Solar eclipse of August 28, 1848
A very small partial solar eclipse occurred on August 28, 1848 during late winter. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. This was the 71st and final solar eclipse from Solar Saros 113.
| Solar eclipse of August 28, 1848 | |
|---|---|
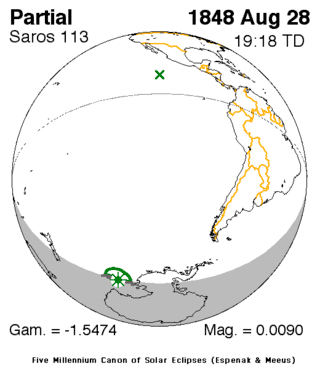 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Partial |
| Gamma | -1.5475 |
| Magnitude | 0.009 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 71.3°S 169.6°W |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 19:18:22 |
| References | |
| Saros | 113 (71 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9161 |
It was one of four partial eclipses that took place that year, each two in two months, It occurred in a smaller part of the same area where the previous solar eclipse happened which was on April 3, the next one was on September 27 and covered a part of the Northern Hemisphere[1]
Description
This minor eclipse was visible offshore from the peninsular Antarctica along with its islands and the Trans-Antarctic Mountains. It was the last eclipse of solar saros 113 with the moon's penumbra touching the earth for just about 30 minutes.[2] The greatest eclipse was at 19:18:22 UTC (8:18:22 local time) just south of the 70th parallel.[1]
See also
- List of solar eclipses in the 19th century
- List of solar eclipses visible from Antarctica
References
- "Solar eclipse of August 28, 1848". NASA. Retrieved March 10, 2017.
- "Solar Saros 113". NASA. Retrieved March 19, 2017.
.jpg.webp)

