Incunable
An incunable, or sometimes incunabulum (plural incunables or incunabula, respectively), is a book, pamphlet, or broadside printed in Europe before the 16th century. Incunabula are not manuscripts, which are documents written by hand. As of 2014, there are about 30,000 distinct known incunable editions extant, but the probable number of surviving copies in Germany alone is estimated at around 125,000.[1][2] Through statistical analysis, it is estimated that the number of lost editions is at least 20,000.[3]



Etymology
Incunable is the anglicised form of incunabulum,[4] reconstructed singular of Latin incunabula,[5] which meant "swaddling clothes", or "cradle",[6] and which metaphorically could and can refer to "the earliest stages or first traces in the development of anything".[7] A former term for incunable is fifteener, in the meaning of "fifteenth-century edition".[8]
The term incunabula as a printing term was first used by the Dutch physician and humanist Hadrianus Iunius (Adriaan de Jonghe, 1511–1575) and appears in a passage from his posthumous work (written in 1569): Hadrianus Iunius, Batavia, [...], [Lugduni Batavorum], ex officina Plantiniana, apud Franciscum Raphelengium, 1588, p. 256 l. 3: «inter prima artis [typographicae] incunabula», a term ("the first infancy of printing") to which he arbitrarily set an end of 1500 which still stands as a convention.[9]
Only by a misunderstanding was Bernhard von Mallinckrodt (1591–1664) considered to be the inventor of this meaning of incunabula; the identical passage is found in his Latin pamphlet De ortu ac progressu artis typographicae ("On the rise and progress of the typographic art", Cologne, 1640): Bernardus a Mallinkrot, De ortu ac progressu artis typographicae dissertatio historica, [...], Coloniae Agrippinae, apud Ioannem Kinchium, 1640 (in frontispiece: 1639), p. 29 l. 16: «inter prima artis [typographicae] incunabula», within a long passage of several pages, which he (correctly) quotes entirely in italic characters (that is between quotation marks), referring to the name of author and work cited: «Primus istorum [...] Hadrianus Iunius est, cuius integrum locum, ex Batavia eius, operae pretium est adscribere; [...]. Ita igitur Iunius» (ibid., p. 27 ll. 27–32, followed by the long passage, «Redeo → sordes», ibid., p. 27, l. 32 – p. 33 l. 32 [= Batavia, p. 253 l. 28 – p. 258 l. 21]). So the source is only one, the other is a quotation.[10]
The term incunabula came to denote the printed books themselves in the late 17th century. John Evelyn, in moving the Arundel Manuscripts to the Royal Society in August 1678, remarked of the printed books among the manuscripts: "The printed books, being of the oldest impressions, are not the less valuable; I esteem them almost equal to MSS."[11] The convenient but arbitrarily chosen end date for identifying a printed book as an incunable does not reflect any notable developments in the printing process, and many books printed for a number of years after 1500 continued to be visually indistinguishable from incunables.
"Post-incunable" typically refers to books printed after 1500 up to another arbitrary end date such as 1520 or 1540. From around this period the dating of any edition becomes easier, as the practice of printers including information such as the place and year of printing became more widespread.
Types
There are two types of incunabula in printing: the block book, printed from a single carved or sculpted wooden block for each page, employing the same process as the woodcut in art (these may be called xylographic); and the typographic book, made with individual pieces of cast-metal movable type on a printing press. Many authors reserve the term incunabula for the latter kind only.[12]
The spread of printing to cities both in the north and in Italy ensured that there was great variety in the texts chosen for printing and the styles in which they appeared. Many early typefaces were modelled on local forms of writing or derived from the various European forms of Gothic script, but there were also some derived from documentary scripts (such as most of Caxton's types), and, particularly in Italy, types modelled on handwritten scripts and calligraphy employed by humanists.
Printers congregated in urban centres where there were scholars, ecclesiastics, lawyers, and nobles and professionals who formed their major customer base. Standard works in Latin inherited from the medieval tradition formed the bulk of the earliest printed works, but as books became cheaper, vernacular works (or translations into vernaculars of standard works) began to appear.
Famous examples

The most famous incunabula include two from Mainz, the Gutenberg Bible of 1455 and the Peregrinatio in terram sanctam of 1486, printed and illustrated by Erhard Reuwich; the Nuremberg Chronicle written by Hartmann Schedel and printed by Anton Koberger in 1493; and the Hypnerotomachia Poliphili printed by Aldus Manutius with important illustrations by an unknown artist.
Other printers of incunabula were Günther Zainer of Augsburg, Johannes Mentelin and Heinrich Eggestein of Strasbourg, Heinrich Gran of Haguenau and William Caxton of Bruges and London. The first incunable to have woodcut illustrations was Ulrich Boner's Der Edelstein, printed by Albrecht Pfister in Bamberg in 1461.[13]
Post-incunable
Many incunabula are undated, needing complex bibliographical analysis to place them correctly. The post-incunabula period marks a time of development during which the printed book evolved fully as a mature artefact with a standard format.[14] After c. 1540 books tended to conform to a template that included the author, title-page, date, seller, and place of printing. This makes it much easier to identify any particular edition.[15]
As noted above, the end date for identifying a printed book as an incunable is convenient but was chosen arbitrarily; it does not reflect any notable developments in the printing process around the year 1500. Books printed for a number of years after 1500 continued to look much like incunables, with the notable exception of the small format books printed in italic type introduced by Aldus Manutius in 1501. The term post-incunable is sometimes used to refer to books printed "after 1500—how long after, the experts have not yet agreed."[16] For books printed in the UK, the term generally covers 1501–1520, and for books printed in mainland Europe, 1501–1540.[17]
Statistical data
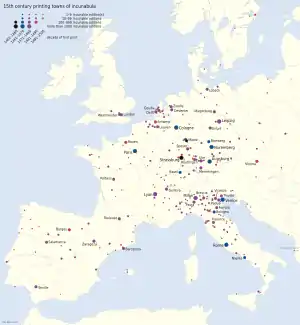

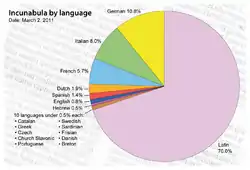
The data in this section were derived from the Incunabula Short-Title Catalogue (ISTC).[18]
The number of printing towns and cities stands at 282. These are situated in some 18 countries in terms of present-day boundaries. In descending order of the number of editions printed in each, these are: Italy, Germany, France, Netherlands, Switzerland, Spain, Belgium, England, Austria, the Czech Republic, Portugal, Poland, Sweden, Denmark, Turkey, Croatia, Montenegro, and Hungary (see diagram).
The following table shows the 20 main 15th century printing locations; as with all data in this section, exact figures are given, but should be treated as close estimates (the total editions recorded in ISTC at May 2013 is 28,395):
| Town or city | No. of editions | % of ISTC recorded editions |
|---|---|---|
| Venice [19] | 3,549 | 12.5 |
| Paris [20] | 2,764 | 9.7 |
| Rome [21] | 1,922 | 6.8 |
| Cologne [22] | 1,530 | 5.4 |
| Lyon [23] | 1,364 | 4.8 |
| Leipzig [24] | 1,337 | 4.7 |
| Augsburg [25] | 1,219 | 4.3 |
| Strasbourg [26] | 1,158 | 4.1 |
| Milan [27] | 1,101 | 3.9 |
| Nuremberg [28] | 1,051 | 3.7 |
| Florence | 801 | 2.8 |
| Basel | 786 | 2.8 |
| Deventer | 613 | 2.2 |
| Bologna | 559 | 2.0 |
| Antwerp | 440 | 1.5 |
| Mainz | 418 | 1.5 |
| Ulm | 398 | 1.4 |
| Speyer | 354 | 1.2 |
| Pavia | 337 | 1.2 |
| Naples | 323 | 1.1 |
| TOTAL | 22,024 | 77.6 |
The 18 languages that incunabula are printed in, in descending order, are: Latin, German, Italian, French, Dutch, Spanish, English, Hebrew, Catalan, Czech, Greek, Church Slavonic, Portuguese, Swedish, Breton, Danish, Frisian and Sardinian (see diagram).
Only about one edition in ten (i.e. just over 3,000) has any illustrations, woodcuts or metalcuts.
The "commonest" incunable is Schedel's Nuremberg Chronicle ("Liber Chronicarum") of 1493, with c 1,250 surviving copies (which is also the most heavily illustrated). Many incunabula are unique, but on average about 18 copies survive of each. This makes the Gutenberg Bible, at 48 or 49 known copies, a relatively common (though extremely valuable) edition. Counting extant incunabula is complicated by the fact that most libraries consider a single volume of a multi-volume work as a separate item, as well as fragments or copies lacking more than half the total leaves. A complete incunable may consist of a slip, or up to ten volumes.
In terms of format, the 29,000-odd editions comprise: 2,000 broadsides, 9,000 folios, 15,000 quartos, 3,000 octavos, 18 12mos, 230 16mos, 20 32mos, and 3 64mos.
ISTC at present cites 528 extant copies of books printed by Caxton, which together with 128 fragments makes 656 in total, though many are broadsides or very imperfect (incomplete).
Apart from migration to mainly North American and Japanese universities, there has been little movement of incunabula in the last five centuries. None were printed in the Southern Hemisphere, and the latter appears to possess less than 2,000 copies, about 97.75% remain north of the equator. However many incunabula are sold at auction or through the rare book trade every year.
Major collections
The British Library's Incunabula Short Title Catalogue now records over 29,000 titles, of which around 27,400 are incunabula editions (not all unique works). Studies of incunabula began in the 17th century. Michel Maittaire (1667–1747) and Georg Wolfgang Panzer (1729–1805) arranged printed material chronologically in annals format, and in the first half of the 19th century, Ludwig Hain published, Repertorium bibliographicum— a checklist of incunabula arranged alphabetically by author: "Hain numbers" are still a reference point. Hain was expanded in subsequent editions, by Walter A. Copinger and Dietrich Reichling, but it is being superseded by the authoritative modern listing, a German catalogue, the Gesamtkatalog der Wiegendrucke, which has been under way since 1925 and is still being compiled at the Staatsbibliothek zu Berlin. North American holdings were listed by Frederick R. Goff and a worldwide union catalogue is provided by the Incunabula Short Title Catalogue.[29]
Notable collections, with the approximate numbers of incunabula held, include:
See also
- Global spread of the printing press
- History of books
- Book collecting
- List of printers of incunabula
References
- British Library: Incunabula Short Title Catalogue gives 30,518 editions as of August 2016, which also includes some prints from the 16th century though (retrieved 5 March 2020).
- According to Bettina Wagner: "Das Second-Life der Wiegendrucke. Die Inkunabelsammlung der Bayerischen Staatsbibliothek", in: Griebel, Rolf; Ceynowa, Klaus (eds.): "Information, Innovation, Inspiration. 450 Jahre Bayerische Staatsbibliothek", K G Saur, München 2008, ISBN 978-3-598-11772-5, pp. 207–224 (207f.) the Incunabula Short Title Catalogue lists 30,375 titles published before 1501.
- J. Green, F. McIntyre, P. Needham (2011), "The Shape of Incunable Survival and Statistical Estimation of Lost Editions", Papers of the Bibliographical Society of America 105 (2), pp. 141–175. doi:https://doi.org/10.1086/680773
- Still in 1891 Rogers in his technical glossary recorded only the form incunabulum: Rogers, Walter Thomas (1891). A Manual of Bibliography (2nd ed.). London: H. Grevel. p. 195.
- The word incunabula is a neuter plural only; the singular incunabulum is never found in Latin and now no more used in English by most bibliographers.
- C.T. Lewis and C. Short, A Latin Dictionary, Oxford 1879, p. 930.
- Oxford English Dictionary, 1933, I:188.
- "Fifteener" is a coinage of the bibliographer Thomas Frognall Dibdin, a term endorsed by William Morris and Robert Proctor. (Carter & Barker 2004, p. 130).
- Glomski, J (2001). "Incunabula Typographiae: seventeenth-century views on early printing". The Library. 2 (4): 336. doi:10.1093/library/2.4.336.
- Sordet, Yann (2009). "Le baptême inconscient de l'incunable: non pas 1640 mais 1569 au plus tard". Gutenberg Jahrbuch (in French). 84: 102–105.
- Evelyn, The Diary of John Evelyn From 1641 to 1705/6.
- Oxford Companion to the Book, ed. M. F. Suarez and H. R. Woudhuysen, OUP, 2010, s.v. 'Incunabulum', p. 815.
- Daniel De Simone (ed), A Heavenly Craft: the Woodcut in Early Printed Books, New York, 2004, p. 48.
- Walsby, Malcolm; Kemp, Graeme, eds. (2011). The Book Triumphant: Print in Transition in the Sixteenth and Seventeenth Centuries. Brill. p. viii. ISBN 9789004207233.
- Walsby & Kemp 2011, p. viii.
- Carter, John; Barker, Nicolas (2004). ABC for Book Collectors (8th ed.). New Castle, Del.: Oak Knoll Press and the British Library. p. 172. ISBN 1-58456-112-2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 November 2017. Retrieved 28 May 2010.
- Carter & Barker 2004, p. 172.
- BL.uk, consulted in 2007. The figures are subject to slight change as new copies are reported. Exact figures are given but should be treated as close estimates; they refer to extant editions.
- "Index: Place of Publication: Venice", Incunabula Short Title Catalogue, retrieved 3 December 2017
- "Index: Place of Publication: Paris", Incunabula Short Title Catalogue, retrieved 3 December 2017
- "Index: Place of Publication: Rome", Incunabula Short Title Catalogue, retrieved 3 December 2017
- "Index: Place of Publication: Cologne", Incunabula Short Title Catalogue, retrieved 3 December 2017
- "Index: Place of Publication: Lyons", Incunabula Short Title Catalogue, retrieved 3 December 2017
- "Index: Place of Publication: Leipzig", Incunabula Short Title Catalogue, retrieved 3 December 2017
- "Index: Place of Publication: Augsburg", Incunabula Short Title Catalogue, retrieved 3 December 2017
- "Index: Place of Publication: Strassburg", Incunabula Short Title Catalogue, retrieved 3 December 2017
- "Index: Place of Publication: Milan", Incunabula Short Title Catalogue, retrieved 3 December 2017
- "Index: Place of Publication: Nuremberg", Incunabula Short Title Catalogue, retrieved 3 December 2017
- "ISTC". Retrieved 16 May 2009.
- "Incunabula". Bayerische Staatsbibliothek. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Early Printed Books". British Library. Retrieved 16 October 2019.
- "Les Incunables". Bibliothèque nationale de France. Retrieved 7 September 2013.
- "All catalogues". Vatican Library. Archived from the original on 16 June 2013. Retrieved 21 May 2013.
- "2019 Jahresbericht" (PDF). Österreichische Nationalbibliothek. p. 53. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- Путеводитель по фондам Отдела редких книг Российской национальной библиотеки. Санкт-Петербург: РНБ. под общ. ред. А.В. Лихоманова ; науч. ред. Н.В. Николаев. 2015. p. 3. ISBN 978-5-8192-0483-2.
- "WLB in Zahlen 2019". Württembergische Landesbibliothek. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Rare Books in Western Languages". Bodleian Library, University of Oxford. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Rare Books and Special Collections: Europe". Library of Congress. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- Выставочный проект На благое просвещение: Румянцевский музей, Московский период, Индрик, 2005, ISBN 9785857593080
- "Early Printed Books and Printing History". The Huntington Library, Art Museum, and Botanical Gardens. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Incunabula". Cambridge University Library. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Biblioteca nazionale di Napoli "Vittorio Emanuele III"" (in Italian). Ministero per i beni e le attività culturali e per il turismo. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Rare Books". Royal Danish Library. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- "Guide to Special Collections : Printed books". The University of Manchester Library. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- "Zahlen und Fakten" (in German). Staatsbibliothek zu Berlin. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- Whitesell, David (2006). First supplement to James E. Walsh's Catalogue of the fifteenth-century printed books in the Harvard University Library. Cambridge, Mass.: Houghton Library. p. xiii. ISBN 978-0-674-02145-7. OCLC 71691077.
- "Incunabula". National Library of the Czech Republic. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- "La Biblioteca – Informazioni generali – Patrimonio librario" (in Italian). Biblioteca Nazionale Centrale di Firenze. Retrieved 7 March 2011.
- "DRUCKE" (in German). Universitätsbibliothek Leipzig. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "The Jagiellonian University Library Collection". Biblioteka Jagiellońska. 31 December 2009. Archived from the original on 7 June 2011. Retrieved 7 March 2011.
- "Historic collections in figures". Universitätsbibliothek der LMU München. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "The State Library in Numbers". Bamberg State Library. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Herzog August Library – Inkunabeln -Bestandsgeschichte" (in German). Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "The University Library in figures". Universitätsbibliothek Freiburg. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Biblioteca Nacional de España – Colecciones – Incunables" (in Spanish). Biblioteca Nacional de España. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Inkunabeln und Seltene Drucke" (in German). Niedersächsische Staats- und Universitätsbibliothek Göttingen. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Die Inkunabelsammlung der UB". Universitätsbibliothek Würzburg. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Alte Drucke" (in German). UB Basel. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Patrimonio librario" (in Italian). Biblioteca Nazionale Marciana. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Handschriften und Inkunabeln" (in German). Universitätsbibliothek Johann Christian Senckenberg. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "The Incunable Collection". Retrieved 4 September 2020.
- "COLLECTIONS". Biblioteca comunale dell'Archiginnasio. Retrieved 4 September 2020.
- "Incunables" (in French). Bibliothèque Mazarine. Retrieved 4 September 2020.
- "Inkunabeln" (in German). Universitäts- und Stadtbibliothek Köln. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Les collections" (in French). Les Dominicains – Bibliothèque patrimoniale Jacques Chirac. Retrieved 4 September 2020.
- "History of the Book". The Newberry. Retrieved 4 September 2020.
- "Incunables (printed works, until 1501)". KB. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Inkunabeln (Wiegendrucke)" (in German). Universitätsbibliothek Tübingen. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Inkunabeln & Blockbücher" (in German). Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek Tirol. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Les incunables" (in French). Bibliothèque nationale et universitaire de Strasbourg. Retrieved 9 January 2020.
- "Inkunabeln" (in German). Stadtbibliothek Nürnberg. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Inkunabeln" (in German). Universitätsbibliothek Erlangen-Nürnberg. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Collezioni" (in Italian). Biblioteca nazionale centrale di Roma. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Early Printed Books". National Széchényi Library. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Heidelberger Inkunabeln – digital" (in German). Universitätsbibliothek Heidelberg. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Incunaboli" (in Italian). Biblioteca Nazionale Universitaria di Torino. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Historische Sammlungen" (in German). Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek Sachsen-Anhalt. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Incunabula". Biblioteca Nacional de Portugal. Retrieved 4 September 2020.
- "Il patrimonio bibliografico" (in Italian). Biblioteca Universitaria di Padova. Retrieved 8 March 2011.
- "Alte Drucke und Rara" (in German). Zentralbibliothek Zürich. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Concise history of the monastic library". Royal Canonry of Premonstratensians at Strahov. Retrieved 16 May 2014.
- "Nos collections" (in French). Bibliothèque Sainte-Geneviève. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- "Collections, University Archives, Provenance Research" (in German). Universität Salzburg. Retrieved 4 September 2020.
- "Inkunabeln: Bestand" (in German). Badische Landesbibliothek. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Inkunabeln" (in German). Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek Bonn. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "La BmL en chiffres" (in French). Bibliothèque municipale de Lyon. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Historische Drucke (1450–1830)" (in German). Universitätsbibliothek Eichstätt-Ingolstadt. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- Roger Catlin (14 November 2014). "Walters Art Museum highlights the bumpy road of publishing, post-Gutenberg". Washington Post. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Fifteenth Century Printed Books at Bryn Mawr (BMC)". Tri-College Libraries. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Bestände" (in German). Ratsschulbibliothek Zwickau. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Distinctive Collections". Rare Book & Manuscript Library, University of Illinois. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- "Incunables de la Biblioteca Colombina" (in Spanish). Institución Colombina. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Universitätsbibliothek der Karl-Franzens-Universität Graz: Jahresbericht 2017" (PDF) (in German). Universitätsbibliothek der Karl-Franzens-Universität Graz. 2017. p. 43. Retrieved 4 September 2020.
- "Glasgow Incunabula Project : A Catalogue of Fifteenth-century Printed Books in Glasgow". University of Glasgow. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- "Incunabula: Printing in Europe before 1501". Bridwell Library, Perkins School of Theology, Southern Methodist University. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- "Recherche" (in German). Stiftsbibliothek St. Gallen. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "CATALOGUE COLLECTIF DE FRANCE : Bibliothèque Ceccano. Avignon, Vaucluse" (in French). Bibliothèque nationale de France. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "INKUNABELN" (in German). Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek Münster. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- As of August 07, 2019, the BML holds 882 incunabula, including a significant number of Hebrew medical texts, according to its president. https://legacy.countway.harvard.edu/bml/index.htm Archived 11 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine. The previously published figure was 565, in Garland, JE (1975). The Centennial History of the Boston Medical Library, 1875–1975. Boston: The Boston Medical Library in the Francis A. Countway Library of Medicine. p. 126.
- "Inkunabeln" (in German). Staats- und Universitätsbibliothek Dresden (SLUB). Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "The History of the Book". Free Library of Philadelphia. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "About the Rare Book Division". New York Public Library. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "INCUNABULA". Princeton University Library. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- Catalogue des incunables du canton de Fribourg par Romain Jurot. Avec la collaboration de Joseph Leisibach et Angéline Rais. Fribourg : Bibliothèque cantonale et universitaire, 2015. ISBN 978-2-9700704-9-8.
- Bibliothèque Interuniversitaire de la Sorbonne. Bibliotheque.sorbonne.fr. Retrieved on 2011-02-20.
- "Bibliothèque municipale de Rouen" (in French). Bibliothèque nationale de France. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- http://guides.bpl.org/incunabula. Retrieved 2 May 2020. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - "Collections: Rare Books & Journals". National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- "Histoire" (in French). Bibliothèque Humaniste de Sélestat. Retrieved 9 January 2020.
- "Médiathèque de la Vieille Ile. Haguenau, Bas-Rhin" (in French). Catalogue collectif de France (CCFr). Retrieved 12 December 2014.
- "IMPRIMÉS ANCIENS : Points fort" (in French). Bibliothèque de Genève. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Biblioteca Antica del Seminario Vescovile di Padova" (in Italian). Biblioteca Antica del Seminario Vescovile di Padova. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- Kopp, Maggie. "Renaissance and Reformation | World History & Culture | L. Tom Perry Special Collections". sites.lib.byu.edu. Harold B. Lee Library. Retrieved 9 November 2017.
- "Printed Books". Folger Shakespeare Library. Retrieved 3 October 2015.
- "Home – Medieval Studies". brown.edu.
- "Incunabula". Harry Ransom Center, The University of Texas at Austin. Archived from the original on 8 June 2010. Retrieved 12 May 2011.
- "Om inkunablerna i Åbo Akademis bibliotek" (in Swedish). Åbo Akademis bibliotek. 2002. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- "State Library Victoria search – incunabula specimens". search.slv.vic.gov.au.
- "Rare Book Collections". University of Chicago Library, Special Collections Research Center. Retrieved 20 August 2011.
- "Early Printed Books". University of Michigan Library. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- "Présentation des Fonds patrimoniaux" (in French). Portail des médiathèques de la ville et de l'Eurométropole de Strasbourg. Retrieved 9 January 2020.
- Bordeaux : Culture – Bibliothèque. Bordeaux.fr. Retrieved on 2011-02-20.
- "Biblioteca Rector Machado y Núñez: Espacios y servicios" (in Spanish). Biblioteca de la Universidad de Sevilla. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- "Incunabula in the Dibner Library of the History of Science and Technology". Smithsonian Libraries. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- "Rare books". Vilnius University Library. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- "Incunabula Guide". library.leeds.ac.uk. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- (in French) Patrimoine documentaire / Documentation / Université Montpellier 1 – Université Montpellier 1. Univ-montp1.fr. Retrieved on 2011-02-20.
- [Hand-list of Incunabula in the National Library of Wales compiled by Victor Scholderer (N.L.W. Journal Supplement Series 1, No. 1, 1940)]
- "Incunabula Collection". Stanford University, Stanford Libraries. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- "La bibliothèque ancienne du Grand Séminaire" (in French). Séminaire Sainte Marie Majeure – Diocèse de Strasbourg. 27 October 2014. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Incunabula specimen search". SL-NSW. Retrieved 9 December 2018.
- "Zámecká knihovna – Kynžvart". zamek-kynzvart.cz.
- "Incunabula". University of Toronto. Retrieved 7 January 2016.
- "Rare Books, Prints, & Maps". Trinity College, Watkinson Library. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- "Thomas Fisher Rare Book Library: Incunabula". University of Toronto Libraries. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- Latimer Family Library brochure, May 2015.
- "UCL Special Collections". University College London Library. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "Incunabula". Cardiff University Library. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- "Dartmouth College Library /All". libcat.dartmouth.edu. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Incunabula. |
- Centre for the History of the Book
- British Library worldwide Incunabula Short Title Catalogue
- Gesamtkatalog der Wiegendrucke (GW), partially English version
- History of Incunabula Studies
- UIUC Rare Book & Manuscript Library
- Grand Valley State University Incunabula & 16th Century Printing digital collections
- Incunable Collection at the US Library of Congress
- Digital facsimiles of several incunabula from the website of the Linda Hall Library
- Kristian Jensen (2016). "Introduction to the study of incunabula". Lyon: Ecole Nationale Superieure des Sciences de l'information et des Bibliotheques, Institut d'histoire du livre. Archived from the original on 27 November 2017. (Includes annotated bibliography)
- "Rinascimento: Manuscripts & Incunabula". Research Guides. US: Harvard University Library.
- Pollard, Alfred W. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. 14 (11th ed.). pp. 369–370.
- "An Introduction to Incunabula". Barber, Phil. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
