Littleton, New Hampshire
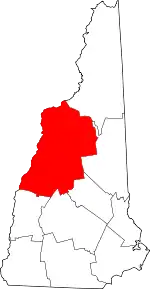
Littleton is a town in Grafton County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 5,928 at the 2010 census.[1] Situated at the northern edge of the White Mountains, Littleton is bounded on the northwest by the Connecticut River.
Littleton, New Hampshire | |
|---|---|
Town | |
 Littleton Courthouse and Post Office | |
 Seal | |
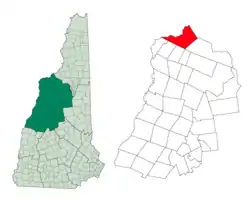 Location in Grafton County, New Hampshire | |
| Coordinates: 44°18′22″N 71°46′12″W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | New Hampshire |
| County | Grafton |
| Incorporated | 1784 |
| Villages | Littleton Apthorp North Littleton |
| Government | |
| • Board of Selectmen | Carrie L. Gendreau, Chair Chad Stearns Roger Emerson |
| • Town Manager | Andrew Dorsett |
| Area | |
| • Total | 54.1 sq mi (140.1 km2) |
| • Land | 50.1 sq mi (129.8 km2) |
| • Water | 4.0 sq mi (10.4 km2) 7.41% |
| Elevation | 820 ft (250 m) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 5,928 |
| • Density | 118/sq mi (45.7/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (Eastern) |
| ZIP code | 03561 |
| Area code(s) | 603 |
| FIPS code | 33-42580 |
| GNIS feature ID | 0873649 |
| Website | www |
The primary settlement in town, where 4,412 people lived at the 2010 census,[1] is defined as the Littleton census-designated place (CDP), and is centered on the intersection of U.S. Route 302 with New Hampshire Route 116, along the Ammonoosuc River.
History
Called "Chiswick" (Saxon for "Cheese Farm") in 1764, the area was settled in 1769. The town was part of Lisbon until 1770, when it was granted as "Apthorp" in honor of George Apthorp, head of one of the wealthiest mercantile establishments in Boston, Massachusetts. The land was later passed to the Apthorp family's associates from Newburyport, Massachusetts, headed by Colonel Moses Little. Colonel Little held the post of Surveyor of the King's Woods, and the town was named in his honor when it was incorporated in 1784, the same year New Hampshire became a state.[2]
Located along the banks of the Ammonoosuc River is the Littleton Grist Mill. The historic mill first opened in 1798, and has been fully restored to its original appearance. Between 1867 and 1909, the local Kilburn Brothers factory published photographs, stereoviews, and sold stereoscopes, double-picture viewers popular in the Victorian age.
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 54.1 square miles (140.1 km2), of which 50.1 square miles (129.8 km2) is land and 4.0 square miles (10.4 km2) is water, comprising 7.41% of the town.[3] The main village of Littleton, a census-designated place, has a total area of 8.6 square miles (22 km2), of which 0.12% is water.
Littleton is drained by the Ammonoosuc River. The Moore Dam on the Connecticut River forms Moore Reservoir in the north. The highest point in the town is the summit of Towns Mountain, at 2,203 feet (671 m) above sea level.
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 96 | — | |
| 1800 | 381 | 296.9% | |
| 1810 | 873 | 129.1% | |
| 1820 | 1,096 | 25.5% | |
| 1830 | 1,435 | 30.9% | |
| 1840 | 1,778 | 23.9% | |
| 1850 | 2,008 | 12.9% | |
| 1860 | 2,292 | 14.1% | |
| 1870 | 2,446 | 6.7% | |
| 1880 | 2,936 | 20.0% | |
| 1890 | 3,365 | 14.6% | |
| 1900 | 4,066 | 20.8% | |
| 1910 | 4,069 | 0.1% | |
| 1920 | 4,239 | 4.2% | |
| 1930 | 4,558 | 7.5% | |
| 1940 | 4,571 | 0.3% | |
| 1950 | 4,817 | 5.4% | |
| 1960 | 5,003 | 3.9% | |
| 1970 | 5,290 | 5.7% | |
| 1980 | 5,558 | 5.1% | |
| 1990 | 5,827 | 4.8% | |
| 2000 | 5,845 | 0.3% | |
| 2010 | 5,928 | 1.4% | |
| 2017 (est.) | 5,881 | [4] | −0.8% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[5] | |||
As of the census of 2010, there were 5,928 people, 2,673 households, and 1,596 families residing in the town. The population density was 118.3 people per square mile (45.7/km2). There were 3,065 housing units at an average density of 61.2 units/sq mi (23.6 units/km2). The racial makeup of the town was 96.2% White, 0.4% African American, 0.3% Native American, 1.0% Asian, 0.5% some other race, and 1.6% from two or more races. 1.9% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.[6]
There were 2,673 households, out of which 26.9% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 43.5% were headed by married couples living together, 11.8% had a female householder with no husband present, and 40.3% were non-families. 33.1% of all households were made up of individuals, and 13.5% were someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.21, and the average family size was 2.77.[6]
In the town, the population was spread out, with 21.4% under the age of 18, 7.4% from 18 to 24, 23.3% from 25 to 44, 30.8% from 45 to 64, and 17.6% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 44.1 years. For every 100 females, there were 90.7 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 88.2 males.[6]
For the time period 2007–11, the estimated median annual income for a household in the town was $45,290, and the median income for a family was $50,921. Male full-time workers had a median income of $40,745 versus $32,972 for females. The per capita income for the town was $24,673. 7.5% of the population and 4.5% of families were below the poverty line. Out of the total people living in poverty, 7.9% were under the age of 18 and 10.1% were 65 or older.[7]
 Downtown on Main Street looking east
Downtown on Main Street looking east Bird's-eye view c. 1910
Bird's-eye view c. 1910 Main Street in 1908
Main Street in 1908 Thayer's Hotel in 1908
Thayer's Hotel in 1908 Town Building and Opera House in 1908
Town Building and Opera House in 1908
Sites of interest
.jpg.webp)
- Bronze statue of Eleanor H. Porter's creation, Pollyanna. Downtown; unveiled 2002[8]
- Kilburn Brothers Building - Where stereo view cards were made
- The Riverwalk and Covered Bridge[9]
- Downtown Historical Walk (marked by plaques on or near various buildings along Main Street)[10]
- Littleton Opera House[11]
- Littleton Coin Company [12]
- Littleton Farmers Market, July to October, on Sundays[13]
- Chutter's Candy Store, which claims to hold the world record for Longest Candy Counter[14]
- The site of punk icon GG Allin's grave.[15]
Transportation
The center of Littleton is accessible from three exits of Interstate 93, and a fourth exit serves the western end of town near the Vermont border. U.S. Route 302 runs east–west through the town center as its Main Street. As of January 2006 Littleton is also served by a public transportation bus route[16] connecting with Whitefield and Lancaster.
Notable people
- Michael Cryans, member of the Executive Council of New Hampshire
- Rich Gale, pitcher with five MLB teams
- Hugh Gallen, 74th governor of New Hampshire
- Geoffrey Hendricks, artist
- Benjamin W. Kilburn, machinist, veteran, photographer, stereoscopic publisher
- Eleanor H. Porter, author (Pollyanna and Pollyanna Grows Up)
- Melinda Rankin (1811–1888), missionary, teacher, and writer
- Tor Seidler, children's author[17]
- Jack Tilton (1951-2017), American art dealer[18]
References
- United States Census Bureau, American FactFinder, 2010 Census figures. Retrieved March 23, 2011.
- Coolidge, Austin J.; John B. Mansfield (1859). A History and Description of New England. Boston, Massachusetts: A.J. Coolidge. pp. 556–557.
coolidge mansfield history description new england 1859.
- "Geographic Identifiers: 2010 Demographic Profile Data (G001) - Littleton town, New Hampshire". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved November 10, 2011.
- "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2017 (PEPANNRES): Minor Civil Divisions – New Hampshire". Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved November 14, 2018.
- "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2016.
- "Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data (DP-1): Littleton town, Grafton County, New Hampshire". U.S. Census Bureau, American Factfinder. Archived from the original on February 12, 2020. Retrieved February 21, 2013.
- "Selected Economic Characteristics: 2007-2011 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates (DP03): Littleton town, Grafton County, New Hampshire". U.S. Census Bureau, American Factfinder. Archived from the original on February 12, 2020. Retrieved February 21, 2013.
- "Pollyanna of Littleton, New Hampshire". GoLittleton.com. Retrieved December 10, 2015.
- "Littleton NH Riverwalk". dudasite.com. Retrieved 2 October 2019.
- "About Littleton". littletonareachamber.com. Littleton Area Chamber of Commerce. Retrieved 18 December 2019.
- "Littleton Opera House". townoflittleton.com. Retrieved 2 October 2019.
- "Welcome to Littleton Coin Company". www.littletoncoin.com.
- "Littleton Farmers Market - Littleton, NH - Local-Farmers-Markets.Com". www.local-farmers-markets.com.
- "The Candy Counter". chutters.com.
- Music at the Extremes
- TheTri-Town Bus Archived 2006-05-02 at the Wayback Machine
- "Tor Seidler". HarperCollins US.
- Grimes, William (10 May 2017). "Jack Tilton, Art Dealer With an Eye for the New, Dies at 66" – via NYTimes.com.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Littleton, New Hampshire. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1905 New International Encyclopedia article "Littleton". |