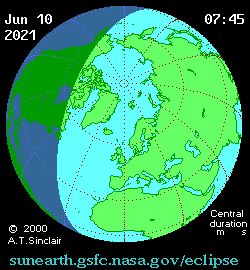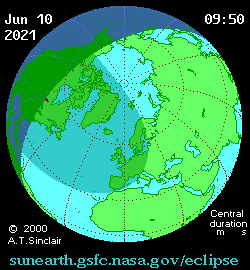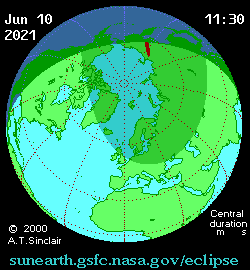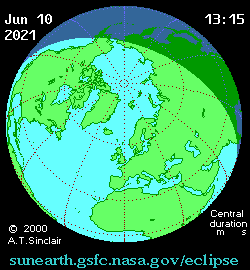
Solar eclipse of June 10, 2021
An annular solar eclipse will occur on June 10, 2021. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.
| Solar eclipse of June 10, 2021 | |
|---|---|
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Annular |
| Gamma | 0.9152 |
| Magnitude | 0.9435 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 231 sec (3 m 51 s) |
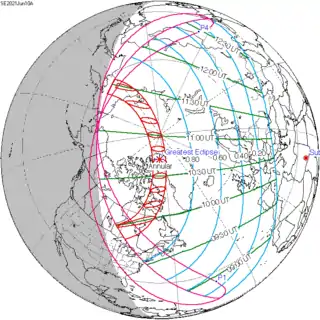
| Coordinates | 80.8°N 66.8°W |
| Max. width of band | 527 km (327 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 10:43:07 |
| References | |
| Saros | 147 (23 of 80) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9555 |
This eclipse is notable for the fact that the path of annularity will pass over the North Pole, the only such eclipse in 21st century.[1]
While the eclipse is visible primarily in northern Canada, in Greenland and in north of Russian Far East, in the northeastern United States and Canada, the sun will be partially eclipsed at sunrise, which will be between 5 and 6 A.M. (EDT)
More details about the annular solar eclipse of 2021 June 10.
Eclipse Magnitude: 0.94350 (94.35%)
Eclipse Obscuration: 0.89019 (89.019%)
Gamma: 0.91516 (91.773%) (Gamma is between 0.915155 and 0.915165)
Greatest Eclipse: Thursday, 2021 June 10 at 10:41:56.6 UTC
Ecliptic Conjunction: Thursday, 2021 June 10 at 10:52:38.1 UTC
Equatorial Conjunction: Thursday, 2021 June 10 at 11:01:04.3 UTC
Sun Right Ascension: 5.259h
Sun Declination: +23.04°
Sun Diameter: 1890.4 arcseconds
Moon Right Ascension: 5.248h
Moon Declination: +23.86°
Moon Diameter: 1773.6 arcseconds
Lunar Latitude: -1.0° (1.0° South)
Lunar Longitude: -2.3° (2.3° West)
Lunar Position Angle: 357.1°
Saros: 147 (23 of 80)
Penumbral Shadow: 0.5644 Earths
Umbral Shadow: 0.01815 Earths
Images
Animated path
Related eclipses
Eclipses of 2021
Solar eclipses of 2018–2021
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[2]
Note: Partial solar eclipses on February 15, 2018, and August 11, 2018, occurred during the previous semester series.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2018–2021 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 107 | 2017 July 23 | -2.14244 | 112 | 2018 January 17 | 1.78677 | |
117.jpg.webp) Partial from Melbourne, Australia | 2018 July 13 Partial |
-1.35423 | 122 Partial from Nakhodka, Russia | 2019 January 6 Partial |
1.14174 | |
127 La Serena, Chile | 2019 July 2 Total |
-0.64656 | 132.jpg.webp) Jaffna, Sri Lanka | 2019 December 26 Annular |
0.41351 | |
137 Beigang, Yunlin, Taiwan | 2020 June 21 Annular |
0.12090 | 142 Gorbea, Chile | 2020 December 14 Total |
-0.29394 | |
| 147 | 2021 June 10 Annular |
0.91516 | 152 | 2021 December 4 Total |
-0.95261 | |
| 157 | 2022 May 30 | 1.65174 | 162 | 2022 November 23 | -1.69875 | |
Saros 147
Solar saros 147, repeating every about 18 years and 11 days, contains 80 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on October 12, 1624. It has annular eclipses from May 31, 2003, to July 31, 2706. There are no total eclipses in this series. The series ends at member 80 as a partial eclipse on February 24, 3049. The longest annular eclipse will be on November 21, 2291, at 9 minutes and 41 seconds.[3]
| Series members 17–27 occur between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 17 | 18 | 19 |
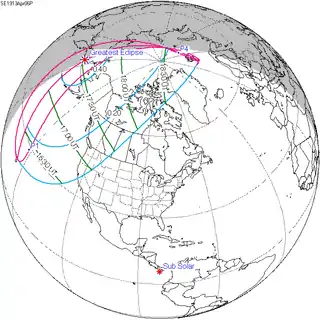 April 6, 1913 |
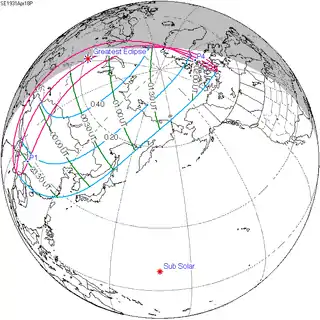 April 18, 1931 |
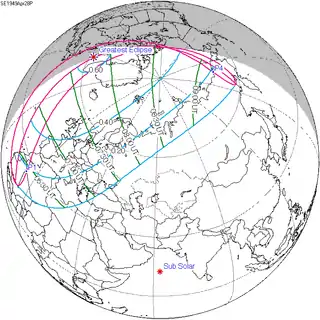 April 28, 1949 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 |
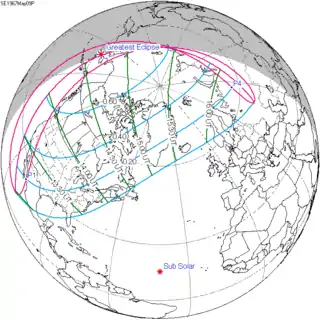 May 9, 1967 |
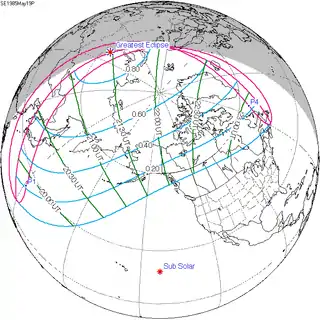 May 19, 1985 |
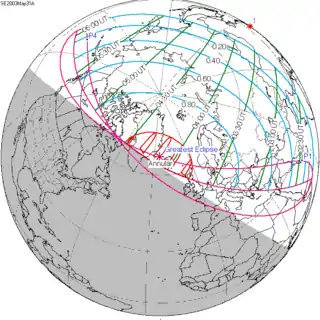 May 31, 2003 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 |
 June 10, 2021 |
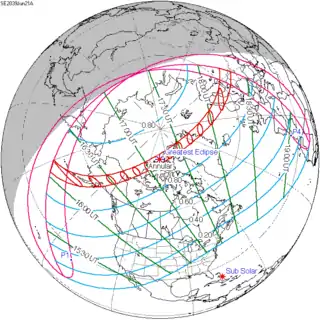 June 21, 2039 |
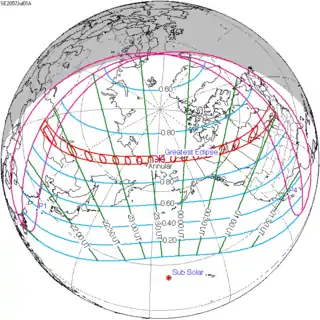 July 1, 2057 |
| 26 | 27 | |
 July 13, 2075 |
 July 23, 2093 | |
Inex series
This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings. In the 19th century:
• Solar Saros 140: Total Solar Eclipse of 1818 Oct 29
• Solar Saros 141: Annular Solar Eclipse of 1847 Oct 09
• Solar Saros 142: Total Solar Eclipse of 1876 Sep 17
| Inex series members between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
 August 30, 1905 (Saros 143) |
 August 10, 1934 (Saros 144) |
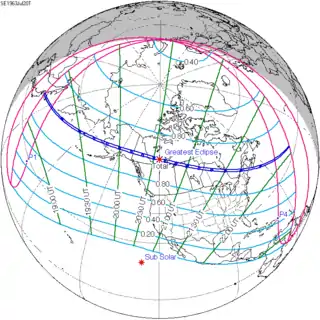 July 20, 1963 (Saros 145) |
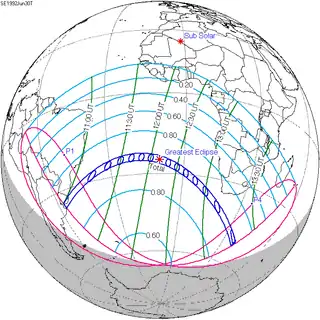 June 30, 1992 (Saros 146) |
 June 10, 2021 (Saros 147) |
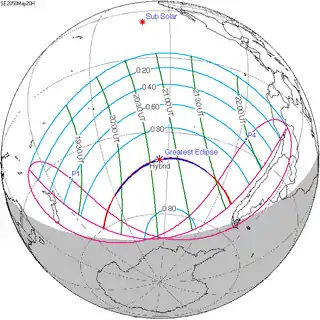 May 20, 2050 (Saros 148) |
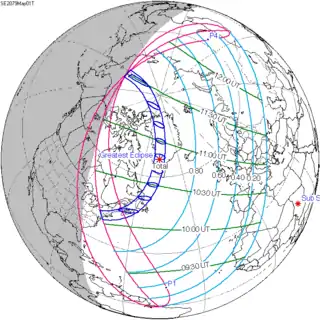 May 1, 2079 (Saros 149) |
||
In the 22nd century:
Solar Saros 150: Partial Solar Eclipse of 2108 Apr 11
Solar Saros 151: Annular Solar Eclipse of 2137 Mar 21
Solar Saros 152: Total Solar Eclipse of 2166 Mar 02
Solar Saros 153: Annular Solar Eclipse of 2195 Feb 10
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's ascending node.
| 21 eclipse events, progressing from south to north between June 10, 1964, and August 21, 2036 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| June 10–11 | March 27–29 | January 15–16 | November 3 | August 21–22 |
| 117 | 119 | 121 | 123 | 125 |
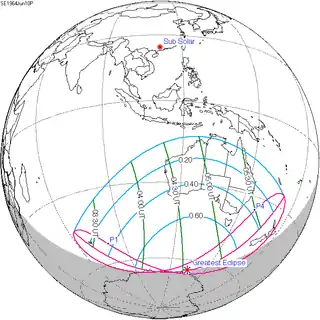 June 10, 1964 |
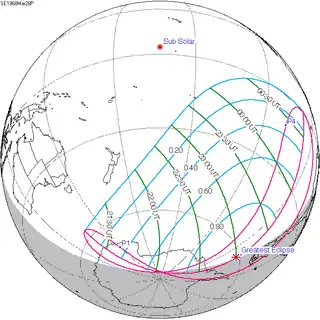 March 28, 1968 |
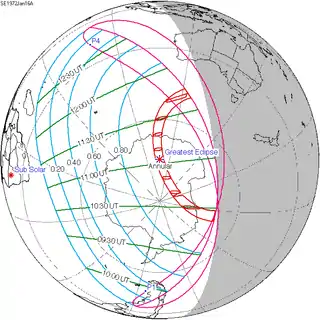 January 16, 1972 |
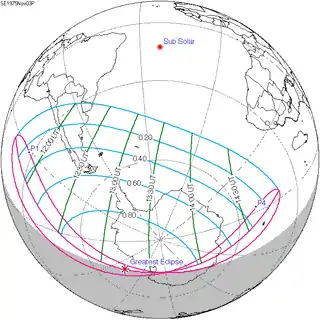 November 3, 1975 |
 August 22, 1979 |
| 127 | 129 | 131 | 133 | 135 |
 June 11, 1983 |
 March 29, 1987 |
 January 15, 1991 |
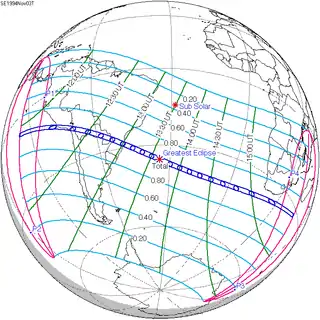 November 3, 1994 |
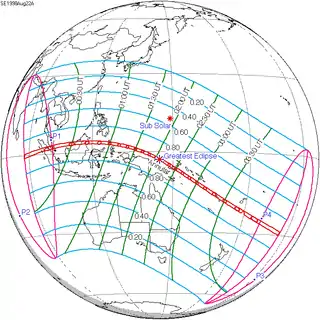 August 22, 1998 |
| 137 | 139 | 141 | 143 | 145 |
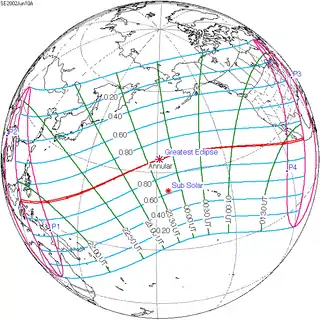 June 10, 2002 |
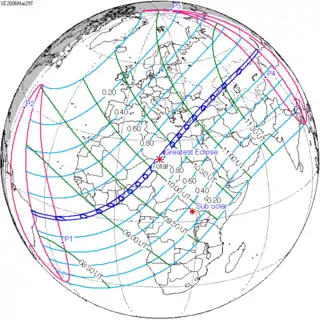 March 29, 2006 |
 January 15, 2010 |
 November 3, 2013 |
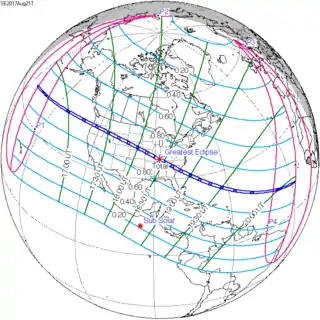 August 21, 2017 |
| 147 | 149 | 151 | 153 | 155 |
 June 10, 2021 |
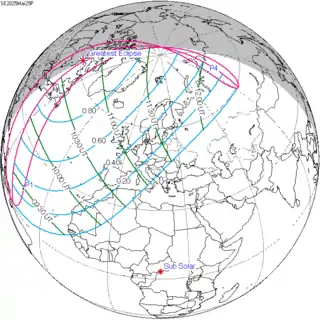 March 29, 2025 |
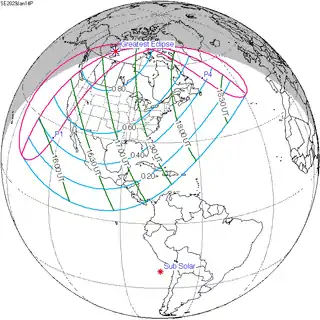 January 14, 2029 |
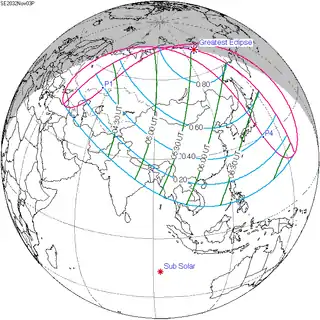 November 3, 2032 |
 August 21, 2036 |
Notes
- JavaScript Solar Eclipse Explorer - Europe (Latitude: 90° 00' 00" N Longitude: 0° 00' 00" W). NASA
- van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- Saros Series Catalog of Solar Eclipses NASA Eclipse Web Site.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 2021 June 10. |
.jpg.webp)

