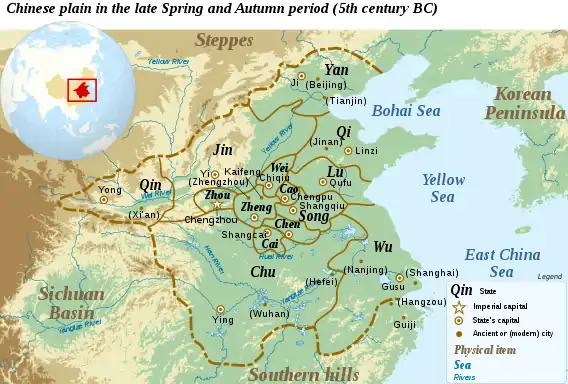
Spring and Autumn period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 771 to 476 BCE (or according to some authorities until 403 BCE[lower-alpha 1])[2] which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives from the Spring and Autumn Annals, a chronicle of the state of Lu between 722 and 479 BCE, which tradition associates with Confucius (551–479 BCE).
| Spring and Autumn period | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 春秋時代 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 春秋时代 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hanyu Pinyin | Chūn-Qiū Shídài | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANCIENT | ||||||||
| Neolithic c. 8500 – c. 2070 BCE | ||||||||
| Xia c. 2070 – c. 1600 BCE | ||||||||
| Shang c. 1600 – c. 1046 BCE | ||||||||
| Zhou c. 1046 – 256 BCE | ||||||||
| Western Zhou | ||||||||
| Eastern Zhou | ||||||||
| Spring and Autumn | ||||||||
| Warring States | ||||||||
| IMPERIAL | ||||||||
| Qin 221–207 BCE | ||||||||
| Han 202 BCE – 220 CE | ||||||||
| Western Han | ||||||||
| Xin | ||||||||
| Eastern Han | ||||||||
| Three Kingdoms 220–280 | ||||||||
| Wei, Shu and Wu | ||||||||
| Jin 266–420 | ||||||||
| Western Jin | ||||||||
| Eastern Jin | Sixteen Kingdoms | |||||||
| Northern and Southern dynasties 420–589 | ||||||||
| Sui 581–618 | ||||||||
| Tang 618–907 | ||||||||
| (Wu Zhou 690–705) | ||||||||
| Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms 907–979 |
Liao 916–1125 | |||||||
| Song 960–1279 | ||||||||
| Northern Song | Western Xia | |||||||
| Southern Song | Jin | Western Liao | ||||||
| Yuan 1271–1368 | ||||||||
| Ming 1368–1644 | ||||||||
| Qing 1636–1912 | ||||||||
| MODERN | ||||||||
| Republic of China on mainland 1912–1949 | ||||||||
| People's Republic of China 1949–present | ||||||||
| Republic of China on Taiwan 1949–present | ||||||||
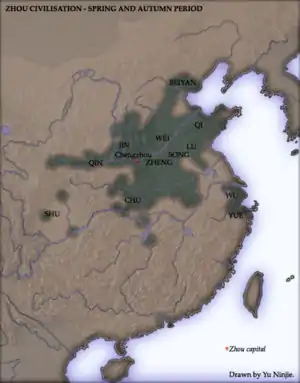
During this period, the Zhou royal authority over the various feudal states eroded as more and more dukes and marquesses obtained de facto regional autonomy, defying the king's court in Luoyi and waging wars amongst themselves. The gradual Partition of Jin, one of the most powerful states, marked the end of the Spring and Autumn period and the beginning of the Warring States period.
Background
In 771 BCE, the Quanrong invasion destroyed the Western Zhou and its capital Haojing, forcing the Zhou king to flee to the eastern capital Luoyi (Chinese: 洛邑). The event ushered in the Eastern Zhou dynasty, which is divided into the Spring and Autumn and the Warring States periods. During the Spring and Autumn period, China's feudal system of fengjian (封建) became largely irrelevant. The Zhou court, having lost its homeland in the Guanzhong region, held nominal power, but had real control over only a small royal demesne centered on Luoyi. During the early part of the Zhou dynasty period, royal relatives and generals had been given control over fiefdoms in an effort to maintain Zhou authority over vast territory.[3] As the power of the Zhou kings waned, these fiefdoms became increasingly independent states.
The most important states (known later as the twelve vassals) came together in regular conferences where they decided important matters, such as military expeditions against foreign groups or against offending nobles. During these conferences one vassal ruler was sometimes declared hegemon (Chinese: 伯; pinyin: bó; later, Chinese: 霸; pinyin: bà).
As the era continued, larger and more powerful states annexed or claimed suzerainty over smaller ones. By the 6th century BCE most small states had disappeared and just a few large and powerful principalities dominated China. Some southern states, such as Chu and Wu, claimed independence from the Zhou, who undertook wars against some of them (Wu and Yue).
Amid the interstate power struggles, internal conflict was also rife: six élite landholding families waged war on each other inside Jin, political enemies set about eliminating the Chen family in Qi, and the legitimacy of the rulers was often challenged in civil wars by various royal family members in Qin and Chu. Once all these powerful rulers had firmly established themselves within their respective dominions, the bloodshed focused more fully on interstate conflict in the Warring States period, which began in 403 BCE when the three remaining élite families in Jin—Zhao, Wei and Han—partitioned the state.
Early Spring and Autumn (771–685 BCE)

Court moves east (771 BCE)
After the Zhou capital was sacked by the Marquess of Shen and the Quanrong barbarians, the Zhou moved the capital east from the now desolated Zongzhou in Haojing near modern Xi'an to Wangcheng in the Yellow River Valley. The Zhou royalty was then closer to its main supporters,[4] particularly Jin, and Zheng;[5][6] the Zhou royal family had much weaker authority and relied on lords from these vassal states for protection, especially during their flight to the eastern capital. In Chengzhou, Prince Yijiu was crowned by his supporters as King Ping.[6] However, with the Zhou domain greatly reduced to Chengzhou and nearby areas, the court could no longer support the six army groups it had in the past; Zhou kings had to request help from powerful vassal states for protection from raids and for resolution of internal power struggles. The Zhou court would never regain its original authority; instead, it was relegated to being merely a figurehead of the feudal states. Though the king de jure retained the Mandate of Heaven, the title held little actual power.
With the decline of Zhou power, the Yellow River drainage basin was divided into hundreds of small, autonomous states, most of them consisting of a single city, though a handful of multi-city states, particularly those on the periphery, had power and opportunity to expand outward.[7] A total of 148 states are mentioned in the chronicles for this period, 128 of which were absorbed by the four largest states by the end of the period.[8]
Shortly after the royal family's move to Chengzhou, a hierarchical alliance system arose where the Zhou king would give the title of hegemon to the leader of the state with the most powerful military; the hegemon was obligated to protect both the weaker Zhou states and the Zhou royalty from the intruding non-Zhou peoples:[9][10] the Northern Di, the Southern Man, the Eastern Yi, and the Western Rong. This political framework retained the fēngjiàn power structure, though interstate and intrastate conflict often led to disregard for feudal customs, respect for the Ji family, and solidarity with other Zhou peoples.[11] The king's prestige legitimized the military leaders of the states, and helped mobilize collective defense of Zhou territory against "barbarians".[12]
Over the next two centuries, the four most powerful states—Qin, Jin, Qi and Chu—struggled for power. These multi-city states often used the pretext of aid and protection to intervene and gain suzerainty over the smaller states. During this rapid expansion,[13] interstate relations alternated between low-level warfare and complex diplomacy.[14]
Zheng falls out with the court (722–685 BCE)
Duke Yin of Lu ascended the throne in 722 BCE.[15] From this year on the state of Lu kept an official chronicle, the Spring and Autumn Annals, which along with its commentaries is the standard source for the Spring and Autumn period. Corresponding chronicles are known to have existed in other states as well, but all but the Lu chronicle have been lost.
In 717 BCE, Duke Zhuang of Zheng went to the capital for an audience with King Huan. During the encounter the duke felt he was not treated with the respect and etiquette which would have been appropriate, given that Zheng was now the chief protector of the capital.[15] In 715 BCE Zheng also became involved in a border dispute with Lu regarding the Fields of Xu. The fields had been put in the care of Lu by the king for the exclusive purpose of producing royal sacrifices for the sacred Mount Tai.[15] For Zheng to regard the fields as just any other piece of land was an insult to the court.
By 707 BCE, relations had soured enough that the king launched a punitive expedition against Zheng. The duke counterattacked and raided Zhou territory, defeating the royal forces in the Battle of Xuge and injuring the king himself.[8][15][16] Zheng was the first vassal to openly defy the king, kicking off the centuries of warfare without respect for titles which would characterize the period.
The display of Zheng's martial strength was effective until succession problems after Zhuang's death in 701 weakened the state.[5]
In 692 BCE, there was a failed assassination attempt against King Zhuang, orchestrated by elements at court.[15]
The Five Hegemons (685–591 BCE)
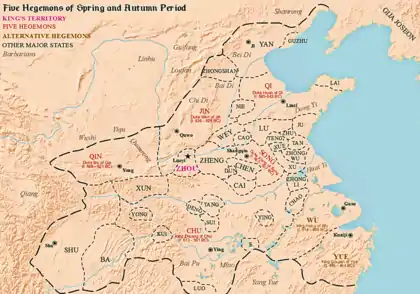
Hegemony of Qi (685–643 BCE)
The first hegemon was Duke Huan of Qi (r. 685–643 BCE). With the help of his prime minister, Guan Zhong, Duke Huan reformed Qi to centralize its power structure. The state consisted of 15 "townships" with the duke and two senior ministers each in charge of five; military functions were also united with civil ones. These and related reforms provided the state, already powerful from control of trade crossroads, with a greater ability to mobilize resources than the more loosely organized states.[17]
By 667 BCE, Qi had clearly shown its economic and military predominance, and Duke Huan assembled the leaders of Lu, Song, Chen, and Zheng, who elected him as their leader. Soon after, King Hui of Zhou conferred the title of bà (hegemon), giving Duke Huan royal authority in military ventures.[18][19] An important basis for justifying Qi's dominance over the other states was presented in the slogan 'supporting the king, and expelling the barbarians' (尊王攘夷 zun wang rang yi); the role of subsequent hegemons would also be framed in this way, as the primary defender and supporter of nominal Zhou authority and the existing order. Using this authority, Duke Huan intervened in a power struggle in Lu; protected Yan from encroaching Western Rong nomads (664 BCE); drove off Northern Di nomads after they'd invaded Wey (660 BCE) and Xing (659 BCE), providing the people with provisions and protective garrison units; and led an alliance of eight states to conquer Cai and thereby block the northward expansion of Chu (656 BCE).[20]
At his death in 643 BCE, five of Duke Huan's sons contended for the throne, badly weakening the state so that it was no longer regarded as the hegemon. For nearly ten years, no ruler held the title.[21]
Hegemony of Song (643–637 BCE)
Duke Xiang of Song attempted to claim the hegemony in the wake of Qi's decline, perhaps driven by a desire to restore the Shang Dynasty from which Song had descended. He hosted peace conferences in the same style as Qi had done, and conducted aggressive military campaigns against his rivals. Duke Xiang however met his end when, against the advice of his staff, he attacked the much larger state of Chu. The Song forces were defeated at the battle of Hong in 638 BCE, and the duke himself died in the following year from an injury sustained in the battle. After Xiang's death his successors adopted a more modest foreign policy, better suited to the country's small size.[22]
As Duke Xiang was never officially recognized as hegemon by the King of Zhou, not all sources list him as one of the Five Hegemons.
Hegemony of Jin (636–628 BCE)
When Duke Wen of Jin came to power in 636 BCE, he capitalized on the reforms of his father, Duke Xian (r. 676–651 BCE), who had centralized the state, killed off relatives who might threaten his authority, conquered sixteen smaller states, and even absorbed some Rong and Di peoples to make Jin much more powerful than it had been previously.[23] When he assisted King Xiang in a succession struggle in 635 BCE, Xiang awarded Jin with strategically valuable territory near Chengzhou.
Duke Wen of Jin then used his growing power to coordinate a military response with Qi, Qin, and Song against Chu, which had begun encroaching northward after the death of Duke Huán of Qi. With a decisive Chu loss at the Battle of Chengpu (632 BCE), Duke Wen's loyalty to the Zhou king was rewarded at an interstate conference when King Xīang awarded him the title of bà.[21]
After the death of Duke Wen in 628 BCE, a growing tension manifested in interstate violence that turned smaller states, particularly those at the border between Jin and Chu, into sites of constant warfare; Qi and Qin also engaged in numerous interstate skirmishes with Jin or its allies to boost their own power.[24]
Hegemony of Qin (628–621 BCE)
Duke Mu of Qin had ascended the throne in 659 BCE and forged an alliance with Jin by marrying his daughter to Duke Wen. In 624 BCE, he established hegemony over the western Rong barbarians and became the most powerful lord of the time. However he did not chair any alliance with other states nor was he officially recognized as hegemon by the king. Therefore, not all sources accept him as one of the Five Hegemons.
Hegemony of Chu (613–591 BCE)
King Zhuang of Chu expanded the borders of Chu well north of the Yangtze River, threatening the Central States in modern Henan. At one point the Chu forces advanced to just outside the royal capital of Zhou, upon which King Zhuang sent a messenger to ask how heavy and bulky the Nine Cauldrons were; implying he might soon arrange to have them moved to his own capital. In the end the Zhou capital was spared, and Chu shifted focus to harassing the nearby state of Zheng. The once-hegemon state of Jin intervened to rescue Zheng from the Chu invaders but were resolutely defeated, which marks the ascension of Chu as the dominant state of the time.[25]
Despite his de facto hegemony, King Zhuang's self-proclaimed title of "king" was never recognized by the Zhou states. In the Spring and Autumn Annals he is defiantly referred to by the Chu ruler's original title "viscount" (the second-lowest noble rank), even at a time when he dominated most of south China. Later historians however always include him as one of the Five Hegemons.
Late Spring and Autumn (591–453 BCE)
The Six Ministers (588 BCE)
In addition to interstate conflict, internal conflicts between state leaders and local aristocrats also occurred. Eventually the dukes of Lu, Jin, Zheng, Wey and Qi would all become figureheads to powerful aristocratic families.[26]
In the case of Jin, the shift happened in 588 BCE when the army was split into six independent divisions, each dominated by a separate noble family: the Zhao, Wei, Han, Fan, Zhi and Zhongxing. The heads of the six families were conferred the titles of viscounts and made ministers,[27] each heading one of the six departments of Zhou Dynasty government.[28] From this point on, historians refer to "The Six Ministers" as the true power brokers of Jin.
The same happened to Lu in 562 BCE, when the Three Huan divided the army into three parts and established their own separate spheres of influence. The heads of the three families were always among the department heads of Lu.
Rise of Wu (584 BCE)
Wu was a "barbarian" state in modern Jiangsu, where the inhabitants sported short hair and tattoos. Although legend ascribed a Chinese origin to the ruling dynasty, Wu did not participate in the politics and wars of China until the last third of the Spring and Autumn period.
Their first documented interaction with the Spring and Autumn states was in 584 BCE, when a Wu force attacked the small border state of Tan, causing some alarm in the various Chinese courts. Jin was quick to dispatch an ambassador to the court of the Wu king, Shoumeng. Jin promised to supply Wu with modern military technology and training in exchange for an alliance against Chu, a neighbour of Wu and Jin's nemesis in the struggle for hegemony. King Shoumeng accepted the offer, and Wu would continue to harass Chu for years to come.[29]
Attempts at peace (579 BCE)
After a period of increasingly exhausting warfare, Qi, Qin, Jin and Chu met at a disarmament conference in 579 BCE and agreed to declare a truce to limit their military strength.[30] This peace didn't last very long and it soon became apparent that the bà role had become outdated; the four major states had each acquired their own spheres of control and the notion of protecting Zhou territory had become less cogent as the control over (and the resulting cultural assimilation of) non-Zhou peoples, as well as Chu's control of some Zhou areas, further blurred an already vague distinction between Zhou and non-Zhou.[31]
In addition, new aristocratic houses were founded with loyalties to powerful states, rather than directly to the Zhou kings, though this process slowed down by the end of the seventh century BCE, possibly because territory available for expansion had been largely exhausted.[31] The Zhou kings had also lost much of their prestige[26] so that, when Duke Dao of Jin (r. 572–558 BCE) was recognized as bà, it carried much less meaning than it had before.
Hegemony of Wu (506–496 BCE)
In 506 BCE King Helü ascended the throne of Wu. With the help of Wu Zixu and Sun Zi, the author of The Art of War, he launched major offensives against the state of Chu. They prevailed in five battles, one of which was the Battle of Boju, and conquered the capital Ying. However, Chu managed to ask the state of Qin for help, and after being defeated by Qin, the vanguard general of Wu troops, Fugai, a younger brother of Helü, led a rebellion. After beating Fugai, Helü was forced to leave Chu. Fugai later retired to Chu and settled there. King Helü died during an invasion of Yue in 496 BCE. Some sources list him as one of the Five Hegemons.
He was succeeded by his son King Fuchai of Wu, who nearly destroyed the Yue state, imprisoning King Goujian of Yue. Subsequently, Fuchai defeated Qi and extended Wu influence into central China.
In 499 BCE, the philosopher Confucius was made acting prime minister of Lu. He is traditionally (if improbably) considered the author or editor of the Spring and Autumn annals, from which much of the information for this period is drawn. After only two years he was forced to resign and spent many years wandering between different states before returning to Lu. After returning to Lu he did not resume a political career, preferring to teach. Tradition holds that it was in this time he edited or wrote the Five Classics, including the Spring and Autumn.
Hegemony of Yue (496–465 BCE)
In 482 BCE, King Fuchai of Wu held an interstate conference to solidify his power base, but Yue captured the Wu capital. Fuchai rushed back but was besieged and died when the city fell in 473 BCE. Yue then concentrated on weaker neighbouring states, rather than the great powers to the north.[32] With help from Wu's enemy Chu, Yue was able to be victorious after several decades of conflict. King Goujian destroyed and annexed Wu in 473 BCE, after which he was recognized as hegemon.
The Zuo Commentary, Guoyu and Shiji provide almost no information about Goujian's subsequent reign or policies. What little is said is told from the perspective of other states, such as Duke Ai of Lu trying to enlist Yue's help in a coup against the Three Huan. Sima Qian notes that Goujian reigned on until his death, and that afterwards his descendants—for whom no biographical information is given—continued to rule for six generations before the state was finally absorbed into Chu during the Warring States period.
Partition of Jin
After the great age of Jin power, the Jin dukes began to lose authority over their nobles. A full-scale civil war between 497 and 453 BCE ended with the elimination of most noble lines; the remaining aristocratic families divided Jin into three successor states: Han, Wei, and Zhao.[32] This is the last event recorded in the Zuo Commentary.
With the absorption of most of the smaller states in the era, this partitioning left seven major states in the Zhou world: the three fragments of Jin, the three remaining great powers of Qin, Chu and Qi, and the weaker state of Yan near modern Beijing. The partition of Jin, along with the Usurpation of Qi by Tian, marks the beginning of the Warring States period.
List of states
A total of 148 states are mentioned in the chronicles for this period.[8]
| Name | Chinese | Capital | Location[33] | Established | Dissolved |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba | 巴 | Yicheng (夷城) | Changyang County, Hubei | King Wu's reign | 316 BCE: to Qin |
| Pingdu (平都) | Fengdu County, Chongqing | ||||
| Zhi (枳) | Fuling District, Chongqing | ||||
| Jiangzhou (江州) | Chongqing | ||||
| Dianjiang (垫江) | Hechuan District, Chongqing | ||||
| Langzhong (閬中) | Langzhong, Sichuan | ||||
| Bi | 畢 | Bi | unknown | King Wu's reign | unknown |
| Biyang, Fuyang | 偪陽 or 傅陽 | Biyang | Yicheng District, Zaozhuang, Shandong | unknown | 563 BCE: to Song |
| Cai | 蔡 | Shangcai (上蔡) | Shangcai County, Henan | King Wu's reign | 447 BCE: to Chu |
| Xincai (新蔡) | Xincai County, Henan | ||||
| Xiacai (下蔡) | Fengtai County, Anhui | ||||
| Cao | 曹 | Taoqiu (陶丘) | Dingtao District, Heze, Shandong | King Wu's reign | 487 BCE: to Song |
| Chao | 巢 | Chao | Chaohu, Anhui | unknown | c. 518 BCE: to Wu |
| Chen | 陳 | Wanqiu (宛丘) | Huaiyang District, Zhoukou, Henan | King Wu's reign | 479 BCE: to Chu |
| Cheng | 郕 or 成 | Cheng | Ningyang County, Shandong | King Wu's reign | 408 BCE: to Qi |
| Chu | 楚 or 荊 | Danyang (丹陽) | Xichuan County, Henan | King Cheng's reign | 223 BCE: to Qin |
| Ying (郢) | Jingzhou, Hubei | ||||
| Chen (陳) | Huaiyang District, Zhoukou, Henan | ||||
| Shouchun (壽春) | Shou County, Anhui | ||||
| Chunyu, Zhou | 淳于 or 州 | Zhou (州) | Anqiu, Shandong | King Wu's reign | 706 BCE: to Qi (杞) |
| Dai | 戴 | Dai | Minquan County, Henan | unknown | 713 BCE: to Zheng |
| Dao | 道 | Dao | unknown | unknown | unknown |
| Deng | 鄧 | Deng | Dengzhou, Henan | before Western Zhou | 678 BCE: to Chu |
| E | 鄂 | E | Nanyang, Henan | before Western Zhou | 863 BCE: to Chu |
| Fan | 番 or 潘 or 鄱 | Fan | Gushi County, Henan | unknown | 504 BCE: to Wu |
| Fan | 凡 | Fan | Huixian, Henan | unknown | unknown |
| Fan | 樊 | Fan | Chang'an District, Xi'an, Shaanxi | King Xuan's reign | 635 BCE: to Jin |
| Yang (陽) | Jiyuan, Henan | ||||
| Gan | 甘 | Gan | Yuanyang County, Henan | King Xiang's reign | unknown |
| Gao | 郜 | Gao | Chengwu County, Shandong | King Wu's reign | 8th century BCE: to Song |
| Ge | 葛 | Ge | Ningling County, Henan | before Western Zhou | unknown |
| Gong | 鞏 | Gong | Xiaoyi, Henan | unknown | 516 BCE: to Jin |
| Gong | 共 | Gong | Huixian, Henan | unknown | mid-7th century BCE: to Wey |
| Guang | 光 | Guang | Guangshan County, Henan | before Western Zhou | 650 BCE: to Chu |
| Guo | 郭 | Guo | Liaocheng, Shandong | unknown | 670 BCE: to Qi |
| Eastern Guo | 東虢 | Zhi (制) | Xingyang, Henan | King Wu's reign | 767 BCE: to Zheng |
| Western Guo | 西虢 | Yongdi (雍地) | Baoji, Shaanxi | King Wu's reign | 687 BCE: to Jin |
| Shangyang (上陽) | Shan County, Henan | ||||
| Hu | 胡 | Hu | Wuyang County, Henan | unknown | 763 BCE: to Zheng |
| Hua | 滑 | Hua | Minquan County, Henan | unknown | 627 BCE: to Qin |
| Fei (費) | Yanshi, Henan | ||||
| 黃 | Huang | Huangchuan County, Henan | unknown | 648 BCE: to Chu | |
| Hui | 鄶 or 會 or 檜 | Hui | Xinzheng, Henan | unknown | 769 BCE: to Zheng |
| Ji | 紀 | Ji | Shouguang, Shandong | unknown | 690 BCE: to Qi |
| Ji | 極 | Ji | Shan County, Shandong | unknown | 721 BCE: to Lu |
| Ji | 祭 | Ji | Changyuan, Henan | King Wu's reign | 750 BCE: to Zheng |
| Guan (管) | Zhengzhou, Henan | ||||
| Jiang | 江 | Jiang | Xi County, Henan | unknown | 623 BCE: to Chu |
| Jiang | 蔣 | Jiang | Gushi County, Henan | King Cheng's reign | 617 BCE: to Chu |
| Jie | 介 | Jie | Jiaozhou, Shandong | unknown | unknown: to Qi |
| Jin | 晉 | Tang (唐), or Jin | Yicheng County, Shanxi | King Cheng's reign | 376 BCE: to Han and Zhao |
| Quwo (曲沃) | Wenxi County, Shanxi | ||||
| Jiang (絳), or Yi (翼) | Yicheng County, Shanxi | ||||
| Xintian (新田), or Xinjiang (新絳) | Houma, Shanxi | ||||
| Ju | 莒 | Jiegen (介根) | Jiaozhou, Shandong | King Wu's reign | 431 BCE: to Chu |
| Ju | Ju County, Shandong | ||||
| Lai | 萊 | Changle (昌樂) | Changle County, Shandong | before Western Zhou | 567 BCE: to Qi |
| Lan | 濫 | Lan | Tengzhou, Shandong | 781 BCE | 521 BCE: to Lu |
| Liang | 梁 | Liang | Hancheng, Shaanxi | unknown | 641 BCE: to Qin |
| Liao, Miu | 蓼 or 繆 | Liao | Gushi County, Henan | unknown | 622 BCE: to Chu |
| Liu | 劉 | Liu | Yanshi, Henan | 592 BCE | c. 5th century BCE: to Zhou dynasty |
| Lu | 魯 | Lu | Lushan County, Henan | King Cheng's reign | 256 BCE: to Chu |
| Yancheng (奄城) | Qufu, Shandong | ||||
| Qufu (曲阜) | Qufu, Shandong | ||||
| Lü | 呂 | Lü | Nanyang, Henan | unknown' | 688 BCE: to Chu |
| Mao | 毛 | Mao | Qishan County, Shaanxi | King Wu's reign | 516 BCE: to Qin |
| Mao | 茅 | Mao | Jinxiang County, Shandong | King Cheng's reign | 6th century BCE: to Zou |
| Ni, Xiaozhu | 郳 or 小邾 | Ni | Shanting District, Zaozhuang, Shandong | King Cheng's reign | 335 BCE: to Chu |
| Qi | 齊 | Yingqiu (營丘), or Linzi (臨淄) | Linzi District, Zibo, Shandong | King Wu's reign | 221 BCE: to Qin |
| Qi | 杞 | Qi | Qi County, Henan | before Western Zhou | 445 BCE: to Chu |
| Pingyang (平陽) | Xintai, Shandong | ||||
| Yuanling (緣陵) | Changle County, Shandong | ||||
| Chunyu (淳于) | Anqiu, Shandong | ||||
| Qin | 秦 | Qin | Qingshui County, Gansu | King Xiao's reign | 206 BCE: to Western Chu |
| Qian (汧) | Long County, Shaanxi | ||||
| Pingyang (平陽) | Mei County, Shaanxi | ||||
| Yong (雍) | Fengxiang County, Shaanxi | ||||
| Yueyang (櫟陽) | Yanliang District, Xi'an, Shaanxi | ||||
| Xianyang (咸阳) | Xianyang, Shaanxi | ||||
| Quan | 權 | Quan | Jingmen, Hubei | unknown | 704 BCE: to Chu |
| Ren | 任 | Ren | Weishan County, Shandong | unknown | Warring States period |
| Ruo | 鄀 | Shangruo (上鄀) or Shangmi (商密) | Xichuan County, Henan | unknown | unknown |
| Xiaruo (下鄀) | Yicheng, Hubei | ||||
| Shao | 召 or 邵 | Shao | Qishan County, Shaanxi | King Wu's reign | 513 BCE: to Zhou dynasty |
| Shan, Tan | 單 or 檀 | Shan | Mengjin County, Henan | King Cheng's reign | unknown |
| Shen, Xie | 申 or 謝 | Shen | Nanyang, Henan | King Xuan's reign | 688 – 680 BCE: to Chu |
| Shen | 沈 | Shen | Linquan County, Anhui | King Cheng's reign | 506 BCE: to Cai |
| Shu | 蜀 | unknown | unknown | unknown | 316 BCE: to Qin |
| Song | 宋 | Shangqiu (商丘) | Shangqiu, Henan | King Cheng's reign | 286 BCE: to Qi |
| Su | 宿 | Su | Dongping County, Shandong | unknown | 7th century BCE: to Song |
| Sui | 遂 | Sui | Ningyang County, Shandong | before Western Zhou | 681 BCE: to Qi |
| Tan | 郯 | Tan | Tancheng County, Shandong | unknown | 414 BCE: to Yue |
| Tan | 譚 | Tan | Zhangqiu, Shandong | c. 1046 BCE | 684 BCE: to Qi |
| Teng | 滕 | Teng | Teng County, Shandong | King Wu's reign | 297 BCE: to Song |
| Wangshu | 王叔 | Wangshu | Mengjin County, Henan | King Xiang of Zhou | 563 BCE: to Zhou dynasty |
| Wei (Wey) | 衛 | Zhaoge (朝歌) | Qi County, Henan | King Cheng's reign | 209 BCE: to Qin |
| Cao (曹) | Hua County, Henan | ||||
| Chuqiu (楚丘) | Hua County, Henan | ||||
| Diqiu (帝丘) | Puyang County, Henan | ||||
| Yewang (野王) | Qinyang, Henan | ||||
| Wen | 溫 | Wen | Wen County, Henan | King Wu's reign | 650 BCE: to Beidi |
| Wu | 吳 | Wu, or Gusu (姑蘇) | Suzhou, Jiangsu | unknown | 473 BCE: to Yue |
| Xi | 息 | Xi | Xi County, Henan | unknown | 684 – 680 BCE: to Chu |
| Xian | 弦 | Xian | Huanggang, Hubei | unknown | 655 BCE: to Chu |
| Xiang | 向 | Xiang | Ju County, Shandong | unknown | 721 BCE: to Ju |
| 邢 | Xingtai, Hebei | King Cheng's reign | 632 BCE: to Wey | ||
| Yiyi (夷儀) | Liaocheng, Shandong | ||||
| Xu | 徐 | Xu | Tancheng County, Shandong | before Western Zhou | 512 BCE: to Wu |
| Xu | 許 or 鄦 | Xu | Xuchang, Henan | King Wu's reign | c. 5th century BCE: to Chu |
| Ye (葉) | Ye County, Henan | ||||
| Yi (夷) or Chengfu (城父) | Bozhou, Anhui | ||||
| Xi (析) | Xixia County, Henan | ||||
| Rongcheng (容城) | Lushan County, Henan | ||||
| Xue, Pi | 薛 or 邳 | Xue | Tengzhou, Shandong | before Western Zhou | 418 BCE: to Qi |
| Xiapi (下邳) | Pi County, Jiangsu | ||||
| Shangpi (上邳) | Pi County, Jiangsu | ||||
| Xuqu | 須句 | Xuqu | Dongping County, Shandong | unknown | 620 BCE: to Lu |
| Yan | 燕 | Bo (亳), or Shengju (聖聚) | Fangshan District, Beijing | King Wu's reign | 222 BCE: to Qin |
| Ji (薊) | Beijing | ||||
| Southern Yan | 南燕 | Yan | Yanjin County, Henan | unknown | unknown |
| Yan | 鄢 | Yan | Yanling County, Henan | King Wu's reign | 769 BCE: to Zheng |
| Yang | 陽 | Yang | Yinan County, Shandong | unknown | 660 BCE: to Qi |
| Yin | 尹 | Yin | Xin'an County, Henan | King Xuan's reign | unknown |
| Ying | 應 | Ying | Pingdingshan, Henan | King Cheng's reign | 646 BCE: to Chu |
| Yu | 邘 or 于 | Yu | Qinyang, Henan | King Wu's reign | unknown |
| Yu | 鄅 | Yu | Linyi, Shandong | unknown | 524 BCE: to Lu |
| Yuan | 原 | Yuan | Jiyuan, Henan | King Wu's reign | 635 BCE: to Jin |
| Yue | 越 | Kuaiji (會稽) | Shaoxing, Zhejiang | unknown | 306 BCE: to Chu |
| Langya (琅邪) | Jiaonan, Shandong | ||||
| Wu (吳) | Suzhou, Jiangsu | ||||
| Zeng, Sui | 曾 or 隨 | Sui | Suizhou, Hubei | unknown | unknown: to Chu |
| Zeng | 鄫 | Zeng | Fangcheng County, Henan | before Western Zhou | 567 BCE: to Ju |
| Zhan | 詹 | unknown | unknown | 827 BCE | unknown |
| Zhang | 鄣 | Zhang | Dongping County, Shandong | early Western Zhou | 664 BCE: to Qi |
| Zheng | 鄭 | Zheng | Hua County, Shaanxi | 806 BCE | 375 BCE: to Han |
| Xinzheng (新鄭) | Xinzheng, Henan | ||||
| Zhongshan | 中山 | Gu (顧) | Dingzhou, Hebei | 506 BCE | 296 BCE: to Zhao |
| Lingshou (靈壽) | Lingshou County, Hebei | ||||
| Zhou | 周 | Zhou | Fengxiang County, Shaanxi | King Wu's reign | unknown |
| Zhoulai | 州來 | Zhoulai | Fengtai County, Anhui | 8th century BCE | 528 BCE: to Chu |
| Zhu | 祝 | Zhu | Changqing District, Jinan, Shandong | King Wu's reign | 768 BCE: to Qi |
| Zhu | 鑄 | Zhu | Feicheng, Shandong | King Wu's reign | unknown: to Qi |
| Zhuan | 鄟 | Zhuan | Tancheng, Shandong | unknown | 585 BCE: to Lu |
| Zhuanyu | 顓臾 | Zhuanyu | Pingyi County, Shandong | King Wu's reign | unknown |
| Zou, Zhu | 鄒 or 邾 | Zhu (邾) | Qufu, Shandong | King Wu's reign | 4th century BCE: to Chu |
| Zou (鄒) | Zoucheng, Shandong | ||||
| Key: | |||||
| Hegemon | |||||
| Note: Capitals are listed in chronological order. | |||||
Important figures

The Five Hegemons (春秋五霸):
Traditional history lists five hegemons during the Spring and Autumn period:[34]
Alternatively:
Bureaucrats or Officers
- Guan Zhong, advisor of Duke Huan of Qi
- Baili Xi, prime minister of Qin.
- Wu Zixu, (Wu Yun), Duke of Shen and important adviser of King Helü
- Bo Pi, bureaucrat under King Helü who played an important diplomatic role in Wu-Yue relations.
- Fan Li and Wen Zhong, two advisors of King Goujian of Yue in his war against Wu
- Zi Chan, leader of self-strengthening movements in Zheng
Influential scholars
- Confucius or Kongzi, leading figure in Confucianism
- Lao-tse or Laozi, teacher of Taoism
- Mo-tse, Mozi, or Micius, founder of Mohism
- Sun Tzu or Sunzi, author of The Art of War
Other people
Interstate relations
Ancient sources such as the Zuo Zhuan and the eponymous Chunqiu record the various diplomatic activities, such as court visits paid by one ruler to another (Chinese: 朝; pinyin: cháo), meetings of officials or nobles of different states (simplified Chinese: 会; traditional Chinese: 會; pinyin: huì), missions of friendly inquiries sent by the ruler of one state to another (Chinese: 聘; pinyin: pìn), emissaries sent from one state to another (Chinese: 使; pinyin: shǐ), and hunting parties attended by representatives of different states (Chinese: 狩; pinyin: shou).
Because of Chu's non-Zhou origin, the state was considered semi-barbarian and its rulers—beginning with King Wu in 704 BCE—proclaimed themselves kings in their own right. Chu intrusion into Zhou territory was checked several times by the other states, particularly in the major battles of Chengpu (632 BCE), Bi (595 BCE) and Yanling (575 BCE), which restored the states of Chen and Cai.
Nobility
King Wu abolished the Shang dynasty title "emperor" (di), making the king the highest office of the Zhou dynasty.
Below the king were five ranks of vassals, which from top to bottom rank were:
- duke – gōng 公(爵)
- marquis or marquess – hóu 侯(爵)
- count or earl – bó 伯(爵)
- viscount – zǐ 子(爵)
- baron – nán 男(爵)
The ranks had been assigned by King Wu upon the foundation of the dynasty and were usually not revised to reflect changing levels of military strength. In the Spring and Autumn Period this led to contradictory situations such as the relatively insignificant state of Song being a duchy while a great power like Chu was only a viscounty.
Literature
Some version of the Five Classics existed in Spring and Autumn period, as characters in the Zuo Commentary and Analects frequently quote the Book of Poetry and Book of Documents. On the other hand, the Zuo Commentary depicts some characters actually composing poems that would later be included in the received text of the Book of Poetry. In the Analects there are frequent references to "The Rites",[35] but as Classical Chinese does not distinguish book titles from regular nouns it is not possible to know if what is meant is the Etiquette and Ceremonial (known then as the Book of Rites) or just the concept of ritual in general. The existence of the Book of Changes on the other hand is well-attested in the Zuo Commentary, as multiple characters use it for divination and correctly quote the received text.
Sima Qian claims that it was Confucius who, towards the close of the Spring and Autumn period, edited the received versions of the Book of Poetry, Book of Documents and Book of Rites, wrote the "Ten Wings" commentary on the Book of Changes and wrote the entirety of the Spring and Autumn Annals.[36] This was long the predominant opinion in China, but modern scholarship considers it unlikely that all five classics could be the product of one man.
While many philosophers such as Lao Zi and Sun Zi were active in the Spring and Autumn period, their ideas were probably not put into writing until the following Warring States period.
Religion
While sources such as the Book of Poetry contain passing references to "The Emperor Above" (Shang Di), there is no proper mythology around supernatural entities preserved in the Confucian Classics. The mythology is instead focused around the founders of the dynasty, kings Wen and Wu, who were worshipped as gods.
The various states also worshipped their respective founders as local patron deities. As such the rulers of Qi worshipped Yu the Great and Song worshipped Tang long after the Xia and Shang dynasties had ceased to exist on a national level.
Notes
- The Partition of Jin, the watershed between the Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods took several decades, thus there is some debate between scholars as to the exact date. 481 BCE, 475 BCE, and 468 BCE are other common dates selected by historians.[1]
References
Citations
- Kiser & Cai 2003.
- Hsu 1990, p. 547.
- Chinn 2007, p. 43.
- Hsu (1990:546)
- Higham (2004:412)
- Shaughnessy (1990:350)
- Lewis (2000:359, 363)
- Hsu (1999:567)
- Lewis 2000, p. 365.
- Hsu 1990, pp. 549–50.
- Hsu 1999, pp. 568, 570.
- Lewis 2000, p. 366.
- Hsu 1990, p. 567.
- Lewis 2000, p. 367.
- Shi Ji, chapter 4
- Pines (2002:3)
- Hsu 1999, pp. 553–54.
- Hsu 1999, p. 555.
- Lewis 2000, pp. 366, 369.
- Hsu 1999, pp. 555–56.
- Hsu 1990, p. 560.
- Zuo Zhuan; Duke Xi years 18–23.
- Hsu 1990, p. 559.
- Hsu 1990, pp. 560–61.
- Zuo Zhuan, Duke Xuan
- Pines 2002, p. 4.
- Shi Ji chapter 39
- Zhou Li
- Zuo Commentary, Duke Cheng year 8
- Hsu 1999, p. 561.
- Hsu 1999, p. 562.
- Hui 2004, p. 186.
- Tan, Qixiang (1996). The Historical Atlas of China, Volume I. Beijing: China Cartographic Publishing House. pp. 22–30. ISBN 9787503118401.
- Ye (2007:34–35)
- E.g. Analects 17:10
- Shi Ji, chapter 17
Sources
- Blakeley, Barry B (1977), "Functional disparities in the socio-political traditions of Spring and Autumn China: Part I: Lu and Ch'i", Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient, 20 (2): 208–43, doi:10.2307/3631778
- Chinn, Ann-ping (2007), The Authentic Confucius, Scribner, ISBN 0-7432-4618-7
- Higham, Charles (2004), Encyclopedia of Ancient Asian Civilizations, Infobase
- Hsu, Cho-yun (1990), "The Spring and Autumn Period", in Loewe, Michael; Shaughnessy, Edward L (eds.), The Cambridge history of ancient China: from the origins of civilization to 221 BC, Cambridge University Press, pp. 545–86
- Hui, Victoria Tin-bor (2004), "Toward a dynamic theory of international politics: Insights from comparing ancient China and early modern Europe", International Organization, 58 (1): 175–205, doi:10.1017/s0020818304581067
- Kiser, Edgar; Cai, Young (2003), "War and bureaucratization in Qin China: Exploring an anomalous case", American Sociological Review, 68 (4): 511–39, doi:10.2307/1519737
- Lewis, Mark Edward (2000), "The City-State in Spring-and-Autumn China", in Hansen, Mogens Herman (ed.), A Comparative Study of Thirty City-State Cultures: An Investigation, 21, Copenhagen: The Royal Danish Society of Arts and Letters, pp. 359–74
- Pines, Yuri (2002), Foundations of Confucian Thought: Intellectual Life in the Chunqiu Period (722–453 BCE), University of Hawaii Press
- Shaughnessy, Edward L (1990), "Western Zhou History", in Loewe, Michael; Shaughnessy, Edward L (eds.), The Cambridge history of ancient China: from the origins of civilization to 221 BC, Cambridge University Press, pp. 292–351
- Ye, L (2007), China: five thousand years of history and civilization, Hong Kong: University of Hong Kong Press
Further reading
- Ebrey, Patricia Buckley (1999). The Cambridge Illustrated History of China. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-66991-X (paperback).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Spring and Autumn Period. |
- "Rulers of the states of Zhou", Dynasty, C text – linked to their occurrences in classical Chinese texts.
 Media related to Art of the Spring and Autumn Period at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Art of the Spring and Autumn Period at Wikimedia Commons