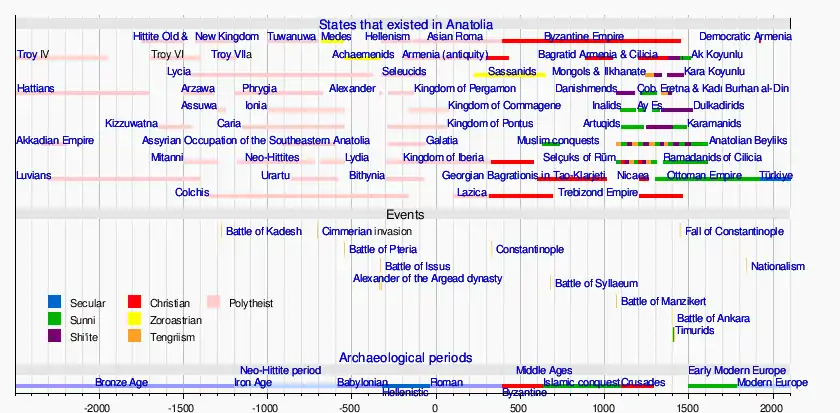
Armeno-Phrygian languages
The name Armeno-Phrygian is used for a hypothetical language branch, which would include the languages spoken by the Phrygians and the Armenians, and would be a branch of the Indo-European language family, or a sub-branch of either the proposed "Graeco-Armeno-Aryan" or "Armeno-Aryan" branches. According to this hypothesis, Proto-Armenian was a language descendant from a common ancestor with Phrygian and was closely related to it. Proto-Armenian differentiated from Phrygian by language evolution over time but also by the Hurro-Urartian language substrate influence. Classification is difficult because little is known of Phrygian, but Proto-Armenian arguably forms a subgroup with Greek and Indo-Iranian.[1][2][3]
| Part of a series on |
| Indo-European topics |
|---|
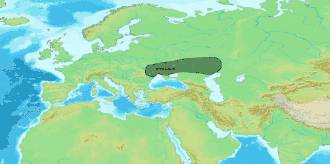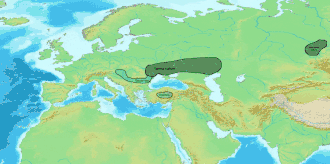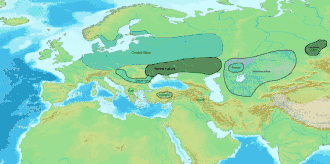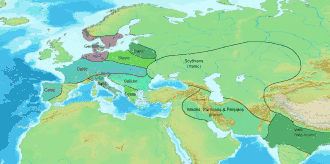 |
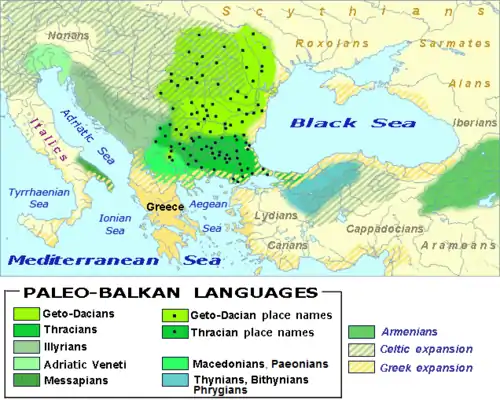
There are two conflicting accounts of the origin and presence of the Armenian language in the lands that were Ancient Armenia:
- Ancient Greek scholars, such as Herodotus, believed that the Phrygians, speakers of Phrygian, had originated as the Bryges of the Balkans, before migrating to western Anatolia and establishing the kingdom of Phyrgia. After the collapse of the kingdom in the late 7th century BC (following an invasion by Cimmerians), some of the Phrygians migrated eastward and settled in Armenia.
- Some modern scholars instead believe that a proto-Armeno-Phrygian population, and their respective language, originated in eastern Anatolia and/or the Armenian Highlands, from where the Phrygians later migrated westward.[4]
A third account of Armenian origin (supported by another group of modern scholars), proposes that Phrygians (and their language Phrygian), ancestors of Proto-Armenians, migrated eastward some centuries earlier than the collapse of the Kingdom of Phrygia (in the late 7th century BC), and they were already present in eastern Anatolia and in the lands that later formed Ancient Armenia, in the Armenian Highlands, with their language (which would be the direct ancestor of Proto-Armenian), since the end of the 2nd millennium BC, about the time of the Bronze Age collapse (at the end of the 13th century and the first half of 12th century) where they were known by the name of Mushki (Eastern Mushki) by the Assyrians and where they blended with local ancient populations, including speakers of Hurro-Urartian languages.[5][6]
According to some scholars, there is evidence of language borrowings (Armenisms) from the Proto-Armenian language into Urartian and also into Kartvelian languages.[7]
See also
References
- Hrach Martirosyan “Origins and historical development of the Armenian language” in Journal of Language Relationship, International Scientific Periodical, n.º10 (2013). Russian State University for the Humanities, Institute of Linguistics of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
- Martirosyan, Hrach (2014). "Origins and Historical Development of the Armenian Language" (PDF). Leiden University: 1–23. Retrieved 5 August 2019. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - I. M. Diakonoff The Problem of the Mushki Archived August 25, 2011, at the Wayback Machine in The Prehistory of the Armenian People
- "Historical Data". Archived from the original on 2011-06-01. Retrieved 2011-05-17.
- I. M. Diakonoff The Problem of the Mushki Archived August 25, 2011, at the Wayback Machine in The Prehistory of the Armenian People
- Hrach Martirosyan “Origins and historical development of the Armenian language” (p. 7-9) in Journal of Language Relationship, International Scientific Periodical, n.º10 (2013). Russian State University for the Humanities, Institute of Linguistics of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
- Hrach Martirosyan “Origins and historical development of the Armenian language” (p. 7-9) in Journal of Language Relationship, International Scientific Periodical, n.º10 (2013). Russian State University for the Humanities, Institute of Linguistics of the Russian Academy of Sciences.