History of the MRT (Singapore)
The history of the Mass Rapid Transit system of Singapore commenced with its planning in the 1960s, which finally led to its opening in 1987 with the launch of the 6 km section of the North South Line from Yio Chu Kang to Toa Payoh. It now has six lines in operation (as of 31 January 2020) with a total combined route length of 202.4 km (125.8 mi) and 122 stations. The Light Rail Transit which opened in 1999 acts as a feeder service to the MRT network.
Construction of backbone network
Conceptualisation
The idea of constructing a rapid transit line in the country was initiated in 1967, when a four-year State and City Planning study conducted by the Singapore government and the United Nations Development Programme. It was part of an urban renewal and development project which aimed to formulate a long-term comprehensive concept plan for guiding the country's future physical development. It was concluded that physical land constraints faced by the island nation, was not able to accommodate more roads to meet the rise in transportation demands. It was noted that the city state needed a rail transit system by 1992.[1]
Bus vs. rail debate
It took 10 years since 1972 to design the MRT system, which continued all the way until the government gave permission to build the MRT.
In 1972, a team of consultants and professional officers seconded from the government embarked on a major transport study known as the Singapore Mass Transit Study. In phase one of the study, the team examined existing and future transport demands, analysed various options and made recommendations for government investment in public transportation. The team recommended the rail mass transit as the best option for meeting the anticipated travel demands of Singapore.
Phase two of the study, which commenced in 1975, examined the technical, economic and financial feasibility of the mass transit system. This study argued that a bus-rail system was a "superior alternative" to an all-bus system, with only a remote chance of a disastrous result.
Despite the study's recommendation for the development of a MRT system, the high costs involved and the possible impact on patterns of land use and economic activities prevented the government from making an immediate decision. The issue was complicated by a review of the phase two study by a team from the World Bank. The World Bank team had issues with the Singapore team's costing and assessment of the relative benefits of the bus-rail plan compared to an all-bus system.
Phase three of the study was conducted between 1979 and 1980, and provided a preliminary engineering design for the recommended transit system. In 1980, a Provisional Mass Rapid Transit Authority was appointed to undertake preparatory work for the construction of a possible MRT system.
Despite the findings of the mass transit studies, the government was still hesitant to commit to the MRT system. A team of foreign consultants (also known as the Harvard team) led by team leader Kenneth Hansen was engaged to review the previous mass transit and other transportation studies.
In their report, the Hansen team argued that the earlier studies were based on incorrect assumptions and thus failed to consider other approaches to solve Singapore's transport problems. Rather than a MRT system, the Hansen team recommended a high performance all-bus system coupled with feeder routes and motorcar restraint. Even if Singapore were to develop a MRT system, the team suggested that only one line be built as they believed that this would be sufficient to relieve traffic congestion and allow the bus system to function.
When the late president Mr Ong Teng Cheong became the then-Minister for Communications (now the Ministry of Transport), he had to convince the cabinet in a debate in early 1980, that the S$ 5 billion needed for the system would be beneficial for the long-term development of Singapore. He argued that:
"This is going to be the most expensive single project to be undertaken in Singapore. The last thing that we want to do is to squander away our hard-earned reserves and leave behind enormous debt for our children and our grandchildren. Now since we are sure that this is not going to be the case, we'll proceed with the MRT, and the MRT will usher in a new phase in Singapore's development and bring about a better life for all of us."
Therefore, a provisional Mass Rapid Transit Authority was established in July 1980, after the debate. However, Mr Ong faced strong opposition from other members of the cabinet, by Finance Minister Goh Keng Swee and Tony Tan, due especially to the heavy investments involved. A team of specialists from Harvard University, recommended that an all-bus system would be sufficient into the 1990s, and would cost 50% less than a rail-based system.
Later on, two independent American transport and urban planning specialist teams were then appointed by the government to conduct their own independent reviews as part of the Comprehensive Traffic Study in 1981. This debate was also brought to national television in September 1980, which was rare at that time. The study came to a conclusion that an all-bus system would be inadequate as it would have to compete for road space which would have been increasingly overcrowded by then. The problem would be solved by building a rail system. Mr Ong hence declared in triumph on 28 May 1982, that:
"The Government has now taken a firm decision to build the MRT. The MRT is much more than a transport investment, and must be viewed in its wider economic perspective. The boost it'll provide to long term investors' confidence, the multiplier effect and how MRT will lead to the enhancement of the intrinsic value of Singapore's real estate are spin-offs that cannot be ignored."
Construction begins
The permission to begin the construction of Singapore's then-largest public works project was given in May 1982. A ground-breaking ceremony commenced the construction on 22 October 1983 at Shan Road. The majority of the work was expected to be completed in 1992. This included 67 km of track to be constructed, with 42 stations, of which 26 would be elevated, 1 at grade and 15 underground. The network was constructed in stages, with the North South Line given priority as the line passed through the Orchard Road corridor as well as the rest of the Central Area, the latter of which faced a high demand for public transport. Also, it was near the more densely populated housing estates such as Toa Payoh and Ang Mo Kio.[2] The MRT Corporation, now Land Transport Authority, was established on 14 October 1983, taking over the roles and responsibilities of the former provisional Mass Rapid Transit Authority. On 6 August 1987, it set up SMRT Corporation.
Construction began in various areas:
- October 1983: Yio Chu Kang – Outram Park (Phase I)
- January 1984: Outram Park – Clementi (Phase IA)
- July 1984: Clementi – Lakeside (Phase II)
- January 1985: Marina Bay – Tanah Merah (Phase II)
- June 1985: Tanah Merah – Pasir Ris, Jurong East – Choa Chu Kang & Yio Chu Kang – Yishun (Phase II)
- January 1988: Lakeside – Boon Lay (Phase II)
Toa Payoh MRT station was the first to do structural works, followed by the tunnels between Outram Park and Tiong Bahru in 1985. The completion of the viaduct for Phase 1 was done on 15 December 1986 at Commonwealth MRT station. The first C151 train was delivered to MRT Corporation on 8 July 1986, by Yeo Ning Hong at Bishan Depot.
One third of the MRT was completed on 15 January 1985, and the Minister for Communications and Information Yeo Ning Hong visited Orchard MRT and Dhoby Ghaut MRT station sites.[3] The pouring of concrete was completed by the end of 1985 at Dhoby Ghaut MRT station.
Initial opening
On 7 November 1987, the first 6 kilometres of the North South Line from Yio Chu Kang to Toa Payoh went into operation.[4][5][6]
The novelty resulted in thousands flocking to the 5 station segment of the line just to experience and try out the system. At the launching of Toa Payoh, the late Mr Ong was quoted as saying that
this is like a 20-year affair from conception to delivery. Now the baby is born, to say that I am happy and pleased is an understatement.
Nine more stations from Novena to Outram Park were officially opened 12 December 1987 by then Deputy Prime Minister Goh Chok Tong. These trains ran as a through service from one end to the other even though Tanjong Pagar and Outram Park were on the East West line.
On 12 March 1988, six more stations from Tiong Bahru to Clementi on the East West line were opened; trains now ran directly from Yio Chu Kang through the city to Clementi. On the same day, the system was officially launched by the late Mr Lee Kuan Yew, then Prime Minister of Singapore.
Nearing completion
.svg.png.webp)
The rest of the system opened rapidly in stages. On 6 July 1990, with the last station opened, the entire system was opened by President Wee Kim Wee.
| Date | Stations | Note |
|---|---|---|
| 5 November 1988 | Jurong East, Chinese Garden, Lakeside (from Clementi) | |
| 20 December 1988 | Khatib, Yishun (from Yio Chu Kang) | |
| 4 November 1989 | Marina Bay (from Raffles Place) | Through train services between the "North" and "West" of the network ended with the opening of the "East". |
| Bugis, Lavender, Kallang, Aljunied, Paya Lebar, Eunos, Kembangan, Bedok, Tanah Merah (from City Hall) | ||
| 16 December 1989 | Simei, Tampines, Pasir Ris (from Tanah Merah) | |
| 10 March 1990 | Bukit Batok, Bukit Gombak, Choa Chu Kang (from Jurong East) | |
| 6 July 1990 | Boon Lay (from Lakeside) |
Subsequent expansions
Woodlands Extension of the North South Line

Less than a year after the completion of the MRT project, the government announced in February 1991, intentions to extend the system to Woodlands. Construction commenced in 1993, and the 16 km, 6 station elevated line was opened on 10 February 1996 at a total cost of S$ 1.2 billion. With this extension, the North South Line included the three stations on the former Choa Chu Kang Branch Line (Jurong East, Bukit Batok, Bukit Gombak and Choa Chu Kang), forming a continuous line from Jurong East to Marina Bay.[7]
The government came up with the proposal to build the Woodlands MRT line in 1990 when it announced its Woodlands MRT line construction plan, prioritizing the most than Changi Airport Line and the North East line. The proposal called for the extension of the existing north–south and east–west lines to connect Choa Chu Kang in the west to Yishun in the north. Many changes were subsequently made to the original plan. The changes were mainly to accommodate the 1991 Concept Plan by the Urban Redevelopment Authority, which aimed to make Woodlands a regional centre for northern Singapore. One of the changes was the number of MRT stations along the line. Due to the expected increase in the number of commuters in the Woodlands area, the government had to increase the number of MRT stations from four to the eventual six in order to serve a bigger and growing estate. The stations were also designed in a more user-friendly fashion. Most of the changes were incorporated by 1992. Woodlands New Town was only half completed, and Sembawang New Town was still in the planning stage at that time.[7][8]
In the original plan, the Woodlands MRT line had only four stations: Admiralty, Woodlands, Marsiling and Yew Tee. They would service commuters in Choa Chu Kang North, Woodlands West, Woodlands Central and Woodlands East. Two more stations were added to the plan later to include Sembawang and Kadut Industrial Estate. Construction work was supposed to take place in two phases, with four stations opening first and the remaining two (Sembawang and Kadut) later. However, the government and the Mass Rapid Transit Corporation (MRTC; now known as SMRT Corporation) subsequently made the decision to open the Sembawang Station with those in the first phase. It was also decided that Kadut Station would be built at a later stage (depending on the development of housing plans in the area), as there was no immediate need for an MRT station there. Instead, a new station, Kranji, was added to the plan. The entire line was to be built above ground and would measure a total of 16 km. The eventual stations built were Yew Tee, Kranji, Marsiling, Woodlands, Admiralty and Sembawang to serve the estates of Choa Chu Kang North, Kadut Industrial Estate, Woodlands West, Woodlands Central, Woodlands East and Sembawang.[7]
In 1991, the government awarded a contract, worth S$1.5 million, to Soil and Foundation Pte Ltd to conduct soil tests on the stretch of land between Chua Chu Kang and Yishun, through Woodlands, for the MRT line. The government then commissioned MRTC to begin work on the construction of the line in the latter part of 1991. The civil engineering construction contract, worth S$65.3 million, was awarded to a joint venture between Balfour Beatty of the United Kingdom and Gammon of Hong Kong, called the Balfour Beatty-Gammon venture. Meanwhile, the electrical and mechanical services contract, worth S$31.24 million, was awarded to General Electric Company of Singapore.[7]
The contract for providing signalling and automatic train control systems was given to Westinghouse Signal Limited for S$33.32 million. A contract for the communications systems, worth $17 million, was awarded to a joint venture comprising JS Telecom, Thomson Surveillance Video and Halberthal, all French companies, and led by Singapore Electronic & Engineering Limited (SEEL). In total, MRTC pre-qualified 30 firms and joint ventures for six civil engineering contracts and one track-work contract. Construction work began at both ends of the line, on the Choa Chu Kang and Yishun stations, simultaneously.[7]
One of the more difficult tasks during the course of the construction was a rock excavation work costing S$1.5 million along Woodlands Avenue 3, in which explosives were used to make way for the train viaduct. Another difficult project was the levelling of land covered in thick vegetation in Kadut, Woodlands and Sembawang. The laying of a 22-metre long concrete beam weighing 165 tonnes in October 1994 marked the completion of the structural link between the existing MRT network and the Woodlands extension line. The entire Woodlands extension line consists of around 1,163 beams. The tracks were then laid, followed by the installation of the electrical and mechanical systems and equipment. A real-time information system, costing S$400,000, was first introduced on the Woodlands MRT line. It provides passengers with train arrival times and informs them if trains are late or disrupted. The information is displayed on electronic boards installed at the entrance of each station.[7]
In 1995, test runs were carried out on the completed Woodlands MRT line to ensure smooth operations. Open houses were held a week before the official opening for users to familiarise themselves with the new stations. The new Woodlands MRT line was officially opened by then Prime Minister Goh Chok Tong on 10 February 1996. The first train took off at 1 pm during the opening ceremony. An estimated 12,000 people travelled on the Woodlands MRT line during the first hour of its opening.[7]
The construction of the extension was not without political fallout. For a long time, the politicians representing residences in the North-East area of the island had been calling for the construction of a planned North East line. The announcement of the Woodlands Extension led to protests especially from opposition members of parliament, in particular from Chiam See Tong and Low Thia Khiang, representatives of Potong Pasir and Hougang constituencies respectively, with both areas potentially benefiting from such a line. The opposition members accused the government of favouring the Woodlands Extension over the North East line due to opposition representation in the north-east area, arguing that there were far more residents in the north-east compared to the north, and questioned the rationale of building the Woodlands extension when the north was relatively undeveloped.[7]
Dover station

Dover, built on the East West line between Clementi and Buona Vista, was officially opened on 18 October 2001 by then Minister for Transport, Mr Yeo Cheow Tong. The first station to be built over an operating rail line with no disruptions to train services (although trains drove by the site at a reduced speed during the construction phase), it was also the first elevated station with two side platforms on either side of the tracks, as opposed to having an island platform as in all other elevated stations.[9][10]
Adjacent to the Singapore Polytechnic on one side, and undeveloped land on the other, the building of the station was met with reservations by some members of the public over its low catchment area. There were criticisms over the spending of "taxpayers' money" chiefly for use only by students of one educational institution. The government proceeded with the construction anyway, citing the catchment area extends to public housing flats on either end of the polytechnic, and that the undeveloped land opposite is slated for extensive development, largely residential in nature. This station has indeed brought much convenience to the students at the polytechnic.
Changi Airport Extension

For a long time following its opening in 1981, Singapore Changi Airport relied on taxis and buses as the primary means of public transportation to the rest of the country. They served the airport well, but concerns over competition from other regional airports, some of which feature quick rail-based services to their city centres, such as the one from Kuala Lumpur International Airport, accelerated the government's plan to build a rail link to the airport.[11][12]
Provision had long been made for a new line branching off from the existing East West line at the Tanah Merah, with some conceptual plans showing a tentative route alignment to the airport along Airport Boulevard, continuing beyond the airport to Changi Point, before turning southwest back toward the city along the east coast of the island. The plans were finally announced by then Deputy Prime Minister Lee Hsien Loong on 15 November 1996.[13] However, the route alignment showed a deviation from previous plans.[14][15]
The final plan involved building only the first two stations, namely Expo, an elevated station directly adjacent to the Singapore Expo, and Changi Airport, an underground station built between Terminal Two and the since constructed Terminal Three. The alignment of the station at the airport was switched perpendicularly to an east–west direction, such that stairs and escalators lead to two of the terminals directly from either end of the station. Construction began in December 1998.[12]

Expo opened on 10 January 2001, sporting a "space age" architecture designed by world-renowned architect Sir Norman Foster. The roof is clad in titanium and its design enabled the platform to be free of any columns, freeing up space in a station which will be used by thousands of visitors to the massive 100,000 square metre Singapore Expo next door.[12][16]
Changi Airport was opened on 8 February 2002, giving the airport its first rail link after less than 21 years of operations. Initially through services were operated from the airport to Boon Lay at the other end of the East West line, however due to ridership falling below expectations the service was reverted to shuttle mode in 2003.[16]
North East line

The North East line, the first line operated by SBS Transit and among the first fully automated heavy rail lines in the world, opened on 20 June 2003, except for Woodleigh and Buangkok stations. System problems delayed the line six months from the scheduled opening date of December 2002. The construction period of the North East line was fraught with many delays and some budget problems. It marked the pinnacle of a long and chequered history of over two decades since the conception of the line had taken place along with that of the original system which was eventually completed in 1990.[17]
Up to May 2005, the line was running at a deficit. Although line operator, SBS Transit, managed a yearly overall profit as profits from its public bus service exceed the losses from its operation of the North East line. Running from HarbourFront where Singapore's former World Trade Centre building lies to Punggol to the northeast of the island, this line allowed for previously isolated or distanced areas to be linked up with the rest of Singapore by rail. Buangkok opened on 15 January 2006 and Woodleigh opened on 20 June 2011.[18][17]
New lines over the revolution: Circle and Downtown
On 28 May 2009, 5.6 km of the Circle Line opened from Bartley to Marymount. On 17 April 2010, another 11.1 km of the Circle Line from Bartley to Dhoby Ghaut commenced operation. On 8 October 2011, the remaining 16.6 km from Marymount to HarbourFront commenced operation, marking the full completion of the line which took 10 years to complete, primarily delayed due to the Nicoll Highway collapse. On 14 January 2012, the 2.4 km of the Circle Line extension from Promenade to Marina Bay commenced operation.
The Downtown Line is the fifth Mass Rapid Transit line in Singapore and opened in three stages, on 22 December 2013,[19] 27 December 2015 and 21 October 2017 respectively. When fully completed, the line will be about 44 km (27 mi) long with 36 stations and serve about half a million commuters daily,[20] making it the longest underground and driverless MRT line in Singapore. Travelling from one end to the other will take about 65 minutes.
On 15 August 2014, the Downtown Line 3 Extension was announced, in conjunction with the announcement of the Thomson-East Coast MRT Line.[21] Two additional stations, Xilin MRT station and Sungei Bedok MRT station will be added to the Downtown Line, with Sungei Bedok as an interchange station with the Thomson-East Coast Line. It will add an additional 2.2 km to the line with the extension.[21] Due in 2024, Stage 3 will join the current East West and future Thomson-East Coast lines that runs through Marine Parade.[22]
Thomson–East Coast line
On 31 January 2020, 2.8 km of the Thomson–East Coast Line opened from Woodlands North to Woodlands South.[23]
Existing line extensions
On 28 February 2009, the 3.8 kilometre Boon Lay Extension to the East West line comprising 2 stations Pioneer and Joo Koon commenced passenger service. Construction had begun in December 2004 after the development of Pioneer New Town had been completed. Similarly, construction began for the Marina South Pier in December 2009 and completed in September 2014, it began operations on 23 November 2014.
The 7.5 kilometre Tuas West Extension (TWE) – Gul Circle, Tuas Crescent, Tuas West Road and Tuas Link – opened for passenger service on 18 June 2017.[24][25]
2020 COVID-19 pandemic
All train services are affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, due to the drop of ridership, coupled with full home-based learning for students and closure of workplaces and several services. These include frequency reduction, early closure and staggered closures.[26][27]
History of the system map
1987 to 1996
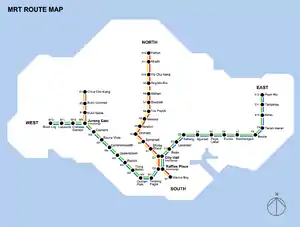
The MRT was a very recent addition for Singapore and as such, the authorities wanted to keep the MRT map as easy to use for Singaporeans as possible. Hence, each direction of travel was colour-coded in a different colour as though it were a line on its own. In that way, confusion in decision-making when taking a certain line in a certain direction would be reduced for passengers. However, this reduced the number of colours available for new lines and was not in line with international practice.
Previously, each direction of travel on the MRT was denoted on system maps as a different colour.
- Northbound services were denoted in yellow
- Southbound services in red
- Eastbound services in green
- Westbound services in blue
- Northbound Choa Chu Kang Branch Line services in beige
- Southbound Choa Chu Kang Branch Line services in brown
Each station was also assigned a unique alphanumeric code, with the alphabet indicating which part of the island the station lies at (North, East, West, Central, Marina Bay region or Choa Chu Kang Branch Line) and the numbers (in ascending order from the centre of the island) indicating which part of that region the station is located at.
| Code | Overview | Examples | Currently |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Bukit Panjang LRT | A1 – A14 | BP1 – BP14 |
| B | Branch Line from Bukit Batok to Choa Chu Kang, superseded in 1996 by the North South Line's extension through Woodlands to Choa Chu Kang | B1 – B3 | NS2 – NS4 |
| C | The two stations at the city's center, City Hall and Raffles Place, including Chinatown, Clarke Quay, Bras Basah, Esplanade and Promenade | C1 – C7 | EW13/NS25, EW14/NS26, NE4, NE5, CC2 - CC4 |
| E | East West line (Eastern stretch) from Bugis to Pasir Ris, Expo and Changi Airport | E1 – E14 | EW1 – EW12, CG1 – CG2 |
| H | HarbourFront MRT station (original) | H1 | NE1/CC29 |
| M | Marina Bay and Marina South Pier | M1 – M2 | NS27 – NS28 |
| N | North South Line from Dhoby Ghaut to Bukit Batok | N1 – N23 | NS24/NE6/CC1 – NS2 |
| P | North East line from Little India to Punggol | P1 – P11 | NE7 – NE17 |
| T | Original Tampines Line | T1 – T15 | N/A |
| W | Western stretch of East West line from Tanjong Pagar to Tuas Link excluding Dover | W1 – W18 | EW15 – EW33 |
| X | Circle Line (from Nicoll Highway to Bayfront) | X1 - X24 | CC5 - CE1 |
These were superseded in 2001 by two-digit codes as the latter might be exhausted with new MRT and LRT lines added to the network, thus only having 15 letters in total. However, "E", "N" and "W" were still found on viaduct pillars of the MRT and some traffic signals on the Westinghouse FS2000 signalling system (before upgrading to Thales SelTrac CBTC GoA 3 signalling system), but the "A" is still being used for the Changi Airport branch line. The codes for viaduct pillars are:
| Viaduct Pillars | ||
| Code | Overview | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| A | Changi Airport Line from Tanah Merah to Expo tunnel portal | A0001 – A0052 |
| B | Branch Line from Jurong East to Choa Chu Kang (1990–1996) | B001 – B226 |
| E | East West line from Kallang tunnel portal to Pasir Ris | E001 – E602 |
| N | North South Line from Bishan to Jurong East | N001 – N346 (1990–1996) N001 – N1154 (1996–present) |
| W | East West line from Redhill tunnel portal to Tuas Link | W001 – W609 (1990–2009) W001 – W732 (2009–2017) W001 – W908 (2017–present) |
| Railway signals | ||
| Code | Summary | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| B | Bishan Depot | N/A |
| C | Changi Depot | N/A |
| E | East West line from Raffles Place to Pasir Ris | E1 – E73 |
| N | North South Line from Raffles Place to Admiralty | N3 – N116 |
| NW | North South Line from Jurong East to Admiralty including the Branch Line | NW1 – NW55 |
| Jurong East Modification Project | NW83 – NW85 | |
| S | North South Line from Raffles Place to Marina South Pier | S7 – S30 |
| SE | Changi Airport Line | SE02 – SE18 |
| U | Ulu Pandan Depot | N/A |
| W | East West line from Raffles Place to Joo Koon | W5 – W75 |
| Jurong East Modification Project | W80 – W82 | |
1996 to 30 July 2001
The colour and alphanumeric codes for each direction of travel remained unchanged, except that with the opening of the Woodlands Extension (connecting Yishun station to Choa Chu Kang station), the Jurong East – Choa Chu Kang Branch Line ceased to exist. As such, the formerly Northbound Choa Chu Kang Branch Line services in khaki travelled southbound to Marina Bay & as such were denoted as red while the formerly Southbound Choa Chu Kang Branch Line services in brown originated from Marina Bay, hence having travelled northbound it was denoted as yellow. The alphanumeric codes for these stations were also replaced. After Sembawang it is N14-N18, N20-N23, with the exception of N13 and N19, reserved for future stations Canberra and Sungei Kadut. The B1-B3 was renumbered to N21-N23.
The Bukit Panjang LRT opened in 1999 and was given the colours purple and orange to represent its direction of travel. Due to the alignment of the route, which was a loop track around Bukit Panjang New Town, the map was different. The stations were given the alphanumeric code A1 to A14, with numbering starting from Choa Chu Kang interchange and going anti-clockwise direction on the loop. The directional arrow on the shared service track (between stations A1 to A6) was split, half purple coloured and half orange coloured. From Bukit Panjang station, the orange arrows travelled in an anti-clockwise direction [(service B) via Petir] while the purple arrows travelled in a clockwise direction (service A) towards Senja. These were standardised into grey colour since 2001 because of additional LRT lines such as Sengkang and Punggol LRT.
31 July 2001 to 30 January 2020
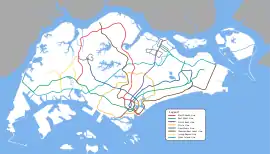
As there were plans to expand the network, the MRT System Map could no longer afford to have each direction of travel represented by a different colour. The map was revamped to have one colour as there would be more MRT lines in the future, which was announced by the Minister of Communications and Information Technology, Mr Yeo Cheow Tong. The pilot trials for new signages were done at Dover and at the North East line.
Colours were used to represent each line rather than each direction of travel, cutting the usage of colours by half and preserving other colours for future lines.
- Red for North South Line
- Green for East West line
- Purple for North East line
- Orange for Circle Line
- Blue for Downtown Line
- Brown for Thomson-East Coast Line
- Grey for all LRT Lines
- Turquoise for Jurong Region Line
- Lime for Cross Island Line
The direction of travel was instead represented by numbers contained within a coloured circle located at the ends of each line, known as the destination number.
Like before, each station was assigned a unique alphanumeric symbol. However under this revamped system map, the letter in each symbol denotes the line instead and the number increases in ascending order from East to West (East West line), North to South (North South Line), South West to North East (North East line), in an anti-clockwise direction (Circle Line), in a clockwise direction from the North-west to the South-east (Downtown Line), and from the Thomson stretch in the North to the East Coast stretch in the East (Thomson-East Coast). Interchange stations will then have at least two or three codes.
Special codes were also used to denote the town centre. "STC" is Sengkang Town Centre and "PTC" is Punggol Town Centre.
| Station Code | Service | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| BP | Bukit Panjang LRT | BP1-BP13 |
| CC | Circle Line | CC1-CC32 |
| CE | Circle Line Extension | CE1-CE2 |
| CG | Changi Airport Line | CG1-CG2 |
| DT | Downtown Line | DT1-DT37 |
| EW | East West Line | EW1-EW33 |
| NE | North East Line | NE1-NE18 |
| NS | North South Line | NS1-NS28 |
| PE | Punggol LRT East Loop | PE1-PE7 |
| PW | Punggol LRT West Loop | PW1-PW7 |
| SE | Sengkang LRT East Loop | SE1-SE5 |
| SW | Sengkang LRT West Loop | SW1-SW8 |
| TE | Thomson-East Coast Line | TE1-TE31 |
| JS | Jurong Region Line (South) | JS1-JS12 |
| JE | Jurong Region Line (East) | JE1-JE7 |
| JW | Jurong Region Line (West) | JW1-JW5 |
| CP | Cross Island Line (Punggol) | CP1-CP4 |
| CR | Cross Island Line | CR2-CR13 |
For example:
- Expo CG1 for the East West line section and DT35 for the Downtown Line section.
- Dhoby Ghaut NS24 for the North South Line section, NE6 for the North East line section and CC1 for the Circle Line section.
- Woodlands NS9 for the North South Line section and TE2 for the Thomson-East Coast Line section.
31 January 2020 to present
During a visit to the upcoming Thomson–East Coast MRT line stations in Woodlands, a redesigned MRT map was launched on 11 December 2019 by the Land Transport Authority to make it easier for commuters to plan their journeys. The new map will feature the Circle MRT line as a focal point on the map, as well as prominent landmarks and waterbodies added to the surrounding areas. In addition, QR codes are included with links to a fare calculator and maps in all four languages. The new map has since been made available to all MRT and LRT stations on 31 January 2020.[28]
History of station and train announcements
SMRT Trains Ltd
The public announcement system in all SMRT operated lines was introduced in 1994, beginning with the announcement of station names when a train arrives at the station. The door closing announcement was later added in 1997 and the next station announcement in 1999. Over time, however, some sections of the announcements were modified, and finally, the entire announcement system was changed in January 2008 in preparation for the installation of STARIS on all trains later that year. The new announcement system features a new voice, and a new chime before each announcement.
The original announcements were made by the late Juanita Melson and contained information on how to purchase single journey tickets as well as how to obtain the deposit back, for the benefit of the tourists. This was eventually removed when the announcement system was upgraded with the current announcer, Chan Hui Yuh. Only the late Juanita Melson announcements are now being operated on the Bukit Panjang LRT when used on the BPLRT trains.
All announcements on the NSEWL were changed again in October 2012 but was met by strong criticism by the public after Chinese announcements were included. This was eventually removed on all trains by December 2012.
SBS Transit Ltd
The North East line and the Downtown line, which are both operated by SBS Transit Ltd, features different announcements from SMRT operated lines. It features different chimes and a different announcer, as well as next station messages in Chinese, and in some cases, Malay and Tamil.
History of the ticketing system
1987 to 2002
When the MRT opened in 1987, fares ranged from S$0.50 to S$1.10 in S$0.10 increments for all adult tickets, regardless of whether they were single-trip or stored-value tickets.[29] Several discounted fares were available: senior citizens and permanent residents above the age of 60 could travel on a flat fare of S$0.50 during off-peak hours; children below the height of 1.2 metres and full-time students in primary, secondary, pre-university and vocational training (VITB) institutions paid a flat fare of S$0.30 at all times.[30]
Magnetic strip plastic tickets were used, in various forms. Stored-value tickets were called farecards and came in three types: the blue farecard was issued to adults, the magenta farecard to senior citizens, and the red farecard to children.[30] Single-trip forms of these tickets were retained at the faregates on exiting the paid area of a destination station.[31] Monthly discounted tickets were available in four values: beige, pink, and purple tickets for primary and tertiary students, and full-time national servicemen came with a value of S$13, S$30 and S$36, respectively;[32] the peach ticket was for secondary, pre-university and VITB students, costing S$17 each. These discounted tickets were valid for a month from the date of purchase, allowed up to four trips a day, and were non-transferable.[32]
Their farecards cannot be used from 1 December 2002 and support has been terminated since June 2003 with the removal of metal holes and convert validators to printing tickets (by cash). It is currently no longer workable.
2002 to 2009
The EZ-Link card is a contactless smart card, initially based on Sony's FeliCa smartcard technology.[33] The cards are mainly used for the payment of transportation fares, but may also be used for payment at selected retail outlets. Established in 2002, the technology was promoted as the means for speedier and more convenient transactions[34] and as well as being an efficient method of reducing fare evasion, although there have been some cases of overcharging users.[35] As a benchmark, fares range from S$0.70 to S$3.20 for adults, S$0.70 to S$1.35 for senior citizens, and S$0.40 to S$0.50 for student EZ-Link cards. Patrons using an EZ-Link card receive a discount for their journey, including a discount if they use a connecting bus after their MRT ride.[36]
The General Ticketing Machines (GTMs) at each station which replaced the older ticketing machines, allow commuters to purchase additional credit to add to their EZ-Link cards or to purchase tickets for single trips. Fares for these single trip tickets are higher than those for EZ-Link cards. In addition, a S$1.00 refundable ticket deposit is charged for each Standard Ticket. This refund can be collected from any General Ticketing Machine so as long as the card is returned to the machine within 30 days of purchase.[37] The card can also be deposited into a charity collection box, with the S$1 deposit going to charity. The rationale behind such a refundable deposit feature was that the smartcard technology contained within each Standard Ticket makes each one costly enough to necessitate the recycling of Standard Tickets. Since November 2007, external readers were installed on GTMs at stations operated by SMRT Corporation to address problems of card jamming in insert slots. The slots, however, remain in use for the purpose of refunding Standard Ticket deposits.[38]
Concession fares are available for children, students, senior citizens and national servicemen. Students are given free personalised cards, complete with their photos, names and national identification numbers. Regardless of its type, each card is assigned a unique card ID that can be used to recover the card if lost. Transport operators have organised lotteries that are based on these card IDs. The Singapore Tourist Pass offers unlimited travel for tourists on Singapore's public transport system. For S$8 a day, tourists can take any number of rides on buses and trains operated by SBS Transit, SMRT Buses and SMRT Trains.[39]
The old EZ-Link card can be used up to September 2009 where the old EZ-Link card usage became limited support. It remains on some MRT stations.
2009 to date
- Main articles: CEPAS
On 26 August 2008, Land Transport Authority announced a two-month trial of the new generation Contactless ePurse Application (CEPAS) card that was developed in-house.[40] It is intended to standardise the technology of cashless payment, allowing for use on public transport, Electronic Road Pricing (ERP), everyday shopping and meals. The card has replaced this generation of EZ-Link cards in 2009 and aims to encourage competition by allowing up to four CEPAS card issuers.[41] Mass replacement of the old Sony FeliCa cards to the new CEPAS cards went on at TransitLink Ticket offices and Singapore Post outlets till 7 October 2009. On 29 February 2009, two new stations were added at the end of the line, the stations were Pioneer and Joo Koon. Joo Koon became the main terminal for the East West Line instead of Boon Lay MRT Station.
History of Passenger Information Systems
The plasma displays which is easier for elderly and wheelchair passengers. The displays announced a train's terminating station when it arrives (or otherwise, a "Do Not Board" warning), although the disadvantage was that it could not tell the duration of a train's arrival time (e.g. the train will arrive at Jurong East Station in 2 mins). The second generation of such displays installed at stations along the Woodlands Extension featured a slightly updated version where the time till the next train arrival would be displayed from 3 minutes prior to the train's arrival.
List of Incidents
Clementi rail accident
Nicoll Highway collapse
The Nicoll Highway collapse was a construction accident that occurred at approximately 3.30 pm on 20 April 2004 in Singapore when a tunnel being constructed for use by Mass Rapid Transit trains collapsed. The tunnel was part of the construction of the underground Circle line, near the Nicoll Highway. The supporting structure for the deep excavation work failed, resulting in a 30-metre (100 ft) deep cave-in that spread across six lanes of Nicoll Highway. The collapse killed four people and injured three. The accident has delayed the construction end date for the MRT station.
2016 staff fatalities
2017 Joo Koon rail accident
References
- Tien Fang Fwa (4 September 2004). "SUSTAINABLE URBAN TRANSPORTATION PLANNING AND DEVELOPMENT — Issues and Challenges for Singapore" (PDF). University of Tokyo. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 May 2006. Retrieved 1 May 2006. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Annual report / Provisional Mass Rapid Transit Authority, Republic of Singapore. Singapore: Provisional Mass Rapid Transit Authority. 1983. p. 5.
- One third of the MRT was completed
- "NORTH-SOUTH LINE". lta.gov.sg. Retrieved 1 January 2018.
- "Toa Payoh MRT station first to be topped out". Business Times. 6 August 1985. Retrieved 15 June 2017 – via NewspaperSG.
- "All aboard for the Subway Age". The Straits Times. 8 November 1987.
- Singapore, National Library Board. "Woodlands MRT line | Infopedia". eresources.nlb.gov.sg. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- "S'pore Poly to be linked to MRT". The Straits Times. 30 July 1997. p. 3.
- "Doorstep train". TODAY news. 5 October 2001. p. 8.
- "MRT Line will not go beyond passenger terminals". The Straits Times. 12 December 1996.
- "Chang! Airport MRT line details". The Business Times. 12 December 1996. Retrieved 12 December 2017.
- "Singapore Mass Rapid Transit Employees' Union (SMRTEU)'s annual Dinner and Dance" (PDF). NAS. 15 November 1996. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- "MRT Line will not go beyond passenger terminals". The Straits Times. 12 December 1996. Retrieved 17 October 2019.
- "Changi Airport MRT line details". The Business Times. 12 December 1996.
- "Boon Lay to Expo: MRT now running". The Straits Times. 20 December 2001.
- "North East Line". Land Transport Authority. Retrieved 22 June 2017.
- "Train finally arrives at Woodleigh MRT station". Channel NewsAsia. 20 June 2011.
- "Land Transport Masterplan: Downtown Line Stage 1 to open on 22 Dec". The Straits Times. 7 October 2013. Retrieved 16 November 2013.
- "12 MRT stations for Bukit Timah by 2015" Archived 8 June 2010 at the Wayback Machine, Luxuryasiahome, 16 July 2008
- "Thomson-East Coast Line, connecting North and East, ready by 2024" Archived 16 August 2014 at the Wayback Machine, Saifulbahri Ismail, Channel NewsAsia, 15 August 2014
- "Downtown Line 3 Extension". Land Transport Authority. 15 August 2014. Archived from the original on 15 October 2014.
- Liu, Vanessa (11 December 2019). "First three stations of Thomson-East Coast Line to begin service on Jan 31; free travel for commuters for three days". The Straits Times. Retrieved 11 December 2019.
- "Tuas West Extension Opens on 18 June 2017". Land Transport Authority. 27 April 2017.
- "Tuas West Extension MRT stations to open Jun 18". Channel NewsAsia. 27 April 2017.
- "Last train services for MRT and LRT (Annex B)" (PDF). LTA. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 April 2020. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
- "LTA | News Room | news-releases | Changes to Public Bus and Train Operating Hours and Frequency". lta.gov.sg. Archived from the original on 17 April 2020. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
- "New MRT network map to be rolled out at all stations by Jan 31". Today. 11 December 2019. Retrieved 11 December 2019.
- Mass Rapid Transit Corporation, Singapore 1988, pg. 8–9
- Singapore MRT Limited 1987, pg. 20–22
- R C Longden & E W Finch (April 1987). "Automatic Fare Collection – Serving the Commuter". MRTC & IES 1987, pg. 319–324.
- Singapore MRT Limited 1987, pg. 23
- "FeliCa in Use". Sony. Archived from the original on 11 November 2007. Retrieved 26 November 2007.
- Sharp 2005, pg. 113–115
- Ansley Ng (20 May 2005). "Buses and the not so ez-link". Today.
- Christopher Tan (13 September 2008). "Bus and MRT fares to go up from Oct 1; But 4 in 10 commuters to pay the same or less; transfers to cost less". The Straits Times.
- "What is a Standard Ticket?". TransitLink. Archived from the original on 24 November 2007. Retrieved 1 December 2007.
- "No more jammed cards". The Straits Times. 8 November 2007.
- Maria Almenoar (13 December 2007). "New unlimited travel pass for visitors; A one-day pass for buses and trains will cost $18 with $10 refundable; also available: two-day and three-day versions". The Straits Times.
- Christoper Tan (26 August 2008). "On trial: New ez-link card". The Straits Times.
- Imelda Saad (26 August 2008). "New e-payment system and next generation card for public transport". Channel NewsAsia.













