New Zealand Government
The New Zealand Government (Māori: Te Kāwanatanga o Aotearoa) is the central government through which governing authority is exercised in New Zealand. As in most parliamentary democracies, the term "Government" refers chiefly to the executive branch, and more specifically to the collective ministry directing the executive.[9] Based on the principle of responsible government, it operates within the framework that "the Queen reigns, but the government rules, so long as it has the support of the House of Representatives".[10] The Cabinet Manual describes the main laws, rules and conventions affecting the conduct and operation of the Government.
| New Zealand Government | |
|---|---|
| Te Kāwanatanga o Aotearoa | |
| Overview | |
| Established | 30 June 1852[1] |
| Country | New Zealand |
| Leader | Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern[2] |
| Appointed by | Governor-General[3] |
| Main organ | |
| Ministries | Ministries and departments of the New Zealand Government |
| Responsible to | House of Representatives[6] |
| Annual budget | NZ$119.3 billion (2018–19)[7] |
| Headquarters | Various locations across Wellington[8] |
| Website | |
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of New Zealand |
| Constitution |
|
|
Executive power is exercised by ministers, all of whom are sworn into the Executive Council and accountable to the elected legislature, the House of Representatives.[11] Several senior ministers (usually 20) constitute a collective decision-making body known as the Cabinet, which is led by the prime minister (currently Jacinda Ardern).[12] A few more ministers (usually junior or supporting) are part of the Executive Council but are outside Cabinet. Most ministers have a portfolio of specific responsibilities such as departments or policy areas, although ministers without portfolio can be appointed.
The position of prime minister belongs to the person who commands the confidence of the majority of members in the House of Representatives. The position is determined also by several other factors, such as support agreements between parties and internal leadership votes in the party that leads the Government. The prime minister and other ministers are formally appointed by the governor-general (who is the Queen's representative in New Zealand).[11] By convention, the governor-general acts on the advice of the prime minister in appointing ministers.
Terminology

In New Zealand, the term Government can have a number of different meanings. At its widest, it can refer collectively to the three traditional branches of government—the executive branch, legislative branch (the Queen-in-Parliament and House of Representatives) and judicial branch (the Supreme Court and subordinate courts).[13] Each branch operates independently of the others in an arrangement described as "separation of powers".[14]
More commonly, the term is used to refer specifically to the executive branch.[14] The largest party or coalition in the House of Representatives, with a sufficient number of MPs to win crucial parliamentary votes, will form a Cabinet—this is the sense intended when it is said that a political party "forms the government".[15][16] The Constitution Act 1986, the principal part of New Zealand's constitution, locates the executive government in the Executive Council,[11] which also includes ministers outside Cabinet.[17]
The Executive Wing of Parliament Buildings, commonly called the "Beehive" because of the building's shape, houses many government offices and is also where the Cabinet meets.[18] Thus the name Beehive is sometimes used metonymically to refer to the New Zealand Government.[19]
The official website of the New Zealand Government uses the web address beehive.govt.nz.[20]
History
New Zealand was granted colonial self-government in 1853 following the New Zealand Constitution Act 1852, which was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Governments were set up at both central and provincial level, with initially six provinces.[21] The provinces were abolished by the Abolition of Provinces Act 1876, during the premiership of Harry Atkinson. For the purposes of the Act, the provinces formally ceased to exist on 1 January 1877.[22]
The Sewell Ministry constituted the first responsible government, with control over all domestic matters other than native policy.[21] Formed in 1856, it lasted from 18 April to 20 May. From 7 May onward, Henry Sewell was titled "Colonial Secretary", and is generally regarded as having been the country's first prime minister.[23] The first ministry that formed along party lines did not appear until 1891, when John Ballance formed the Liberal Party and the Liberal Government.[24][25] The prime minister became the leader and public face of the governing party.[26] The status of the monarch's representative was upgraded from governor to "Governor-General" in 1917 letters patent.[21][27]
Government and the Crown

The New Zealand Government is formally termed Her Majesty's Government on the Seal of New Zealand.[28] This is a reference to the monarch, currently Queen Elizabeth II, who is identified as the head of state in the Constitution Act 1986.[11] The legal authority of the state that is vested in the monarch, known as "the Crown", remains the source of the executive power exercised by the Government.[14][29] Sovereignty in New Zealand has never rested solely with the monarch due to the English Bill of Rights 1689, later inherited by New Zealand, which establishes the principle of parliamentary sovereignty.[30] Nonetheless, the Constitution Act describes the monarch as the "Sovereign".[11]
In many areas the Crown possesses a body of powers known as the royal prerogative.[31][32] For example, the Royal Assent (the monarch's approval)[33] is required to enact laws and the royal sign-manual gives authority to letters patent and orders in council.[34][35] The royal prerogative also includes summoning and dissolving the Parliament in order to call an election,[36] and extends to foreign affairs: the negotiation and ratification of treaties, alliances, international agreements, the right to declare war and peace, and the deployment and armament of defence forces.[37][38]
The Queen rarely personally exercises her executive powers; since the sovereign does not normally reside in New Zealand, she appoints a governor-general to represent her and exercise most of her powers.[39] The person who fills this role is selected on the advice of the prime minister and other ministers.[39] "Advice" in this sense is a choice generally without options since it would be highly unconventional for the prime minister's advice to be overlooked—a convention that protects the monarchy. As long as the monarch is following the advice of her ministers, she is not held personally responsible for the decisions of the Government. The governor-general has no official term limit, and is said to serve "at Her Majesty's pleasure".[40]
As per the conventional stipulations of constitutional monarchy, the Queen and her representative rarely intervene directly in political affairs.[39] Just as the sovereign's choice of governor-general is on the prime minister's advice, the governor-general exercises the executive powers of state on the advice of ministers.[11] For example, the governor-general's power to withhold the Royal Assent to Bills has been rendered ineffective by convention.[36]
Government in Parliament
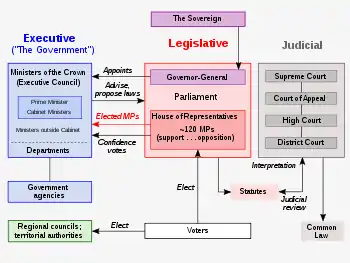
Under the conventions of the Westminster system, the Government is accountable to the House of Representatives, the democratically elected component of Parliament, rather than to the sovereign. This is called responsible government.[13][14] For example, ministers make statements in the House and take questions from other members of the House.[41] The Government is required by convention and for practical reasons to maintain the support, or confidence, of the House of Representatives. It also requires the support of the House for the maintenance of supply (by voting through the government's budgets) and in order to pass primary legislation.[42][43] By convention, if a government loses the confidence of the House then it must either resign or a general election is held.[14][44] Not since 1928 has a government been defeated on a confidence vote and therefore been obliged to resign.[45]
Upon the dissolution of Parliament, which must occur at least every three years, ministers are no longer members of the House of Representatives; however, they can remain members of the Executive Council for up to thirty days after leaving the House.[11]
Ministers
Also known as "ministers of the Crown", these are members of Parliament who hold ministerial warrants from the Crown to perform certain functions of government. This includes formulating and implementing policies and advising the governor-general.[46] Before 1996 nearly all ministers were members of the Cabinet, but since the introduction of proportional representation, which has led to complex governing arrangements, there are currently three categories of minister: ministers in Cabinet, ministers outside Cabinet, and ministers from supporting parties.[47]
Executive Council

The Executive Council is a formal body established by the Letters Patent 1983 which exists and meets to give legal effect to decisions made by the Cabinet, and to carry out various other functions. All ministers are members of the Executive Council and are entitled to be styled "The Honourable" for life,[48] except for the prime minister, who is styled "The Right Honourable", a privilege they retain for life.[49] Although not a member of the Executive Council, the governor-general usually presides at Council meetings.[50]
Cabinet
Cabinet (Māori: Te Rūnanga) is the senior decision-making body of the Government.[51][52] Constitutional law, such as the Constitution Act 1986, does not recognise the Cabinet as a legal entity; it exists solely by constitutional convention.[53] Its decisions do not in and of themselves have legal force. However, it serves as the practical expression of the Executive Council, which is New Zealand's highest formal governmental body.[46]
The prime minister is responsible for chairing meetings of Cabinet.[26] The governor-general will appoint as prime minister the person most likely to receive the confidence of the House of Representatives to lead the Government. In practice, the appointment is determined by size of each political party, support agreements between parties, and leadership votes in the party that leads the Government.[26][54] The prime minister then advises the governor-general to appoint other ministers. Each minister is responsible for the general administration of at least one portfolio, and heads a corresponding public service department .[52][55] The most important minister, following the prime minister, is the finance minister, while other high-profile portfolios include foreign affairs, justice, health and education.
Traditionally, all members are collectively responsible for the actions taken by Cabinet—typically all Cabinet ministers must publicly support the decisions of Cabinet.[56] However, since the introduction of the mixed-member proportional (MMP) electoral system in 1993,[57] processes were developed to allow different parties within a coalition cabinet to "agree to disagree" on some issues.[58]
The legislative agenda of Parliament is determined by the Cabinet. At the start of each new parliamentary term, the governor-general gives an address prepared by the Cabinet that outlines the Government's policy and legislative proposals.[59]
Ministers outside Cabinet
A few other ministers serve outside of Cabinet. Since the introduction of MMP, governments have been formed following agreements between a major party and smaller support parties. Government ministers from the support parties are often ministers outside Cabinet.[58] Non-Cabinet ministers may also be from the major governing party.[60] Ministers outside the Cabinet have the same overall duties and responsibilities as their senior colleagues inside Cabinet.[52][12]
Departments and other public sector organisations
New Zealand's "public service" includes 32 core government institutions—most have ministry or department in their name, e.g. Ministry for Culture and Heritage, or Department of Internal Affairs—which are listed in the first schedule to the State Sector Act 1988.[61][62] Staffed by around 45,000 public servants,[63] they provide the government of the day with advice and deliver services to the public. Since the 1980s, the public service has been marketised.[64] Each department is headed by a chief executive who answers to a government minister for that department's performance. In turn, a minister bears the ultimate responsibility for the actions of their department, being answerable to the House of Representatives.[62] This principle is called individual ministerial responsibility.[47]
The wider state sector[61] also includes about 2,800 Crown entities (including some 2,600 school boards of trustees and 20 district health boards), 17 state-owned enterprises, three officers of Parliament and the Reserve Bank of New Zealand.[65]
Relationship with local government
There are two main tiers of elected local authorities—regional councils and territorial authorities—in some places merged into unitary authorities. While the central government deals with issues relevant to New Zealand and its people as a nation, local government exists "to enable democratic local decision-making and action by, and on behalf of, communities", and "to meet the current and future needs of communities for good-quality local infrastructure, local public services, and performance of regulatory functions in a way that is most cost-effective for households and businesses."[66]
List of successive governments
There have been three distinctly different periods of New Zealand government—firstly, the period before responsible government; second, from 1856 to 1890, the period in which responsible government begins; and the third period starting with the formation of political parties in 1891.[67]
By convention, a distinct government is named for the largest party that leads it.[68][69][70]
Current government
The current ministry, since November 2020, is a Labour Party government, led by Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern. The majority government has a cooperation agreement with the Green Party.[71]
See also
- Kāwanatanga, a Māori word for "governorship", appearing in the Treaty of Waitangi
- Politics of New Zealand, for a description of other jurisdictions, politics and political institutions
- New Zealand order of precedence
- Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet (New Zealand)
- Official Opposition (New Zealand)
References
- 30 June 1852 is the date the Constitution Act 1852 was assented to. See "New Zealand's first Constitution Act passed 165 years ago", New Zealand Parliament, 30 June 2017, retrieved 25 May 2020
- "Supporting the Prime Minister and Cabinet". Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet. 9 January 2017. Retrieved 25 May 2020.
- "Prime Minister". Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet. 24 June 2017. Retrieved 25 May 2020.
- "The Executive Council". The Governor-General of New Zealand. Retrieved 25 May 2020.
- "What is cabinet?". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. 20 June 2012. Retrieved 25 May 2020.
- "Parliament Brief: Government Accountability to the House". New Zealand Parliament. 21 March 2014. Retrieved 25 May 2020.
- "Revenue and expenditure". The Treasury. 11 December 2019. Retrieved 25 May 2020.
- "Contact us". New Zealand Government. 21 May 2020. Retrieved 25 May 2020.
- "How government works". New Zealand Government. Archived from the original on 15 April 2017. Retrieved 7 December 2016.
- Sir Kenneth Keith, quoted in the Cabinet Manual Archived 9 October 1999 at the Wayback Machine
- "Constitution Act 1986 No 114 (as at 17 May 2005), Public Act – New Zealand Legislation". Parliamentary Counsel Office. Archived from the original on 23 December 2016. Retrieved 7 December 2016.
- Dowding, Keith; Dumont, Patrick (2014). The Selection of Ministers around the World. Routledge. pp. 27–28. ISBN 9781317634454.
- "Our system of government". New Zealand Parliament. Archived from the original on 8 March 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "Glossary of Constitutional Terms". New Zealand Constitutional Advisory Panel. Archived from the original on 6 April 2017. Retrieved 1 May 2017.
- "New Zealand's Central Government | New Zealand Now". New Zealand Now. Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment. Archived from the original on 22 April 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "So who gets to become the Government?" (PDF). Electoral Commission New Zealand. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 May 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "Ministerial List". Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet. Archived from the original on 17 May 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "The Beehive – Executive Wing". New Zealand Parliament. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 1 May 2017.
- "the definition of beehive". Dictionary.com. See: definition 2 of 2. Archived from the original on 6 April 2017. Retrieved 1 May 2017.
- "About this website". beehive.govt.nz. New Zealand Government. Retrieved 18 August 2020.
Beehive.govt.nz is the official website of the New Zealand Government.
- "Political and constitutional timeline". Ministry for Culture and Heritage. 4 November 2016. Archived from the original on 8 April 2017. Retrieved 1 May 2017.
- "Provinces 1848–77". rulers.org. Retrieved 26 April 2013.
- McIntyre, W. David. "Sewell, Henry Archived 13 May 2015 at the Wayback Machine", from the Dictionary of New Zealand Biography. Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "Responsible government". Ministry for Culture and Heritage. 14 July 2014. Retrieved 1 May 2017.
- Wilson, John (8 February 2005). "History – Liberal to Labour". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Archived from the original on 27 April 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
The watershed election of 1890 put the Liberals, who were to become New Zealand’s first 'modern' political party, into power.
- McLean, Gavin (13 December 2016). "Premiers and prime ministers". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Archived from the original on 17 May 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "Letters Patent Constituting the Office of Governor-General of New Zealand (SR 1983/225) (as at 22 August 2006)". Parliamentary Counsel Office. Retrieved 1 May 2017.
- "Seal of New Zealand Act 1977". Parliamentary Counsel Office. Archived from the original on 17 August 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- Boyce, Peter John (2008). The Queen's Other Realms: The Crown and Its Legacy in Australia, Canada and New Zealand. Federation Press. p. 2008. ISBN 9781862877009. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017.
- "Parliament Brief: What is Parliament?". New Zealand Parliament. Archived from the original on 10 May 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- Cox, Noel (1 December 2007). "The Royal Prerogative in the Realms". Commonwealth Law Bulletin. ALTA Law Research Series. 33 (4): 611–638. doi:10.1080/03050710701814839. S2CID 143050540. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
- "Q&A: Royal Prerogative". BBC News. 15 February 2005. Archived from the original on 10 May 2014. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "The Royal Assent". New Zealand Parliament. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "On the Constitution of New Zealand: An Introduction to the Foundations of the Current Form of Government". Archived from the original on 6 April 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "The Queen's constitutional and public ceremonial roles". Ministry for Culture and Heritage. 11 July 2014. Archived from the original on 18 May 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "The New Zealand Constitution". New Zealand Parliament. 3 October 2005. pp. 4–5. Archived from the original on 6 March 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- Joseph, Philip A. (2001). Constitutional and Administrative Law in New Zealand (2nd ed.). Wellington: Brookers. p. 628.
- McKeown, Deirdre (22 March 2010). "Parliamentary involvement in declaring war and deploying forces overseas". www.aph.gov.au. Canberra: Parliament of Australia. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
The formal right to declare war was clearly part of the Royal Prerogative inherited from Great Britain in 1840 and it remains an acknowledged part of New Zealand law.
- "The Role of the Governor-General". The Governor-General of New Zealand Te Kawana Tianara o Aotearoa. Archived from the original on 19 April 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "Letters Patent Constituting the Office of Governor-General of New Zealand". Parliamentary Counsel Office. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "Question time in the House". New Zealand Parliament. 16 October 2012. Archived from the original on 28 February 2018. Retrieved 2 June 2018.
- Galligan, Brian; Brenton, Scott (2015). Constitutional Conventions in Westminster Systems. Cambridge University Press. p. 209. ISBN 9781107100244.
- Bracewell-Worrall, Anna (4 October 2017). "What is confidence and supply… and how does it differ from a coalition?". Newshub. Archived from the original on 21 April 2018. Retrieved 2 June 2018.
- Arwine, A.; Mayer, L. (2013). The Changing Basis of Political Conflict in Advanced Western Democracies: The Politics of Identity in the United States, the Netherlands, and Belgium. Springer. p. 119. ISBN 9781137306654.
- "Parties and Government". www.parliament.nz. New Zealand Parliament. Retrieved 10 September 2019.
- "Executive Council". Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet. Archived from the original on 14 May 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- Eichbaum, Chris (20 June 2012). "Cabinet government – Ministers and prime ministers in cabinet". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Archived from the original on 2 April 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "The Honourable". Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet. Archived from the original on 8 April 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "The Right Honourable". Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet. Archived from the original on 8 April 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "Executive Council – Cabinet Manual". 2008. Archived from the original on 7 April 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- McLeay, Elizabeth (1995). The Cabinet and Political Power in New Zealand. 5. Oxford University Press. p. 11. ISBN 9780195583120.
- Eichbaum, Chris (20 June 2012). "Cabinet government - What is cabinet?". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "On the Constitution of New Zealand: An Introduction to the Foundations of the Current Form of Government – Cabinet Manual". 2008. Archived from the original on 6 April 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "Cainet Manual 2008". cabinetmanual.cabinetoffice.govt.nz. Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet. 2008. Archived from the original on 2 June 2008. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- "Guide to the New Zealand Parliament" (PDF). Retrieved 2 June 2018.
- Palmer, Matthew (20 June 2012). "Collective cabinet responsibility". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 4 December 2020.
- "Electoral Act 1993 No 87 (as at 01 April 2020), Public Act – New Zealand Legislation". Parliamentary Counsel Office. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
- Eichbaum, Chris (20 June 2012). "Cabinet government – Collective responsibility". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 17 September 2018.
- "Speech from the Throne – Cabinet Manual". cabinetmanual.cabinetoffice.govt.nz. 2008. Archived from the original on 7 April 2017. Retrieved 1 May 2017.
- "The full list of Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern's new Cabinet". Stuff. 2 November 2020. Retrieved 4 December 2020.
- "State Sector Act 1988". Parliamentary Counsel Office. Retrieved 9 November 2018.
- Shaw, Richard (20 June 2012). "Public service - What is the public service?". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 9 November 2018.
- "Civil servant numbers static". Stuff.co.nz. 4 December 2014. Retrieved 1 May 2017.
- Shaw, Richard (20 June 2012). "Public service - Revolution, 1980s and 1990s". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 9 November 2018.
- "Government A-Z". govt.nz. New Zealand Government. Retrieved 9 November 2018.
- "Local Government Act 2002". Parliamentary Counsel Office. Retrieved 9 November 2018.
- "List of Governments of New Zealand – The Grid – FInd Anything in New Zealand". The Grid. 17 February 2014. Archived from the original on 12 May 2018. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- Boston, Jonathan; Holland, Martin (1990). The Fourth Labour Government: Politics and Policy in New Zealand. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195582130. Archived from the original on 7 November 2017.
- Garfield, Norton Fausto (2012). Fifth National Government of New Zealand. Anim Publishing. ISBN 9786138498315. Archived from the original on 7 November 2017.
- Hickey, Bernard (20 October 2017). "It's the Sixth Labour Government". Newsroom. Archived from the original on 13 May 2018. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- New Zealand Labour Party (31 October 2020). "Cooperation Agreement Between The NZ Labour Party And The Green Party Of Aotearoa NZ". Scoop.co.nz (Press release). Retrieved 12 November 2020.
Further reading
- Palmer, Geoffrey; Palmer, Matthew (2004). Bridled Power: New Zealand's constitution and government (4th ed.). South Melbourne, Vic. [u.a.]: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-195-58463-9.
External links
- Official website
- Govt.nz – public sector information website