McDonnell Douglas Phantom in UK service
The United Kingdom operated the McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II as one of its principal combat aircraft from 1968 to 1992. The UK was the first export customer for the Phantom, which was ordered in the context of political and economic difficulties around British designs for the roles that it eventually undertook. The Phantom was procured to serve in both the Royal Navy's Fleet Air Arm (FAA) and the Royal Air Force in several roles including air defence, close air support, low-level strike and tactical reconnaissance.

Although assembled in the United States, the UK's early Phantoms were a special batch built separately with a significant amount of British technology as a means of easing the pressure on the domestic aerospace industry in the wake of major project cancellations.[1] Two variants were initially built for the UK: the F-4K variant was designed from the outset as an air defence interceptor to be operated by the FAA from the Royal Navy's aircraft carriers, and the F-4M version was procured for the RAF to serve in the tactical strike and reconnaissance roles. In the mid-1980s, a third Phantom variant was obtained when 15 second-hand F-4J aircraft were purchased to augment the UK's air defences following the Falklands War.
The Phantom entered service with both the FAA and the RAF in 1969. In FAA service, it had a secondary strike role, while in the RAF it was soon replaced in the strike role by other aircraft designed specifically for strike and close air support. By the mid-1970s, the Phantom had become the UK's principal interceptor, a role in which it continued until the early 1990s.
Background


In the late 1950s, the British Government began the process of replacing its early second-generation jet combat aircraft in service with the Royal Air Force (RAF) and Fleet Air Arm (FAA). At the time, the British aerospace industry was still the major provider of aircraft to the British armed forces, and designs from several companies were in service. The 1957 Defence White Paper precipitated a significant change in the industry as the Government compelled major aerospace manufacturers to amalgamate using new aircraft contracts as an incentive. As a result two large groups emerged; The British Aircraft Corporation was formed by the merger of English Electric, Vickers-Armstrongs, Bristol and Hunting, and Hawker Siddeley was formed from the merger of Hawker Siddeley Aviation, Folland, de Havilland and Blackburn.[2]
At this time, the RAF wished to replace the English Electric Canberra light bomber in the long-range interdictor role, and the Hawker Hunter in the close air support role, while the Royal Navy sought an aircraft to assume the fleet air defence role from the de Havilland Sea Vixen. BAC, through its English Electric subsidiary, had begun developing a new high-performance strike aircraft, the TSR-2,[3] which was intended for long-range, low-level strike missions with conventional and tactical nuclear weapons, as well as tactical reconnaissance. Hawker Siddeley was also developing the P.1154, a proposed supersonic version of its P.1127 V/STOL demonstrator, that could be marketed to both the RAF and Royal Navy to fulfil a number of roles: close air support, air superiority and fleet air defence.[4]
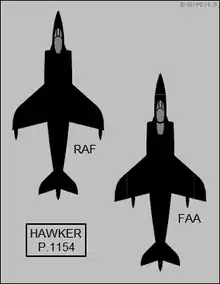
During the early 1960s, aircraft development became increasingly expensive, resulting in major projects often becoming mired in political and economic concerns. The TSR-2 project experienced increasing cost overruns.[5] The P.1154 was subject to the ongoing inter-service rivalry between the Royal Navy and RAF, which led to two wildly differing specifications being submitted for the aircraft that were impossible to fulfil with a single airframe.[6]
In February 1964, the Royal Navy withdrew from the P.1154 project, and moved to procure a new fleet air defence interceptor.[7] It eventually selected the McDonnell F-4 Phantom[lower-roman 1], then in service with the United States Navy (USN) as its primary air defence aircraft, intended to be operated from both existing and planned aircraft carriers. This better suited the Royal Navy, as the Phantom had two engines (providing redundancy in the event of an engine failure), was cheaper than the P.1154, and was available immediately.[10] In October the same year, the general election brought the Labour Party back into power. The new government undertook a defence review, which led to the publication in February 1966 of a white paper that cancelled several projects, including both the P.1154 and the TSR-2. As a consequence, the government had to find alternatives to replace the Canberra and Hunter for the RAF. To replace the Canberra in the long-range role (which was intended for the TSR-2), the F-111 was selected, with plans for a redesigned variant, while the roles undertaken by the Hunter (for which P.1154 was to be procured) would be undertaken by a further purchase of F-4 Phantoms.[11]
The Royal Navy was happy with the choice of the aircraft as its Sea Vixen replacement, given that the type had been operational in the fleet air defence role with the USN since 1961. US aircraft had also successfully undertaken touch-and-go landings on both HMS Hermes and HMS Victorious.[12][13][14] The RAF was less enthusiastic, as the Phantom was not optimised for the close air support role, and had been selected as its Hunter replacement more as a way of decreasing the per-unit cost of the overall UK order.[15]
%252C_Ark_Royal_(R09)_and_Hermes_(R12)_underway_c1961.jpg.webp)
Partly as a means of maintaining employment in the British aerospace industry, agreement was reached that major portions of the UK's Phantoms would be built domestically.[1] Hawker Siddeley Aviation was appointed as McDonnell's primary UK partner in January 1965, to be responsible for repair, maintenance, design and modification work on Phantoms for the RAF and RN at Brough Aerodrome.[17] Further work was delegated to both BAC, at its Warton facility, and Short Brothers in Belfast.[18]
The F-4J variant, which was then the primary version in service with the USN, was taken as the basis for the UK aircraft, subject to major redesign. The most significant change was the use of the larger and more powerful Rolls-Royce Spey turbofan in place of the GE J79 turbojet to allow operations from the Royal Navy's smaller carriers.[19] To accommodate the larger engines, BAC redesigned and built the entire rear fuselage section.[18] The Westinghouse AN/AWG-10 radar carried by the F-4J was to be procured and built under licence by Ferranti as the AN/AWG-11 for FAA aircraft and AN/AWG-12 for those of the RAF.[20] In total, approximately half of the structure and equipment of the UK's Phantoms was produced by British manufacturers, with all of the components then shipped for assembly by McDonnell in St Louis.[18] The changes to the aircraft led to the two variants being given their own separate series letters, with the FAA version being designated as the F-4K and the RAF version as the F-4M.[21]
Initially, there was an intention to procure up to 400 aircraft for the Royal Navy and the RAF, but the development cost for the changes to accommodate the new engines meant that the per-unit price eventually ended up three times the price of an F-4J. Due to government policy the budget for the Phantom procurement was fixed, therefore these costs could not be evened out by a large production run and only 170 were ordered.[22]
Variants

Prototypes
The British Government ordered four prototypes (two F-4K and two F-4M), together with a pair of pre-production F-4K aircraft. The first UK Phantom, a prototype F-4K (designated YF-4K), first flew on 27 June 1966 at the McDonnell plant in St. Louis. The second made its first flight on 30 August 1966. The two pre-production F-4K aircraft were constructed alongside the prototypes, and were initially used for fit check trials of the various systems to be fitted. The first was used for catapult/arrestor and deck landing trials, and the second was primarily for testing the radar and missile systems. All four were delivered to the UK from 1969 to 1970 for continued test work by the Aeroplane and Armament Experimental Establishment (A&AEE), Ministry of Defence Procurement Executive, Rolls-Royce and BAC (and later its successor, British Aerospace).[23][24] The first F-4M prototype (designated YF-4M) first flew on 17 February 1967, and was also used for fit checks before delivery to the UK.[25]
F-4K Phantom FG.1
| F-4K Phantom FG.1 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| A Royal Air Force Phantom FG.1 of 43 Squadron in 1980. | |
| Role | Fleet air defence fighter Air defence interceptor |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | McDonnell Douglas |
| First flight | 27 June 1966 |
| Introduction | 30 April 1968 (FAA) 1 September 1969 (RAF) |
| Retired | 27 November 1978 (FAA) 30 January 1990 (RAF) |
| Status | Withdrawn |
| Primary user | Royal Air Force Fleet Air Arm |
| Produced | 1966–69 |
| Number built | 52 (incl. 2 prototypes) |
| Career | |
| Serial | XT595 – XT598[26] XT857 – XT876[26] XV565 – XV592[27] XV604 – XV610 (cancelled)[27] |
Royal Navy
In 1964, the Phantom was ordered for the FAA to serve as the Royal Navy's primary fleet air defence aircraft, with a secondary strike capability. It was intended that these aircraft would operate from the decks of four aircraft carriers; Eagle and Ark Royal, which would be rebuilt to enable the operation of the aircraft,[29][lower-roman 2] and two planned new ships.[lower-roman 3][33]
| Ship | Displacement | Length | Beam | Number of aircraft | Notes | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ark Royal | 53,000 long tons (54,000 t) | 803.5 ft (244.9 m) | 171 ft (52 m) | 50 | [34] | |
| Eagle | 54,100 long tons (55,000 t) | 811.5 ft (247.3 m) | 171 ft (52 m) | 45 | Major reconstruction 1959–64 | [35] |
| Victorious | 35,500 long tons (36,100 t) | 781 ft (238 m) | 157 ft (48 m) | 36 | Major reconstruction 1950–58 to allow operation of modern aircraft | [35] |
| Hermes | 28,700 long tons (29,200 t) | 744 ft (227 m) | 144.5 ft (44.0 m) | 28 | [35] | |
| Centaur | 27,000 long tons (27,000 t) | 737 ft (225 m) | 123 ft (37 m) | 26 | Used primarily during absence of other ships due to reconstruction | [36] |
_in_1963.jpg.webp)
%252C_November_1975.jpg.webp)
The requirements for the intended force of four carriers meant that five squadrons of Phantoms would be needed.[22] However, in its 1966 Defence White Paper, the Government decided to cancel the two new carriers, which led to a reduction in the total order from 140 to just 48, with options for another seven.[38] The intention was to form a pair of front-line squadrons, each of twelve aircraft, that would operate from the two remaining, heavily modernised fleet carriers. The remaining 24 aircraft were to be used to form a training unit, and to provide a reserve pool in the event of aircraft losses.[31]
The Royal Navy received its first F-4K Phantoms, which carried the British designation FG.1, in April 1968.[39] These were assigned to 700P Naval Air Squadron (NAS), which was to serve as the Intensive Flying Trials Unit. Upon completion of the successful flight trials, 767 Naval Air Squadron was commissioned in January 1969 as the FAA's training squadron. This was followed at the end of March 1969 by 892 Naval Air Squadron, which was commissioned as the Royal Navy's first operational Phantom unit.[40][41] During 892 NAS's initial work up, three of its aircraft were entered in the Daily Mail Trans-Atlantic Air Race, a competition to commemorate the 50th anniversary of the first trans-Atlantic flight.[42] One aircraft set a record of four hours and 46 minutes for the west to east crossing between Floyd Bennett Field in New York City and Wisley Airfield outside London, a record that stood for five years.[43][44]
At the same time as the FAA was receiving its first aircraft, the A&AEE had three FG.1s delivered to its 'C' Squadron for flight deck trials aboard Eagle. Two sets of trials were successfully carried out in March and June 1969; the first comprised approaches and touch-and-go landings,[45] while the second set of trials involved full catapult launch and arrested recovery.[46] As a result of the reheat from the Spey turbofans, the ship's jet blast deflectors (JBD) were not used; instead a steel plate was fixed to the deck to absorb the heat of the engines building to launch, and fire hoses were used after each launch to prevent them melting.[47]
Ark Royal had entered refit to accommodate the Phantom in 1967; this involved a major reconstruction, including several elements to allow the ship to operate the aircraft – the flight deck was increased in area and fully angled to 8½°, the arresting gear was replaced with a new water-spray system[48] to accommodate the Phantom's higher weight and landing speed, and bridle catchers[lower-roman 4] and water-cooled JBDs[lower-roman 5] were fitted to the catapults.[37] Once this work was complete, Eagle was scheduled to undergo a similar modernisation. However, the planned phasing-out of fixed-wing aviation in the Royal Navy led to the intended refit of Eagle being cancelled, with the options for seven additional FG.1s not taken up.[27] As a consequence, it was decided to further reduce the FAA's Phantom fleet to just 28 aircraft.[38]
In 1970, Ark Royal embarked 892 NAS as part of her air group for the first time, with a total of 12 aircraft. The first operational use of the Royal Navy's Phantoms had come in 1969, when 892 NAS had embarked for training with the US aircraft carrier USS Saratoga in the Mediterranean, and had undertaken air defence missions alongside the ship's own F-4Js.[49] This deployment showed the necessity for the modifications fitted to Ark Royal. During the initial launches from Saratoga, the heat from the afterburners, combined with the increased angle of attack resulting from the extendable nosewheel, caused the deck plates to distort, leading to subsequent catapult launches being undertaken at reduced weight without the use of re-heat.[30]
During Ark Royal's first three-year commission, 892 NAS, which had initially used RNAS Yeovilton in Somerset as its home base, moved to RAF Leuchars in Fife where, during the periods when it was not embarked, it undertook Quick Reaction Alert (QRA) duties alongside the RAF's 43 Squadron. At the same time, 767 NAS was disbanded as the Royal Navy's Phantom training unit - the squadron had been the joint training unit for both the FAA and the RAF in using the FG.1. In its place, an RAF-operated Phantom Training Flight was established at RAF Leuchars in August 1972.[50][51]
The Phantom served in the FAA until 1978, when Ark Royal was withdrawn from service, leaving no ship in the Royal Navy capable of operating the type. The final catapult launch from Ark Royal was a Phantom of 892 NAS on 27 November 1978 during the disembarkation of the air group;[52] the squadron's aircraft were delivered to RAF St Athan in Wales, where they were handed over to the RAF.[53] During the type's service with the Royal Navy, 10 of the total FAA fleet of 28 were lost in crashes.[54]
Royal Air Force
Following the cancellation of the planned refit of HMS Eagle to allow her to operate the Phantom, a total of 20 airframes that had originally been ordered for the FAA were diverted to the RAF to serve in the air defence role.[28] At the time, the RAF's primary interceptor was the English Electric Lightning, which had comparatively poor range, loiter time and weapons fit. These limitations hampered its effectiveness, especially in long interceptions of Soviet Air Forces and Soviet Naval Aviation bombers and reconnaissance aircraft over the North Sea and North Atlantic. A new Phantom squadron was formed at RAF Leuchars,[50] the UK's most northerly air defence base at the time, to take advantage of the improvements that the Phantom provided over the Lightning – it could carry more fuel, and had consequently better range and endurance; it was fitted with a more powerful radar; and it could carry more missiles (up to 8, compared to 2 for the Lightning).[lower-roman 6] On 1 September 1969, 43 Squadron was formed at Leuchars, operating as part of the UK's northern QRA zone alongside the Lightnings of 11 Squadron and 23 Squadron. In 1972, when 11 Squadron was redeployed to join 5 Squadron at RAF Binbrook, it was replaced at Leuchars by the Royal Navy Phantoms of 892 NAS.[41][56]
Upon the withdrawal of HMS Ark Royal in 1978, the Phantoms of the FAA were handed over to the RAF and used to form a second squadron at Leuchars. At the time, 111 Squadron was stationed there operating the FGR.2 version of the Phantom, having been there since 1975.[57] In 1979, to save costs resulting from the differences between the FG.1 and FGR.2, the squadron converted to the ex-Navy aircraft and the FGR.2 airframes were distributed to other Phantom units. Upon 111 Squadron's conversion to the FG.1, the Phantom Training Flight, which had been resident at Leuchars since 1972, was disbanded, and responsibility for all Phantom conversion training turned over to 228 Operational Conversion Unit.[50]
Both 43 and 111 Squadrons retained the FG.1 until 1989, when they converted to the new Tornado F.3. Following the standing down of the two operational squadrons and the final withdrawal of the type from service, the bulk of the RAF's FG.1 Phantoms were scrapped.[58][59] The RAF lost eight of their FG.1s in crashes throughout the type's twenty year service.[54]
Operators (FG.1)
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
- Aeroplane and Armament Experimental Establishment[60]
 Royal Navy[41]
Royal Navy[41]
- 700P Naval Air Squadron
- 767 Naval Air Squadron
- 892 Naval Air Squadron
 Royal Air Force[50]
Royal Air Force[50]
- No. 43 Squadron
- No. 64 (R) Squadron
- No. 111 Squadron
- Phantom Training Flight
F-4M Phantom FGR.2
| F-4M Phantom FGR.2 | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) | |
| A Royal Air Force Phantom FGR.2 of 92 Squadron in 1990. | |
| Role | Air defence interceptor Low level strike Close air support |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | McDonnell Douglas |
| First flight | 17 February 1967 |
| Introduction | 23 August 1968 |
| Retired | 1 November 1992 |
| Status | Withdrawn |
| Primary user | Royal Air Force |
| Produced | 1966–69 |
| Number built | 118 (incl. 2 prototypes) |
| Career | |
| Serial | XT852 – XT853[26] XT891 – XT914[26] XV393 – XV442[27] XV460 – XV501[27] XV520 – XV551 (cancelled)[27] |
Close air support
Following the cancellation of both the TSR-2 and P.1154 programmes, the RAF was still left with a requirement for aircraft in the long-range strike, close air support and reconnaissance roles. This resulted in orders for two aircraft types, the General Dynamics F-111K, intended for the long-range interdiction role, and the F-4M Phantom, which would be used for close air support; both aircraft were to be fitted for reconnaissance.[61][62] The F-111K was cancelled within a year of being ordered, but the order for 150 Phantoms went ahead alongside the Phantom order for the Royal Navy; the final 32 units of the RAF order were eventually cancelled.[63] The RAF Phantom, given the designation FGR.2, was broadly similar to the naval version, with some minor variations in terms of engines, avionics and structure, relating to its use as a land-based, rather than carrier-based aircraft.[64]
The first RAF Phantom unit was 228 Operational Conversion Unit, which was stood up in August 1968.[50] The Phantom entered operational service as part of Strike Command in May 1969, when 6 Squadron was formed at RAF Coningsby in the tactical strike role. 54 Squadron was formed in September the same year, followed by 41 Squadron in 1972 as a tactical reconnaissance unit. A further four squadrons were formed under RAF Germany in 1970 and 1971: 2, 14, 17 and 31 Squadrons, all at RAF Brüggen.[50]
Along with their conventional strike role, 14, 17 and 31 Squadrons were assigned a tactical nuclear strike role by SACEUR, using weapons supplied by the United States.[65][66] After initial work-up, 2 Squadron operated from RAF Laarbruch in the tactical reconnaissance role. The aircraft assigned to the two tactical reconnaissance units were fitted with a pod containing four optical cameras, an infrared linescan and a sideways looking radar.[67]
During the 1970s, France and the UK were developing a new aircraft which could fill the RAF tactical strike and reconnaissance missions: the SEPECAT Jaguar was introduced into service in 1974, and led to a re-think of the Phantom's role as, at the same time, the limitations of the Lightning as an interceptor were becoming more apparent. The conversion of the RAF's FGR.2 squadrons to operate the Jaguar, combined with its use of the Blackburn Buccaneer, meant that it was possible to begin transferring Phantoms to operate purely as interceptors in the air defence role.[50]
Air defence
In October 1974, 111 Squadron converted from the Lightning to the Phantom FGR.2, becoming the first unit to operate the type in the air defence role (notwithstanding 43 Squadron, which had used the FG.1 version since 1969). As more Jaguars were delivered, more Phantoms were released enabling existing Lightning squadrons to be converted;[68] 19 Squadron and 92 Squadron, the forward deployed air defence units in Germany, converted in 1976 and 1977 respectively, at the same time moving from RAF Gütersloh, which was the closest RAF base to the East German border, to RAF Wildenrath, taking advantage of the Phantom's superior range over the Lightning.[22] Three further UK based squadrons, 23, 29 and 56, were also converted between 1974 and 1976.[22] 111 Squadron, which had been the first unit to use the FGR.2 as an interceptor, converted to the FG.1 version in 1979 following the transfer of the Royal Navy's remaining airframes to the RAF.[50] The Phantom subsequently served as the RAF's primary interceptor for over a decade until the introduction into service of the Panavia Tornado F.3 in 1987.[69][70]
When Phantoms were first delivered to interceptor squadrons, they remained in the grey-green camouflage colour scheme more associated with the strike and close air support missions they had undertaken. During the late 1970s, the RAF began experimenting with new colours for its air defence units, with 56 Squadron tasked with trialling proposed new schemes. In October 1978, a Phantom FGR.2 of 56 Squadron became the first to be painted in the new air superiority grey colour, combined with small, low visibility roundels and markings. However, although the roundel remained in low visibility colours, individual squadron markings eventually returned to more observable sizes and colours.[71][72]
In May 1982, three Phantoms from 29 Squadron were forward deployed to RAF Wideawake on Ascension Island to provide air cover for the RAF's operations during the Falklands War, replacing Harriers of 1 Squadron, which were transiting to the war zone.[73] In October 1982, following the end of the conflict and the reconstruction of the runway, 29 Squadron detached nine of its aircraft to RAF Stanley to provide air defence for the Falkland Islands.[74] In March 1983 23 Squadron took up the role, remaining stationed there until October 1988, when they were replaced by 1435 Flight. To make up for the loss of an entire squadron from the UK Air Defence Region, the RAF procured 15 ex-USN F-4J Phantoms. These aircraft were operated by 74 Squadron from 1984 until 1991, when they were replaced by FGR.2 Phantoms that had been released by other squadrons following their conversion to the Tornado.[75]
Initially, it was intended that Phantoms and Tornados would serve alongside each other. A total of 152 Tornado F.3s were ordered for the RAF, enough to convert four squadrons of Phantoms and two of Lightnings, but insufficient to completely convert every air defence squadron. Both 23 and 29 Squadrons converted from the Phantom FGR.2 to the Tornado between 1987 and 1988, alongside the conversion of the final two remaining Lightning squadrons. The intention was to retain a pair of UK based Phantom squadrons at RAF Wattisham, alongside a pair of Tornado units at RAF Coningsby to provide air defence cover for the southern half of the UK Air Defence Region.[76] Another two squadrons stationed in Germany would also be retained.[77][78]
However the end of the Cold War saw the Phantom withdrawn from service under the Options for Change defence review. This saw the disbanding of 228 Operational Conversion Unit in January 1991, with the Phantom Training Flight, which had previously operated FG.1 training between 1972 and 1978, re-established for twelve months to run refresher courses on the type.[50] As part of the gradual run down of the RAF's presence in Germany, the two forward based units were to be disbanded, while there would also be a reduction in the number of air defence squadrons leading to the two UK based units being disbanded in late 1992.[79][75] However, just prior to the final withdrawal of the Phantom, it was recalled operationally as a result of Operation Granby, the UK's participation in the First Gulf War, when aircraft from 19 and 92 Squadrons were forward deployed to provide air defence cover at RAF Akrotiri; this was to replace the Tornados that had been originally deployed there on exercise, and were subsequently sent to the Gulf region.[80] Following their final withdrawal from service, with a few exceptions, the bulk of the RAF's FGR.2 fleet was scrapped.[59] Over its service life, 37 FGR.2s were lost to crashes.[54]
Operators (FGR.2)
|
|
|
F-4J(UK) Phantom F.3
| F-4J(UK) Phantom F.3 | |
|---|---|
_Phantom_of_74_Squadron_in_flight_1984.jpg.webp) | |
| A Royal Air Force Phantom F.3 of 74 Squadron in 1984. | |
| Role | Air defence interceptor |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | McDonnell Douglas |
| First flight | 10 August 1984 |
| Introduction | 19 October 1984 |
| Retired | 31 January 1991 |
| Status | Withdrawn |
| Primary user | Royal Air Force |
| Produced | 1984 |
| Number built | 15 |
| Career | |
| Serial | ZE350 – ZE364[82] |
After the Falklands War, the UK government began upgrading the defences of the Falkland Islands to guard against any further aggression from Argentina. One of the measures taken was the deployment of 9 FGR2’s from 29 Squadron to RAF Stanley in October 1982, 23 Squadron taking the aircraft over in March 1983.[83] The removal of a squadron of Phantoms to the Falkland Islands left a gap in the UK's air defences and nothing immediately available to fill it. As a result, the UK government decided to purchase another squadron of Phantoms.[84]
Because the aircraft in RAF service were a special production batch built to UK specifications, it would not be possible to obtain identical aircraft, so 15 airframes were procured from among the best of the ex-USN F-4Js stored at the Aerospace Maintenance and Regeneration Center at Davis–Monthan Air Force Base in Arizona.[84] The F-4J was chosen because it was the variant from which the RAF's F-4Ks and F-4Ms were developed, and was thus the closest available to the British aircraft. The 15 that were selected were extensively refurbished at the Naval Air Rework Facility at NAS North Island and brought to a standard almost equivalent to the F-4S, which was the last variant in service with the USN, the only differences being the absence of leading-edge slats and a helmet gun sight.[84][85]
The major difference between the F-4J and the British Phantoms was the absence of the Rolls-Royce Spey turbofan, the former being fitted with the General Electric J79-10B turbojet. This produced less power than the British engine, but had a faster afterburner light up, giving it better performance at high altitude, at the expense of slightly poorer acceleration at low level. The high-altitude performance was helped by the reduced drag from its smaller air intakes.[84] Initially capable of carrying the AIM-7 Sparrow and AIM-9 Sidewinder air-to-air missiles (AAM), they were soon made compatible with the Skyflash and SUU-23A gun pod, bringing them into line with the rest of the RAF's Phantoms.[84] Despite modifications to allow them to operate with the rest of the fleet, the F-4Js retained the vast bulk of the equipment they were originally fitted with, even requiring their crews to use American flying helmets.[22]
Although the new Phantoms were assigned a British designation as the F.3,[86][87] they were generally referred to as the F-4J(UK).[38][88] They were assigned to 74 Squadron at RAF Wattisham, which stood up in October 1984, two months after the first flight.[50] The aircraft remained in service through the transition to the Tornado, which began entering service in 1987. In 1990, thanks to the conversion of F-4M squadrons to the Tornado, the RAF were able to transfer the best of its remaining FGR.2s to 74 Squadron, which meant that the F.3 was able to be withdrawn in January 1991.[75] With a couple of exceptions, all of the RAF's F-4Js were broken up for scrap.[59] One of the 15 airframes was lost in a crash in 1987, killing both crew members.[54]
Operators (F.3)
 Royal Air Force[50]
Royal Air Force[50]
- No. 74 Squadron
Variations
FG.1 and FGR.2

The Phantom FG.1 and FGR.2 as built were similar, being fitted with broadly the same engines and avionics, although there were minor differences. The FG.1 was initially fitted with the Mark 201 version of the Rolls-Royce Spey turbofan, while the FGR.2 had the Mark 202; the Mark 201 had a degree of lag between throttle selection and engine response, which was remedied in the 202. The 201 was eventually upgraded to the Mark 203 version, which had a modified control system for the afterburner, allowing it to light faster and enable power to be applied quickly in the event of a bolter on the small decks of the Royal Navy's aircraft carriers.[89][18] Both variants were fitted with a licence built version of the Westinghouse AN/AWG-10 avionics package; the FG.1 was fitted with the AN/AWG-11, which differed primarily in having a nose radome that was hinged and able to fold backwards against the aircraft's fuselage to allow for storage in the hangar of an aircraft carrier;[lower-roman 8] the system was designed to be integrated with both the AGM-12 Bullpup missile and WE.177 free-fall nuclear weapon as required. The AN/AWG-12 fitted to the FGR.2 was not foldable, and featured a better ground mapping mode, to take into account the strike role for which the type was originally procured; allied to this was a Ferranti inertial navigation/attack system (removed when the type converted to the air defence role).[22] It was also configured to be able to control the SUU-23/A gun pod; FG.1s used by the RAF were also able to use the gun pod, but the Royal Navy's FG.1s lacked this capability.[92][93]
British Phantoms and other Phantoms
Although there were minor differences between the two types of Phantom built for the UK, there were many significant ones between the British Phantoms and those built for the United States. The most obvious was the substitution of the Rolls-Royce Spey turbofan for the General Electric J79 turbojet. The Spey was shorter but wider than the J79, which meant that the British Phantoms' intakes had to be redesigned for a higher airflow, making them 20% larger (with a consequent increase in drag), while the fuselage was widened by 152 mm (6.0 in). The position of the afterburner also meant that the rear of the fuselage had to be made deeper.[95] Auxiliary intake doors were fitted on the rear fuselage.[96]
Performance estimates of the British Phantom compared to its American equivalent indicated that the former had a 30% shorter take-off distance, 20% faster climb to altitude, higher top speed and longer range.[95] The Spey was more efficient at lower altitudes, and had better acceleration at low speed, giving British Phantoms better range and acceleration, which was shown during the deployment of 892 NAS to the Mediterranean aboard USS Saratoga in 1969, when the F-4K was repeatedly quicker off the deck than the F-4J used by the Americans.[97] It was less efficient at higher altitudes, the British Phantoms lacking speed compared to J79-powered versions owing to the increased drag of the re-designed fuselage.[18][95] This discrepancy became apparent when the F-4J was obtained by the UK in 1984; it was regarded as being the best of the three variants to serve in the RAF.[85]
The small size of the aircraft carriers Eagle and Ark Royal, from which the Royal Navy's Phantoms were intended to operate, compared to the USN carriers of the period, meant that the F-4K version required significant structural changes compared to the F-4J, from which it was descended, and which performed a similar role. As well as the folding nose radome to allow for storage in the smaller hangars of the British ships, it had to have a significantly strengthened undercarriage to account for the higher landing weight (British policy was to bring back unused ordnance). The F-4J featured a nosewheel oleo that extended by 20 inches (51 cm) to provide the correct attitude for launch from American catapults.[94] The F-4K's nosewheel oleo extended by 40 inches (100 cm) to increase the take-off attitude (the extension of the nosewheel put the Phantom at a 9° attitude[98]) due to the shorter and less powerful British catapults. It was also fitted with drooping ailerons, enlarged leading edge flaps and a slotted tailplane, and increased flap and leading edge blowing, all to improve the lift and handling characteristics of operation from the much smaller carriers of the Royal Navy.[30][lower-roman 6]
As the Phantom continued in service, other changes were made, most notably the Marconi ARI.18228 Radar Warning Receiver (RWR) fitted on top of the vertical stabiliser of FG.1 and FGR.2 Phantoms in the mid-1970s, but not to the F.3.[99] From 1978, the Skyflash AAM, derived from the AIM-7 Sparrow, began to be delivered to RAF Phantom units, and was used concurrently with the Sparrow; all three UK Phantom variants were eventually fitted to operate the Skyflash.[92]
- UK versions compared[lower-roman 6]
 FG.1; 40 cm telescopic nosewheel oleo; hinged nose radome; wider and shorter engine exhausts; bigger air intakes; deeper rear fuselage; RWR installation on tailfin
FG.1; 40 cm telescopic nosewheel oleo; hinged nose radome; wider and shorter engine exhausts; bigger air intakes; deeper rear fuselage; RWR installation on tailfin FGR.2; no telescopic nosewheel; fixed nose radome; wider and shorter engine exhausts; bigger air intakes; deeper rear fuselage; RWR installation on tailfin
FGR.2; no telescopic nosewheel; fixed nose radome; wider and shorter engine exhausts; bigger air intakes; deeper rear fuselage; RWR installation on tailfin F.3; 20 cm telescopic nosewheel oleo; fixed nose radome; narrower and longer exhausts; narrower air intakes; shallower rear fuselage; no RWR installation on tail
F.3; 20 cm telescopic nosewheel oleo; fixed nose radome; narrower and longer exhausts; narrower air intakes; shallower rear fuselage; no RWR installation on tail
Aircraft production
The first batch of Phantoms produced for the UK received serials in the XT range, with a total of 44 production models (20 FG.1s and 24 FGR.2s), as well as the four prototypes and two pre-production models being given XT serial numbers.[26] The bulk of the UK's specially built Phantoms were delivered with XV serials (94 FGR.2s and 28 FG.1s), while the two cancelled sets of airframes (32 FGR.2 and 7 FG.1) also received XV numbers.[27] The second-hand examples (15 F.3) obtained in 1984 received serials in the ZE range.[82]
Phantom locations
The RAF operated the Phantom from a number of bases in the UK, Germany and the Falkland Islands during its operational service, while the Royal Navy initially based its Phantom units at its main air station at Yeovilton; following the disbanding of the FAA's dedicated training squadron, its sole operational Phantom squadron was subsequently moved to take up residence at the RAF's base at Leuchars.[100][51]
| Bases utilised by Royal Navy and Royal Air Force Phantom squadrons[41][50] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Base | Years used | Number of squadrons[lower-roman 6] | |
| Phantom bases in the UK | |||
| RNAS Yeovilton | Apr 1968 - Sep 1972 | 3 × RN squadrons | |
| RAF Leuchars | Sep 1969 - Jan 1990 | 1 × RN squadron | |
| 3 × RAF squadrons | |||
| 1 × RAF flight | |||
| RAF Coningsby | May 1969 - Apr 1987 | 5 × RAF squadrons | |
| RAF Wattisham | Nov 1975 - Sep 1992 | 3 × RAF squadrons | |
| 1 × RAF flight | |||
| Phantom bases in Germany (map displays North Rhine-Westphalia) | |||
| RAF Laarbruch | Dec 1970 - Feb 1976 | 1 × RAF squadron | |
| RAF Brüggen | Jun 1970 - Jun 1976 | 3 × RAF squadrons | |
| RAF Wildenrath | Dec 1976 - Jan 1992 | 2 × RAF squadrons | |
| Phantom bases in the Falkland Islands | |||
| RAF Stanley | Oct 1982 - May 1985 | 2 × RAF squadrons | |
| RAF Mount Pleasant | May 1985 - Jun 1992 | 1 × RAF squadron | |
| 1 × RAF flight | |||
Other UK Phantom proposals
Although the Phantom was ordered in 1966, the variants that were eventually constructed were not the first to be offered to the UK. McDonnell Aircraft had been conducting studies into the possibility of the Royal Navy using the Phantom on its carriers since 1959.
Other proposed Spey-powered Phantoms
McDonnell concluded that more power was needed than the J79 turbojet could provide to operate from the smaller decks of British carriers and as a result consulted Rolls-Royce about whether the RB-168 Spey turbofan, then in development for use in the Blackburn Buccaneer, could be fitted to the aircraft.[101] In 1960, McDonnell approached the RAF with its model number 98CJ, which was an F4H-1 (later F-4B) with various modifications, including the installation of the Spey Mk.101 turbofan.[102] McDonnell continued studies, proposing afterburning Mk.101 engines in 1962, while trials of an F-4B fitted with an extendable nosewheel oleo took place aboard USS Forrestal in 1963.[101] In 1964, the company proposed the model 98FC, which was identical to the F-4D variant but would have been fitted with the RB.168-25R.[103]
RF-4M
A further proposal came after the order for the F-4M was being finalised, and was a result of the UK's need for an aircraft to perform the tactical reconnaissance role. For this, McDonnell offered two options:[104]
- The standard F-4M fitted with a reconnaissance pod in place of the centreline fuel tank
- A modified airframe, designated as RF-4M, with the reconnaissance equipment carried internally
Although the RF-4M would have had some advantages, it was discounted as the cost would have been greater, with consequently fewer aircraft purchased, while only those that had been modified would have been able to undertake the reconnaissance mission. Ultimately, the RAF chose the standard F-4M and external pod, which allowed all of its aircraft to perform all designated roles.[62]
F-4(HL)
Another McDonnell proposal was a variation of the carrier-based Phantom, with the goal of improving catapult performance and lowering approach speeds. The F-4(HL), also known as Model 98HL, was planned as a Spey-powered aircraft with a longer fuselage and wingspan, less sweep, stabilators with increased area and air intakes with auxiliary blow-in doors to increase airflow at low speeds. This proposal was not taken forward.[105][106]
Replacement
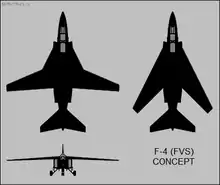
In the early 1970s, the RAF issued an Air Staff Requirement for the development of a new interceptor intended to replace both the Phantom and the Lightning.[78] An early proposal was McDonnell Douglas's plan for a Phantom with a variable-geometry wing.[107] This was rejected by the RAF owing to the fact that there was little apparent improvement in performance over the existing Phantom, and that it might affect the development of the "Multi-Role Combat Aircraft" (MRCA).[108] An alternative idea was to take the MRCA, which evolved into the Panavia Tornado, and develop an interceptor version. The UK's partners in the MRCA project displayed no enthusiasm for this air defence version of the Tornado, so the UK alone began the process, and the authorisation for what came to be known as the Tornado Air Defence Variant (ADV) was issued in March 1976.[78] The initial plan was for the Tornado to replace the remaining two squadrons of Lightnings, as well as all seven squadrons of Phantoms.[109]
While the Tornado was in development, the RAF looked at interim measures to replace the Phantom, which had been in service for over a decade by 1980, and was beginning to suffer from fatigue;[110] one proposal was the lease or purchase of F-15 Eagles to re-equip 19 and 92 Squadrons, the units stationed in Germany.[69] Further suggestions were that up to 80 F-15s be procured, to replace the Phantom and Lightning squadrons then in service, or even cancel the Tornado entirely and purchase the F-15 with UK adaptations (specifically fitting of the AI.24 Foxhunter radar developed for the Tornado, and the Skyflash air-to-air missile).[111]
Ultimately, the F-15 option was not seriously considered, as it was felt there would not be time or cost savings over the Tornado ADV.[111] It was later decided that the Tornado, once it had entered service, would only re-equip three of the Phantom squadrons; two Phantom units would be retained in the UK, and two in Germany.[113] Ultimately, the Tornado replaced the Phantom in four squadrons - the two FG.1 units at RAF Leuchars (43 and 111 Squadrons), plus two FGR.2 units (23 and 29 Squadrons), while 56 and 74 Squadrons, and the two Germany based units (19 and 92 Squadrons) retained the Phantom.[75]
In 1963, the prototype Hawker Siddeley P.1127 Short Take-Off and Vertical Landing (STOVL) aircraft undertook initial landings aboard Ark Royal, while three years later pre-production Hawker Siddeley Kestrel (which subsequently became the Harrier), conducted a series of extensive trials from HMS Bulwark, which proved the concept of using vertical landing aircraft aboard carriers.[114][115] At the same time, the 1966 Defence White Paper had laid out plans to withdraw all of the Royal Navy's conventional aircraft carriers, which would bring to an end the FAA's operation of fixed-wing aircraft from ships at sea, with it instead becoming a primarily rotary-winged organisation.[116] Because it was believed that 892 Naval Air Squadron would be the final carrier-based fixed-wing squadron to be commissioned into the FAA, their Phantoms each a capital Omega (Ω) letter on their tailfins, intended to symbolise their place at the end of the Royal Navy's era of fixed-wing aviation.[28]
However, in the 1970s the Royal Navy was developing what was known as the "Through Deck Cruiser", a 20,000 ton ship with a full-length flight deck intended to embark a squadron of large anti-submarine warfare helicopters. Almost as soon as the first ship, HMS Invincible, was ordered, another specification was added to the design: as well as the helicopters, a small squadron of STOVL aircraft would form part of the air group to act as a deterrent to long-range reconnaissance aircraft.[112] To this end, a navalised version of the Harrier was developed. Over the life of the design process, the Sea Harrier's air defence role was augmented by responsibility for reconnaissance and maritime strike missions. In March 1980, 14 months after 892 Naval Air Squadron was decommissioned and its Phantoms turned over to the RAF, 800 Naval Air Squadron was formed as the first operational Sea Harrier squadron.[117]
Aircraft replaced by and replacing the Phantom
Sir Sydney Camm, the Chief Designer at Hawker for many years, once said that no British aircraft could be considered a success until it was able to match the capabilities of the Phantom.[22] In the RAF and Royal Navy, it was the direct replacement in squadron service for a total of four different aircraft types, comprising nine separate variants. In turn, the Phantom was replaced in squadron service by three different aircraft (see table):
| Role | Aircraft replaced by Phantom | No of squadrons | Date | Aircraft replacing Phantom | No of squadrons | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fleet air defence | Sea Vixen FAW.2[40] | One[41] | 1969 | Sea Harrier FRS.1[lower-roman 9][118] | Two[118] | 1980 |
| Tactical Reconnaissance | Hunter FR.10[119] | One[120] | 1970 | Jaguar GR.1[50] | Seven[50] | 1976 |
| Canberra PR.7[121] | Two[122][123] | |||||
| Close Air Support / Tactical Strike | Canberra B.16[124] | One[125] | 1969 | 1974 | ||
| Canberra B(I).8[126] | One[127] | 1970 | ||||
| Hunter FGA.9[128] | Two[129][130] | 1969 | ||||
| Air defence | Lightning F.2A[56] | Two[131][132] | 1977 | Tornado F.3[50] | Four[50] | 1987 |
| Lightning F.3[56] | Five[56] | 1974 | ||||
| Lightning F.6[56] |
Aircraft on display



The below list details aircraft that were placed on display after service with the Royal Air Force or Royal Navy. The remaining aircraft were either lost in crashes or scrapped following withdrawal.[59]
- YF-4K (prototype)
- XT596 Fleet Air Arm Museum, RNAS Yeovilton, Somerset, England.[133]
- F-4K
- XT597 Bentwaters Cold War Museum, Woodbridge, Suffolk, England – not on public display.[134]
- XT864 Ulster Aviation Society, Maze-Long Kesh, Lisburn, Northern Ireland.[135]
- XV582 South Wales Aviation Museum, St Athan, Wales.[136]
- XV586 RNAS Yeovilton, Somerset, England – stored not on display.[137]
- F-4M
- XT891 RAF Coningsby, Lincolnshire, England.[138]
- XT889 Kbely Museum, Czech Republic.[139]
- XT905 Bentwaters Cold War Museum, Woodbridge, Suffolk, England – not on public display.[134]
- XT914 Wattisham Airfield, Suffolk, England.[140]
- XV401 Bentwaters Cold War Museum, Woodbridge, Suffolk, England.[141]
- XV406 Solway Aviation Museum, Carlisle Airport, Cumbria, England.[142]
- XV408 Tangmere Military Aviation Museum, West Sussex, England.[143]
- XV411 Defence Fire Training and Development Centre, Manston Airport, Kent, England – not on public display.[144]
- XV415 RAF Boulmer, Alnwick, Northumberland, England.[145]
- XV424 Royal Air Force Museum London, Hendon, London, England.[146]
- XV470 RAF Akrotiri, Cyprus – stored and not on public display.[147]
- XV474 Imperial War Museum Duxford, Cambridgeshire, England.[148]
- XV497 Bentwaters Cold War Museum, Woodbridge, Suffolk, England, England.[141]
- F-4J(UK)
- ZE359 American Air Museum, Duxford Aerodrome, Cambridgeshire, England. Painted in USN markings.[149]
- ZE360 Defence Fire Training and Development Centre, Manston Airport, Kent, England – not on public display.[144]
- Future preservation
In October 2019, the British Phantom Aviation Group announced plans to restore two of the remaining Phantoms not on public display, with the aim of finding display locations for them. In partnership with the 74 Squadron Association, the BPAG obtained ZE360, a Phantom F.3 stored at Manston in Kent, and one of only two remaining examples, with the ultimate goal of displaying it in its original RAF markings. The other planned restoration is of XT597, one of the two pre-production FG.1 aircraft that was used for its entire career by the A&AEE. Upon restoration, this will form part of the BPAG's collection.[150]
Specifications (F-4K)
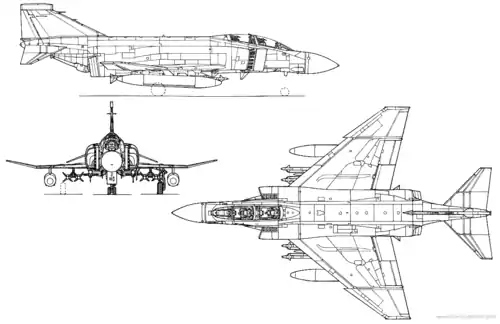
Data from Aircraft of the Royal Navy since 1945,[41]
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 57 ft 7 in (17.55 m)
- Wingspan: 38 ft 4.5 in (11.7 m)
- Height: 16 ft 1 in (4.9 m)
- Empty weight: 31,000 lb (14,061 kg)
- Max. takeoff weight: 56,000 lb (25,402 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Rolls-Royce Spey 203 low bypass turbofans, 12,140 lbf dry thrust (54 kN), 20,500 lbf in afterburner (91.2 kN) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: Mach 1.9 (1,386 mph (2,231 km/h)) at 40,000 ft (12,190 m)
- Ferry range: 1,750 mi (2,816 km)
- Service ceiling: 60,000 ft (18,300 m)
Armament
- Air defence
- 4 × AIM-7 Sparrow or Skyflash in fuselage recesses plus 4 × AIM-9 Sidewinders and 2 × Sparrow / Skyflash on wing pylons
- SUU-23/A gun pod on centreline pylon (RAF aircraft only)
- Strike
Avionics
- Ferranti AN/AWG-11 Multi-Mode Radar
- Marconi ARI18228 Radar Warning Receiver
- Marconi AN/ASN-39A computer
- AN/ARN-91 TACAN bearing/distance navigation system
- Cossor IFF
- STR-70P Radio Altimeter
The F.3 retained a high degree of American equipment, and was longer, lighter, and faster at altitude.[151][152][lower-roman 6] The FG.1 and FGR.2 were broadly identical, with the only significant difference, aside from those already stated, being the ability of the FGR.2 to carry the dedicated reconnaissance pod built by EMI and containing the following:[153]
- 2 × F.135 forward facing camera
- 4 × F.95 oblique facing camera
- Texas Instruments RS700 Infra-Red Linescan
- MEL/EMI Q-Band Sideways Looking Reconnaissance Radar
References
- Notes
- McDonnell merged with the Douglas Aircraft Company in 1967 to form McDonnell Douglas[8]
- Although Eagle and Ark Royal were the largest ships in the UK's carrier fleet, some sources have stated that the plan for Phantom operation was to see aircraft obtained for use aboard Ark Royal and Victorious.[30][31]
- There were initial plans for as many as four CVA-01 class aircraft carriers, with at least three intended to replace Eagle, Ark Royal, Victorious and Hermes[32]
- The launch bridle for the Phantom could only be used on that type, and was thus considerably more expensive than those used for other types. As a consequence, bridle catchers were fitted to the ends of the ship's new catapults so that the bridles could be reused.[37]
- While undertaking trials aboard US carriers, the higher exhaust temperatures caused by the Spey turbofan led to significant damage to the flight decks of the American ships.[37]
- see data
- 64 Squadron was the "shadow" squadron number of 228 OCU[81]
- On 3rd June 1980, a Phantom FG.1 of 111 Squadron crashed as a result of the latches securing the radome failing in flight, causing the radome itself to swing open.[90][91]
- Following the decommissioning of HMS Ark Royal in 1978, the Royal Navy was no longer able to operate conventional fixed wing aircraft at sea. The British Aerospace Sea Harrier was introduced into both the air defence (replacing the Phantom) and strike (replacing the Buccaneer) roles in the FAA with 800 NAS and 801 NAS in 1980[118]
- Citations
- Davies 2016, p.25
- "An Industry Regrouped". Flight. Iliffe & Sons. 78 (2686): 367–373. 2 September 1960. Archived from the original on 19 October 2009. Retrieved 12 June 2013.
- "Lessons of the TSR.2 Story". Flight International. Iliffe & Sons. 96 (3161): 570–571. 9 October 1969. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- Buttler 2000, pp. 118–119.
- Burke 2010, p. 274.
- "The Rise and Fall of the P.1154" (PDF). Hawker Association Newsletter. Hawker Association: 4–5. Summer 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 August 2018. Retrieved 29 May 2016.
- Buttler, Tony (2003). British Secret Projects: Jet Bombers since 1949. Hinckley, UK: Midland Publishing. p. 121. ISBN 978-1-85780-130-9.
- "McDonnell Douglas merger cleared". Fort Scott Tribune. 27 April 1967.
- McLelland 2017, p. 348.
- Proctor 2014, p. 122
- Thornborough and Davies 1994, p. 260.
- HMS Hermes 1962-1964 Commissioning Book (PDF). p. 19.
- Hobbs 2014, p. 280
- McLelland 2016, p. 368
- Benbow 2011, p. 179
- Wilson, Michael (21 September 1967). "Preparing for the Phantom" (PDF). Flight. Iliffe Transport Publications. 92 (3054): 483–487. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 December 2017. Retrieved 12 June 2013.
- Hobbs 2020, p. 257
- Richardson 1984, p. 26.
- Chant 2013, p. 434
- "McDonnell Douglas Phantom". Tangmere Military Aviation Museum. 2019. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- Hobbs, David (2008). "British F-4 Phantoms". Air International. Key Publishing. 74 (5): 30–37.
- "McDonnell Phantom FG1". Fleet Air Arm Museum. National Museum of the Royal Navy. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- "Not a lot of people know that..." National Cold War Exhibition. Royal Air Force Museum. 2013. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- Petit et al 1983, p. 172.
- "Serials in range XT". UK Serials Resource Centre. Wolverhampton Aviation Group. 2016. Retrieved 9 June 2016.
- "Serials in range XV". UK Serials Resource Centre. Wolverhampton Aviation Group. 2016. Retrieved 9 June 2016.
- Kent, Rick (22 September 2006). "McDonnell Phantom in British Service". IPMS Stockholm. Retrieved 1 June 2015.
- Caygill 2005, p. 44
- Davies 2016, p. 31.
- Beedle 2011, p. 197.
- Sturton, Ian (2014). "CVA-01: Portrait of a Missing Link". In Dent, Stephen; Jordan, John (eds.). Warship 2014. London: Conway. p. 30. ISBN 978-1-59114-923-1.
- Jordan, David (Summer 2001). "Future Carrier Aviation Options: A British Perspective". Naval War College Review. 54 (3): 79. Retrieved 11 June 2020.
- Hobbs 2013, p. 293
- Hobbs 2013, p. 267
- Hobbs 2013, p. 237
- Caygill 2005, pp. 42-43.
- "McDonnell Douglas Phantom FG1 (Nose section only)". National Cold War Exhibition. Royal Air Force Museum. 2013. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- Winchester 2010, p. 73.
- HMS Ark Royal 1970–73 Commissioning Book (PDF). p. 75.
- Hobbs 1982, p. 38.
- Transatlantic Race (Newsreel). London: British Movietone. 1 May 1969. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- Snook, Colin. "Brian Davies AFC RN". Old Cicestrians. Chichester High School Old Boys Association. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- Davies 2016, p. 52
- "Not a Lot of People Know That..." National Cold War Exhibition. RAF Museum. 11 May 2013. Retrieved 19 June 2013.
- Phantoms on HMS Eagle (Film). British Pathé. 8 June 1969. Retrieved 29 April 2016.
- HMS Eagle 1969-1970 Commissioning Book (PDF). p. 35.
- "Spray-type Arresting Gear". Flight International. Hiffe Transport Publications. 82 (2787): 183. 9 August 1962. Archived from the original on 8 August 2016. Retrieved 10 June 2016.
- McLelland 2017, p. 354
- "Royal Air Force Phantom Squadrons". RAF Yearbook. IAT Publishing: 16–18. 1992.
- "Leuchars". Airfields of Britain Conservation Trust. Retrieved 17 June 2020.
- "On this day 27 November 1978". Fleet Air Arm Officer's Association. 27 November 2012. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- McLelland 2017, p. 357
- "F-4 Phantom – UK". ejection-history.org.uk. 15 November 2012. Archived from the original on 24 August 2015. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- Darling 2012, p. 234
- Jackson, Paul (1988). "Farewell Lightning, Welcome Tornado". RAF Yearbook. Leicester: IAT Publishing: 62.
- "RAF Leuchars saying farewell to Treble One's Tornado F3s". The Courier. 18 March 2011. Retrieved 25 September 2016.
- "Clydeside Carnage: The Battered Remains of RAF Leuchars' Phantom Fleet". Urban Ghosts. 30 August 2013. Archived from the original on 8 July 2015. Retrieved 1 June 2015.
- "Aircraft Histories". The Phantom Shrine. Corsair Publishing. 3 December 2019. Retrieved 22 June 2020.
- McLelland 2017, p. 365
- Logan, Don (1998). General Dynamics F-111 Aardvark. Atglen, PA: Schiffer. p. 278. ISBN 0-7643-0587-5.
- Gledhill 2017, p. 18
- Davies 2016, p.33
- "Equipment Fit". National Cold War Exhibition. Royal Air Force Museum. 2013. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- "Tactical Nuclear Weapons. 1971–1972". The National Archives. p. 5. DEFE 11/470 E30. Retrieved 11 June 2016.
- Norris 1994, p. 64.
- Williams 2016, p. 166
- Braybrook, Ray (1981). "Lightning". RAF Yearbook. Leicester: WM Caple: 53.
- Fricker, John (1980). "The RAF Looks Ahead". RAF Yearbook. Leicester: Royal Air Force Benevolent Fund.
- "Tornado F.3: Tremblers' Farewell – the end of the Tornado F.3". Global Aviation Resource. 22 March 2011. Retrieved 29 May 2016.
- Eade, David. "The Wattisham Chronicles – Part five: Phantastic Phantom's arrival". Wattisham Aviation Society. Retrieved 28 March 2019.
- "The Phantom". Wattisham Heritage Museum. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- Smith, Gordon (31 May 2013). "Part 15. Royal Air Force – Role & Operations". Battle Atlas of the Falklands War 1982 by Land, Sea and Air. naval-history.net. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- "29(R) Squadron". Royal Air Force. 2015. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- Archer, Bob (1992). "Sunset for the Phantom". RAF Yearbook. IAT Publishing: 13–15.
- Peacock, Lindsay (1990). "For F4 Read F3". RAF Yearbook. Fairford: IAT Publishing.
- Jackson, Paul (1988). "Farewell Lightning, Welcome Tornado". RAF Yearbook. Fairford: IAT Publishing.
- Darling 2012, p. 189.
- Tom King, Secretary of State for Defence (25 July 1990). "Defence (Options for Change)". Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). United Kingdom: House of Commons. col. 468–486.
- Gledhill 2017, p. 413
- Gledhill 2012, p. 186
- "Serials in range ZE". UK Serials Resource Centre. Wolverhampton Aviation Group. 2016. Retrieved 9 June 2016.
- Macfadyen, Ian (1992). "Phantoms over the South Atlantic". RAF Yearbook. Leicester: IAT Publishing: 63–66.
- Rawlings, John (1985). "The Tigers Are Back". RAF Yearbook. ABC: 33.
- Davies 2016, p. 30.
- "RAF Timeline 1980–1989". Royal Air Force. Archived from the original on 31 August 2013. Retrieved 23 March 2015.
No 74 Squadron reforms at Wattisham with the delivery of the first of the F4J Phantoms, given the RAF designation Phantom F3
- "No 74 Squadron". National Cold War Exhibition. Royal Air Force Museum. Archived from the original on 17 May 2016. Retrieved 17 May 2016.
- Davies 2016, p.30
- "Engine". National Cold War Exhibition. Royal Air Force Museum. 2013. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- Gledhill 2012, p. 89
- "Radome Open". ejection-history.org.uk. 15 November 2012. Archived from the original on 25 August 2015. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- "Weaponry". National Cold War Exhibition. RAF Museum. Retrieved 20 September 2016.
- Davies 2016, p. 24.
- Hobbs 2009, p. 220
- The Phantom and the Spey (Information plaque in museum). RAF Museum, Hendon: Royal Air Force Museum. 2003.
- Davies 2016, p.31
- Seider, Michael (January 1975). "Yank in the Royal Navy". Naval Aviation News. Chief of Naval Operations. pp. 22–26. Retrieved 11 June 2020.
- Burns, J.G.; Edwards, M. (14 January 1971). "Blow, Blow Thou BLC Wind". Flight International. Flight Global. 99 (3227): 56–59. Archived from the original on 11 February 2018. Retrieved 31 March 2016.
- "Equipment Fit". National Cold War Exhibition. RAF Museum. Retrieved 20 September 2016.
- HMS Ark Royal 1970–73 Commissioning Book (PDF). p. 76.
- Davies 2016, p. 14.
- McDonnell model numbers (PDF) (Report). McDonnell Douglas Aviation. 1 July 1974. p. 66. Retrieved 9 June 2016.
- McDonnell model numbers (PDF) (Report). McDonnell Douglas Aviation. 1 July 1974. p. 83. Retrieved 9 June 2016.
- The Royal Air Force Phantom II (PDF) (Report). McDonnell Aircraft. 1 August 1966. pp. 44–49. Retrieved 9 June 2016.
- McDonnell model numbers (PDF) (Report). McDonnell Douglas Aviation. 1 July 1974. p. 93. Retrieved 9 June 2016.
- Lake 1992, p. 164
- Davies 2013, p. 35
- Rogoway, Tyler (18 October 2015). "The F-4 Phantom's Manufacturer Wanted To Give It Swing-Wings". Foxtrot Alpha. Retrieved 18 May 2016.
- Simpson, R.C. (1978). "Tornado means trouble...for WARPAC!". RAF Yearbook. Leicester: Royal Air Force Benevolent Fund.
- "RAF faces the Fighter Gap" (PDF). Flight International. IPC Transport Press. 114 (3624): 727. 2 September 1978. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 February 2019. Retrieved 26 May 2016.
- "F-15s for the Royal Air Force?" (PDF). Flight International. IPC Transport Press. 114 (3625): 935. 9 September 1978. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 November 2012. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- Wilson, Harold (7 October 1975). "Up, Up and Almost Away" (PDF). Naval Review. 64 (4): 291–298. Retrieved 31 May 2015.
- Jackson, Paul (1985). "A Refurbished Umbrella". RAF Yearbook. Leicester: Royal Air Force Benevolent Fund.
- "Audacious class: Overview". National Cold War Exhibition. Royal Air Force Museum. 2013. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- Dow 2014, p. 214
- White, Rowland (2010). Phoenix Squadron. London: Corgi Books. p. 40. ISBN 978-0-552-15290-7.
- Parker, John (2003). Task Force - Untold Stories of the Heroes of the Royal Navy. London: Headline. p. 92. ISBN 978-0755312023.
- Hobbs 1982, p. 8
- Walpole, Martin (2006). Best of Breed: The Hunter in Fighter Reconnaissance. Barsnley: Pen & Sword. p. 88. ISBN 978-1844154128.
- "2 Squadron". Royal Air Force. Archived from the original on 3 June 2016. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- Barrymore-Halpenny, Bruce (2014). English Electric Canberra: The History and Development of a Classic Jet. Barnsley: Pen & Sword. p. 203. ISBN 978-1783461905.
- "17 Squadron". Royal Air Force. Archived from the original on 28 October 2016. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- "31 Squadron". Royal Air Force. Archived from the original on 26 June 2015. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- "6 Squadron". Royal Air Force. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- "6 Squadron". Royal Air Force. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- "14 Squadron". Royal Air Force. Archived from the original on 2 February 2017. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- "14 Squadron". Royal Air Force. Archived from the original on 2 February 2017. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- Smith Watson, Ian (2018). History of the Gloster Javelin. Stroud: Fonthill Media. p. 157. ISBN 978-1781553749.
- "43 Squadron". Royal Air Force. Archived from the original on 30 May 2016. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- "54 Squadron". Royal Air Force. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- "No 19 Squadron". National Cold War Exhibition. Royal Air Force Museum. 2013. Retrieved 13 June 2020.
- "No 92 Squadron". National Cold War Exhibition. Royal Air Force Museum. 2013. Retrieved 13 June 2020.
- Ellis 2014, p. 209.
- Ellis 2014, p. 222.
- "Legendary F4 Phantom jet fighter comes ashore in Larne". Larne Times. 19 June 2015. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- "Black Mike heading to South Wales". Aviation News. Archived from the original on 28 March 2019. Retrieved 5 December 2018.
- Ellis 2014, p. 212.
- Ellis 2014, p. 138.
- Davies 2016, p. 53
- Ellis 2014, p. 258.
- Ellis 2014, p. 217.
- Ellis 2014, p. 41.
- Ellis 2014, p. 270.
- Ellis 2014, p. 90.
- Ellis 2014, p. 177.
- Ellis 2014, p. 153.
- Ellis 2014, Appendix A.
- Ellis 2014, p. 29.
- Ellis 2014, p. 24.
- Winston, George (15 October 2019). "Two British Phantoms to Be Restored". War History Online. Retrieved 5 December 2019.
- Wright 2018, p. 50
- "F-4 Phantom II". Boeing. Retrieved 22 June 2020.
- Wright 2018, p. 45
Further reading
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to F-4 Phantom II in service with the United Kingdom. |
- Baker, A.D. (1998). The Naval Institute Guide to Combat Fleets of the World 1998–1999: Their Ships, Aircraft and Systems. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-0-13017-120-7.
- Beedle, Jimmy (2011). The Fighting Cocks: 43 (Fighter) Squadron. Barnsley, UK: Pen & Sword Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84884-385-1.
- Benbow, Tim (2011). British Naval Aviation: The First 100 Years. Farnham, Surrey, UK: Ashgate Publishing. ISBN 978-1-40940-612-9.
- Burke, Damien (2010). TSR2: Britain's Lost Bomber. Marlborough, Wiltshire, UK: The Crowood Press. ISBN 978-1-84797-211-8.
- Buttler, Tony (2003). British Secret Projects: Jet Bombers Since 1949. Hinckley, UK: Midland Publishing. ISBN 978-1-85780-130-9.
- Chant, Christopher (2013). A Compendium of Armaments and Military Hardware. Abingdon: Routledge Revival. ISBN 978-0-41571-068-8.
- Caygill, Peter (2005). Phantom from the Cockpit. Barnsley: Casemate Publishers. p. 43. ISBN 978-1-84415-225-4.
- Darling, Kev (2012). RAF Strike Command 1968–2007: Aircraft, Men and Action. Barnsley: Pen & Sword Aviation. ISBN 978-1-84884-898-6.
- Davies, Peter E. (2016). USN McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II. Oxford: Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1-47280-495-2.
- Davies, Peter E. (2013). USAF McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II. Oxford: Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1-78096-608-3.
- Dow, Andrew (2014). Pegasus - The Heart of the Harrier. Barnsley: Pen & Sword. ISBN 978-1-47382-760-8.
- Ellis, Ken (2014). Wrecks and Relics – 24th Edition. Manchester, England: Crecy Publishing. ISBN 978-0-85979-177-9.
- Gledhill, David (2017). Phantom in the Cold War: RAF Wildenrath, 1977–1992. Barnsley: Pen & Sword Books. ISBN 978-1-52670-408-5.
- Gledhill, David (2012). The Phantom in Focus: A Navigator's Eye on Britain's Cold War Warrior. Stroud: Fonthill Media. ISBN 978-1-78155-048-9.
- Hampshire, Edward (2013). From East of Suez to the Eastern Atlantic: British Naval Policy 1964–70. Farnham: Ashgate Publishing. ISBN 978-1-13827-134-0.
- Hobbs, David (1982). Aircraft of the Royal Navy since 1945. Liskeard: Maritime Books. ISBN 978-0-90777-106-7.
- Hobbs, David (2009). A Century of Carrier Aviation. Barnsley: Seaforth Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84832-019-2.
- Hobbs, David (2013). British Aircraft Carriers: Design, Development & Service Histories. Barsnley: Seaforth Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84832-138-0.
- Hobbs, David (2020). The British Carrier Strike Fleet: After 1945. Barsnley: Pen & Sword. ISBN 978-1-52678-544-2.
- Lake, Jon (1992). Phantom Spirit in the Skies. London: Aerospace Publishing. ISBN 978-1-880588-04-8.
- Martin, Patrick (2012). British Phantoms: The Phantom FG Mk.1 and FGR Mk.2 in Royal Navy and RAF Service 1966–1978. Erlangen: Double Ugly Books. ISBN 978-3-935687-84-3.
- Martin, Patrick (2013). British Phantoms: The Phantom FG Mk.1, FGR Mk.2 and F-4J(UK) in Royal Air Force Service 1979–1992. Erlangen: Double Ugly Books. ISBN 978-3-935687-85-0.
- McLelland, Tim (2016). Britain's Cold War Bombers. London: Fonthill. ISBN 978-1-78155-534-7.
- McLelland, Tim (2017). Britain's Cold War Fighters. London: Fonthill. ISBN 978-1-78155-630-6.
- Nicholas, Jack (July 2005). "Big Bangs For A Buck: Britain's Tactical Nuclear Forces 1960–1998". Air International. Vol. 69 no. 1. pp. 45–49. ISSN 0306-5634.
- Norris, Robert (1994). British, French and Chinese Nuclear Weapons, Nuclear Weapons Databook, Vol. V. Boulder: Westview Press. ISBN 978-0-81331-612-3.
- Pettit, Martin, ed. (1983). British Military Aircraft Serials and Markings. British Aviation Research Group / Nostalgair / The Aviation Hobby Shop. ISBN 978-0-90633-904-6.
- Proctor, Ian (2014). The Royal Air Force in the Cold War, 1950–1970. Barnsley: Pen & Sword. ISBN 978-1-78383-189-0.
- Richardson, Doug (1984). "Chapter 3: Propulsion". Modern Fighting Aircraft F4. London: Salamander Books. ISBN 978-0-86101-133-9.
- Sumner, E.K. (January 1971). "Ark Royal: Pride of Great Britain". Naval Aviation News. Chief of Naval Operations. pp. 36–39.
- Sturtivant, Ray (2004). Fleet Air Arm Fixed-Wing Aircraft Since 1946. Tonbridge: Air-Britain. ISBN 978-0-85130-283-6.
- Thetford, Owen (1991). British Naval Aircraft Since 1912. London: Putnam. ISBN 978-0-85177-849-5.
- "RAF and FAA Phantom losses". Ejection History. 15 November 2012. Archived from the original on 24 August 2015. Retrieved 1 June 2015.
- Williams, Graham (2016). Rhapsody in Blue: An RAF Fighter Pilot's Life During the Cold War. London: Fonthill Media. ISBN 978-1-78155-535-4.
- Winchester, Jim (2010). Jet Fighters: Inside & Out. London: Amber Books. ISBN 978-1-90744-619-1.
- Wright, Kevin (October 2018). "Phantoms in RAF service" (PDF). Aviation News. Stamford: Key Publishing Limited. pp. 42–51. Retrieved 17 July 2020.
_1972.jpg.webp)