Legislative Assembly of Samoa
The Legislative Assembly is the Parliament of Samoa based in the capital, Apia, where the country's central administration is situated.
Legislative Assembly of Samoa Fono Aoao Faitulafono o Samoa | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Leadership | |
Toleafoa Faafisi since 16 March 2016 | |
| Structure | |
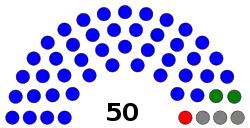
| Seats | 50 |
 | |
Political groups |
|
Length of term | 5 years |
| Elections | |
| First-past-the-post | |
Last election | 4 March 2016 |
Next election | 2021 |
| Meeting place | |
| Maota, Tiafau, Apia[1] | |
| Website | |
| www | |
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Samoa |
| Constitution |
In the Samoan language, the Legislative Assembly of Samoa is sometimes referred to as the Samoan Fono while the government of the country is referred to as the Malo.
The word fono is a Samoan and Polynesian term for councils or meetings great and small and applies to national assemblies and legislatures, as well as local village councils.
The modern government of Samoa exists on a national level alongside the country's fa'amatai indigenous chiefly system of governance and social organisation.[2]
History

The Samoan Fono is descended from the Western Samoa Legislative Assembly established under New Zealand rule in the early 1900s. On the country's political independence in 1962, the 5th Legislative Assembly became the 1st Samoan Parliament.[3]
Members of Parliament
The Samoan Fono has 49 Members of Parliament. 47 members are matai (traditional heads of families), elected in six two-seat and 35 single-seat constituencies. The other 2 Members are elected by, and represent, individual voters, i.e. "Samoan citizens descended from non-Samoans".[4] An extra Member of Parliament was added after the 2016 election in order to meet the quota of 10% female MPs.[5]
Members of Parliament in Samoa are directly elected by universal suffrage, and serve a five-year term.
Head of State
The Head of State or O le Ao o le Malo is elected for a five-year term by the Fono.
Elections
Elections are held under a simple plurality system. Samoan electors are divided into six two-seat and 35 single-seat constituencies. In addition, two seats are reserved for "individual voters", non-indigenous citizens who may not hold a chiefly title or any customary interest in Samoan land.
Electors must be Samoan citizens and aged over 21.[6] Candidates must be qualified as electors, and in addition those for territorial seats must hold a matai title.[7]
Last election results
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human Rights Protection Party | 45,816 | 57.30 | 35 | +6 | |
| Tautua Samoa Party | 6,432 | 8.04 | 2 | –11 | |
| Independents | 27,704 | 34.65 | 13 | +6 | |
| Invalid/blank votes | – | – | – | ||
| Total | 79,952 | 100 | 50 | +1 | |
| Registered voters/turnout | – | – | |||
| Source: OEC | |||||
Other functions
The Fono is responsible for electing the O le Ao o le Malo, the Samoan head of state.
Terms of the Fono
The Fono is currently in its 16th term.
| Term | Elected in | Government |
|---|---|---|
| 1st Legislative Assembly | 1948 election | No parties |
| 2nd Legislative Assembly | 1951 election | No parties |
| 3rd Legislative Assembly | 1954 election | No parties |
| 4th Legislative Assembly | 1957 election | No parties |
| 5th Legislative Assembly / 1st Parliament | 1961 election | No parties |
| 2nd Parliament | 1964 election | No parties |
| 3rd Parliament | 1967 election | No parties |
| 4th Parliament | 1970 election | No parties |
| 5th Parliament | 1973 election | No parties |
| 6th Parliament | 1976 election | No parties |
| 7th Parliament | 1979 election | No parties |
| 8th Parliament | 1982 election | Human Rights Protection Party |
| 9th Parliament | 1985 election | Human Rights Protection Party / Christian Democratic Party (Samoa) |
| 10th Parliament | 1988 election | Human Rights Protection Party |
| 11th Parliament | 1991 election | Human Rights Protection Party |
| 12th Parliament | 1996 election | Human Rights Protection Party |
| 13th Parliament | 2001 election | Human Rights Protection Party |
| 14th Parliament | 2006 election | Human Rights Protection Party |
| 15th Parliament | 2011 election | Human Rights Protection Party |
| 16th Parliament | 2016 election | Human Rights Protection Party |
Building
The Fono is housed in a bee-hive shaped building based on the traditional Samoan fale.
See also
References
- http://www.palemene.ws/new/wp-content/uploads//Infosheet/Infosheet-01-Legislative-Assembly-of-Samoa.pdf
- Fana'afi Le Tagaloa, Aiono (1986). Western Samoa the Sacred Covenant. Land rights of Pacific women. University of the South Pacific;Institute of Pacific Studies. p. 103. ISBN 982-02-0012-1. Retrieved 2 March 2010.
- Parliament of Samoa: general information Archived June 24, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- "Samoa PM accused of racism over anti-Chinese remark". RNZ. 21 January 2005. Retrieved 22 September 2020.
- "Fa'aulusau Rosa Duffy-Stowers secures 5th Parliamentary seat for women". Talamua Online. 11 March 2016. Archived from the original on 22 March 2016. Retrieved 16 March 2016.
- Electoral Act 1963, s16 Archived March 6, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- Electoral Act 1963, s5 Archived October 2, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
