Qara Khitai
The Qara Khitai or Kara Khitai (alternatively known as "Black Khitan" or "Black Cathay",[6] Mongolian: Хар Хятан; 1124[note 1]–1218), also known as the Western Liao (traditional Chinese: 西遼; simplified Chinese: 西辽; pinyin: Xī Liáo), officially the Great Liao (大遼; 大辽; Dà Liáo),[7][8] was a sinicized[9][10][11] empire in Central Asia, a successor state to the Liao dynasty ruled by the Khitan Yelü clan. The dynasty was founded by Yelü Dashi (Emperor Dezong of Liao), who led the remnants of the Liao dynasts from Manchuria to Central Asia after fleeing from the Jin dynasty conquest of their homeland in the north and northeast of modern-day China. The empire was usurped by the Naimans under Kuchlug in 1211; traditional Chinese, Persian, and Arab sources consider the usurpation to be the end of the dynasty,[12] even though the empire would not fall until the Mongol conquest in 1218. The Qara Khitai is considered by Chinese historians to be a legitimate dynasty of China, as is the case for the preceding Liao dynasty.[13]
Qara Khitai (喀喇契丹) Western Liao (西遼) 大遼 (Great Liao) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1124–1218 | |||||||||||||||
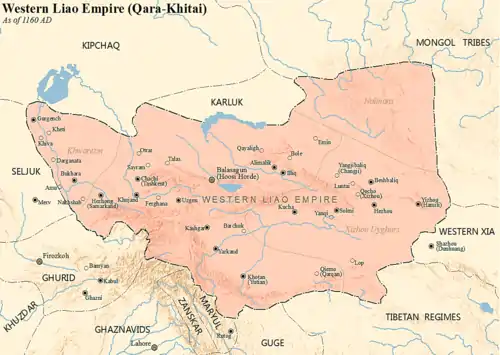 Qara Khitai c. 1160 | |||||||||||||||
| Status | Sinicized Khitan empire in Central Asia | ||||||||||||||
| Capital | Balasagun | ||||||||||||||
| Common languages |
| ||||||||||||||
| Religion | |||||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Kara Khitan | ||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||||||
• 1124–1143 | Emperor Dezong | ||||||||||||||
• 1144–1150 | Empress Gantian (regent) | ||||||||||||||
• 1150–1164 | Emperor Renzong | ||||||||||||||
• 1164–1178 | Empress Dowager Chengtian (regent) | ||||||||||||||
• 1178–1211 | Yelü Zhilugu | ||||||||||||||
• 1211–1218 | Kuchlug | ||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||||||||
• Fall of Liao dynasty | 1125 | ||||||||||||||
• Yelü Dashi proclaims himself king | 1124 | ||||||||||||||
• Yelü Dashi adopts the title of Gurkhan | 1132 | ||||||||||||||
• Yelü Dashi captures Balasagun and establishes capital | 1134 | ||||||||||||||
• Kuchlug usurps power | 1211 | ||||||||||||||
• Kuchlug executed by Mongols | 1218 | ||||||||||||||
• All former territories fully absorbed into Mongol Empire | 1220 | ||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||
| 1130 est.[4] | 1,000,000 km2 (390,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| 1210 est.[5] | 1,500,000 km2 (580,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| Currency | cash coins | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Today part of | China Kazakhstan Kyrgyzstan Mongolia Tajikistan Uzbekistan | ||||||||||||||
Names
The Qara Khitai took on trappings of a Chinese state and inherited the dynastic name "Great Liao" (大遼).[8][14][15] Hence, Chinese, Korean, Japanese and Vietnamese historians generally refer to the empire as the "Western Liao" (西遼), emphasizing its continuation from the Liao dynasty.
The name "Qara Khitai" (喀喇契丹; commonly used by Central Asian tribes to refer to the dynasty) is also commonly used in Western scholarly works. The phrase is often translated as the Black Khitans in Turkish, but its original meaning is unclear today.[16] In Mongolian, "Kara-Khitan" is rendered "Хар Хятан" (Khar Kidan). Since no direct records from the empire survive today, the only surviving historical records about the empire come from foreign sources.
Black Khitans (黑契丹) has also been seen used in Chinese. "Qara," which literally means "black," corresponds with the Liao's dynastic color black and its dynastic element Water, according to the theory of Five Elements (wuxing).[17] The Jurchens referred to the empire as Dashi or Dashi Linya (after its founder), to reduce any claims the empire may have had to the old territories of the Liao dynasty. Muslim historians initially referred to the state simply as Khitay or Khitai; they may have adopted this form of "Khitan" via the Uyghurs of Kocho in whose language the final -n or -ń became -y.[18] Only after the Mongol conquest did the state begin to be referred to in the Muslim world as the Kara-Khitai or Qara-Khitai.[19] Qara Khitai or Khitan is the origin of "Cathay", a foreign name for China.
History
 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANCIENT | ||||||||
| Neolithic c. 8500 – c. 2070 BCE | ||||||||
| Xia c. 2070 – c. 1600 BCE | ||||||||
| Shang c. 1600 – c. 1046 BCE | ||||||||
| Zhou c. 1046 – 256 BCE | ||||||||
| Western Zhou | ||||||||
| Eastern Zhou | ||||||||
| Spring and Autumn | ||||||||
| Warring States | ||||||||
| IMPERIAL | ||||||||
| Qin 221–207 BCE | ||||||||
| Han 202 BCE – 220 CE | ||||||||
| Western Han | ||||||||
| Xin | ||||||||
| Eastern Han | ||||||||
| Three Kingdoms 220–280 | ||||||||
| Wei, Shu and Wu | ||||||||
| Jin 266–420 | ||||||||
| Western Jin | ||||||||
| Eastern Jin | Sixteen Kingdoms | |||||||
| Northern and Southern dynasties 420–589 | ||||||||
| Sui 581–618 | ||||||||
| Tang 618–907 | ||||||||
| (Wu Zhou 690–705) | ||||||||
| Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms 907–979 |
Liao 916–1125 | |||||||
| Song 960–1279 | ||||||||
| Northern Song | Western Xia | |||||||
| Southern Song | Jin | Western Liao | ||||||
| Yuan 1271–1368 | ||||||||
| Ming 1368–1644 | ||||||||
| Qing 1636–1912 | ||||||||
| MODERN | ||||||||
| Republic of China on mainland 1912–1949 | ||||||||
| People's Republic of China 1949–present | ||||||||
| Republic of China on Taiwan 1949–present | ||||||||
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Xinjiang |
 |
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Kyrgyzstan |
 |
Part of a series on the |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History of Kazakhstan | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ancient | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Khanates | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Colonization and post-nomadic period | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Topics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Founding of the Qara Khitai
The Qara Khitai empire was established by Yelü Dashi, who led nomadic Khitans west by way of Mongolia after the collapse of the Liao dynasty. The Jurchens, once vassals of the Khitans, had allied with the Song dynasty and overthrown the Liao. Yelü recruited Khitans and other tribes to form an army, and in 1134 captured Balasagun from the Kara-Khanid Khanate, which marks the start of the Qara Khitai empire in Central Asia. The Khitan forces were soon joined by 10,000 Khitans, who had been subjects of the Kara-Khanid Khanate. The Khitans then conquered Kashgar, Khotan, and Beshbalik. The Khitans defeated the Western Kara-Khanid Khanate at Khujand in 1137, eventually leading to their control over the Fergana Valley. They won the Battle of Qatwan against the Western Kara-Khanids and the Seljuk Empire on September 9, 1141, which allowed the Khitans to gain control over Transoxiana.[2]
Yelü Dashi had originally hoped to recapture northern China from the Jin dynasty and restore the territories once held by the Liao dynasty.[20][21] However, he soon discovered the relative weakness of his empire vis-a-vis the Jin dynasty and gave up the idea[21] after a disastrous attack on the Jin dynasty in 1134.[22] The Western Liao continued to defy Jin supremacy in 1146, and continued sending scouts and small military units against the Jin in 1156, 1177, 1185, 1188. This indicates that for the first 2 generations there remained considerable interest in reconquest.[23]
Yelü Dashi's successors
When Yelü Dashi died his wife, Xiao Tabuyan (1143-1150) became regent for their son. The son, Yelü Yilie, ruled from 1150 to 1163, to be succeeded by his sister, Yelü Pusuwan (1164-1177). She then fell in love with her husband's younger brother, Xiao Fuguzhi. They were executed in 1177 by her husband's father, Xiao Wolila, who then placed his son Yelü Zhilugu (1178–1211) on the throne. The empire was weakened by rebellions and internal wars among its vassals, especially during the latter parts of its history.
During this period the empire contracted in the northeast when in 1175 the Naimans east of the Altai and the Qangli north of Lake Balkhash made a partial submission to the Jurchens. In the west there were many conflicts with Khwarezm involving non-payment of tribute and rival claimants to the throne. Late in the period it expanded far to the south as the Khwarezmian Empire until it was conquered by the Mongols in 1220, two years after the Qara Kitai. In the south the Kara-Khanid vassals were lightly held and engaged in various conflicts with each other, the Qara Kitai, Khwarezm and the Gurids.[24]
Kuchlug's usurpation and end of the Khanate
In 1208, a Naiman prince, Kuchlug, fled his homeland after being defeated by Mongols. Kuchlug was welcomed into the empire of the Qara-Khitans, and was allowed to marry Zhilugu's daughter. However, in 1211, Kuchlug revolted, and later captured Yelü Zhilugu while the latter was hunting. Zhilugu was allowed to remain as the nominal ruler but died two years later, and many historians regarded his death as the end of the Qara-Khitan empire. In 1216, Genghis Khan dispatched his general Jebe to pursue Kuchlug; Kuchlug fled, but in 1218, he was finally captured and decapitated. The Mongols fully conquered the former territories of the Qara-Khitans in 1220.
Aftermath
The Qara Khitais became absorbed into the Mongol Empire; a segment of the Qara-Khitan troops had previously already joined the Mongol army fighting against Kuchlug. Another segment of the Qara-Khitans, in a dynasty founded by Buraq Hajib, survived in Kirman as a vassal of the Mongols, but ceased to exist as an entity during the reign of Öljaitü of the Ilkhanate.[25] The Qara-Khitans were dispersed widely all over Eurasia as part of the Mongol army. In the 14th century, they began to lose their ethnic identity, traces of their presence however may be found as clan names or toponyms from Afghanistan to Moldova. Today a Khitay tribe still lives in northern Kyrgyzstan.[18]
Administration
The Khitans ruled from their capital at Balasagun (in today's Kyrgyzstan), directly controlling the central region of the empire. The rest of their empire consisted of highly autonomous vassalized states, primarily Khwarezm, the Karluks, the Kingdom of Qocho of the Uyghurs, the Kankalis, and the Western, Eastern, and Fergana Kara-Khanids. The late-arriving Naimans also became vassals, before usurping the empire under Kuchlug.
The Khitan rulers adopted many administrative elements from the Liao dynasty, including the use of Confucian administration and imperial trappings. The empire also adopted the title of Gurkhan (universal Khan). The Khitans used the Chinese calendar, maintained Chinese imperial and administrative titles, gave its emperors reign names, used Chinese-styled coins, and sent imperial seals to its vassals.[26] Although most of its administrative titles were derived from Chinese, the empire also adopted local administrative titles, such as tayangyu (Turkic) and vizier.
The Khitans maintained their old customs, even in Central Asia. They remained nomads, adhered to their traditional dress, and maintained the religious practices followed by the Liao dynasty Khitans. The ruling elite tried to maintain the traditional marriages between the Yelü king clan and the Xiao queen clan, and were highly reluctant to allow their princesses to marry outsiders. The Qara-Khitai Khitans followed a mix of Buddhism and traditional Khitan religion, which included fire worship and tribal customs, such as the tradition of sacrificing a gray ox with a white horse. In an innovation unique to the Qara Khitai, the Khitans paid their soldiers salary.
The empire ruled over a diverse population that was quite different from its rulers. The majority of the population was sedentary, although the population suddenly became more nomadic during the end of the empire, due to the influx of Naimans. The majority of their subjects were Muslims, although a significant minority practiced Buddhism and Nestorianism. Although Chinese and Khitan were the primary languages of administration, the empire also administered in Persian and Uyghur.[1]
Association with China
In Chinese historiography, the Qara Khitai is most commonly called the "Western Liao" (西遼) and is considered to be a legitimate Chinese dynasty, as is the case for the Liao dynasty.[13] The history of the Qara Khitai was included in the History of Liao (one of the Twenty-Four Histories), which was compiled officially during the Yuan dynasty by Toqto'a et al.
After the Tang dynasty, non-Han Chinese empires gained prestige by connecting themselves with China, and the Khitan Gurkans used the title of "Chinese emperor",[27][28] and was also called the "Khan of Chīn".[29] The Qara Khitai used the "image of China" to legitimize their rule to the Central Asians. The Chinese emperor, together with the rulers of the Turks, Arabs, India and the Byzantine Romans, were known to Islamic writers as the world's "five great kings".[30] Qara Khitai kept the trappings of a Chinese state, such as Chinese coins, Chinese imperial titles, the Chinese writing system, tablets, seals, and used Chinese products like porcelein, mirrors, jade and other Chinese customs. The adherence to Liao Chinese traditions has been suggested as a reason why the Qara Khitai did not convert to Islam.[31] Despite the Chinese trappings, there were comparatively few Han Chinese among the population of the Qara Khitai.[32] These Han Chinese had lived in Kedun during the Liao dynasty,[33] and in 1124 migrated with the Khitans under Yelü Dashi along with other people of Kedun, such as the Bohai, Jurchen, and Mongol tribes, as well as other Khitans in addition to the Xiao consort clan.[34]
Qara Khitai's rule over the Muslim-majority Central Asia has the effect of reinforcing the view among some Muslim writers that Central Asia was linked to China even though the Tang dynasty had lost control of the region a few hundred years ago. Marwazī wrote that Transoxania was a former part of China,[35] while Fakhr al-Dīn Mubārak Shāh defined China as part of "Turkestan", and the cities of Balāsāghūn and Kashghar were considered part of China.[36]
Legacy
The association of Khitai with China meant that the most enduring trace of the Khitan's power is names that are derived from it, such as Cathay, which is the medieval Latin appellation for China. Names derived from Khitai are still current in modern usage, such as the Russian, Bulgarian, Uzbek and Mongolian names for China.[18] However, the use of the name Khitai to mean "China" or "Chinese" by Turkic speakers within China, such as the Uyghurs, is considered pejorative by the Chinese authorities, who tried to ban it.[37]
Sovereigns of Qara Khitai
| Temple names (廟號 miàohào) | Posthumous names (諡號 shìhào) | Birth Names | Convention | Period of Reign | era names (年號 niánhào) and their according range of years |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Dezong (德宗 Dézōng) | Emperor Tianyou Wulie (天祐武烈帝 Tiānyòu Wǔliè Dì) | Yelü Dashi (耶律大石 Yēlǜ Dàshí or 耶律達實 Yēlǜ Dáshí) 1 | use birth name | 1124–1144 | Yanqing (延慶 Yánqìng) 1124 or 1125–1134 Kangguo (康國 Kāngguó) 1134–1144 |
| Not applicable | Empress Gantian (感天皇后 Gǎntiān Huánghòu) (regent) | Xiao Tabuyan (蕭塔不煙 Xiāo Tǎbùyān) | "Western Liao" + posthumous name | 1144–1150 | Xianqing (咸清 Xiánqīng) 1144–1150 |
| 2. Emperor Renzong (仁宗 Rénzōng) | Too tedious thus not used when referring to this sovereign | Yelü Yilie (耶律夷列 Yēlǜ Yíliè) | "Western Liao" + temple name | 1150–1164 | Shaoxing (紹興 Shàoxīng) or Xuxing (Xùxīng 續興)2 1150–1164 |
| Not applicable | Empress Dowager Chengtian (承天太后 Chéngtiān Tàihòu) (regent) | Yelü Pusuwan (耶律普速完 Yēlǜ Pǔsùwán) | "Western Liao" + posthumous name | 1164–1178 | Chongfu (崇福 Chóngfú) 1164–1178 |
| 3. Did not exist | Mozhu (末主 Mòzhǔ "Last Lord") or Modi (末帝 Mòdì "Last Emperor") | Yelü Zhilugu (耶律直魯古 Yēlǜ Zhílǔgǔ) | use birth name | 1178–1211 | Tianxi (天禧 Tiānxī) 1178–1218 |
| Did not exist | Did not exist | Kuchlug (Ch. 屈出律 Qūchūlǜ) | use birth name | 1211–1218 | |
| 1 "Dashi" might be the Chinese title "Taishi", meaning "vizier"; or, it could mean "Stone" in Turkish, as the Chinese transliteration suggests. 2 Recently discovered Western Liao coins have the era name "Xuxing", suggesting that the era name "Shaoxing" recorded in Chinese sources may be incorrect.[38] | |||||
Gallery
 The Khitans in the 10th century, forebears of the Kara-Khitans.
The Khitans in the 10th century, forebears of the Kara-Khitans. European maps showed the land of "Kara-Kithay" somewhere in Central Asia centuries after the collapse of the Qara Khitai. This 1610 map by Jodocus Hondius places it north of Tashkent.
European maps showed the land of "Kara-Kithay" somewhere in Central Asia centuries after the collapse of the Qara Khitai. This 1610 map by Jodocus Hondius places it north of Tashkent. Portrait of a Kara-Khitan man.
Portrait of a Kara-Khitan man.
See also
Notes
- 1124 was the year in which Yelü Dashi proclaimed himself king, while still in Mongolia.
References
Citations
- Biran 2005, p. 94.
- Grousset 1991, p. 165.
- Pozzi, Janhunen & Weiers 2006, p. 114.
- Taagepera, Rein (September 1997). "Expansion and Contraction Patterns of Large Polities: Context for Russia". International Studies Quarterly. 41 (3): 497. doi:10.1111/0020-8833.00053. JSTOR 2600793.
- Turchin, Peter; Adams, Jonathan M.; Hall, Thomas D. (December 2006). "East-West Orientation of Historical Empires". Journal of World-Systems Research. 12 (2): 222. ISSN 1076-156X. Retrieved 16 September 2016.
- Lamb, Harold (1927). Genghis Khan: Emperor of All Men. International Collectors Library. p. 53.
- Morgan & Stewart 2017, p. 57.
- 中国历史大辞典:辽夏金元史 (in Chinese). 1986. p. 131.
- Sicker, Martin (2000). The Islamic World in Ascendancy: From the Arab Conquests to the Siege of Vienna. p. 57. ISBN 9780275968922.
- Grousset, René (1970). The Empire of the Steppes: A History of Central Asia. p. 166. ISBN 9780813513041.
- Komaroff, Linda (2006). Beyond the Legacy of Genghis Khan. p. 77. ISBN 9789047418573.
- Biran 2005, p. 2.
- Biran 2005, p. 93.
- Morgan & Stewart 2017, pp. 56–57.
- Schouenborg, Laust (2016). International Institutions in World History: Divorcing International Relations Theory from the State and Stage Models. p. 133. ISBN 9781315409887.
- Biran 2005, pp. 216–217.
- Chen, Yuan Julian (2014). "Legitimation Discourse and the Theory of the Five Elements in Imperial China". Journal of Song-Yuan Studies. 44 (44): 325–364. doi:10.1353/sys.2014.0000. S2CID 147099574.
- Sinor, D. (1998), "Chapter 11 – The Kitan and the Kara Kitay" (PDF), in Asimov, M.S.; Bosworth, C.E. (eds.), History of Civilisations of Central Asia, 4 part I, UNESCO Publishing, ISBN 978-92-3-103467-1
- Biran 2005, pp. 215–217.
- Morgan & Stewart 2017, p. 56.
- Biran, Michael (2001). Chinggis Khan: Selected Readings. ISBN 9781780742045.
- Denis Twitchett, Herbert Franke, John K. Fairbank, in The Cambridge History of China: Volume 6, Alien Regimes and Border States (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1994), p. 153.
- Michal Biran (2005). The Empire of the Qara Khitai in Eurasian History: Between China and the Islamic World. Cambridge University Press. p. 95. ISBN 0521842263.
- Biran, pp 48–80 for the complex details
- Biran 2005, p. 87.
- Biran 2005, p. 93-131.
- Millward, James A. (2007). Eurasian Crossroads: A History of Xinjiang. Columbia University Press. pp. 42–. ISBN 978-0-231-13924-3.
- Biran, Michal (2001). "Like a Might Wall: The armies of the Qara Khitai" (PDF). Jerusalem Studies in Arabic and Islam. 25: 46. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-12-10.
- Biran 2005, p. 34.
- Biran 2005, p. 97.
- Biran 2005, p. 102, 196–201.
- Biran 2005, p. 96–.
- Biran 2005, p. 27–.
- Biran 2005, p. 146.
- Biran 2005, p. 98–99.
- Biran 2005, p. 99–101.
- James A. Millward; Peter C. Perdue (2004). S.F.Starr (ed.). Xinjiang: China's Muslim Boarderland. M.E. Sharpe. p. 43. ISBN 9781317451372.
- Belyaev, V.A.; Nastich, V.N.; Sidorovich, S.V. (2012). "The coinage of Qara Khitay: a new evidence (on the reign title of the Western Liao Emperor Yelü Yilie)". Proceedings of the 3rd Simone Assemani Symposium, September 23–24, 2011, Rome.
Sources
- Biran, Michal (2005). The Empire of the Qara Khitai in Eurasian History: Between China and the Islamic World. Cambridge Studies in Islamic Civilization. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0521842266.
- Grousset, Rene (1991). The Empire of the Steppes: A History of Central Asia. Rutgers University Press.
- Morgan, David; Stewart, Sarah, eds. (2017). The Coming of the Mongols. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 9781786733832.
- Pozzi, Alessandra; Janhunen, Juha Antero; Weiers, Michael, eds. (2006). Tumen Jalafun Jecen Aku: Manchu Studies in Honour of Giovanni Stary. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. ISBN 978-3-447-05378-5.
.png.webp)