Bellows Falls, Vermont
Bellows Falls is an incorporated village located in the town of Rockingham in Windham County, Vermont, United States. The population was 3,148 at the 2010 census. Bellows Falls is home to the Green Mountain Railroad, a heritage railroad; the annual Roots on the River Festival;[5] and the No Film Film Festival.[6]
Bellows Falls, Vermont | |
|---|---|
 Bellows Falls in the early spring, viewed from Fall Mountain | |
 Bellows Falls, Vermont Location within the state of Vermont | |
| Coordinates: 43°8′0″N 72°26′38″W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Vermont |
| County | Windham |
| Incorporated | 1909 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1.39 sq mi (3.59 km2) |
| • Land | 1.37 sq mi (3.55 km2) |
| • Water | 0.02 sq mi (0.05 km2) |
| Elevation | 312 ft (95 m) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 3,148 |
| • Estimate (2019)[2] | 2,965 |
| • Density | 2,165.81/sq mi (836.19/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| ZIP code | 05101 |
| Area code(s) | 802 |
| FIPS code | 50-04225[3] |
| GNIS feature ID | 1456381[4] |
| Website | Official website |
History
Great Falls[7] was once an important fishing place on the Connecticut River for the nomadic Abenaki tribes, who were part of the Algonquian language family. They caught plentiful salmon and shad. Indigenous peoples had fished at the falls and inhabited the area for thousands of years before European arrival. They carved two sets of faces in the rocks just below the falls (see Bellows Falls Petroglyph Site (VT-WD-8)).

The community was settled in 1753 by colonists of English descent, who called it Great Falls. Later the settlers renamed the town for Colonel Benjamin Bellows, a landowner.,[8][9] but they kept the name Great Falls for the waterfall, a translation of their Abenaki name, "Kitchee pontegu."[7] In 1785, Colonel Enoch Hale built at the falls the first bridge over the Connecticut River. It was the only bridge across the river until 1796, when another was built at Springfield, Massachusetts.[10] The bridge was later replaced. Two bridges currently link Bellows Falls to New Hampshire: the New Arch Bridge (also called the Church Street Bridge), which replaced the Arch Bridge in 1982, and the Vilas Bridge,[11] which was closed due to safety concerns in 2009.
The Bellows Falls Canal, one of the first canals built in the United States, was dug by a British-owned company from 1791-1802. The original canal was 22 feet wide and four feet deep, and had 9 locks, each 75 feet long and 20 feet wide, which allowed shipping to go around Great Falls by being lifted 52 feet (16 m) around the gorge. River traffic declined after railroads were built to the Connecticut Valley in 1849, and by 1858 the canal had become used exclusively for water power to run the paper mills which became established there. In 1874 the canal was enlarged to 75 feet wide and 17 feet deep. By 1908 it was delivering 15,000 horsepower to the mills. When the mills replaced water power with electrical power, the canal was widened again in 1927-28 to 100 feet, and the water was used to power turbines to generate electricity. The canal's bottom was lined with concrete, and the sides secured with rip-rap set in concrete. A fish ladder allows salmon to continue upstream at times when the bulk of the river's flow is diverted to the canal. The canal is now part of the Bellows Falls Downtown Historic District.[12][13][14]
In 1802, entrepreneurs built the first paper mill in Windham County. Two railroads converged in 1849 at Bellows Falls, helping it develop into a major mill town. By 1859, a woolen textile mill was operating, in addition to factories that produced furniture, marble, sashes and blinds, iron castings, carriages, cabinetware, rifles, harness, shoe pegs and organs.[15] The principal products, however, were paper and farm machinery. Bellows Falls was incorporated as a village in 1909.
The years of industry created wealth in the town, and substantial Victorian houses and mercantile buildings were constructed. Bellows Falls today attracts visitors through heritage tourism based on its historic Victorian architecture. The commercial town center, along with the canal, the bridges spanning it, and several neighborhoods of houses, were listed as historic districts on the National Register of Historic Places, as were individual landmarks such as the historic railroad station and the Adams Gristmill Warehouse.[16][17]
Geography
The village is located within the town of Rockingham. According to the United States Census Bureau, the village has a total area of 1.4 square miles (3.6 km2), all land. Bellows Falls is bounded on the east by the Connecticut River.
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1870 | 697 | — | |
| 1880 | 2,229 | 219.8% | |
| 1890 | 3,092 | 38.7% | |
| 1900 | 4,337 | 40.3% | |
| 1910 | 4,883 | 12.6% | |
| 1920 | 4,860 | −0.5% | |
| 1930 | 3,930 | −19.1% | |
| 1940 | 4,236 | 7.8% | |
| 1950 | 3,881 | −8.4% | |
| 1960 | 3,831 | −1.3% | |
| 1970 | 3,505 | −8.5% | |
| 1980 | 3,456 | −1.4% | |
| 1990 | 3,313 | −4.1% | |
| 2000 | 3,165 | −4.5% | |
| 2010 | 3,148 | −0.5% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 2,965 | [2] | −5.8% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[18] | |||
Demographics
As of the census[3] of 2000, there were 3,165 people, 1,329 households, and 782 families residing in the village. The population density was 2,286.1 people per square mile (885.5/km2). There were 1,443 housing units at an average density of 1,042.3/sq mi (403.7/km2). The racial makeup of the village was 97.28% White, 0.35% African American, 0.16% Native American, 0.51% Asian, 0.03% Pacific Islander, 0.22% from other races, and 1.45% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 1.14% of the population.
There were 1,329 households, out of which 32.2% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 40.0% were couples living together and joined in either marriage or civil union, 14.1% had a female householder with no husband present, and 41.1% were non-families. 34.5% of all households were made up of individuals, and 16.7% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.35 and the average family size was 3.01.
In the village, the population was spread out, with 26.1% under the age of 18, 7.8% from 18 to 24, 28.3% from 25 to 44, 21.5% from 45 to 64, and 16.2% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 37 years. For every 100 females, there were 94.1 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 88.6 males.
The median income for a household in the village was $29,608, and the median income for a family was $45,688. Males had a median income of $29,137 versus $22,340 for females. The per capita income for the village was $15,276. About 5.6% of families and 12.6% of the population were below the poverty line, including 14.3% of those under age 18 and 15.9% of those age 65 or over.
Arts and culture
Tourism
Bellows Falls has several cultural attractions including:
- Adams Grist Mill Museum
- Bellows Falls Historical Society & Museum
- Bellows Falls Opera House
- Green Mountain Railroad, a heritage railroad
- Rockingham Arts & Museum Project
- Vilas Bridge, a defunct bridge over the Connecticut river
- Just downstream of the bridge are petroglyphs on large boulders at the Bellows Falls Petroglyph Site.[19]


Historic districts
Historic districts listed on the National Register of Historic Places are:
- Bellows Falls Neighborhood Historic District – a neighborhood on streets adjacent to downtown. (added February 17, 2002)
- Bellows Falls Downtown Historic District – Depot, Canal, Rockingham, Bridge, Mill and Westminster Sts. (added September 16, 1982)
- George–Pine–Henry Street Historic District, a historic residential area
- Westminster Terrace Historic District – Westminster Terrace (added July 13, 2010)
Historic Sites on the National Register
Historic sites listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Bellows Falls are:
- Adams Gristmill Warehouse – Bridge Street (added February 22, 1990)
- Andrews Inn/Hotel Windham – On the Downtown Square (added June 24, 2020)
- Bellows Falls Co-operative Creamery Complex – Island Street (added February 22, 1990)
- Bellows Falls Times Building – Bridge and Island Streets (added February 22, 1990)
- Bellows Falls Petroglyph Site (VT-WD-8) – (added February 22, 1990)
- Gas Station at Bridge and Island Streets – (added January 22, 1990)
- Hall Covered Bridge – W of Bellows Falls Across Saxtons River, off VT 121 (added September 28, 1973)
- William A. Hall House – 1 Hapgood Street (added June 5, 1999)
- Howard Hardware Storehouse – Bridge Street (added February 22, 1990)
- Miss Bellows Falls Diner – 90 Rockingham Street (added March 15, 1983)
- Moore and Thompson Paper Mill Complex – Bridge Street (added April 16, 1984)
- Oak Hill Cemetery Chapel – off Pleasant Street (added December 14, 1991)
- Robertson Paper Company Complex – Island Street (added February 22, 1990)
Transportation
Amtrak, the national passenger rail system, provides daily service through Bellows Falls, operating its Vermonter between Washington, D.C. and St. Albans, Vermont. The Bellows Falls Station, on Depot Street, also serves as the headquarters for the Green Mountain Railroad. Greyhound, the nationwide intercity bus service, also serves Bellows Falls from this same rail station.
Connecticut River Transit, a private, non-profit personal mobility specialist, provides scheduled bus service with local and direct buses linking Bellows Falls, Brattleboro, Springfield, Ludlow, the White River Junction and Lebanon, New Hampshire areas and other local communities as needed by private arrangement.
Green Mountain Railroad, a part of the Vermont Rail System, operates seasonal and holiday scenic train excursions between Bellows Falls and Chester. The New England Central Railroad also serves Bellows Falls.
The village is crossed by Interstate 91, U.S. Route 5, and Vermont Route 121.
Media
Radio
- WOOL 91.5 (Freeform, "Black Sheep Radio")
- WZLF 107.1 (Country, "95.3 and 107.1 The Wolf") a simulcast of WXLF from Hartford, Vermont
Gallery
 Bellows Falls (Great Falls) at high flow
Bellows Falls (Great Falls) at high flow
(ndg) Island House Hotel
Island House Hotel
(c.1850s) Robertson Paper Company Complex, built c.1890-c.1960
Robertson Paper Company Complex, built c.1890-c.1960
(2013)
 Westminster High Bridge over Saxton's River
Westminster High Bridge over Saxton's River
(1906) Paper mills
Paper mills
(1907) The Square has been the commercial center of Bellows Falls practically since the first residents settled there.[20]
The Square has been the commercial center of Bellows Falls practically since the first residents settled there.[20]
(c.1908) The Gas Station at Bridge and Island Streets was built c.1935 in the Colonial Revival style and was added to the NRHP in 1990
The Gas Station at Bridge and Island Streets was built c.1935 in the Colonial Revival style and was added to the NRHP in 1990
(2017) A house on Westminster Terrace, part of the Westminster Terrace Historic District, designated in 2010
A house on Westminster Terrace, part of the Westminster Terrace Historic District, designated in 2010
(2013) The falls under the Vilas Bridge at medium flow in 2014; taken looking north
The falls under the Vilas Bridge at medium flow in 2014; taken looking north
- Bellows Falls Downtown Historic District
 The Depot Street Bridge over the Bellows Falls Canal
The Depot Street Bridge over the Bellows Falls Canal
(2016) The Frank Adams Grist Mill was founded in 1831 and ran continuously until the early 1960s[12]
The Frank Adams Grist Mill was founded in 1831 and ran continuously until the early 1960s[12]
(2017)
 Looking south down Canal Street towards The Square; the Brown Block can be seen in the background
Looking south down Canal Street towards The Square; the Brown Block can be seen in the background
(2016) The Edward Arms Block was built in 1890 and had an additional floor added in 1910[12]
The Edward Arms Block was built in 1890 and had an additional floor added in 1910[12]
(2017)
 The Centennial Block, built by the National Bank of Bellows Falls in 1875[22]
The Centennial Block, built by the National Bank of Bellows Falls in 1875[22]
(2016) The commercial block at 20 Square was built in 1912[12]
The commercial block at 20 Square was built in 1912[12]
(2017) United States Post Office, built in 1930 in the Georgian Revival style with Spanish Colonial Revival style elements[12]
United States Post Office, built in 1930 in the Georgian Revival style with Spanish Colonial Revival style elements[12]
(2017)
- Bellows Falls Neighborhood Historic District
 The Bellows Falls Masonic Temple, formerly the Wyman & Almira Flint House, was built c.1870 in the Second Empire style[24]
The Bellows Falls Masonic Temple, formerly the Wyman & Almira Flint House, was built c.1870 in the Second Empire style[24]
(2017) A Victorian house at 6 Temple Street
A Victorian house at 6 Temple Street
(2017)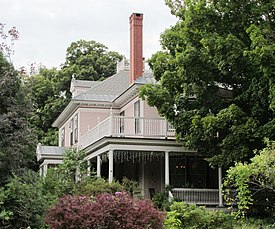 The William A. Hall House was built in 1890-92 in the Colonial Revival stye. It is now the Readmore Inn.
The William A. Hall House was built in 1890-92 in the Colonial Revival stye. It is now the Readmore Inn.
(2013)
 The former armory of Company E of the First Infantry of the Vermont National Guard was built in 1915. It is now low-income housing.[24]
The former armory of Company E of the First Infantry of the Vermont National Guard was built in 1915. It is now low-income housing.[24]
(2017)
Notable people
- Donald H. Balch, general in the United States Air Force
- Colleen Barrett, president of Southwest Airlines
- Sean O. Cota, businessman and financial commentator
- Nicholas P. Massucco, Automotive entrepreneur
- Carlton Fisk, catcher with the Boston Red Sox and Chicago White Sox baseball teams
- Jay H. Gordon, Vermont Auditor of Accounts
- Warner A. Graham, Associate Justice of the Vermont Supreme Court[25]
- Hetty Green, businesswoman, known as the richest woman in America during the Gilded Age, and called the world's greatest miser by Guinness World Records
- Henry Alfred Hosking, member of the House of Commons of Canada
- James F. Howard, Jr., professor of neurology and medicine
- Michael Palma, poet and translator
- Charles Henry Robb, federal judge
- Roger Robb, federal judge
- Thomas M. Salmon, Vermont Auditor of Accounts
- Thomas P. Salmon, 75th Governor of Vermont
- Jennie Maria Arms Sheldon, entomologist, science educator, historian, author, and museum curator, born in Bellows Falls
- Gary Smith, record producer
- Ernest Thompson, playwright (On Golden Pond) and actor
- Todd T. Semonite, Chief of Engineers for the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
See also
References
- "2019 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 7, 2020.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". United States Census Bureau. May 24, 2020. Retrieved May 27, 2020.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Bellows Falls
- "Roots on the River" Vermont Festivals
- No Film Film Festival Facebook
- GNIS page for Great Falls
- Coolidge, Austin J.; John B. Mansfield (1859). A History and Description of New England. Boston, Massachusetts. pp. 886–888. OcoMAAAAYAAJ&lpg=PA9&dq=coolidge%20mansfield%20history%20description%20new%20england%201859&pg=PA886#v=onepage&q=&f=false.
- Geographic Names Information System, Bellows Falls,VT.
- The First Toll Bridge at Bellows Falls
- Collins, Anne L.; Lisai, Virginia; and Luring Louise (2002) Around Bellows Falls: Rockingham, Westminster, and Saxtons River Arcadia Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7385-1033-0
- "Bellows Falls Downtown Historic District"
- Historic marker on site at Bridge Street, Bellows Falls
- "Bellows Falls Canal"
- Coolidge, A. J. and Mansfield, J. B. (1859) A. J. Coolidge & J. B. Mansfield, A History and Description of New England Boston, Massachusetts
- "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. July 9, 2010.
- "NRHP nomination for Bellows Falls Downtown Historic District". National Park Service. Retrieved 2015-10-31.
- "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- "Face Value: The Bellows Falls Petroglyphs". 9 August 2015.
- Historical marker on the Windham Hotel
- "Windham Hotel History"
- "Centennial Block"
- "Andrews Inn Oral History Project" Green Mountain Crossroads
- "Bellows Falls Neighborhood Historic District Self-Guided Walking Tour" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-10-20. Retrieved 2017-06-20.
- Cutler, William Richard (1914). New England Families, Genealogical and Memorial. 3. New York, NY: Lewis Historical Publishing Company. p. 1468.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |