National Assembly (Botswana)
The National Assembly is the legislative body within Botswana's unicameral Parliament. It is advised by the Ntlo ya Dikgosi which is not a house of Parliament.[2]
National Assembly Palamente ya Botswana | |
|---|---|
| 12th Parliament | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
Term limits | None |
| History | |
| Founded | 1966 |
New session started | 5 November 2019 |
| Leadership | |
Deputy Speaker | Mabuse Pule, BDP |
Leader of the House | |
Attorney General | Abraham Keetshabe |
Leader of the Opposition | |
Government Whip | Liakat Kablay, BDP |
Opposition whip | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 65 |
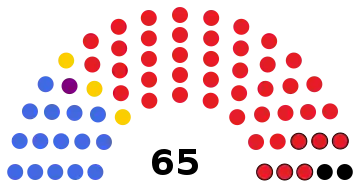 | |
Political groups | Government (47)
Official opposition (14) Other (4) |
Length of term | 5 years |
| Elections | |
| First-past-the-post | |
Last election | 23 October 2019 |
Next election | 2024 |
| Motto | |
| Pula | |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| National Assembly Chamber Gaborone | |
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Botswana |
| Constitution |
The current National Assembly, formed following elections held on 23 October 2019, has a total of 65 members. 57 members are directly elected in single member constituencies using the simple-majority (or first-past-the-post) system for a term of five years. Six members are co-opted (by secret ballot of the rest of the Assembly) while the remaining two (the President and Attorney-general) are ex officio.
Current composition
| Party | Seats | |
|---|---|---|
| Botswana Democratic Party | 39 | |
| Specially elected MPs | 6 | |
| President of Botswana | 1 | |
| Attorney General | 1 | |
| Umbrella for Democratic Change | 14 | |
| Botswana Patriotic Front | 3 | |
| Alliance for Progressives | 1 | |
| Total | ||
Previous National Assembly election results
| Political party | Election year | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1965 | 1969 | 1974 | 1979 | 1984 | 1989 | 1994 | 1999 | 2004 | 2009 | 2014 | 2019 | |
| Botswana Democratic Party (BDP) | 28 | 24 | 27 | 29 | 29 | 31 | 27 | 33 | 44 | 45 | 37 | 38 |
| Botswana Movement for Democracy (BMD) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 17 | – |
| Botswana National Front (BNF) | – | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 13 | 6 | 12 | 6 | 15 | |
| Botswana People's Party (BPP) | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | ||
| Botswana Congress Party (BCP) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | 1 | 4 | 3 | |
| Botswana Independence Party (BIP) | – | 1 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Botswana Alliance Movement (BAM) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – |
| Botswana Patriotic Front (BPF) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 3 |
| Alliance for Progressives (AP) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 |
| Independents | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – |
| Total | 31 | 31 | 32 | 32 | 34 | 34 | 40 | 40 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 |
Note: In the pre-independence 1965 election, the Botswana Democratic Party was known as the Bechuanaland Democratic party and the Botswana People's Party was known as the Bechuanaland People's Party. The chart also does not include ex-officio and co-opted members.
Despite being a one party dominant state since independence, all elections held in the country have been considered democratic, free, and fair.
See also
Notes
- Pono Moatlhodi who served as the opposition whip had resigned from the UDC on 18 December 2020.
References
- https://www.mmegi.bw/index.php?aid=83361&dir=2019/november/04
- Norton, Philip (2006-08-07). "How many bicameral legislatures are there?". The Journal of Legislative Studies. doi:10.1080/1357233042000322436.