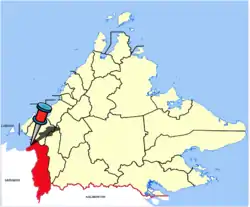
Sipitang District
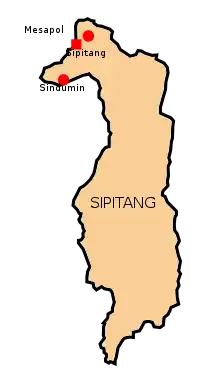
The Sipitang District (Malay: Daerah Sipitang) is an administrative district in the Malaysian state of Sabah, part of the Interior Division which also includes the districts of Beaufort, Keningau, Kuala Penyu, Nabawan, Tambunan and Tenom. The capital of the district is in Sipitang Town. The ecotourism village of Long Mio and Long Pasia is located in this district, while the small town of Sindumin serves as a gateway to the state of Sarawak.
Sipitang District
Daerah Sipitang | |
|---|---|
 Sipitang District office. | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 5°5′N 115°33′E | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Division | Interior |
| Capital | Sipitang |
| Government | |
| • District Officer | Abdul Wahap Abd. Hamid |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,732.5 km2 (1,055.0 sq mi) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 34,862 |
| Website | ww2 |
History
Before 1884, Sipitang are a former territory of the Sultanate of Brunei. On 5 November 1884, the sultan of Brunei ceded the territory from Sipitang to Kuala Penyu to the North Borneo Chartered Company (NBCC).[1] On 7 December 1901, the company expand the area around the territory from Sipitang River to Trusan River.[2] In addition, on 12 September 1901, the NBCC acquired the Mengalong and Merantaman area, which today is also within the district of Sipitang through a grant from Pengiran Tengah Damit ibni al-Marhum Pengiran Anak Bongsu, who is the hereditary ruler of the territory.[3][4] Until the year 1900, the Sipitang River marked the border between North Borneo and the Sultanate of Brunei. The land acquisition between the river and Trusan River in 1901 resulted in the establishment of an administrative office in Sipitang called the Province Clarke (named after Andrew Clarke). The main purpose of this administrative post was primarily due to the planned acquisition of additional territories. However, several problems led to the return of some lands, so that the demarcation line to Sarawak was finally placed on the still valid border line at Mengalong (now Sindumin). When the Brunei Revolt broke out in Brunei on 8 December 1962, the rebellion spread rapidly across the border into Limbang, Lawas and Miri in Sarawak and Weston until Sipitang in northern Borneo, especially when these places were traditionally linked to the Sultanate of Brunei. With the intervention of the North Borneo Governor William Goode, many rebels in Sipitang and Weston been isolated and disarmed within several days. Another 73 rebels were arrested with a smaller amount of weapons been confiscated.[5]
Geography
Sipitang district is located at the southwest portion of the state of Sabah. It is located between latitude 5°5' North and between longitude 115°33’ East. It spans an area of approximately 273,249.69 hectare.[6]
Sipitang district is located within a national and international route. Southern Sabah Federal Route 1 of the Pan Borneo Highway passes through this district, hence it can be reached from Beaufort from the north, Tenom from the east and Lawas, Sarawak from southwest. At the same time, the coastline stretches 16 kilometre off Brunei Bay and is an entry point for travellers from Brunei and Labuan. The district has a long coastline and has 4 main rivers flowing through it, that is the Lukutan river, Sipitang river, Mengalong river and Padas river. The Crocker Range can also be seen from this district as it crosses the district from south to southwest. The presence of small hills and flat lands near the coastal area is one of the main reasons for the frequent floods in Sipitang during the monsoon season. This topography has also influenced the temperature and rainfall distribution of the district. At lower lands less than 1,524 metres, the temperature is around 28 °C – 34 °C, while the rainfall distribution in the lowlands is much lower than the highlands.
Demographics
According to the last census in 2010, the population of the district of Sipitang is 34,862 inhabitants. As the census only categorizes 6 major ethnics while others are lumped under Other Bumiputras and Others, majority of the inhabitants are of other Bumiputras not listed in the main categories.[7]
|
Ethnicity of Sipitang |
Population of Sipitang |
|---|---|
| Other Bumiputeras | 13,419 |
| Malay | 5,534 |
| Murut | 4,709 |
| Kadazan | 3,874 |
| Bajau | 942 |
| Total Bumiputera | 28,478 |
| Chinese | 1,225 |
| India | 57 |
| Others | 1,384 |
| Total Malaysian Citizen | 31,144 |
| Non-Malaysian Citizen | 3,718 |
| Total | 34,842 |
A local census estimates that the population comprises 60% Kedayan, 30% Murut, Lun Bawang and Lundayeh, 10% Bruneian Malay as well as Chinese. The population is divided among the larger communities and the total area of the district as follows:
| Sipitang District | 34,862 inhabitants |
|---|---|
| Malaman | 32 |
| Mesapol | 888 |
| Sindumin | 115 |
| Sipitang | 4,298 |
| Remaining areas | 29,529 |
Notable people
Statesmen
- TYT Sabah Pengiran Ahmad Raffae - The Second of The Head of State of Sabah
Politicians
- Datuk Sapawi Ahmad - politician
- Datuk Dr. Haji Yusuf Haji Yacob - the former deputy Speaker of the Dewan Rakyat and incumbent Ministry of Education and Innovation of Sabah
Sportsmen
- Ronny Harun - Malaysian Football Player
- Mafry Balang - Malaysian Football Player
Gallery
 Haji Hassim Mosque.
Haji Hassim Mosque. St. John the Baptist Catholic Church.
St. John the Baptist Catholic Church. Lukutan River.
Lukutan River. Sipitang Bridge.
Sipitang Bridge. Sipitang-Tenom Road.
Sipitang-Tenom Road.
See also
References
- "Cession by Sultan of Brunei Pangeran Bandhara and Pangeran di Gadong of territory from Si Putong to Kwala Paniow" (PDF). Sabah State Attorney's General Chambers. 1884. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 November 2017. Retrieved 5 November 2017.
- "Grant by Sultan of Brunei of Territory between the Sepitong and Trusan Rivers" (PDF). Sabah State Attorney's General Chambers. 1884. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 November 2017. Retrieved 5 November 2017.
- "Grant by Pengeran Pengah Damit of the tulin rights in Mengalong and Merantaman". The National Archives. 1901. Retrieved 5 November 2017.
- R. Haller-Trost (1994). The Brunei-Malaysia Dispute Over Territorial and Maritime Claims in International Law. IBRU. ISBN 978-1-897643-07-5.
- Abdul Harun Majid (15 August 2007). Rebellion in Brunei: The 1962 Revolt, Imperialism, Confrontation and Oil. I.B.Tauris. ISBN 978-1-84511-423-7.
- "Maklumat Am Destinasi Pelancongan Domestik" (in Malay). Pusat Perkhidmatan Ilmu Komuniti Sipitang. Retrieved 16 July 2012.
- "Population by ethnic group, Local Authority area and state, Malaysia" (PDF). Department of Statistics, Malaysia. 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 February 2012. Retrieved 5 November 2017.
Further reading
- Treacher, W. H (1891). "British Borneo: sketches of Brunai, Sarawak, Labuan, and North Borneo". University of California Libraries. Singapore, Govt. print. dept. p. 190.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Rutter, Owen (1922). "British North Borneo - An Account of its History, Resources and Native Tribes". Cornell University Libraries. Constable & Company Ltd, London. p. 157.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Tregonning, K. G. (1965). A History Of Modern Sabah (North Borneo 1881–1963). University of Malaya Press.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links
![]() Media related to Sipitang District at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Sipitang District at Wikimedia Commons
- (in Malay) Sipitang District Office
