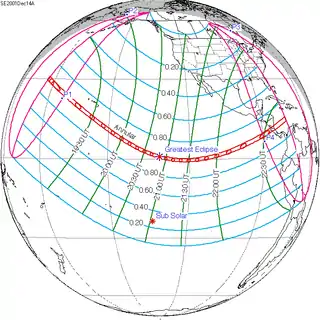
Solar eclipse of October 14, 2023
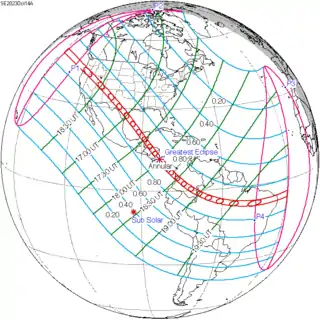
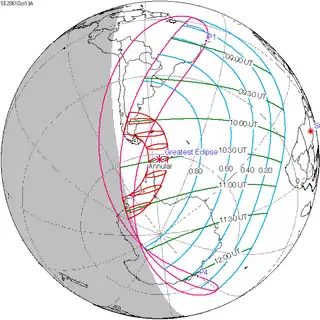
An annular solar eclipse will occur on October 14, 2023. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres or miles wide. This will be the second annular eclipse visible from Albuquerque in 11 years, where it crosses the path of the May 2012 eclipse. Occurring only 4.6 days after apogee (Apogee on October 10, 2023), the moon's apparent diameter will be smaller.
| Solar eclipse of October 14, 2023 | |
|---|---|
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Annular |
| Gamma | 0.3753 |
| Magnitude | 0.952 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 317 sec (5 m 17 s) |
| Coordinates | 11.4°N 83.1°W |
| Max. width of band | 187 km (116 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 18:00:41 |
| References | |
| Saros | 134 (44 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9560 |
Future total solar eclipses will cross the United States in April 2024 (12 states) (Saros 139, Ascending Node) and August 2045 (10 states) (Saros 136, Descending Node), and an annular solar eclipse will occur in June 2048 (9 states) (Saros 128, Descending Node).
Visibility
United States
The path of the eclipse will begin to cross the United States in Oregon, entering at Dunes City, and passing over Newport, Crater Lake National Park, Umpqua and Fremont National Forests, Eugene, and Medford. After passing over the northeast corner of California (in the Modoc National Forest), it will travel through Nevada (passing over Black Rock Desert, Winnemucca and Elko) and Utah (passing over Fishlake National Forest, Canyonlands National Park, Glen Canyon National Recreation Area, and Bluff). After that, it will cover the northeast corner of Arizona (including Kayenta) and the southwest corner of Colorado (including Cortez and the Ute Mountain Reservation). In New Mexico, it will pass over Farmington, Albuquerque, Santa Fe, Roswell and Carlsbad. Afterwards, it will enter Texas, passing over Midland, Odessa, San Angelo, San Antonio and Corpus Christi before entering the Gulf of Mexico.[1]
Mexico
In Mexico, the eclipse will pass over the Yucatan Peninsula, covering Campeche City in Campeche State, Oxkutzcab in Yucatan State (coming close to Mérida), and Chetumal in Quintana Roo.
Central America
In Belize, the eclipse will pass over Belmopan and Belize City before leaving land again; when it re-enters in Honduras, it will pass over La Ceiba, and in Nicaragua it will pass over Bluefields. The point of greatest eclipse will occur near the coast of Nicaragua. After that, in Costa Rica it will pass over Limon, and in Panama it will pass over Santiago and come close to Panama City. Its point of greatest duration will occur just off the coast of Nata, Panama.[1]
South America
In South America, the eclipse will enter Colombia from the Pacific Ocean and pass over Pereira, Cali, Ibagué and Neiva. In Brazil, it will pass over the states of Amazonas (covering Fonte Boa, Tefé and Coari), Pará (covering Parauapebas and Xinguara), Tocantins (Araguaína) Maranhão (Balsas), Piauí (Picos), Ceará (Juazeiro do Norte), Pernambuco (Araripina), Paraíba (João Pessoa) and Rio Grande do Norte (Natal) before ending in the Atlantic Ocean.[1]
Images
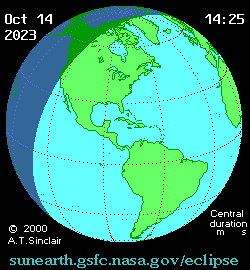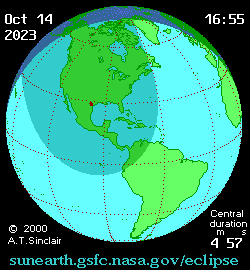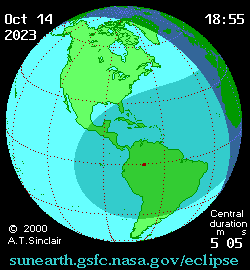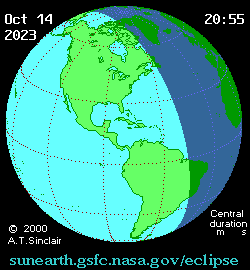
Animated path
Related eclipses
Eclipses of 2023
Solar eclipses of 2022–2025
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[2]
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2022–2025 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 119 | 2022 April 30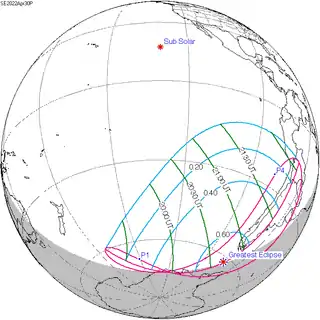 Partial | -1.19008 | 124 | 2022 October 25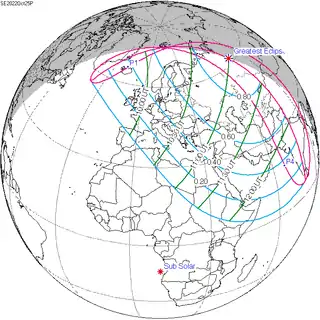 Partial | 1.07014 | |
| 129 | 2023 April 20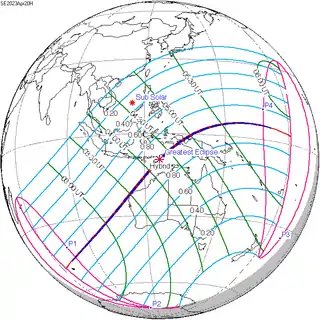 Hybrid | -0.39515 | 134 | 2023 October 14 Annular | 0.37534 | |
| 139 | 2024 April 8 Total | 0.34314 | 144 | 2024 October 2 Annular | -0.35087 | |
| 149 | 2025 March 29 Partial | 1.04053 | 154 | 2025 September 21 Partial | -1.06509 | |
Saros 134
It is a part of Saros cycle 134, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 71 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on June 22, 1248. It contains total eclipses from October 9, 1428 through December 24, 1554 and hybrid eclipses from January 3, 1573 through June 27, 1843, and annular eclipses from July 8, 1861 through May 21, 2384. The series ends at member 71 as a partial eclipse on August 6, 2510. The longest duration of totality was 1 minutes, 30 seconds on October 9, 1428. All eclipses in this series occurs at the Moon’s descending node.[3]
| Series members 32–48 occur between 1801 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 32 | 33 | 34 |
 June 6, 1807 |
 June 16, 1825 |
 June 27, 1843 |
| 35 | 36 | 37 |
 July 8, 1861 |
 July 19, 1879 |
 July 29, 1897 |
| 38 | 39 | 40 |
 August 10, 1915 |
 August 21, 1933 |
 September 1, 1951 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 |
 September 11, 1969 |
 September 23, 1987 |
 October 3, 2005 |
| 44 | 45 | 46 |
 October 14, 2023 |
 October 25, 2041 |
 November 5, 2059 |
| 47 | 48 | |
 November 15, 2077 |
 November 27, 2095 | |
Inex series
This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Inex series members between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
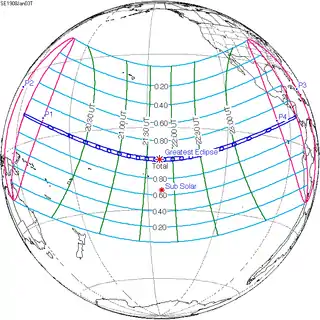 January 3, 1908 (Saros 130) |
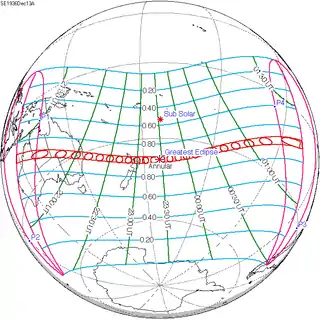 December 13, 1936 (Saros 131) |
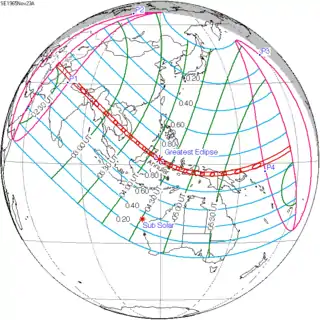 November 23, 1965 (Saros 132) |
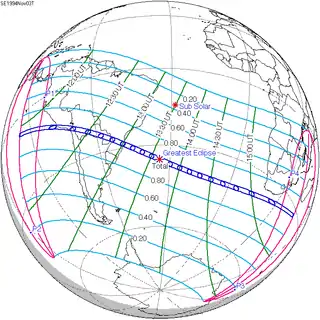 November 3, 1994 (Saros 133) |
 October 14, 2023 (Saros 134) |
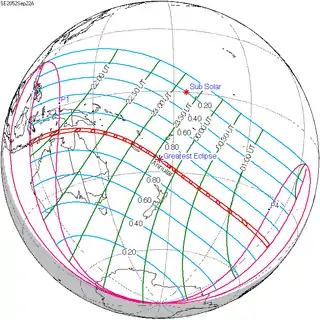 September 22, 2052 (Saros 135) |
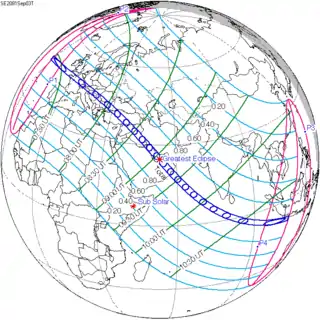 September 3, 2081 (Saros 136) |
||
Tritos series
This eclipse is a part of a tritos cycle, repeating at alternating nodes every 135 synodic months (≈ 3986.63 days, or 11 years minus 1 month). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee), but groupings of 3 tritos cycles (≈ 33 years minus 3 months) come close (≈ 434.044 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1901 and 2100 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
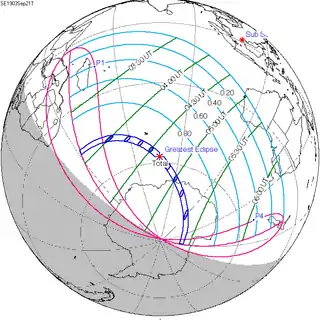 September 21, 1903 (Saros 123) |
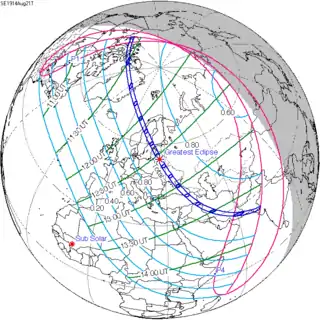 August 21, 1914 (Saros 124) |
 July 20, 1925 (Saros 125) | |
 June 19, 1936 (Saros 126) |
 May 20, 1947 (Saros 127) |
 April 19, 1958 (Saros 128) | |
 March 18, 1969 (Saros 129) |
 February 16, 1980 (Saros 130) |
 January 15, 1991 (Saros 131) | |
 December 14, 2001 (Saros 132) |
 November 13, 2012 (Saros 133) |
 October 14, 2023 (Saros 134) | |
 September 12, 2034 (Saros 135) |
 August 12, 2045 (Saros 136) |
 July 12, 2056 (Saros 137) | |
 June 11, 2067 (Saros 138) |
 May 11, 2078 (Saros 139) |
 April 10, 2089 (Saros 140) | |
 March 10, 2100 (Saros 141) |
|||
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.[4]
| Octon series with 21 events between May 21, 1993 and August 2, 2065 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| May 20–21 | March 8–9 | December 25–26 | October 13–14 | August 1–2 |
| 98 | 100 | 102 | 104 | 106 |
| May 21, 1955 | March 9, 1959 | December 26, 1962 | October 14, 1966 | August 2, 1970 |
| 108 | 110 | 112 | 114 | 116 |
| May 21, 1974 | March 9, 1978 | December 26, 1981 | October 14, 1985 | August 1, 1989 |
| 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 | 126 |
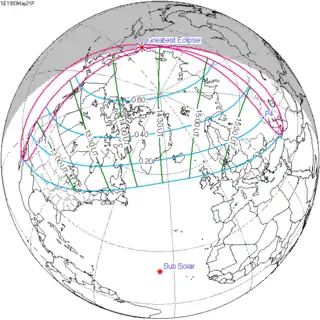 May 21, 1993 |
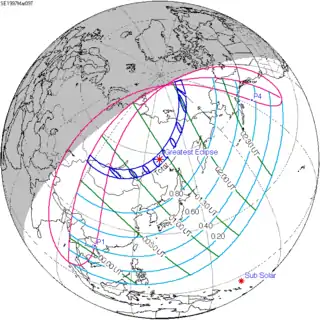 March 9, 1997 |
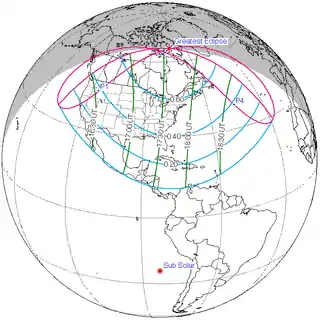 December 25, 2000 |
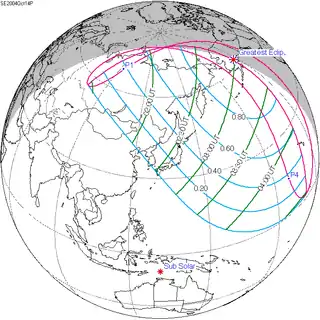 October 14, 2004 |
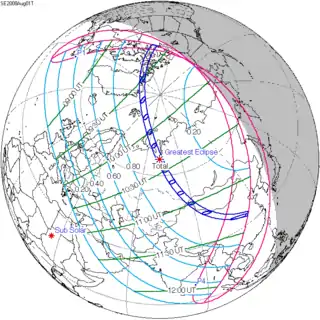 August 1, 2008 |
| 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 | 136 |
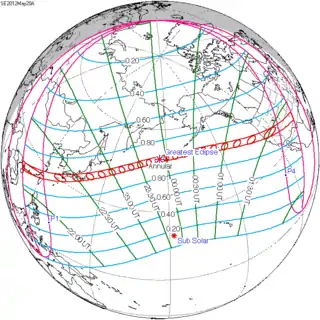 May 20, 2012 |
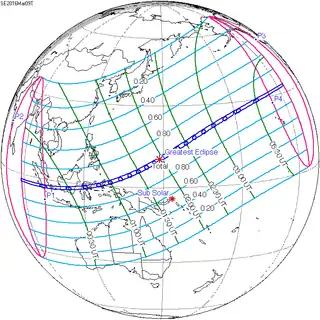 March 9, 2016 |
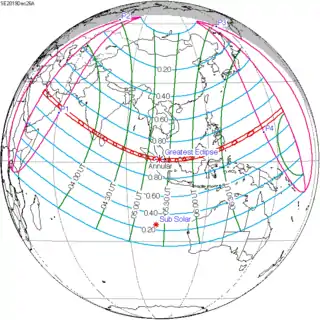 December 26, 2019 |
 October 14, 2023 |
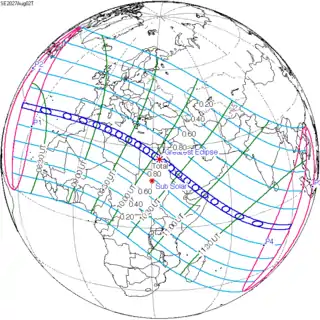 August 2, 2027 |
| 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 | 146 |
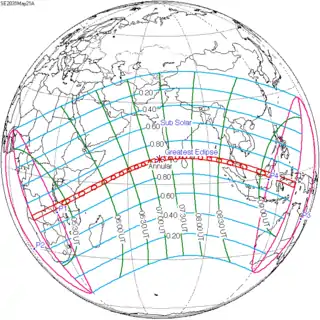 May 21, 2031 |
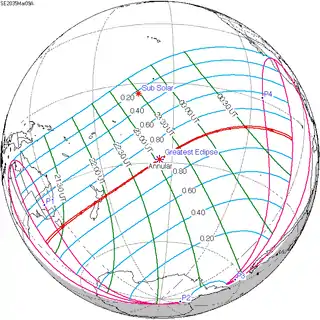 March 9, 2035 |
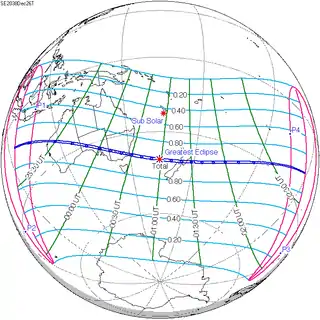 December 26, 2038 |
 October 14, 2042 |
 August 2, 2046 |
| 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 | 156 |
 May 20, 2050 |
 March 9, 2054 |
 December 26, 2057 |
 October 13, 2061 |
 August 2, 2065 |
| 158 | 160 | 162 | 164 | 166 |
 May 20, 2069 |
March 8, 2073 | December 26, 2076 | October 13, 2080 | August 1, 2084 |
References
- https://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/SEgoogle/SEgoogle2001/SE2023Oct14Agoogle.html
- van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- http://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/SEsaros/SEsaros134.html
- Freeth, Tony. "Note S1: Eclipses & Predictions". plos.org. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 2023 October 14. |
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- NationalEclipse.com An educational site with overviews, maps, city data, events, animations, merchandise, historical information, and other resources for the 2023 eclipse and others.
.jpg.webp)

