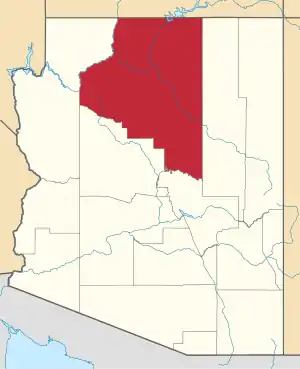
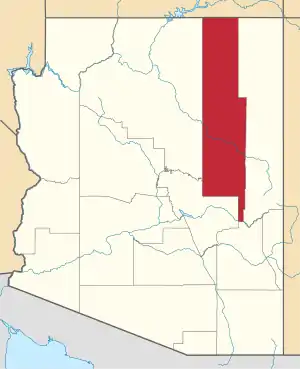
Hopi Reservation
The Hopi Reservation is a Native American reservation for the Hopi and Arizona Tewa people, surrounded entirely by the Navajo Nation, in Navajo and Coconino counties of Arizona, United States. The site in north-eastern Arizona has a land area of 2,531.773 sq mi (6,557.262 km²) and as of the 2000 census had a population of 6,946. The Hopi Reservation, like most of Arizona but unlike the surrounding Navajo Nation, does not observe daylight saving time. Until recently, the two nations shared the Navajo–Hopi Joint Use Area. The partition of this area, commonly known as Big Mountain, by Acts of Congress in 1974 and 1996, has resulted in continuing controversy.[2][3] The system of villages unites three mesas in the pueblo style traditionally used by the Hopi. Walpi is the oldest village on First Mesa, having been established in 1690 after the villages at the foot of mesa Koechaptevela were abandoned for fear of Spanish reprisal after the 1680 Pueblo Revolt. The Tewa people live on First Mesa. Hopi also occupy the Second Mesa and Third Mesa. The community of Winslow West is off-reservation trust land of the Hopi tribe. The Hopi Tribal Council is the local governing body consisting of elected officials from the various reservation villages. Its powers were given to it under the Hopi Tribal Constitution. The Hopi consider their life on the reservation (in particular the traditional clan residence, the spiritual life of the kivas on the mesa, and their dependence on corn) an integral and critically sustaining part of the "fourth world". Hopi High School is the secondary education institute for reservation residents. Hopi Radio, a station with a mix of traditional Hopi and typical American programming is run for the reservation and provides internships for Hopi High School.
Hopi Reservation | |
|---|---|
 Hopi Nation landscape | |
 Flag | |
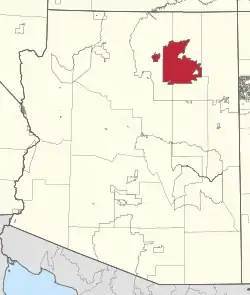 Location in Arizona | |
| Tribe | Hopi |
| Country | United States |
| State | Arizona |
| Counties | Coconino Navajo |
| Established | December 16, 1882 |
| Constitution | December 19, 1936 |
| Capital | Kykotsmovi (de facto) |
| Subdivisions | |
| Government | |
| • Body | Hopi Tribal Council |
| • Chairman | Herman G. Honanie |
| • Vice Chairman | Alfred Lomahquahu Jr. |
| Area | |
| • Total | 6,557.262 km2 (2,531.773 sq mi) |
| Population (2017)[1] | |
| • Total | 9,268 |
| • Density | 1.4/km2 (3.7/sq mi) |
| Time zone | Mountain: UTC −7 (no DST) |
| Website | hopi-nsn.gov |

Communities

- Keams Canyon
- Lower and Upper Moenkopi
- Polacca
- Winslow West
- Yuuwelo Paaki (Spider Mound)
- New Oraibi (Kiqotsmovi, Kykotsmovi)
First Mesa
- Waalpi (Walpi)
- Hanoki (Hano or Tewa)
- Sitsomovi (Sichomovi)
Second Mesa
- Songoopavi (Shongopavi)
- Musangnuvi (Mishongnovi)
- Sipawlavi (Shipaulovi)
Aerial views
Aerial views looking north along the central three of the reservation's five major washes,[4] from west to east:
 Dinnebito Wash, with Third Mesa in the distance
Dinnebito Wash, with Third Mesa in the distance Oraibi Wash and Indian Route 2
Oraibi Wash and Indian Route 2 Polacca Wash, crossed by Arizona Route 87, with First Mesa and Second Mesa visible in the distance
Polacca Wash, crossed by Arizona Route 87, with First Mesa and Second Mesa visible in the distance
See also
- Hopi flag
References
- 2013-2017 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates. "My Tribal Area". United States Census Bureau.
- "Short History of Big Mountain–Black Mesa". Archived from the original on 11 August 2014. Retrieved 5 Aug 2013.
- "Navajo–Hopi Long Land Dispute". Retrieved 5 Aug 2013.
- Lionel Puhuyesva, James A. Duffield, and Max Taylor. "Wetland Program Development via the Clean Water Act, Hopi Reservation, Arizona" (PDF). Coconino Plateau Water Advisory Council. Retrieved 27 June 2019.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)