Millbrae, California
Millbrae is a city located in northern San Mateo County, California, United States. To its northeast is San Francisco International Airport, San Bruno is on its northwest, and Burlingame on its southeast. It is bordered by San Andreas Lake to the southwest. The population was 21,536 at the 2010 census.
City of Millbrae | |
|---|---|
City in California | |
 General view of Millbrae | |
 Seal | |
| Motto(s): A City In The Sun | |
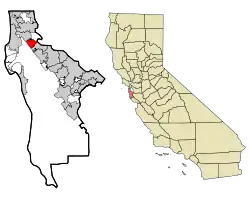 Location in San Mateo County and the state of California | |
 City of Millbrae Location in the United States | |
| Coordinates: 37°36′3″N 122°24′5″W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | San Mateo |
| Incorporated | January 14, 1948[1] |
| Government | |
| • Type | Council–manager[2] |
| • Mayor | Reuben Holober (preceded by Wayne J. Lee)[3] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 3.29 sq mi (8.53 km2) |
| • Land | 3.27 sq mi (8.47 km2) |
| • Water | 0.02 sq mi (0.06 km2) 0.36% |
| Elevation | 33 ft (10 m) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 21,532 |
| • Estimate (2019)[7] | 22,394 |
| • Density | 6,850.41/sq mi (2,645.20/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-8 (Pacific) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-7 (PDT) |
| ZIP code | 94030 |
| Area code(s) | 650 |
| FIPS code | 06-47486 |
| GNIS feature ID | 1659756 |
| Website | www |
History
The Ohlone people have been living in the Bay Area for hundreds of years. The closest villages to what is now Millbrae were located by the banks of San Bruno Creek, and they are known as Urebure and Siplichiquin.[8][9] A third nearby village—whose original name is unknown—is called CA-SMA-299. The local Ohlone people are today called the Ramaytush Ohlone; however this name is a linguistic designation that arose relatively recently. Prior to colonization, the Ohlone did not operate as a single consolidated unit; they identified more with their local tribe and village than with the nation at large. The several local tribes that lived in the area prior to colonization coalesced into the modern Ramaytush people following the precipitous decline of their population in the 1800s.[10]
1800s
In 1827, sub lieutenant José Antonio Sánchez, who was stationed at the Presidio, was granted permission by Mexican governor José María de Echeandía to occupy the rancho for “grazing and agricultural purposes”, as grazing land for Mission Dolores and the Presidio of San Francisco.[11] The original Sixteen Mile House, a historical restaurant and rest stop, was a direct link to Millbrae's early days. The rest stop was built in 1872 by members of the Sánchez family, the original landholders of the Rancho Buri Buri, which at one time comprised parts of present-day Millbrae and Burlingame.
Darius Ogden Mills purchased land in the 1860s from José de la Cruz Sánchez and family of Rancho Buri Buri to build a country estate. The former Mills estate was bordered by what is now Skyline Boulevard, Bayshore Highway U.S. Route 101, Millbrae Avenue and Trousdale Drive. The estate became known as "Millbrae" from "Mills" and the Scottish word "brae," which means "rolling hills" or "hill slope." The Millbrae estate mansion burned down in June 1954.[12] After the fire the estate was subdivided and sold, with the bulk of the land going to the Paul W. Trousdale Construction Company in 1953 and eventually becoming the location for Mills High School, Spring Valley Elementary School, and Peninsula Hospital.[13][14]
1900s
Millbrae is home to Green Hills Country Club, built in 1929, and designed by famed golf course architect Dr. Alister MacKenzie (who designed other noteworthy courses such as Augusta National, Cypress Point, Royal Melbourne, Pasatiempo, and many more). The course was originally known as the Union League Golf Club of San Francisco (1930 to 1933) and Millbrae Country Club (1933 to 1945). The course provides a green belt in the center of the city that is the home of many animals, such as the red-tail fox, that otherwise would not be able to survive in the urban setting. It also may be the only area of the city where natural creeks still flow overground.
Millbrae used a private patrol financed by fees from merchants and residents until 1941, when the San Mateo County Board of Supervisors created the Millbrae Police District. Records of the Internal Revenue Service document the licensing of several Millbrae bars for gambling; only after incorporation were gambling laws enforced in Millbrae and not until the 1950s was gambling defeated. In 1931, citizens organized a volunteer fire department, which remained entirely volunteer until 1938. The police and fire departments were housed together for several years at Hillcrest Boulevard and El Camino Real before the vital services moved to their permanent location in Millbrae's civic center, a few blocks west of El Camino.
Spurred largely by the desire to secure the Mills' estate for residential use and by the efforts of Millbrae's weekly newspaper, the Millbrae Sun, residents heatedly discussed incorporation for over a decade before voting to incorporate. Finally, on January 14, 1948, residents of Millbrae traveled to Sacramento to present their new city's charter. W.F. Leutenegger was elected mayor to represent Millbrae's nearly 8,000 residents. That year, Green Hills Elementary School opened as Millbrae's first new school in over 25 years, in anticipation of the educational needs of the post-war "baby boom" children. The new city's chief industries were agriculture, floriculture, dairy, and porcelain manufacturing. Many families that built the new city have never left.
In the 1950s, Millbrae residents united to resist efforts to divide the city by the planned Junipero Serra Freeway (I-280), which was later routed parallel to Junipero Serra Boulevard, then through a canyon in San Bruno up to Skyline Boulevard.
Transportation has shaped Millbrae's growth. From the start of the 20th century, San Francisco MUNI's #40 "interurban" streetcar traveled through Millbrae, linking the city with San Francisco and San Mateo. Millbrae's high school students rode the streetcar to attend Burlingame High School until Capuchino High School opened on September 11, 1950. The streetcar line was dismantled just after Millbrae's incorporation, leaving the Southern Pacific Railroad as the only railway linking Millbrae with surrounding areas. The Sixteen Mile House marked Millbrae along the railroad route, located where the Millbrae O'Reilly Auto Parts stands today. In the 1940s, a hilltop was shaved away to produce landfill for the expanding San Francisco Airport, which received an "international" designation in 1954 with the completion of the Central Terminal.
An unsuccessful effort to save the original Sixteen Mile House in the 1970s led to the birth of the Millbrae Historical Society and eventual successful crusades to save the Millbrae train station and the historic building that has become the Millbrae Historical Museum. Such challenges, though inevitable, have only strengthened Millbrae's resolve to preserve the city's unique character and rich history.[15]
2000s
Today, Millbrae boasts over 21,000 residents. Residents are employed in various industries throughout the Bay Area and children attend one of five public elementary schools, or private schools. Millbrae has Sister City relationships with La Serena, Chile; Hanyu, Japan; and Mosta, Malta.[16]
Geography
Millbrae has a total area of 3.26 sq mi (8.4 km2), of which, 3.25 sq mi (8.4 km2) is land and 0.01 sq mi (0.0 km2) (0.36%) is water.[17]
Climate
According to the National Weather Service, Millbrae enjoys a typical Mediterranean climate featuring cool, wet winters and dry, mild summers. Night and morning fog are common during the summer months. Frequent, westerly sea breezes keep temperatures relatively mild throughout the year with highs in the mid-to-upper fifties (~15 °C) and lows in the mid-to-upper forties (~8 °C) during the winter and highs in the low seventies (~22 °C) and lows in the mid-to-upper fifties (~13 °C) during the summer. Annual precipitation ranges from 20 inches (51 cm) in the lowlands to 32 inches (81 cm) in the hills near Skyline Boulevard and I-280; most of the rain falls from November through April. Snow is very rare; the last measurable occurrence was on February 5, 1976. The nearest National Weather Service station is at the nearby San Francisco International Airport, where records go back to early 1927. For more details, see San Bruno, California.
| Climate data for Millbrae, California | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 74 (23) |
78 (26) |
82 (28) |
93 (34) |
95 (35) |
98 (37) |
100 (38) |
96 (36) |
106 (41) |
102 (39) |
81 (27) |
73 (23) |
106 (41) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 57.3 (14.1) |
59.4 (15.2) |
61.2 (16.2) |
63.7 (17.6) |
65.6 (18.7) |
68.7 (20.4) |
71.7 (22.1) |
72.6 (22.6) |
73.5 (23.1) |
70.2 (21.2) |
62.2 (16.8) |
56.9 (13.8) |
65.3 (18.5) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 48.3 (9.1) |
48.5 (9.2) |
50.1 (10.1) |
52.3 (11.3) |
53.9 (12.2) |
55.7 (13.2) |
57.8 (14.3) |
58.6 (14.8) |
58.8 (14.9) |
56.2 (13.4) |
52.3 (11.3) |
48.2 (9.0) |
53.4 (11.9) |
| Record low °F (°C) | 32 (0) |
27 (−3) |
33 (1) |
37 (3) |
38 (3) |
44 (7) |
42 (6) |
40 (4) |
45 (7) |
40 (4) |
31 (−1) |
23 (−5) |
23 (−5) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 6.19 (157) |
6.30 (160) |
4.31 (109) |
2.02 (51) |
1.03 (26) |
0.21 (5.3) |
0.03 (0.76) |
0.26 (6.6) |
0.36 (9.1) |
1.64 (42) |
3.60 (91) |
6.18 (157) |
32.13 (814.76) |
| Source: "The Weather Channel[18] | |||||||||||||
Environmental features
A wetland area in the eastern part of the city adjacent to U.S. Highway 101 is habitat to the endangered San Francisco garter snake, a species endemic to San Mateo County. At the western edge of the city, the San Andreas Lake and the San Andreas Fault may be found.
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1880 | 195 | — | |
| 1890 | 243 | 24.6% | |
| 1950 | 8,972 | — | |
| 1960 | 15,873 | 76.9% | |
| 1970 | 20,920 | 31.8% | |
| 1980 | 20,058 | −4.1% | |
| 1990 | 20,412 | 1.8% | |
| 2000 | 20,718 | 1.5% | |
| 2010 | 21,532 | 3.9% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 22,394 | [7] | 4.0% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[19] | |||
2012
According to a 2012 estimate, the median income for a household in the city was $86,364, and the median family income was $124,027.[20] Males had a median income of $84,008 versus $70,975 for females. About 2.2% of families and 3.4% of the population were below the poverty line, including 2.2% of those under age 18 and 4.6% of those age 65 or over.[21]
2010
At the 2010 census Millbrae had a population of 21,532. The population density was 6,608.5 people per square mile (2,551.6/km2). The racial makeup of Millbrae was 10,177 (47.3%) White, 179 (0.8%) African American, 33 (0.2%) Native American, 9,205 (42.8%) Asian, 214 (1.0%) Pacific Islander, 776 (3.6%) from other races, and 948 (4.4%) from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 2,555 persons (11.9%).[22]
The census reported that 21,217 people (98.5% of the population) lived in households, 58 (0.3%) lived in non-institutionalized group quarters, and 257 (1.2%) were institutionalized.
There were 7,994 households, 2,593 (32.4%) had children under the age of 18 living in them, 4,543 (56.8%) were opposite-sex married couples living together, 868 (10.9%) had a female householder with no husband present, 315 (3.9%) had a male householder with no wife present. There were 268 (3.4%) unmarried opposite-sex partnerships, and 40 (0.5%) same-sex married couples or partnerships. 1,883 households (23.6%) were one person and 1,059 (13.2%) had someone living alone who was 65 or older. The average household size was 2.65. There were 5,726 families (71.6% of households); the average family size was 3.15.
The age distribution was 4,337 people (20.1%) under the age of 18, 1,523 people (7.1%) aged 18 to 24, 4,960 people (23.0%) aged 25 to 44, 6,476 people (30.1%) aged 45 to 64, and 4,236 people (19.7%) who were 65 or older. The median age was 44.8 years. For every 100 females, there were 90.0 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 86.7 males.
There were 8,372 housing units at an average density of 2,569.5 per square mile, of the occupied units 5,076 (63.5%) were owner-occupied and 2,918 (36.5%) were rented. The homeowner vacancy rate was 0.7%; the rental vacancy rate was 4.8%. 13,968 people (64.9% of the population) lived in owner-occupied housing units and 7,249 people (33.7%) lived in rental housing units.
2000
At the 2000 census there were 20,718 people in 7,956 households, including 5,513 families, in the city. The population density was 6,446.4 people per square mile (2,492.0/km2). There were 8,113 housing units at an average density of 2,524.4 per square mile (975.8/km2).[17] Of the 7,956 households 28.3% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 55.7% were married couples living together, 9.9% had a female householder with no husband present, and 30.7% were non-families. 25.1% of households were one person and 13.7% were one person aged 65 or older. The average household size was 2.56 and the average family size was 3.08.
The age distribution was 20.6% under the age of 18, 6.4% from 18 to 24, 27.5% from 25 to 44, 24.7% from 45 to 64, and 20.8% 65 or older. The median age was 42 years. For every 100 females, there were 89.8 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 87.0 males.
Government
In the California State Legislature, Millbrae is in the 13th Senate District, represented by Democrat Josh Becker, and in the 22nd Assembly District, represented by Democrat Kevin Mullin.[23]
In the United States House of Representatives, Millbrae is in California's 14th congressional district, represented by Democrat Jackie Speier.[24]
According to the California Secretary of State, as of February 10, 2019, Millbrae has 12,850 registered voters. Of those, 5,733 (44.6%) are registered Democrats, 2,049 (16%) are registered Republicans, and 4,584 (35.7%) have declined to state a political party.[25]
Education
Millbrae has a reputation for having good schools in the San Francisco Bay Area and in the state of California, despite enduring years of state budget cuts.[26] Millbrae School District (MSD) oversees four public elementary schools including Meadows, Green Hills, Lomita Park, and Spring Valley and one middle school, Taylor Middle School. MSD is state-funded and does not receive local property taxes, and has endured budget cuts from the state since 2007. Millbrae has one public high school, Mills High School, which is part of the San Mateo Union High School District.
The city is served by the Millbrae Public Library of the San Mateo County Libraries, a member of the Peninsula Library System.
Millbrae has one private school at Saint Dunstan's, a Catholic church.
Police and fire
On March 4, 2012, the San Mateo County Sheriff's Office took over responsibility for providing police services in Millbrae and closed the local police department.[27]
On December 29, 2014, the City of Millbrae combined services with Central County Fire which provides fire services to the cities of Millbrae and Burlingame and the town of Hillsborough. Millbrae has two fire stations within its city limits.
Transportation
Millbrae is located between San Francisco and San Jose. U.S. Route 101 and Interstate 280 run along the eastern and western boundaries of the city, respectively. San Francisco International Airport is adjacent to the city.
The Millbrae Intermodal Station serves as a major transit hub for the Peninsula, connecting the BART, Caltrain, and SamTrans networks. It is the largest intermodal station west of the Mississippi river, in terms of construction size and land usage. The BART Antioch–SFO/Millbrae line and Richmond–Millbrae line serve the Millbrae Intermodal Terminal A SamTrans local line 43 serves Millbrae.

Economy
Millbrae's economy is driven in-part by its long strips of hotels located near transit. Because of its close proximity to San Francisco International Airport and to the city of San Francisco, and its advanced transit center that can connect people to all major cities/events in the Bay Area, many tourists opt to stay in Millbrae. Its downtown is mainly along El Camino Real and Broadway Avenue. There are many small shops, restaurants, a Safeway, Walgreens, Trader Joe's, and Office Depot.
Top employers
According to the City's 2014 Comprehensive Annual Financial Report,[28] the top employers in the city are:
| # | Employer | # of Employees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | City and County of San Francisco | 300 |
| 2 | Millbrae School District | 212 |
| 3 | Westin Hotel | 210 |
| 4 | 24 Hour Fitness | 208 |
| 5 | Safeway | 187 |
| 6 | A & C Health Care | 160 |
| 7 | Best Western | 149 |
| 8 | Mills High School | 143 |
| 9 | City of Millbrae | 125 |
| 10 | Magnolia of Millbrae | 100 |
Sister cities
Millbrae has three sister cities, as designated by Sister Cities International:
Footnotes
- "California Cities by Incorporation Date". California Association of Local Agency Formation Commissions. Archived from the original (Word) on October 17, 2013. Retrieved August 25, 2014.
- "Government". City of Millbrae. Archived from the original on February 17, 2015. Retrieved February 4, 2015.
- "Meet the City Council". City of Millbrae. Retrieved April 3, 2018.
- "2019 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 1, 2020.
- "Millbrae". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey.
- "Millbrae (city) QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 19, 2015. Retrieved February 18, 2015.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". United States Census Bureau. May 24, 2020. Retrieved May 27, 2020.
- "Rancho Buri Buri | Resolute". resoluteoldwest. Retrieved August 15, 2020.
- Milliken, Randall; Shoup, Laurence H.; Ortiz, Beverly R. (2009). Ohlone/Costanoan Indians of the San Francisco Peninsula and their Neighbors, Yesterday and Today (PDF). National Park Service, Golden Gate National Recreation Area, San Francisco, California.
- "Ramaytush Ohlone". Ramaytush Ohlone. Retrieved December 13, 2020.
- Igler, David (January 28, 2005). Industrial Cowboys: Miller & Lux and the Transformation of the Far West, 1850-1920. Univ of California Press. p. 46. ISBN 978-0-520-24534-1.
- Niekerken, Bill Van (October 10, 2017). "When the Peninsula's most lavish 19th century mansion went up in flames". SFChronicle.com. Retrieved August 15, 2020.
- "Millbrae History Walk". Millbrae Historical Society. Retrieved August 14, 2020.
- Niekerken, Bill Van (October 10, 2017). "When the Peninsula's most lavish 19th century mansion went up in flames". SFChronicle.com. Retrieved August 14, 2020.
- "City News | City of Millbrae". www.ci.millbrae.ca.us. Retrieved July 5, 2020.
- "City of Millbrae : Sister Cities Commission". Archived from the original on August 15, 2009. Retrieved September 13, 2009.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- "Average Climate for Millbrae, California". The Weather Channel. February 2018. Retrieved February 26, 2018.
- "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- American FactFinder. Factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved on 2014-06-12.
- U.S. Census Bureau
- "2010 Census Interactive Population Search: CA - Millbrae city". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 15, 2014. Retrieved July 12, 2014.
- "Statewide Database". UC Regents. Archived from the original on February 1, 2015. Retrieved November 23, 2014.
- "California's 14th Congressional District - Representatives & District Map". Civic Impulse, LLC. Retrieved March 12, 2013.
- "CA Secretary of State – Report of Registration – February 10, 2019" (PDF). ca.gov. Retrieved March 12, 2019.
- "Millbrae School Named Among Best Public High Schools In CA". Millbrae, CA Patch. February 8, 2019. Retrieved August 15, 2020.
- "Millbrae Police Department closes down". San Jose Mercury News. March 3, 2012. Retrieved January 10, 2013.
- City of Millbrae CAFR (2014) Archived 2015-09-16 at the Wayback Machine