KCNK4
Potassium channel subfamily K member 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNK4 gene.[5][6][7] KCNK4 protein channels are also called TRAAK channels.
Function
Potassium channels play a role in many cellular processes including the maintenance of the action potential, muscle contraction, hormone secretion, osmotic regulation, and ion flow. This gene encodes the K2P4.1 protein, a lipid-gated ion channel that belongs to the superfamily of potassium channel proteins containing two pore-forming P domains. K2P4.1 homodimerizes and functions as an outwardly rectifying channel. It is expressed primarily in neural tissues and is stimulated by membrane stretch and polyunsaturated fatty acids.[7]
TRAAK channels are found in mammalian neurons and are part of a protein family of weakly inward rectifying potassium channels. This subfamily of potassium channels is mechanically gated. The C-terminal of TRAAK has a charged cluster that is important in maintaining the mechanosensitive properties of the channel.[8]
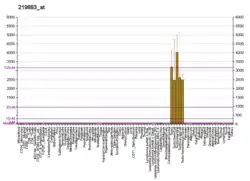
TRAAK is only expressed in neuronal tissue, and can be found in the brain, spinal cord, and retina, which suggests that it has a function beyond mechanotransduction in terms of neuronal excitability.[9] The highest levels of TRAAK expression are in the olfactory system, cerebral cortex, hippocampal formation, habenula, basal ganglia, and cerebellum.[9] TRAAK channels are mechanically activated when there is a convex curvature in the membrane that alters the channel’s activity. TRAAK channels are thought to have a role in axonal pathfinding, growth cone motility, and neurite elongation, as well as possibly having a role in touch or pain detection.[10][11]
See also
- Tandem pore domain potassium channel
References
Scrmfclh åznxjzodus
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000182450 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000024957 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Lesage F, Maingret F, Lazdunski M (May 2000). "Cloning and expression of human TRAAK, a polyunsaturated fatty acids-activated and mechano-sensitive K(+) channel". FEBS Lett. 471 (2–3): 137–40. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01388-0. PMID 10767409. S2CID 31793244.
- Goldstein SA, Bayliss DA, Kim D, Lesage F, Plant LD, Rajan S (Dec 2005). "International Union of Pharmacology. LV. Nomenclature and molecular relationships of two-P potassium channels". Pharmacol Rev. 57 (4): 527–40. doi:10.1124/pr.57.4.12. PMID 16382106. S2CID 7356601.
- "Entrez Gene: KCNK4 potassium channel, subfamily K, member 4".
- Patel AJ, Honoré E, Lesage F, Fink M, Romey G, Lazdunski M (1999). "Inhalational anesthetics activate two-pore-domain background K+ channels". Nature Neuroscience. 2 (5): 422–426. doi:10.1038/8084. PMID 10321245. S2CID 23092576.
- Fink M, Lesage F, Duprat F, Heurteaux C, Reyes R, Fosset M, Lazdunski M (1998). "A neuronal two P domain K+ channel stimulated by arachidonic acid and polyunsaturated fatty acids". The EMBO Journal. 17 (12): 3297–3308. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.12.3297. PMC 1170668. PMID 9628867.
- Vandorpe DH, Morris CE (1992). "Stretch activation of the Aplysia S-channel". The Journal of Membrane Biology. 127 (3): 205–214. doi:10.1007/bf00231508. PMID 1495087. S2CID 29622155.
- Maingret F, Fosset M, Lesage F, Lazdunski M, Honoré E (1999). "TRAAK is a mammalian neuronal mechano-gated K+ channel". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (3): 1381–1387. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.3.1381. PMID 9880510.
Further reading
- Goldstein SA, Bockenhauer D, O'Kelly I, Zilberberg N (2001). "Potassium leak channels and the KCNK family of two-P-domain subunits". Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2 (3): 175–84. doi:10.1038/35058574. PMID 11256078. S2CID 9682396.
- Chapman CG, Meadows HJ, Godden RJ, et al. (2001). "Cloning, localisation and functional expression of a novel human, cerebellum specific, two pore domain potassium channel". Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 82 (1–2): 74–83. doi:10.1016/S0169-328X(00)00183-2. PMID 11042359.
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (2001). "DNA Cloning Using In Vitro Site-Specific Recombination". Genome Res. 10 (11): 1788–95. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948. PMID 11076863.
- Meadows HJ, Chapman CG, Duckworth DM, et al. (2001). "The neuroprotective agent sipatrigine (BW619C89) potently inhibits the human tandem pore-domain K(+) channels TREK-1 and TRAAK". Brain Res. 892 (1): 94–101. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(00)03239-X. PMID 11172753. S2CID 37830674.
- Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R, et al. (2001). "Toward a Catalog of Human Genes and Proteins: Sequencing and Analysis of 500 Novel Complete Protein Coding Human cDNAs". Genome Res. 11 (3): 422–35. doi:10.1101/gr.GR1547R. PMC 311072. PMID 11230166.
- Simpson JC, Wellenreuther R, Poustka A, et al. (2001). "Systematic subcellular localization of novel proteins identified by large-scale cDNA sequencing". EMBO Rep. 1 (3): 287–92. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvd058. PMC 1083732. PMID 11256614.
- Ozaita A, Vega-Saenz de Miera E (2003). "Cloning of two transcripts, HKT4.1a and HKT4.1b, from the human two-pore K+ channel gene KCNK4. Chromosomal localization, tissue distribution and functional expression". Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 102 (1–2): 18–27. doi:10.1016/S0169-328X(02)00157-2. PMID 12191490.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Hillman RT, Green RE, Brenner SE (2005). "An unappreciated role for RNA surveillance". Genome Biol. 5 (2): R8. doi:10.1186/gb-2004-5-2-r8. PMC 395752. PMID 14759258.
- Harinath S, Sikdar SK (2004). "Trichloroethanol enhances the activity of recombinant human TREK-1 and TRAAK channels". Neuropharmacology. 46 (5): 750–60. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2003.11.023. PMID 14996553. S2CID 10938867.
- Wiemann S, Arlt D, Huber W, et al. (2004). "From ORFeome to Biology: A Functional Genomics Pipeline". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2136–44. doi:10.1101/gr.2576704. PMC 528930. PMID 15489336.
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, et al. (2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: Large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes". Genome Res. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560.
- Mehrle A, Rosenfelder H, Schupp I, et al. (2006). "The LIFEdb database in 2006". Nucleic Acids Res. 34 (Database issue): D415–8. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj139. PMC 1347501. PMID 16381901.
External links
- KCNK4+protein,+human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.