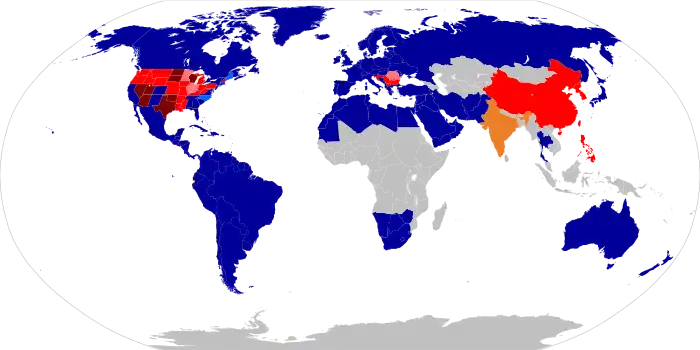
1For information on US states see the map below.
2See sections on India and Hinduism.
East Asia/Southeast Asia
In the Far East, South Korea is especially restrictive with bans on marriage out to third cousins, with all couples having the same surname and region of origin having been prohibited from marrying until 1997.[101]
Taiwan and North Korea also prohibit first-cousin marriage.[5][102]
China has prohibited first-cousin marriage since 1981.[103] Currently, according to the Marriage Law of the People's Republic of China, Article 7, "No marriage may be contracted under any of the following circumstances: (1) if the man and the woman are lineal relatives by blood, or collateral relatives by blood up to the third degree of kinship."[104]
Southeast Asia
In Vietnam, Clause 3, Article 10 of the 2000 Vietnamese Law on Marriage and Family forbids marriages of people related by blood up to the third degree of kinship.[105][106] Cousin marriage is also prohibited in the Philippines.
United States
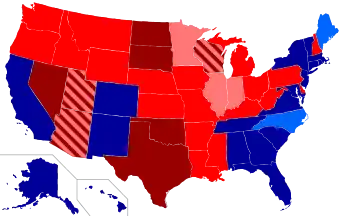
1Some US states recognize marriages performed elsewhere, especially when the spouses were not residents of the state when married.clarification needed
Several states of the United States have bans on cousin marriage.[107][108] As of February 2014, 24 U.S. states prohibit marriages between first cousins, 19 U.S. states allow marriages between first cousins, and 7 U.S. states allow only some marriages between first cousins.[4] Six states prohibit first-cousin-once-removed marriages.[8] Some states prohibiting cousin marriage recognize cousin marriages performed in other states, but this does not hold true in general despite occasional claims to the contrary.[109]
Prevalence
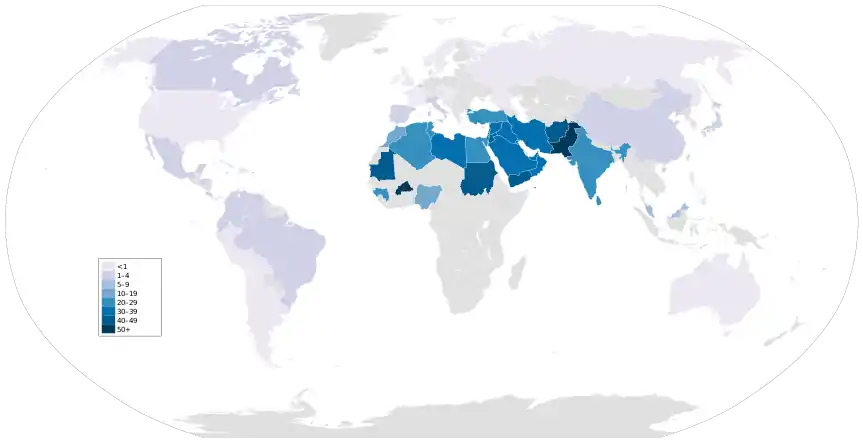
World map showing prevalence of marriage between cousins, up to and including second cousins, according to data published in 2012 by the United States National Center for Biotechnology Information.[110]
Brazil
Recent 2001 data for Brazil indicate a rate of cousin marriage of 1.1%, down from 4.8% in 1957.[111] The geographic distribution is heterogeneous: in certain regions, the rate is at typical European levels, but in other areas is much higher. Newton Freire-Maia found paternal parallel cousin marriage to be the most common type.[112] In his 1957 study, the rate varied from 1.8% in the south to 8.4% in the northeast, where it increased moving inward from the coast,[113] and was higher in rural regions than in urban. Consanguinity has decreased over time and particularly since the 19th century. For example, in São Paulo in the mid-19th century, the rate of cousin marriage apparently was 16%,[114] but a century later, it was merely 1.9%.[111]
East Asia
First-cousin marriage is allowed in Japan, though the incidence has declined in recent years.[17]
China has prohibited first-cousin marriage since 1981,[103] although cross-cousin marriage was commonly practised in China in the past in rural areas.[17][115] An article in China Daily from the 1990s reported on the ban's implementation in the northeastern province of Liaoning, along with a ban on marriage of the physically and mentally handicapped, all justified on "eugenic" grounds.[115] Limited existing data indicate some remaining cousin marriage of types besides father's brother's daughter in many villages, with percentages usually in the lower single digits.[111] A 2002 Time article claims that an increasing imbalance in the number of males and females is causing more cousin marriages, as "desperate" males struggle to find brides.[116]
Germany
A fourth of all marriages among Turks in Germany are marriages to a family relative according to Essener Zentrum für Türkeistudien.[117]
The Netherlands
The Netherlands has also had a recent debate that has reached the level of the Prime Minister proposing a cousin marriage ban. The proposed policy is explicitly aimed at preventing "import marriages" from certain nations like Morocco with a high rate of cousin marriage. Critics argue that such a ban would contradict Section 8 of the European Convention on Human Rights, is not based on science, and would affect more than immigrants. While some proponents argue such marriages were banned until 1970, according to Frans van Poppel of the Netherlands Interdisciplinary Demographic Institute, they are confusing cousin marriage with uncle-niece marriage.[118]
Norway
Norway banned cousin marriage in November 2020, in order to improve the integration of immigrants into Norwegian society.[119][120]
United Kingdom
In the English upper and upper-middle classes, the prevalence of first-cousin marriage had remained steady at between 4% and 5% for much of the 19th century. However, after the First World War, there was a sudden change, and cousin marriage became very unusual. By the 1930s, only one marriage in 6,000 was with a first cousin. A study of a middle-class London population conducted in the 1960s found that just one marriage in 25,000 was between first cousins.[121]
There has been a great deal of debate in the United Kingdom about whether to discourage cousin marriages through government public relations campaigns, or ban them entirely. In the 1980s researchers found that children to closely related Pakistani parents had an autosomal recessive condition rate of 4% compared to 0.1% for the European group.[122] For example, Environment Minister (later Immigration Minister) Phil Woolas said in 2008, "If you have a child with your cousin the likelihood is there'll be a genetic problem" and that such marriages were the "elephant in the room".[123] Physician Mohammad Walji has spoken out against the practice, saying that it is a "very significant" cause of infant death, and his practice has produced leaflets warning against it.[124] However, Alan Bittles of the Centre for Comparative Genomics in Australia states that the risk of birth defects rises from roughly 2% in the general population to 4% for first cousins, and therefore that "It would be a mistake to ban it".[125] Aamra Darr of the University of Leeds has also criticized what she called an "alarmist presentation of data" that exaggerates the risk.[126]
A 2008 analysis of infant mortality in Birmingham showed that South Asian infants had twice the normal infant mortality rate and three times the usual rate of infant mortality due to congenital anomalies.[122][15]
Middle East
The Middle East has uniquely high rates of cousin marriage among the world's regions. Iraq was estimated in one study to have a rate of 33% for cousins marrying.
All Arab countries in the Persian Gulf currently require advance genetic screening for prospective married couples. Qatar was the last Persian Gulf nation to institute mandatory screening in 2009, mainly to warn related couples who are planning marriage about any genetic risks they may face. The current rate of cousin marriage there is 54%, an increase of 12–18% over the previous generation.[127] A report by the Dubai-based Centre for Arab Genomic Studies (CAGS) in September 2009 found that Arabs have one of the world's highest rates of genetic disorders, nearly two-thirds of which are linked to consanguinity. Research from Ahmad Teebi suggests consanguinity is declining in Lebanon, Jordan, Morocco and among Palestinians in Israel, but is increasing in the United Arab Emirates.[128]
Ahmad Teebi links the increase in cousin marriage in Qatar and other Arab states of the Persian Gulf to tribal tradition and the region's expanding economies. "Rich families tend to marry rich families, and from their own – and the rich like to protect their wealth," he said. "So it's partly economic, and it's also partly cultural." In regard to the higher rates of genetic disease in these societies, he says: "It's certainly a problem," but also that "The issue here is not the cousin marriage, the issue here is to avoid the disease."[14]
In many Middle Eastern nations, a marriage to the father's brother's daughter (FBD) is considered ideal, though this type may not always actually outnumber other types.[129] One anthropologist, Ladislav Holý, argues that it is important to distinguish between the ideal of FBD marriage and marriage as it is actually practiced, which always also includes other types of cousins and unrelated spouses. Holý cites the Berti people of the Sudan, who consider the FBD to be the closest kinswoman to a man outside of the prohibited range. If more than one relationship exists between spouses, as often results from successive generations of cousin marriage, only the patrilineal one is counted. Marriage within the lineage is preferred to marriage outside the lineage even when no exact genealogical relationship is known. Of 277 first marriages, only 84 were between couples unable to trace any genealogical relationship between them. Of those, in 64, the spouses were of the same lineage. However, of 85 marriages to a second or third wife, in 60, the spouses were of different lineages.[130][131] The Marri have a very limited set of incest prohibitions that includes only lineal relatives, the sister, and aunts except the mother's brother's wife. Female members of the mother's lineage are seen as only loosely related. Finally, the Baggara Arabs favor MBD marriage first, followed by cross-cousin marriage if the cross cousin is a member of the same surra, a group of agnates of five or six generations depth. Next is marriage within the surra. No preference is shown for marriages between matrilateral parallel cousins.
India
| State | |
|---|---|
| Northern India | |
| Jammu and Kashmir (incl. Ladakh) | 16.0 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 7.7 |
| Delhi | 5.1 |
| Uttarakhand | 4.3 |
| Haryana | 3.6 |
| Rajasthan | 2.8 |
| Punjab | 1.7 |
| Himachal Pradesh | 0.5 |
| Western India | |
| Maharashtra | 12.1 |
| Goa | 6.9 |
| Gujarat | 6.2 |
| Central India | |
| Madhya Pradesh | 6.2 |
| Chhattisgarh | 3.4 |
| Eastern India | |
| Odisha | 4.8 |
| Bihar | 3.6 |
| West Bengal | 3.1 |
| Jharkhand | 2.3 |
| Northeast India | |
| Arunachal Pradesh | 2.1 |
| Mizoram | 2.1 |
| Nagaland | 2.0 |
| Meghalaya | 1.6 |
| Manipur | 1.5 |
| Assam | 0.9 |
| Sikkim | 0.6 |
| Tripura | 0.2 |
| South India | |
| Tamil Nadu | 29.5 |
| Andhra Pradesh | 25.9 |
| Karnataka | 23.8 |
| Telangana | 22.0 |
| Kerala | 3.6 |
| Religion | |
| Hindu | 9.19 |
| Muslim | 14.62 |
| Other | 8.47 |
| Caste | |
| Scheduled Caste (SC) | 10.0 |
| Scheduled Tribe (ST) | 8.4 |
| Other Backward Class (OBC) | 11.1 |
| Other | 8.0 |
| Educational attainment | |
| No education | 9.2 |
| Primary | 10.1 |
| Secondary | 10.7 |
| Higher | 8.0 |
| All-India | 9.9 |
Attitudes in India on cousin marriage vary sharply by region and culture. The family law in India takes into account the religious and cultural practices and they are all equally recognized. For Muslims, governed by uncodified personal law, it is acceptable and legal to marry a first cousin, but for Hindus, it may be illegal under the 1955 Hindu Marriage Act, though the specific situation is more complex. The Hindu Marriage Act makes cousin marriage illegal for Hindus with the exception of marriages permitted by regional custom.[133] Practices of the small Christian minority are also location-dependent: their cousin marriage rates are higher in southern states with high overall rates.[134] Apart from the religion-based personal laws governing marriages, the civil marriage law named Special Marriage Act, 1954 governs. Those who do not wish to marry based on the personal laws governed by religious and cultural practices may opt for marriage under this law. It defines the first-cousin relationship, both parallel and cross, as prohibited. Conflict may arise between the prohibited degrees based on this law and personal law, but in absence of any other laws, it is still unresolved.[135]
Cousin marriage is proscribed and seen as incest for Hindus in North India. In fact, it may even be unacceptable to marry within one's village or for two siblings to marry partners from the same village.[136] The northern kinship model prevails in the states of Assam, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Punjab, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and West Bengal.[137]
In many North Indian communities, such as certain Brahmins, Rajputs, Vaishyas, Jats, Gurjars, Yadavs, everyone who is immediately associated with specifically paternal gotra falls outside the permissible marriage circle. Any two candidates who want to marry cannot have a common gotra. The marriage is allowed only when paternal gotras are different for both the candidates, so this automatically rules out closer cousin marriages.
However, for many communities in South India, especially in Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh, it is common for Hindu cross cousins to marry, with matrilateral cross-cousin (mother's brother's daughter) marriages being especially favored.[138] In the region, "uncle-niece and first-cousin unions are preferential and jointly account for some 30% of marriages." These practices are particularly followed in landed communities such as the Reddys or Vellalars, who wish to keep wealth within the family. Also unlike North India, this practice is also common in Brahmins in the region.[139]
Practices in West India overall are closer to the northern than the southern,[140] but differences exist here again. For instance, in Mumbai, studies done in 1956 showed 7.7% of Hindus married to a second cousin or closer. By contrast, in the northern city of New Delhi, only 0.1% of Hindus were married to a first cousin during the 1980s. At the other extreme, studies were done in the South Indian state of Karnataka during that period show fully one-third of Hindus married to a second cousin or closer.[141] Pre-2000 Madhya Pradesh, from which Chhattisgarh has now split, and Maharashtra, which contains Mumbai, are states that are intermediate in their kinship practices.
India's Muslim minority represents about 14% of its population and has an overall rate of cousin marriage of 22% according to a 2000 report. This may be a legacy of the partition of the subcontinent into India and Pakistan, when substantial Muslim migration to Pakistan occurred from the eastern parts of the former unified state of Punjab. In south India, by contrast, the rates are fairly constant, except for the South Indian Malabar Muslims of Kerala (9%) who claim descent from Arab traders who settled permanently in India in the eighth century. Most Indian Muslims, by contrast, are the result of Hindus' conversions to Islam in the 16th century or later. The lowest rate for a whole Indian region was in East India (15%). Consanguinity rates were generally stable across the four decades for which data exist, though second-cousin marriage appears to have been decreasing in favor of first-cousin marriage.
Pakistan
In Pakistan, cousin marriage is legal and common. Reasons for consanguinity are for economic, religious and cultural reasons.[142] Consanguineous marriage in Pakistan was reported to be higher than 60% of the population in 2014.[143][144][145] In some areas, higher proportion of first-cousin marriages in Pakistan has been noted to be the cause of an increased rate of blood disorders in the population.[145]
Afghanistan
Consanguineous marriages are legal and relatively common in Afghanistan. The proportion of consanguineous marriages in the country stands at 46.2%, with significant regional variations ranging from 38.2% in Kabul province to 51.2% in Bamyan province.[146]
United States
Data on cousin marriage in the United States is sparse. It was estimated in 1960 that 0.2% of all marriages between Roman Catholics were between first or second cousins, but no more recent nationwide studies have been performed.[141] It is unknown what proportion of that number were first cousins, which is the group facing marriage bans. To contextualize the group's size, the total proportion of interracial marriages in 1960, the last census year before the end of anti-miscegenation statutes, was 0.4%, and the proportion of black-white marriages was 0.13%.[147] While recent studies have cast serious doubt on whether cousin marriage is as dangerous as is popularly assumed, professors Diane B. Paul and Hamish G. Spencer speculate that legal bans persist in part due to "the ease with which a handful of highly motivated activists—or even one individual—can be effective in the decentralized American system, especially when feelings do not run high on the other side of an issue."[148]
A bill to repeal the ban on first-cousin marriage in Minnesota was introduced by Phyllis Kahn in 2003, but it died in committee. Republican Minority Leader Marty Seifert criticized the bill in response, saying it would "turn us into a cold Arkansas".[149] According to the University of Minnesota's The Wake, Kahn was aware the bill had little chance of passing, but introduced it anyway to draw attention to the issue. She reportedly got the idea after learning that cousin marriage is an acceptable form of marriage among some cultural groups that have a strong presence in Minnesota, namely the Hmong and Somali.[150]
In contrast, Maryland delegates Henry B. Heller and Kumar P. Barve sponsored a bill to ban first-cousin marriages in 2000.[151] It got further than Kahn's bill, passing the House of Delegates by 82 to 46 despite most Republicans voting no, but finally died in the state senate. In response to the 2005 marriage of Pennsylvanian first cousins Eleanor Amrhein and Donald W. Andrews Sr. in Maryland, Heller said that he might resurrect the bill because such marriages are "like playing genetic roulette".[152]
Texas actually did pass a ban on first-cousin marriage the same year as Amrhein and Andrews married, evidently in reaction to the presence of the polygamous Fundamentalist Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-Day Saints (FLDS). Texas Representative Harvey Hilderbran, whose district includes the main FLDS compound, authored an amendment[153] to a child protection statute to both discourage the FLDS from settling in Texas and to "prevent Texas from succumbing to the practices of taking child brides, incest, welfare abuse and domestic violence".[154] While Hilderbran stated that he would not have authored a bill solely to ban first-cousin marriage, he also said in an interview, "Cousins don't get married just like siblings don't get married. And when it happens you have a bad result. It's just not the accepted normal thing."[2] Some news sources then only mentioned the polygamy and child abuse provisions and ignored the cousin marriage portion of the bill, as did some more recent sources.[155][156][157][158] The new statute made sex with an adult first cousin a more serious felony than with adult members of one's immediate family. However, this statute was amended in 2009; while sex with close adult family members (including first cousins) remains a felony, the more serious penalty now attaches to sex with an individual's direct ancestor or descendant.[159]
The U.S. state of Maine allows first-cousin marriage if the couple agrees to have genetic counseling, while North Carolina allows it so long as the applicants for marriage are not rare double first cousins, meaning cousins through both parental lines.[160] In the other 25 states permitting at least some first-cousin marriage, double cousins are not distinguished.[161]
States have various laws regarding marriage between cousins and other close relatives,[162] which involve factors including whether or not the parties to the marriage are half-cousins, double cousins, infertile, over 65, or whether it is a tradition prevalent in a native or ancestry culture, adoption status, in-law, whether or not genetic counselling is required, and whether it is permitted to marry a first cousin once removed.
Social aspects
Robin Bennett, a University of Washington researcher,[165] has said that much hostility towards married cousins constitutes discrimination.
It's a form of discrimination that nobody talks about. People worry about not getting health insurance—but saying that someone shouldn't marry based on how they're related, when there's no known harm, to me is a form of discrimination."[7]
In a different view, William Saletan of Slate magazine accuses the authors of this study of suffering from the "congenital liberal conceit that science solves all moral questions". While readily conceding that banning cousin marriage cannot be justified on genetic grounds, Saletan asks rhetorically whether it would be acceptable to legalize uncle-niece marriage or "hard-core incest" between siblings and then let genetic screening take care of the resulting problems.[8] An article in The New York Times by Sarah Kershaw documents fear by many married cousins of being treated with derision and contempt. "While many people have a story about a secret cousin crush or kiss, most Americans find the idea of cousins marrying and having children disturbing or even repulsive," notes the article. It gives the example of one mother, Mrs. Spring, whose daughter Kimberly Spring-Winters, 29, married her cousin Shane Winters, 37. She stated that when she has told people about her daughter's marriage, they have been shocked and that consequently she is afraid to mention it. They live in a small Pennsylvania town and she worries that her grandchildren will be treated as outcasts and ridiculed due to their parental status. Another cousin couple stated that their children's maternal grandparents have never met their two grandchildren because the grandparents severed contact out of disapproval for the couple's marriage. This couple withheld their names from publication.[2]
In most societies, cousin marriage apparently is more common among those of low socio-economic status, among the illiterate and uneducated, and in rural areas.[17] This may be due in part to the token or significantly reduced dowries and bridewealths that exist in such marriages and also the much smaller pool of viable marriage candidates in rural areas. Some societies also report a high prevalence among land-owning families and the ruling elite: here the relevant consideration is thought to be keeping the family estate intact over generations.[18] The average age at marriage is lower for cousin marriages, the difference in one Pakistani study being 1.10 and 0.84 years for first and second cousins, respectively. In Pakistan, the ages of the spouses were also closer together, the age difference declining from 6.5 years for unrelated couples to 4.5 years for first cousins. A marginal increase in time to first birth, from 1.6 years generally to 1.9 years in first cousins, may occur due to the younger age at marriage of consanguineous mothers and resultant adolescent subfertility or delayed consummation.[166]
Predictions that cousin marriage would decline during the late 20th century in areas where it is preferential appear to have been largely incorrect. One reason for this is that in many regions, cousin marriage is not merely a cultural tradition, but is also judged to offer significant social and economic benefits. In South Asia, rising demands for dowry payments have caused dire economic hardship and have been linked to "dowry deaths" in a number of North Indian states. Where permissible, marriage to a close relative is hence regarded as a more economically feasible choice. Second, improvements in public health have led to decreased death rates and increased family sizes, making it easier to find a relative to marry if that is the preferred choice. Increases in cousin marriage in the West may also occur as a result of immigration from Asia and Africa. In the short term, some observers have concluded that the only new forces that could discourage such unions are government bans like the one China enacted in 1981. In the longer term, rates may decline due to decreased family sizes, making it more difficult to find cousins to marry.[167]
Cousin marriage is important in several anthropological theories by prominent authors such as Claude Lévi-Strauss, Sir Edward Tylor, and Lewis Henry Morgan. Lévi-Strauss viewed cross-cousin marriage as a form of exogamy in the context of a unilineal descent group, meaning either matrilineal or patrilineal descent. Matrilateral cross-cousin marriage in societies with matrilineal descent meant that a male married into the family his mother's brother, building an alliance between the two families. However, marriage to a mother's sister daughter (a parallel cousin) would be endogamous, here meaning inside the same descent group, and would therefore fail to build alliances between different groups. Correspondingly, in societies like China with patrilineal descent, marriage to a father's brother's daughter would fail at alliance building. And in societies with both types of descent, where a person belongs to the group of his mother's mother and father's father but not mother's father or father's mother, only cross-cousin marriages would successfully build alliances.[168]
Lévi-Strauss postulated that cross-cousin marriage had the two consequences of setting up classes which automatically delimit the group of possible spouses and of determining a relationship that can decide whether a prospective spouse is to be desired or excluded. Whereas in other kinship systems one or another of these aspects dominates, in cross-cousin marriage they overlap and cumulate their effects. It differs from incest prohibitions in that the latter employs a series of negative relationships, saying whom one cannot marry, while cross-cousin marriage employs positive relationships, saying whom should marry. Most crucially, cross-cousin marriage is the only type of preferential union that can function normally and exclusively and still give every man and woman the chance to marry a cross-cousin. Unlike other systems such as the levirate, the sororate, or uncle-niece marriage, cross-cousin marriage is preferential because for obvious reasons these others cannot constitute the exclusive or even preponderant rule of marriage in any group. Cross-cousin marriage divides members of the same generation into two approximately equal groups, those of cross-cousins and "siblings" that include real siblings and parallel cousins. Consequently, cross-cousin marriage can be a normal form of marriage in a society, but the other systems above can only be privileged forms. This makes cross-cousin marriage exceptionally important.[169]
Cross-cousin marriage also establishes a division between prescribed and prohibited relatives who, from the viewpoint of biological proximity, are strictly interchangeable. Lévi-Strauss thought that this proved that the origin of the incest prohibition is purely social and not biological. Cross-cousin marriage in effect allowed the anthropologist to control for biological degree by studying a situation where the degree of prohibited and prescribed spouses were equal. In understanding why two relatives of the same biological degree would be treated so differently, Lévi-Strauss wrote, it would be possible to understand not only the principle of cross-cousin marriage but of the incest prohibition itself. For Lévi-Strauss cross-cousin marriage was not either socially arbitrary or a secondary consequence of other institutions like dual organization or the practice of exogamy. Instead, the raison d'etre of cross-cousin marriage could be found within the institution itself. Of the three types of institution of exogamy rules, dual organization, and cross-cousin marriage, the last was most significant, making the analysis of this form of marriage the crucial test for any theory of marriage prohibitions.[170]
Matrilateral cross-cousin marriage has been found by some anthropological researchers to be correlated with patripotestal jural authority, meaning rights or obligations of the father. According to some theories, in these kinship systems a man marries his matrilateral cross-cousin due to associating her with his nurturant mother. Due to this association, possibly reinforced by personal interaction with a specific cousin, he may become "fond" of her, rendering the relationship "sentimentally appropriate".[171] Patrilateral cross-cousin marriage is the rarest of all types of cousin marriage, and there is some question as to whether it even exists.[172]
In contrast to Lévi-Strauss who viewed the exchange of women under matrilateral cross-cousin marriage as fundamentally egalitarian, anthropologist Edmund Leach held that such systems by nature created groups of junior and senior status and were part of the political structure of society. Under Leach's model, in systems where this form of marriage segregates descent groups into wife-givers and wife-takers, the social status of the two categories also cannot be determined by a priori arguments. Groups like the Kachin exhibiting matrilateral cross-cousin marriage do not exchange women in circular structures; where such structures do exist they are unstable. Moreover, the exchanging groups are not major segments of the society, but rather local descent groups from the same or closely neighboring communities. Lévi-Strauss held that women were always exchanged for some "prestation" which could either be other women or labor and material goods. Leach agreed but added that prestations could also take the form of intangible assets like "prestige" or "status" that might belong to either wife-givers or wife-takers.[173]
Anthropologists Robert Murphy and Leonard Kasdan describe preferential parallel cousin marriage as leading to social fission, in the sense that "feud and fission are not at all dysfunctional factors but are necessary to the persistence and viability of Bedouin society". Their thesis is the converse of Fredrik Barth's, who describes the fission as leading to the cousin marriage.[174] Per Murphy and Kasdan, the Arab system of parallel cousin marriage works against the creation of homogenous "bounded" and "corporate" kin groups and instead creates arrangements where every person is related by blood to a wide variety of people, with the degree of relationship falling off gradually as opposed to suddenly. Instead of corporate units, Arab society is described as having "agnatic sections", a kind of repeating fractal structure in which authority is normally weak at all levels but capable of being activated at the required level in times of war. They relate this to an old Arab proverb: "Myself against my brother; my brother and I against my cousin; my cousin, my brother and I against the outsider."[175] "In such a society even the presence of a limited amount of cross-cousin marriage will not break the isolation of the kin group, for first cross cousins often end up being second parallel cousins."[176] Instead of organizing horizontally through affinal ties, when large scale organization is necessary it is accomplished vertically, by reckoning distance from shared ancestors. This practice is said to possess advantages such as resilience and adaptability in the face of adversity.[177]
A recent research study of 70 nations has found a statistically significant negative correlation between consanguineous kinship networks and democracy. The authors note that other factors, such as restricted genetic conditions, may also explain this relationship.[178] This follows a 2003 Steve Sailer essay published for The American Conservative, where he claimed that high rates of cousin marriage play an important role in discouraging political democracy. Sailer believes that because families practicing cousin marriage are more related to one another than otherwise, their feelings of family loyalty tend to be unusually intense, fostering nepotism.[179]
Religious views
Hebrew Bible
Cousins are not included in the lists of prohibited relationships set out in the Hebrew Bible, specifically in Leviticus 18:8–18 and 20:11–21 and in Deuteronomy.[3] However, the Bible prohibits relationships with any blood relative in Leviticus 18:6.
There are several examples in the Bible of cousins marrying. Isaac married Rebekah, his first cousin once removed (Genesis 24:12–15). Also, Isaac's son Jacob married Leah and Rachel, both his first cousins (Genesis 28–29). Jacob's brother Esau also married his first cousin Mahalath, daughter of Ishmael, Isaac's half-brother. According to many English Bible translations, the five daughters of Zelophehad married the "sons of their father's brothers" in the later period of Moses; although other translations merely say "relatives". (For example, the Catholic RSV-CE and NAB differ in Numbers 36:10–12.) During the apportionment of Israel following the journey out of Egypt, Caleb gives his daughter Achsah to his brother's son Othniel according to the NAB (Joshua 15:17), though the Jewish Talmud says Othniel was simply Caleb's brother (Sotah 11b). The daughters of Eleazer also married the sons of Eleazer's brother Kish in the still later time of David (1 Chronicles 23:22). King Rehoboam and his wives Maacah and Mahalath were grandchildren of David (2 Chronicles 11:20). Finally, according to the book of Tobit, Tobias had a right to marry Sarah because he was her nearest kinsman (Tobit 7:10), though the exact degree of their cousinship is not clear.
Christianity
In Roman Catholicism, all marriages more distant than first-cousin marriages are allowed,[180] and first-cousin marriages can be contracted with a dispensation.[181] This was not always the case, however: the Catholic Church has gone through several phases in kinship prohibitions. At the dawn of Christianity in Roman times, marriages between first cousins were allowed. For example, Emperor Constantine, the first Christian Roman Emperor, married his children to the children of his half-brother. First and second cousin marriages were then banned at the Council of Agde in AD 506, though dispensations sometimes continued to be granted. By the 11th century, with the adoption of the so-called canon-law method of computing consanguinity, these proscriptions had been extended even to sixth cousins, including by marriage. But due to the many resulting difficulties in reckoning who was related to whom, they were relaxed back to third cousins at the Fourth Lateran Council in AD 1215. Pope Benedict XV reduced this to second cousins in 1917,[99] and finally, the current law was enacted in 1983.[181] In Catholicism, close relatives who have married unwittingly without a dispensation can receive an annulment.
There are several explanations for the rise of Catholic cousin marriage prohibitions after the fall of Rome. One explanation is increasing Germanic influence on church policy. G.E. Howard states, "During the period preceding the Teutonic invasion, speaking broadly, the church adhered to Roman law and custom; thereafter those of the Germans ... were accepted."[182] On the other hand, it has also been argued that the bans were a reaction against local Germanic customs of kindred marriage.[183] At least one Frankish King, Pepin the Short, apparently viewed close kin marriages among nobles as a threat to his power.[184] Whatever the reasons, written justifications for such bans had been advanced by St. Augustine by the fifth century. "It is very reasonable and just", he wrote, "that one man should not himself sustain many relationships, but that various relationships should be distributed among several, and thus serve to bind together the greatest number in the same social interests".[3] Taking a contrary view, Protestants writing after the Reformation tended to see the prohibitions and the dispensations needed to circumvent them as part of an undesirable church scheme to accrue wealth, or "lucre".[3]
Since the 13th century the Catholic Church has measured consanguinity according to what is called the civil-law method. Under this method, the degree of relationship between lineal relatives (i.e., a man and his grandfather) is simply equal to the number of generations between them. However, the degree of relationship between collateral (non-lineal) relatives equals the number of links in the family tree from one person, up to the common ancestor, and then back to the other person. Thus brothers are related in the second degree, and first cousins in the fourth degree.[185]
Protestant churches generally allow cousin marriage,[186] in keeping with criticism of the Catholic system of dispensations by Martin Luther and John Calvin during the Reformation.[98] This includes most of the major US denominations, such as Baptist, Pentecostal, Lutheran, Presbyterian, and Methodist. The Anglican Communion has also allowed cousin marriage since its inception during the rule of King Henry VIII. According to Luther and Calvin, the Catholic bans on cousin marriage were an expression of Church rather than divine law and needed to be abolished. Protestants during the Reformation struggled to interpret the Biblical proscriptions against incest in a sensible manner, a task frustrated by facts like their omission of the daughter (but inclusion of the granddaughter) as a directly prohibited relation.[3] John Calvin thought of the Biblical list only as illustrative and that any relationship of the same or smaller degree as any listed, namely the third degree by the civil-law method, should therefore be prohibited. The Archbishop of Canterbury reached the same conclusion soon after.[99] But in contrast to both Protestantism and Catholicism, the Eastern Orthodox Church prohibits up to second cousins from marrying.[17] But, according to the latest constitution (of 2010) of The Orthodox Church of Cyprus, second cousins may marry as the restriction is placed up to relatives of the 5th degree.[187] The reasoning is that marriage between close relatives can lead to intrafamily strife. The 1913 Catholic Encyclopedia refers to a theory by the Anglican bishop of Bath and Wells speculating that Mary and Joseph, the mother of Jesus and her husband, were first cousins.[188] Jack Goody describes this theory as a "legend".[189]
Islam
The Qur'an does not state that marriages between first cousins are forbidden. In Sura An-Nisa (4:22–24), Allah mentioned the women who are forbidden for marriage: to quote the Qur'an, "... Lawful to you are all beyond those mentioned, so that you may seek them with your wealth in honest wedlock…" In Sura Al-Ahzab (33:50),
O Prophet, indeed We have made lawful to you your wives to whom you have given their due compensation and those your right hand possesses from what Allah has returned to you [of captives] and the daughters of your paternal uncles and the daughters of your paternal aunts and the daughters of your maternal uncles and the daughters of your maternal aunts who emigrated with you and a believing woman if she gives herself to the Prophet [and] if the Prophet wishes to marry her, [this is] only for you, excluding the [other] believers. We certainly know what We have made obligatory upon them concerning their wives and those their right hands possess, [but this is for you] in order that there will be upon you no discomfort. And ever is Allah Forgiving and Merciful.[190][191]
Muslims have practiced marriages between first cousins in non-prohibited countries since the time of Muhammad. In a few countries the most common type is between paternal cousins.[190]
Muhammad actually did marry two relatives.[18] One was a first cousin, Zaynab bint Jahsh, who was not only the daughter of one of his father's sisters but was also divorced from a marriage with Muhammad's adopted son, Zayd ibn Haritha. It was the issue of adoption and not cousinship that caused controversy due to the opposition of pre-Islamic Arab norms.[192]
Many of the immediate successors of Muhammad also took a cousin as one of their wives. Umar married his cousin Atikah bint Zayd ibn Amr ibn Nifayl,[193][194] while Ali married Fatimah,[195] the daughter of his paternal first cousin Muhammad and hence his first cousin once removed.[196]
Although marrying his cousin himself, Umar, the second Caliph, discouraged marrying within one's bloodline or close cousins recurringly over generations and advised those who had done so to marry people unrelated to them, by telling a household that did so, "You have become frail, so marry intelligent people unrelated to you."[197]
Even though many Muslims practice cousins marriage now, two of the Sunni Muslims madhhabs (schools, four in total) like Shafi'i (about 33.33% of Sunni Muslims, or 29% of all Muslims) and Hanbali consider it as Makruh (disliked),[198] and there are three Hadiths that prefer marriage outside family but all of them are considered ḍaʿīf (weak). Some scholars like Ibn Qudamah and Al-Ghazali prefer marriage outside the family, because if a divorce happens between the couple, the family bond – which is considered as sacred in Islam – will be weakened or broken due to that, but other scholars such as Ibn Baz said that if there was no better non-family potential bride (none of the "potential in-family bride" and the "potential non-family bride" was better than the other) it's advised to marry the one who is in the family to make the family bond stronger.[199]
Imam Shafi'i, the founder of the Shafi'i madhab, went further in his condemnation of persistent generational bloodline marriages and said, "Whenever the people of a household do not allow their women to marry men outside of their line, there will be fools among their children.”[197]
Hinduism
The Hindu Marriage Act prohibits marriage for five generations on the father's side and three on the mother's side, but allows cross-cousin marriage where it is permitted by custom.[133][200]
Hindu rules of exogamy are often taken extremely seriously, and local village councils in India administer laws against in-gotra endogamy.[201] Social norms against such practices are quite strong as well.[202]
In the 18th and 19th Centuries, Hindu Kurmis of Chunar and Jaunpur are known to have been influenced by their Muslim neighbors and taken up extensively the custom of cousin marriage.[203]
In the Mahabharata, one of the two great Hindu Epics, Arjuna took as his fourth wife his first and cross cousin Subhadra, the sister of Krishna. Arjuna had gone into exile alone after having disturbed Yudhishthira and Draupadi in their private quarters. It was during the last part of his exile, while staying at the Dvaraka residence of his cousins, that he fell in love with Subhadra. While eating at the home of Balarama, Arjuna was struck with Subhadra's beauty and decided he would obtain her as his wife. Subhadra and Arjuna's son was the tragic hero Abhimanyu. According to Andhra Pradesh oral tradition, Abhimanyu himself married his first cross-cousin Shashirekha, the daughter of Subhadra's brother Balarama.[204][205] Cross cousins marriages are evident from Arjuna's marriage with Subhadra, Pradyumna's (Eldest son of Krishna) marriage with Rukmi's (Brother of Rukmini) daughter. Also Krishna married his cross cousin Mitravinda (Daughter of Vasudeva's sister Rajadhi who was Queen of Avanti) and Bhadra (Daughter of Vasudeva's sister Shrutakirti who was the Queen of Kekaya Kingdom.)
Other religions
Buddhism does not proscribe any specific sexual practices, only ruling out "sexual misconduct" in the Five Precepts.[206] Zoroastrianism allows cousin marriages.[207] Sikhism largely follows the pattern of ban on the same clan marriages, many Sikhs choose to marry their children with a partner from a different village or town, just to avoid chances of consanguinity between them.[208]
Biological aspects
Genetics
Cousin marriages have genetic aspects arising an increased chance of sharing genes for recessive traits. The percentage of consanguinity between any two individuals decreases fourfold as the most recent common ancestor recedes one generation. First cousins have four times the consanguinity of second cousins, while first cousins once removed have half that of first cousins. Double first cousins have twice that of first cousins and are as related as half-siblings.
In April 2002, the Journal of Genetic Counseling released a report which estimated the average risk of birth defects in a child born of first cousins at 1.1–2.0 percentage points over an average base risk for non-cousin couples of 3%, or about the same as that of any woman over age 40.[209] In terms of mortality, a 1994 study found a mean excess pre-reproductive mortality rate of 4.4%,[210] while another study published in 2009 suggests the rate may be closer to 3.5%.[2] Put differently, a single first-cousin marriage entails a similar increased risk of birth defects and mortality as a woman faces when she gives birth at age 41 rather than at 30.[211]
Repeated consanguineous marriages within a group are more problematic. After repeated generations of cousin marriage the actual genetic relationship between two people is closer than the most immediate relationship would suggest. In Pakistan, where there has been cousin marriage for generations and the current rate may exceed 50%, one study estimated infant mortality at 12.7 percent for married double first cousins, 7.9 percent for first cousins, 9.2 percent for first cousins once removed/double second cousins, 6.9 percent for second cousins, and 5.1 percent among nonconsanguineous progeny. Among double first cousin progeny, 41.2 percent of prereproductive deaths were associated with the expression of detrimental recessive genes, with equivalent values of 26.0, 14.9, and 8.1 percent for first cousins, first cousins once removed/double second cousins, and second cousins respectively.[212]
Even in the absence of preferential consanguinity, alleles that are rare in large populations can randomly increase to high frequency in small groups within a few generations due to the founder effect and accelerated genetic drift in a breeding pool of restricted size.[213] For example, because the entire Amish population is descended from only a few hundred 18th-century German-Swiss settlers, the average coefficient of inbreeding between two random Amish is higher than between two non-Amish second cousins.[214] First-cousin marriage is taboo among Amish, but they still suffer from several rare genetic disorders. In Ohio's Geauga County, Amish make up only about 10 percent of the population but represent half the special needs cases. In the case of one debilitating seizure disorder, the worldwide total of 12 cases exclusively involves Amish sufferers.[215] Similar disorders have been found in the Fundamentalist Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-Day Saints, who do allow first-cousin marriage and of whom 75 to 80 percent are related to two 1830s founders.[216][217]
Studies into the effect of cousin marriage on polygenic traits and complex diseases of adulthood have often yielded contradictory results due to the rudimentary sampling strategies used. Both positive and negative associations have been reported for breast cancer and heart disease. Consanguinity seems to affect many polygenic traits such as height, body mass index, intelligence and cardiovascular profile.[218][219][220] Long-term studies conducted on the Dalmatian islands in the Adriatic Sea have indicated a positive association between inbreeding and a very wide range of common adulthood disorders, including hypertension, coronary heart disease, stroke, cancer, uni/bipolar depression, asthma, gout, peptic ulcer, and osteoporosis. However, these results may principally reflect village endogamy rather than consanguinity per se. Endogamy is marrying within a group and in this case the group was a village. The marital patterns of the Amish are also an example of endogamy.[221]
The Latin American Collaborative Study of Congenital Malformation found an association between consanguinity and hydrocephalus, postaxial polydactyly, and bilateral oral and facial clefts. Another picture emerges from the large literature on congenital heart defects, which are conservatively estimated to have an incidence of 50/1,000 live births. A consistent positive association between consanguinity and disorders such as ventricular septal defect and atrial septal defect has been demonstrated, but both positive and negative associations with patent ductus arteriosus, atrioventricular septal defect, pulmonary atresia, and Tetralogy of Fallot have been reported in different populations. Associations between consanguinity and Alzheimer's disease have been found in certain populations.[221] Studies into the influence of inbreeding on anthropometric measurements at birth and in childhood have failed to reveal any major and consistent pattern, and only marginal declines were shown in the mean scores attained by consanguineous progeny in tests of intellectual capacity. In the latter case, it would appear that inbreeding mainly leads to greater variance in IQ levels, due in part to the expression of detrimental recessive genes in a small proportion of those tested.[222]
A BBC report discussed Pakistanis in Britain, 55% of whom marry a first cousin.[223] Given the high rate of such marriages, many children come from repeat generations of first-cousin marriages. The report states that these children are 13 times more likely than the general population to produce children with genetic disorders, and one in ten children of first-cousin marriages in Birmingham either dies in infancy or develops a serious disability. The BBC also states that Pakistani-Britons, who account for some 3% of all births in the UK, produce "just under a third" of all British children with genetic illnesses. Published studies show that mean perinatal mortality in the Pakistani community of 15.7 per thousand significantly exceeds that in the indigenous population and all other ethnic groups in Britain. Congenital anomalies account for 41 percent of all British Pakistani infant deaths.[224] The BBC story contained an interview with Myra Ali, whose parents and grandparents were all first cousins. She has a very rare recessive genetic condition, known as epidermolysis bullosa which will cause her to lead a life of extreme physical suffering, limited human contact and probably an early death from skin cancer. Knowing that cousin marriages increase the probability of recessive genetic conditions, she is understandably against the practice. Finally, in 2010 the Telegraph reported that cousin marriage among the British Pakistani community resulted in 700 children being born every year with genetic disabilities.[225]
The increased mortality and birth defects observed among British Pakistanis may, however, have another source besides current consanguinity. This is population subdivision among different Pakistani groups. Population subdivision results from decreased gene flow among different groups in a population. Because members of Pakistani biradari have married only inside these groups for generations, offspring have higher average homozygosity even for couples with no known genetic relationship.[226] According to a statement by the UK's Human Genetics Commission on cousin marriages, the BBC also "fails to clarify" that children born to these marriages were not found to be 13 times more likely to develop genetic disorders. Instead they are 13 times more likely to develop recessive genetic disorders. The HGC states, "Other types of genetic conditions, including chromosomal abnormalities, sex-linked conditions and autosomal dominant conditions are not influenced by cousin marriage." The HGC goes on to compare the biological risk between cousin marriage and increased maternal age, arguing that "Both represent complex cultural trends. Both however, also carry a biological risk. They key difference, GIG argue, is that cousin marriage is more common amongst a British minority population."[227] Genetic effects from cousin marriage in Britain are more obvious than in a developing country like Pakistan because the number of confounding environmental diseases is lower. Increased focus on genetic disease in developing countries may eventually result from progress in eliminating environmental diseases there as well.[228]
Comprehensive genetic education and premarital genetic counseling programs can help to lessen the burden of genetic diseases in endogamous communities. Genetic education programs directed at high-school students have been successful in Middle Eastern countries such as Bahrain. Genetic counseling in developing countries has been hampered, however, by lack of trained staff, and couples may refuse prenatal diagnosis and selective abortion despite the endorsement of religious authorities.[229] In Britain, the Human Genetics Commission recommends a strategy comparable with previous strategies in dealing with increased maternal age, notably as this age relates to an increased risk of Down syndrome. All pregnant women in Britain are offered a screening test from the government-run national health service to identify those at an increased risk of having a baby with Down syndrome. The HGC states that similarly, it is appropriate to offer genetic counseling to consanguineous couples, preferably before they conceive, in order to establish the precise risk of a genetic abnormality in offspring. Under this system the offering of genetic counseling can be refused, unlike, for example, in the US state of Maine where genetic counseling is mandatory to obtain a marriage license for first cousins. Leading researcher Alan Bittles also concluded that though consanguinity clearly has a significant effect on childhood mortality and genetic disease in areas where it is common, it is "essential that the levels of expressed genetic defect be kept in perspective, and to realize that the outcome of consanguineous marriages is not subject to assessment solely in terms of comparative medical audit".[230] He states that the social, cultural, and economic benefits of cousin marriage also need to be fully considered.[231]
Fertility
Higher total fertility rates are reported for cousin marriages than average, a phenomenon noted as far back as George Darwin during the late 19th century. There is no significant difference in the number of surviving children in cousin marriages because this compensates for the observed increase in child mortality.[232] The total fertility increase may be partly explained by the lower average parental age at marriage, and age at first birth, observed in consanguineous marriages. Other factors include shorter birth intervals and possibly a lower likelihood of using reliable contraception.[17] There is also the possibility of more births as a compensation for increased child mortality, either via a conscious decision by parents to achieve a set family size or the cessation of lactational amenorrhea following the death of an infant.[233] According to a recent paper the fertility difference is probably not due to any underlying biological effect.[234] In Iceland, where marriages between second and third cousins were common, in part due to limited selection, studies show higher fertility rates.[235] Earlier papers claimed that increased sharing of human leukocyte antigens, as well as of deleterious recessive genes expressed during pregnancy, may lead to lower rates of conception and higher rates of miscarriage in consanguineous couples. Others now believe there is scant evidence for this unless the genes are operating very early in the pregnancy. Studies consistently show a lower rate of primary infertility in cousin marriages, usually interpreted as being due to greater immunological compatibility between spouses.[236]
See also
- Affinity (Catholic canon law)
- Assortative mating
- Coefficient of relationship
- Cousin marriage in the Middle East
- Cousin marriage law in the United States
- Endogamy
- Genetic distance
- Genetic diversity
- Genetic sexual attraction
- Inbreeding
- Inbreeding avoidance
- Inbreeding depression
- Incest taboo
- Jewish views on incest
- Legality of incest
- List of coupled cousins
- Mahram
- Pedigree collapse
- Proximity of blood
- Watta satta
- Westermarck effect
References
- History, Mr (24 January 2017). "When Did Cousin Marriage Become Unacceptable?". HistoryNet. Retrieved 10 August 2019.
- Kershaw, Sarah (26 November 2009). "Shaking Off the Shame". The New York Times.
- Ottenheimer, Martin (1996). "Chapter 5". Forbidden Relatives: The American Myth of Cousin Marriage. University of Illinois.
- "The Surprising Truth About Cousins and Marriage". 14 February 2014.
- Paul, Diane B.; Spencer, Hamish G. (23 December 2008). ""It's Ok, We're Not Cousins by Blood": The Cousin Marriage Controversy in Historical Perspective". PLOS Biology. 6 (12): 2627–30. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0060320. PMC 2605922. PMID 19108607.
- "Final Thoughts". Cousin Couples. Retrieved 4 June 2016.
- Brandon Keim (23 December 2008). "Cousin Marriage OK by Science". Wired.
- Saletan, William (10 April 2002). "The Love That Dare Not Speak Its Surname" – via Slate.
- Hamamy, Hanan (July 2012). "Consanguineous marriages". Journal of Community Genetics. 3 (3): 185–192. doi:10.1007/s12687-011-0072-y. ISSN 1868-310X. PMC 3419292. PMID 22109912.
- "When Incest Is Best: Kissing Cousins Have More Kin". Scientific American. 8 February 2008.
- Ottenheimer 1996, pp. 58, 92
- Freire-Maia 1957
- Bittles 1994, p. 563
- The National 2009
- Bittles 2000
- "Go Ahead, Kiss Your Cousin - DiscoverMagazine.com".
- Bittles, Alan H. (May 2001). A Background Summary of Consanguineous Marriage (PDF) (Technical report). Edith Cowan University.
- Bittles 1994, p. 567
- Bittles and Black 2009, Section 7
- Dawson 1915, p. 143
- Chen 1932, pp. 628–9
- Feng 1967, p. 37
- Feng 1967, p. 44
- Feng 1967, p. 38
- Chen 1932, pp. 650–1
- Feng 1967, p. 43
- Chen 1932, p. 630
- Hsu 1945, p. 91
- Zhaoxiang 2001, p. 353
- Zhaoxiang 2001, p. 355
- Zhaoxiang 2001, p. 356–57
- Goody, Marriage and the Family in Europe
- Patai
- Meriwether
- Holy, also Patai, p. 140
- Patai, Golden River to Golden Road, 145–153
- Patai 153–161
- Patai 166
- Meriwether p. 135
- Patai 141
- Women in Ancient Persia, 559–331 BC By Maria Brosius, p. 68
- Givens 1994
- Patai, The Myth of the Jewish Race, "Cousin Marriage"
- Holy, 110–17
- Holy, 118–20
- Holy, 120–7
- Holy, Chapter 2
- Patai 144–145
- Patai 173–75
- Tadmour 2009 (Table 1).
- Tadmour, Ghazi O.; Pratibha Nair1; Tasneem Obeid1; Mahmoud T Al Ali1; Najib Al Khaja1; Hanan A Hamamy (2009). "Consanguinity and reproductive health among Arabs". Reproductive Health. 6 (17): 17. doi:10.1186/1742-4755-6-17. PMC 2765422. PMID 19811666.
- Korotayev A. V. Parallel Cousin (FBD) Marriage, Islamization, and Arabization // Ethnology 39/4 (2000): 395–407. Islam forbids marrying one's nephew or niece, this can be found in the Holy Quran 4:23 which states (translated from Arabic): "Prohibited to you [for marriage] are your mothers, your daughters, your sisters, your father's sisters, your mother's sisters, your brother's daughters, your sister's daughters, your [milk] mothers who nursed you, your sisters through nursing, your wives' mothers, and your step-daughters under your guardianship [born] of your wives unto whom you have gone in. But if you have not gone in unto them, there is no sin upon you. And [also prohibited are] the wives of your sons who are from your [own] loins, and that you take [in marriage] two sisters simultaneously, except for what has already occurred. Indeed, Allah is ever Forgiving and Merciful."
- Bittles 1994, p. 565
- CIA 2010
- Swanson
- Karo 1982, p. 268
- Karo 1982, p. 9
- Karo 1982, p. 264
- Karo 1982, pp. 102–103
- Suberu 2001, p. 3
- Scott-Emuakpor 1974
- Schwimmer 2003
- Crummey 1983, p. 207
- Crummey 1983, p. 213
- Abbink 1998, p. 113
- Abbink 1998, pp. 112, 118
- Save the Children USA 2007, pp. 6–8
- de Colquhoun, Patrick MacChombaich, A summary of the Roman civil law (William Benning and Co., Cambridge, 1849), p. 513
- Bouchard, Constance B., 'Consanguinity and Noble Marriages in the Tenth and Eleventh Centuries', Speculum, Vol. 56, No. 2 (Apr., 1981), p. 269
- Constance Bouchard, Those of My Blood: Creating Noble Families in Medieval Francia (Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2001), p. 40
- Constance B. Bouchard, 'Consanguinity and Noble Marriages in the Tenth and Eleventh Centuries', Speculum, Vol. 56, No. 2 (April 1981), pp. 269–70
- Constance B. Bouchard, 'Consanguinity and Noble Marriages in the Tenth and Eleventh Centuries', Speculum, Vol. 56, No. 2 (April 1981), pp. 270, 271
- "Lateran 4 - 1215". www.ewtn.com.
- John W. Baldwin, The Language of Sex: Five Voices from Northern France around 1200 (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1994), p. 78
- Constance B. Bouchard, 'Consanguinity and Noble Marriages in the Tenth and Eleventh Centuries', Speculum, Vol. 56, No. 2 (April 1981), p. 270
- James A. Brundage, Law, Sex, and Christian Society in Medieval Europe (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1995), p. 356
- Other examples are: Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor and Margarita, William III and Mary II, Philippe I and Henrietta, Frederick William I of Prussia and Sophia Dorothea, Christian VII of Denmark and Caroline Matilda, George IV and Caroline, Albert and Queen Victoria, Prince Henry of Prussia and Princess Irene, Olav V of Norway and Princess Märtha, Ernest Louis and Princess Victoria Melita of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, who also married Kirill Vladimirovich, another first cousin.
- Ottenheimer 1996, p. 90.
- Ottenheimer. p. 81.
- "There's nothing wrong with cousins getting married, scientists say". 24 December 2008.
- Darwin 1875.
- Ottenheimer. p. 84
- Jones, Steve (19 January 2009). "We ought to be exterminated". The Guardian. London.
- Ottenheimer, Martin (1996). "Chapter 4". Forbidden Relatives: The American Myth of Cousin Marriage. University of Illinois.
- Cascio, Justin. "Rates of consanguineous marriage among Mafia families in Corleone.docx". Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Forbes, Hamish (October 2007). Meaning and Identity in a Greek Landscape: An Archaeological Ethnography. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521866996.
- Ottenheimer 1996, p. 63
- Grubbs 2002, p. 163
- Goody 1983, pp. 51–2
- Shaw 1984
- Patterson 1998, p. 98
- Goody 1983, p. 45
- Goody 1983, p. 44
- Bouchard, Constance B., 'Consanguinity and Noble Marriages in the Tenth and Eleventh Centuries', Speculum, Vol. 56, No. 2 (Apr., 1981), pp. 269-70
- Westermarck 1921, Vol. 2, p. 101
- "Index of /~omar". www-personal.ksu.edu.
- Ottenheimer. p. 111.
- Ottenheimer, Martin (1996). "Chapter 2". Forbidden Relatives: The American Myth of Cousin Marriage. University of Illinois.
- Ottenheimer, Martin (1996). "Chapter 3". Forbidden Relatives: The American Myth of Cousin Marriage. University of Illinois.
- Bittles and Black 2009, Section 2
- See Article 809 of the Korean Civil Code and "THE FIRST TEN YEARS OF THE KOREAN CONSTITUTIONAL COURT" (PDF). Constitutional Court of Korea: 242 (p.256 of the PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 February 2012. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help). - Family Code of the Philippines. Article 38.
- Marriage Law of 1981
- "Marriage Law of the People's Republic of China". Consulate-General of the People's Republic of China in New York. 14 November 2003. Archived from the original on 11 February 2010. Retrieved 1 July 2012.
- "The Marriage and Family Law". Ministry of Justice (Vietnam). Retrieved 28 June 2013.
- Francis I.; K. Hsu (28 October 2009). "Observations on Cross-Cousin Marriage in China". American Anthropologist. 47J (1): 83–103. doi:10.1525/aa.1945.47.1.02a00050.
- Ottenheimer 1996, p. 90
- "Facts About Cousin Marriage." Cousin Couples.
- Wolfson, Evan (2004). Why marriage matters: America, equality, and gay people's right to marry. Simon & Schuster. p. 256. ISBN 978-0-7432-6458-7.
- Hamamy, H. (July 2012). "Consanguineous marriages Preconception consultation in primary health care settings". Journal of Community Genetics. US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health. 3 (3): 185–192. doi:10.1007/s12687-011-0072-y. PMC 3419292. PMID 22109912.
- Bittles 2009
- Hajnal 1963, p. 135
- Freire-Maia 1957, p. 286
- Freire-Maia 1957, p. 292
- Bittles 1991, p. 780
- Hannah Beech Nanliang. In Rural China, It's a Family Affair. Time. 27 May 2002.
- Wöhrle, Christoph (25 February 2007). "Inzest: Wenn der Cousin mit der Cousine schläft". DIE WELT. Archived from the original on 28 March 2012. Retrieved 2 April 2018.
- "Can cousin marriages be banned?". 23 September 2009.
- AS, TV 2. "Stortingsflertall forbyr søskenbarnekteskap". TV 2 (in Norwegian). Retrieved 14 November 2020.
- "Stortingsflertall forbyr søskenbarnekteskap". www.vg.no (in Norwegian Bokmål). Retrieved 14 November 2020.
- New Humanist. 9 Sept 2009.
- Enhanced Genetic Services Project - Evaluation Report (PDF). PHG Foundation / NHS. 2008. p. 9.
- "No 10 steps back from cousins row." BBC News. 11 February 2008.
- "War in medical community over cousin marriage." Archived 30 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine inthenews.co.uk. 30 May 2008.
- Emma Wilkinson. "Cousin marriage: Is it a health risk?" BBC News. 16 May 2008.
- Aamra Darr. "Cousin marriage is a social choice: it needn't be a problem." The Guardian. 2 December 2005.
- Bener and Hussain 2006, p. 377
- Dr. Ahmad Teebi. "Marriages among cousins increasing in UAE". Khaleejtimes.
- Holy p. 6
- Holy, p. 66
- Holý, Ladislav (1989). Kinship, honour, and solidarity: cousin marriage in the Middle East. Manchester University Press. p. 22. ISBN 978-0-7190-2890-8.
- Sharma, Santosh Kumar; Kalam, Mir Azad; Ghosh, Saswata; Roy, Subho (9 July 2020). "Prevalence and determinants of consanguineous marriage and its types in India: evidence from the National Family Health Survey, 2015–2016". Journal of Biosocial Science: 1–11. doi:10.1017/s0021932020000383. ISSN 0021-9320. PMID 32641190.
- Bittles 1991, p. 791
- http://lawcommissionofindia.nic.in/reports/report212.pdf
- Dhavendra Kumar. Genetic Disorders of the Indian Subcontinent. Kluwer Academic Publishers: AA Dordrecht, Netherlands, 2000. 127.
- Arthur P. Wolf, Inbreeding, Incest, and the Incest Taboo The State of Knowledge at the Turn of the Century, Stanford University Press (2005), p. 46
- W. H. R. Rivers. "The Marriage of Cousins in India." Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland. 1907.
- Subrahmanyam, Y. Subhashini (1 January 1967). "A Note on Cross-Cousin Marriage among Andhra Brahmins". Journal of Asian and African Studies. 2 (3–4): 266–272. doi:10.1163/156852167X00289 (inactive 15 January 2021). ISSN 1568-5217.CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of January 2021 (link)
- "India - Marriage". countrystudies.us.
- "Global prevalence tables". www.consang.net.
- Shaw 2001, p. 322
- Zahid, Muhammad; Bittles, Alan H.; Sthanadar, Aftab Alam (September 2014). "Civil Unrest and the Current Profile of Consanguineous Marriage in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province, Pakistan". Journal of Biosocial Science. 46 (5): 698–701. doi:10.1017/S0021932013000552. ISSN 1469-7599.
- Hakim, A. (1994). "Comments on "Consanguineous Marriages in Pakistan"". Pakistan Development Review. 33 (4 Pt 2): 675–676. ISSN 0030-9729. PMID 12346200.
- Shami, Schmitt & Bittles 1989.
- Saify, K.; Saadat, M. (2012). "Consanguineous marriages in Afghanistan". Journal of Biosocial Science. 44 (1): 73–81. doi:10.1017/S0021932011000253. PMID 21729362.
- U.S. Census. "Race of Wife by Race of Husband: 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991, and 1992." 5 July 1994.
- Paul and Spencer.
- "TPT St. Paul. "Quotes for Inspiration." June 25, 2009". Archived from the original on 6 September 2009.
- "The Wake. Vol. 3, Issue 8" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 30 November 2009.
- "BILL INFO-2000 Regular Session-HB 459". mlis.state.md.us.
- "Steve Chapman. "Keeping Marriage in the Family."".
- C.S.H.B. 3006. Texas Legislature 79(R).
- Plocek, Keith (27 April 2006). "Big Love, Texas-Style".
- "Bill takes aim at polygamists". www.dentonrc.com.
- Writer, NATALIE GOTT Associated Press. "Lawmaker files bill raising age of marriage consent".
- "Trish Choate. "FLDS TRIAL: All eyes still on Jessop, for now". St. Angelo Standard-Times.
- "85th Texas Legislature: News, issues, commentary & more".
- "PENAL CODE CHAPTER 25. OFFENSES AGAINST THE FAMILY". www.statutes.legis.state.tx.us.
- N.C. Gen. Stat. § 51–3 (West 2009).
- "State Laws Regarding Marriages Between First Cousins". National Conference of State Legislatures. Retrieved 10 September 2013.
- US State Laws, cousincouples.com.
- "Global prevalence tables - ConsangWiki - Consang.net". www.consang.net. Retrieved 18 January 2017.
- Hammami, Abdelmajid; Elgazzeh, Mohamed; Chalbi, Noureddine; Mansour, Ben Abdallah (1 January 2005). "[Endogamy and consanguinity in Mauritania]". La Tunisie Médicale. 83 (1): 38–42. ISSN 0041-4131. PMID 15881720.
- "National Society of Genetic Counselors : NSGC Home Page". www.nsgc.org.
- Bittles 1994, p. 570
- Bittles 1994, p. 577
- Ottenheimer. p. 139.
- Elementary Structures of Kinship, Chapter 9, pp. 119–20
- Elementary Structures of Kinship, Chapter 9, p. 122
- Spiro, Melford E (1968). "10". In Manners, Robert Alan; Kaplan, David (eds.). Theory in anthropology: a source-book. Routledge & Kegan Paul Books. pp. 105, 107. ISBN 978-0-7100-6172-0.
- Claude Lévi-Strauss, Les structures élémentaires de la parenté, Paris, Mouton, 1967, 2ème édition.
- Leach 1951, pp. 51–53
- Murphy and Kasdan, pp. 17–18
- Murphy and Kasdan, pp. 19–20
- Murphy and Kasdan, p. 22
- Murphy and Kasdan, pp. 27–28
- Woodley, Michael A.; Edward Bell (2013). "Consanguinity as a Major Predictor of Levels of Democracy: A Study of 70 Nations". Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology. 44 (2): 263–280. doi:10.1177/0022022112443855. S2CID 145714074.
- Sailer, Steve (January 2003). McConnell, Scott (ed.). "Cousin Marriage Conundrum". The American Conservative: 20–22.
- "Code of Canon Law - IntraText". www.vatican.va.
- John P. Beal, James A. Coriden and Thomas J. Green. New Commentary on the Code of Canon Law. Mahwah, NJ: Paulist Press, 2000. 1293.
- Howard, G.E. (1904). A History of Matrimonial Institutions. 1. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 291.
- Goody, Jack (1983). The Development of the Family and Marriage in Europe. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 59.
- Gies, Joseph; Gies, Frances (1983). Marriage and the Family in the Middle Ages. New York: Harper and Row.
- "Can. 108". The Holy See. Archived from the original on 15 January 2010.
- Amy Strickland. "An Afternoon With Amy Strickland, JCL." Cousin Couples. 4 February 2001. Accessed December 2009.
- "CATHOLIC ENCYCLOPEDIA: Heli (Eli)". Retrieved 6 June 2007.
- Goody 1983, p. 53
- Andrey Korotayev. "Parallel-Cousin (FBD) Marriage, Islamization, and Arabization." Ethnology, Vol. 39, No. 4, pp. 395–407.
- "Chapter (33) sūrat l-aḥzāb (The Combined Forces)". corpus.quran.com.
- Watt, Muhammad at Medina, p. 330
- History of the Prophets and Kings 4/ 199 by Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari
- al-Bidayah wa al-Nihayah 6/352 by ibn Kathir
- See:
- Fatimah bint Muhammad Archived 28 May 2009 at Archive.today. MSA West Compendium of Muslim Texts.
- "Fatimah", Encyclopaedia of Islam. Brill Online.
- Nasr, Seyyed Hossein. "Ali". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Retrieved 12 October 2007.
- Elias, Abu Amina (10 August 2019). "Umar on Inbreeding: Do not to marry within bloodlines, close cousins | Daily Hadith Online الحديث اليومي". Retrieved 20 May 2020.
- زواج الأقارب... وما يثار حوله من شبهات وأخطار – إسلام ويب – مركز الفتوى (in Arabic). Islamweb, Fatwa Center. Retrieved 10 September 2013.
- موقع الإسلام سؤال وجواب – زواج الأقارب وحديث: (غربوا النكاح) (in Arabic). Islam Q&A. Retrieved 10 September 2013.
- "Hindu Marriage Act, 1955". Government of Punjab: Department of Revenue, Rehabilitation and Disaster Management. Archived from the original on 7 April 2010. Retrieved 27 March 2010.
- Vashisht, Dinker (20 July 2009). "Haryana panchayat takes on govt over same-gotra marriage". The Indian Express Limited.
- Chowdhry 2004
- Christopher Bayly, Townsmen and Bazaars: North Indian Society in the Age of British Expansion, 1770–1870, p. 49
- Do 2006, p. 5
- Indrajit Bandyopadhyay (29 October 2008). "A Study In Folk "Mahabharata": How Balarama Became Abhimanyu's Father-in-law". Epic India: A New Arts & Culture Magazine. Archived from the original on 27 May 2011. Retrieved 4 December 2010.
- Higgins, W. "Buddhist Sexual Ethics". BuddhaNet Magazine. Retrieved 15 January 2007.
- "Zoroastrians - Marriage and Family". World Culture Encyclopedia.
- "Marriage and Family Encyclopedia". JRank. Retrieved 8 March 2017.
- Connor, Steve (24 December 2008). "There's nothing wrong with cousins getting married, scientists say". The Independent. London. Retrieved 30 April 2010.
- Bittles, A.H. (May 2001). "A Background Background Summary of Consaguineous marriage" (PDF). consang.net consang.net. Retrieved 19 January 2010., citing Bittles, A.H.; Neel, J.V. (1994). "The costs of human inbreeding and their implications for variation at the DNA level". Nature Genetics. 8 (2): 117–121. doi:10.1038/ng1094-117. PMID 7842008. S2CID 36077657.
- Connor, Steve (24 December 2008). "There's nothing with cousins getting married, scientists say". The Independent. London.
- Bittles 1994, p. 572, 574
- Bittles 1994, p. 572
- Hostetler 1963, p. 330
- McKay 2005
- Dougherty 2005
- Reuters 2007
- Fareed, M; Afzal M (2014). "Evidence of inbreeding depression on height, weight, and body mass index: a population-based child cohort". American Journal of Human Biology. 26 (6): 784–795. doi:10.1002/ajhb.22599. PMID 25130378. S2CID 6086127.
- Fareed, M; Afzal M (2014). "Estimating the inbreeding depression on cognitive behavior: a population based study of child cohort". PLOS ONE. 9 (10): e109585. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...9j9585F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0109585. PMC 4196914. PMID 25313490.
- Fareed, M; Afzal M (2016). "Increased cardiovascular risks associated with familial inbreeding: a population-based study of adolescent cohort". Annals of Epidemiology. 26 (4): 283–292. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2016.03.001. PMID 27084548.
- Bittles and Black, 2009, Section 6
- Bittles 1994, p. 575
- Rowlatt, J, (2005) "The risks of cousin marriage", BBC Newsnight. Accessed 28 January 2007
- Bittles 1994, p. 576
- Lefort, Rebecca (22 August 2010). "700 children born with genetic disabilities due to cousin marriages every year" – via www.telegraph.co.uk.
- Bittles and Black, 2009, Section 5
- "Statement on cousins who marry", Human Genetics Commission. Accessed 1 November 2009
- Bittles 1994, p. 579
- Bittles and Black, 2009, Section 4
- Bittles 1994, p. 578
- Bittles 1994, p. 793
- Bittles 1994, p. 790
- Bittles 1994, p. 571
- Hussein, R.; Bittles, A.H. (1999), Consanguineous marriage and differentials in age at marriage, contraceptive use and fertility in Pakistan, Journal of Biosocial Science, pp. 121–138
- Third Cousins Have Greatest Number Of Offspring, Data From Iceland Shows, Science Daily, 7 February 2008
- Bittles 1994, pp. 568–569
Sources
- Bener, Abdulbari; Hussain, Rafat (2006). "Consanguineous Unions and Child Health in the State of Qatar". Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology. 20 (5): 372–378. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3016.2006.00750.x. PMID 16911015.
- Bittles, Alan H. (September 1994). "The Role and Significance of Consanguinity as a Demographic Variable". Population and Development Review. 20 (3): 561–584. doi:10.2307/2137601. JSTOR 2137601.
- Bittles, Alan; Hussain, Rafat (2000). "An analysis of consanguineous marriage in the Muslim population of India at regional and state levels". Annals of Human Biology. 27 (2): 163–171. doi:10.1080/030144600282271. PMID 10768421.
- Bittles, Alan (2009). "Commentary: The background and outcomes of the first-cousin marriage controversy in Great Britain". International Journal of Epidemiology. 38 (6): 1453–1458. doi:10.1093/ije/dyp313. PMID 19926668.
- Bittles, Alan; Black, Michael (September 2009). "Consanguinity, human evolution, and complex diseases". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 107 (suppl 1): 1779–1786. doi:10.1073/pnas.0906079106. PMC 2868287. PMID 19805052.
- Bittles, Alan (2009). "Tables of the global prevalence of consanguinity". consang.net. Retrieved 8 February 2010.
- Darwin, George H (1875). "Marriages between first cousins in England and their effects". Journal of the Statistical Society. XXXVIII Part II (2): 153–184. JSTOR 2338660.
- Đõ, Quý Toàn; Iyer, Sriya; Joshi, Shareen (2006). The Economics of Consanguineous Marriages. World Bank, Development Research Group, Poverty Team.
- Dougherty, John (29 December 2005). "Forbidden Fruit". Phoenix New Times. Retrieved 10 February 2010.
- Freire-Maia, Newton (December 1957). "Inbreeding in Brazil". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 9 (4): 284–298. PMC 1932014. PMID 13497997.
- Givens, Benjamin P.; Hirschman, Charles (November 1994). "Modernization and Consanguineous Marriage in Iran". Journal of Marriage and Family. 56 (4): 820–834. doi:10.2307/353595. JSTOR 353595.
- Goody, Jack (1983). The development of the family and marriage in Europe. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Grubbs, Judith Evans (2002). Women and the law in the Roman Empire. New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-15240-2. Retrieved 13 February 2010.
- Hajnal, J.; et al. (10 December 1963). "Concepts of Random Mating and the Frequency of Consanguineous Marriages". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 159 (974): 125–177. Bibcode:1963RSPSB.159..125H. doi:10.1098/rspb.1963.0071. PMID 14087988. S2CID 45211684.
- Holý, Ladislav (1989). Kinship, honour, and solidarity: cousin marriage in the Middle East. Manchester University Press ND. ISBN 978-0-7190-2890-8.
- Hostetler, John Andrew (1993). Amish Society. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-4442-3.
- Leach, Edmund (2009). "The Structural Implications of Matrilateral Cross-Cousin Marriage". The Journal of the Royal Anthropological Institute. 1/2 (6): 23–55. JSTOR 2844015.
- McKay, Mary Jayne (8 June 2005). "Genetic Disorders Hit Amish Hard". CBS. Retrieved 10 February 2010.
- Murphy, Robert F.; Kasdan, Leonard (February 1959). "The Structure of Parallel Cousin Marriage". American Anthropologist. 61 (1): 17–29. doi:10.1525/aa.1959.61.1.02a00040. JSTOR 666210.
- Ottenheimer, Martin (1996). Forbidden Relatives: The American Myth of Cousin Marriage. Chicago: University of Illinois Press.
- Patterson, Cynthia B. (1998). The Family in Greek History. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-29270-3.
- Prem, Chowdhry (2004). "Consanguineous Unions and Child Health in the State of Qatar". Modern Asian Studies. 38 (1): 55–84.
- "Polygamist community faces genetic disorder". Reuters. 15 June 2007. Archived from the original on 13 December 2010. Retrieved 10 February 2010.
- Shami, S A; Schmitt, L H; Bittles, A H (1989). "Consanguinity related prenatal and postnatal mortality of the populations of seven Pakistani Punjab cities". Journal of Medical Genetics. 26 (4): 267–271. doi:10.1136/jmg.26.4.267. PMC 1017301. PMID 2716036.
- Shaw, Brent; Saller, Richard (September 1984). "Close-Kin Marriage in Roman Society?". Man, New Series. 19 (3): 432–444. JSTOR 2802181.
- Shaw, Alison (2009). "Kinship, Cultural Preference and Immigration: Consanguineous Marriage among British Pakistanis". The Journal of the Royal Anthropological Institute. 7 (2): 315–334. doi:10.1111/1467-9655.00065. JSTOR 2661225.
- Westermarck, Edward (1922). The History of Human Marriage. New York: Allerton Book Co.
Further reading
- Abbink, Jon (December 1998). "An Historical-Anthropological Approach to Islam in Ethiopia: Issues of Identity and Politics". Journal of African Cultural Studies. 11 (2): 109–124. doi:10.1080/13696819808717830. hdl:1887/9486. JSTOR 1771876.
- Baba of Karo; Smith, Mary Felice (1981). Baba of Karo. Yale University. ISBN 978-0-300-02741-9.
- Bittles, Alan H.; et al. (10 May 1991). "Reproductive Behavior and Health in Consanguineous Marriages". Science. 252 (5007): 789–794. Bibcode:1991Sci...252..789B. doi:10.1126/science.2028254. PMID 2028254. S2CID 1352617.
- "Census of India, Population by Religious Communities". Census of India. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. 2001. Retrieved 7 February 2010.
- Chen, T. S.; Shryock, J. K. (October–December 1932). "Chinese Relationship Terms". American Anthropologist. 34 (4): 623–669. doi:10.1525/aa.1932.34.4.02a00080. JSTOR 662675.
- "Nigeria". The CIA World Factbook. US Central Intelligence Agency. 15 January 2010. Retrieved 7 February 2010.
- Crummey, Donald (1983). "Family and Property amongst the Amhara Nobility". The Journal of African History. 24 (2): 207–220. doi:10.1017/S0021853700021940. JSTOR 181641.
- Dawson, Miles Menander, ed. (1915). "The Family". The Ethics of Confucius. New York: Putnam.
- Dyson, Tim; Moore, Mick (March 1983). "On Kinship Structure, Female Autonomy, and Demographic Behavior in India". Population and Development Review. 9 (1): 35–60. doi:10.2307/1972894. JSTOR 1972894.
- "2007 Census" (PDF). Central Statistical Agency of Ethiopia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 February 2012.
- Feng, Han-yi (1967). The Chinese Kinship System. Cambridge: Harvard.
- Givens, Benjamin P.; Hirschman, Charles (November 1994). "Modernization and Consanguineous Marriage in Iran". Journal of Marriage and Family. 56 (4): 820–834. doi:10.2307/353595. JSTOR 353595.
- Hsu, Francis L. K. (January–March 1945). "Observations on Cross-Cousin Marriage in China". American Anthropologist. 47 (1): 83–103. doi:10.1525/aa.1945.47.1.02a00050. JSTOR 663208.
- "Marriage Law of the People's Republic of China". Consulate-General of the People's Republic of China in New York. 14 November 2003. Archived from the original on 11 February 2010. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
- Meriwether, Margaret Lee (1999). The kin who count: family and society in Ottoman Aleppo, 1770–1840. University of Texas Press. ISBN 978-0-292-75224-5.
- Qin, Zhaoxiong (22 September 2001). "Rethinking Cousin Marriage in Rural China". Ethnology. 40 (4): 347–360. doi:10.2307/3773881. JSTOR 3773881.
- "Learning from Children, Families, and Communities to Increase Girls' Participation in Primary School (Ethiopia)" (PDF). Save the Children USA. 31 July 2007. Retrieved 8 February 2010.
- Schwimmer, Brian (September 2003). "Census of India, Population by Religious Communities". Kinship and Social Organization. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 7 February 2010.
- Scott-Emuakpori, Ajovi B. (1974). "The Mutation Load in an African Population". Am J Hum Genet. 26 (2): 674–682.
- Suberu, Rotimi T. (2001). Federalism and ethnic conflict in Nigeria. Washington, DC: Endowment of the United States Institute of Peace. ISBN 978-1-929223-28-2.
- Swanson, Eleanor C.; Robert O. Lagace. "Hausa". Ethnographic Atlas. Centre for Social Anthropology and Computing, University of Kent at Canterbury. Archived from the original on 17 February 2010. Retrieved 8 February 2010.
- "Marriages between cousins has become more common in the UAE". khaleejtimes. 20 November 2009. Retrieved 11 June 2017.
External links
| Look up cousincest in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Consanguinity/Endogamy Resource by Dr. Alan Bittles and Dr. Michael Black
- Shaking Off the Shame by Sarah Kershaw for The New York Times
- Forbidden Fruit by John Dougherty

