Solar eclipse of June 21, 1982
A partial solar eclipse occurred on June 21, 1982. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. Occurring only 7 minutes before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was completely larger.
| Solar eclipse of June 21, 1982 | |
|---|---|
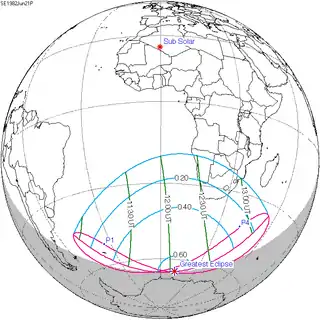 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Partial |
| Gamma | -1.2102 |
| Magnitude | 0.6168 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 65.9°S 13.2°E |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 12:04:33 |
| References | |
| Saros | 117 (67 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9470 |
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses of 1982–1985
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
Note: Partial solar eclipses on January 25, 1982 and July 20, 1982 occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1982–1985 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 117 |  1982 June 21 Partial | -1.21017 | 122 | 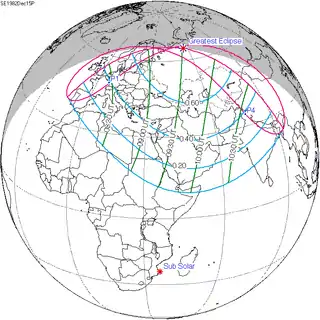 1982 December 15 Partial | 1.12928 | |
| 127 | 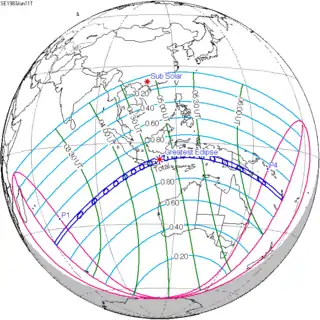 1983 June 11 Total | -0.49475 | 132 | 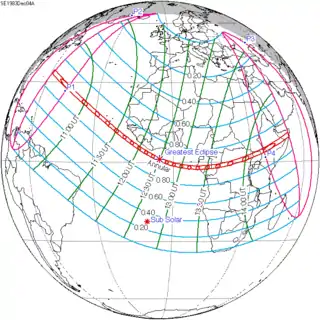 1983 December 4 Annular | 0.40150 | |
| 137 | 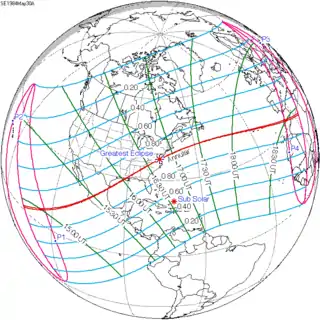 1984 May 30 Annular | 0.27552 | 142 Partial from Gisborne, NZ | 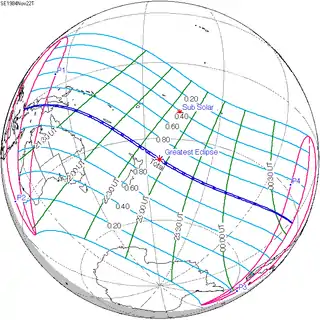 1984 November 22 Total | -0.31318 | |
| 147 | 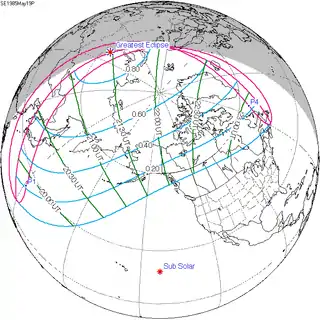 1985 May 19 Partial | 1.07197 | 152 | 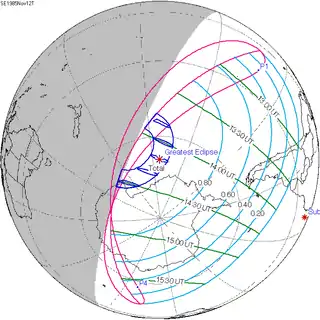 1985 November 12 Total | -0.97948 | |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's ascending node.
| 21 eclipse events between June 21, 1982, and June 21, 2058 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| June 21 | April 8–9 | January 26 | November 13–14 | September 1–2 |
| 107 | 109 | 111 | 113 | 115 |
| June 21, 1963 | April 9, 1967 | January 26, 1971 | November 14, 1974 | September 2, 1978 |
| 117 | 119 | 121 | 123 | 125 |
 June 21, 1982 |
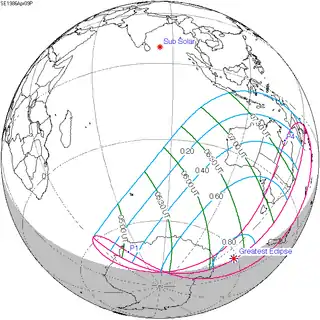 April 9, 1986 |
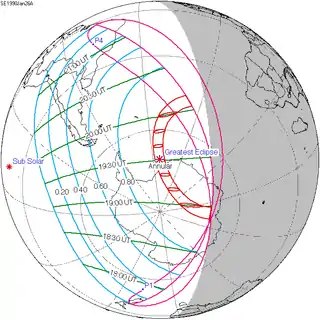 January 26, 1990 |
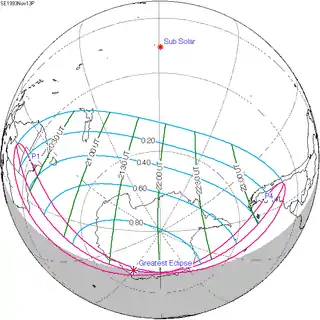 November 13, 1993 |
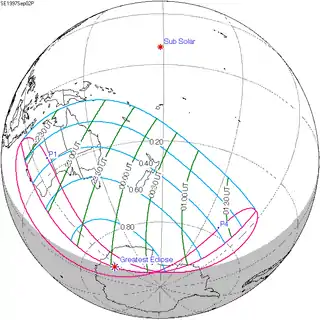 September 2, 1997 |
| 127 | 129 | 131 | 133 | 135 |
 June 21, 2001 |
 April 8, 2005 |
 January 26, 2009 |
 November 13, 2012 |
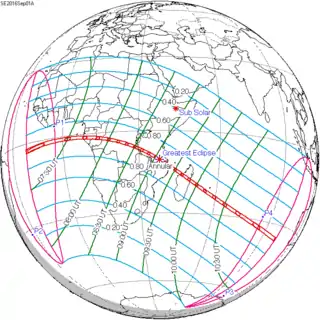 September 1, 2016 |
| 137 | 139 | 141 | 143 | 145 |
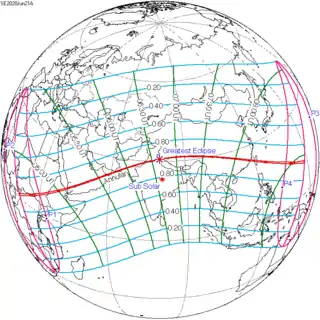 June 21, 2020 |
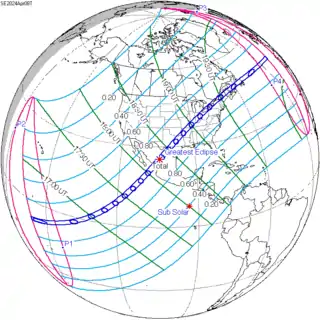 April 8, 2024 |
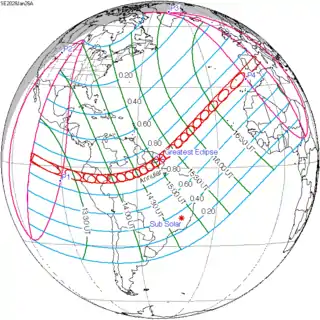 January 26, 2028 |
 November 14, 2031 |
 September 2, 2035 |
| 147 | 149 | 151 | 153 | 155 |
 June 21, 2039 |
 April 9, 2043 |
 January 26, 2047 |
 November 14, 2050 |
 September 2, 2054 |
| 157 | ||||
 June 21, 2058 | ||||
References
- van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
External links
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
.jpg.webp)

