Monarchy of New Zealand
The monarchy of New Zealand[n 1] is the constitutional system of government in which a hereditary monarch is the sovereign and head of state of New Zealand.[3] The current monarch, Queen Elizabeth II, ascended the throne on the death of her father, King George VI, on 6 February 1952. Elizabeth's eldest son, Charles, Prince of Wales, is heir apparent.
| Queen of New Zealand | |
|---|---|
| Kuini o Aotearoa (Māori) | |
.svg.png.webp) Royal arms of New Zealand | |
| Incumbent | |
.jpg.webp) The Queen wearing her New Zealand insignia | |
| Elizabeth II since 6 February 1952 | |
| Details | |
| Style | Her Majesty |
| Heir apparent | Charles, Prince of Wales |
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of New Zealand |
| Constitution |
|
|
The Treaty of Waitangi between Queen Victoria and Māori was signed in 1840, and as a result, the British sovereign became New Zealand's head of state. New Zealand gradually became independent from Britain and the monarchy evolved to become a distinctly New Zealand institution, represented by unique symbols. The person who is the New Zealand monarch is today shared with 15 other countries within the Commonwealth of Nations, all being independent and the monarchy of each legally distinct. As a result, the current monarch is officially titled Queen of New Zealand (Māori: Kuini o Aotearoa) and, in this capacity, she, her consort, and other members of the royal family undertake various public and private functions across New Zealand and on behalf of the country abroad. However, the Queen is the only member of the royal family with any constitutional role.
All executive authority is vested in the monarch, and royal assent is required for parliament to enact laws and for letters patent and Orders in Council to have legal effect. However, the monarch's authority is subject to the conventional stipulations of constitutional monarchy, and her direct participation in these areas of governance is limited.[4] Most of the related powers are instead exercised by the elected members of parliament, the ministers of the Crown generally drawn from amongst them, and the judges and justices of the peace. Other powers vested in the monarch, such as the appointment of a prime minister, are significant, but are treated only as reserve powers and as an important security part of the role of the monarchy.
Since the monarch resides in the United Kingdom, most of the royal constitutional and ceremonial duties within the Realm of New Zealand are typically carried out by a viceregal representative, the governor-general of New Zealand.[5]
The role of the monarchy is a recurring topic of public discussion.[6] Some New Zealanders think New Zealand should become a republic with a New Zealand resident as the head of state, while others wish to retain the monarchy.[7]
International and domestic aspects
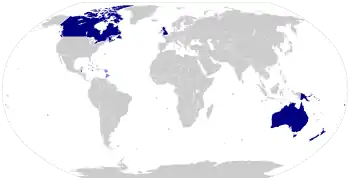
New Zealand is one of the Commonwealth realms, 16 independent members of the Commonwealth of Nations that share the same person as sovereign and head of state, and have in common the same royal line of succession. The monarch, currently Queen Elizabeth II, resides in the oldest and most populous realm, the United Kingdom, though she has occasionally toured New Zealand.[8][9]
This arrangement emerged during the course of the 20th century. Since the passage of the Statute of Westminster in 1931[n 2] the pan-national Crown has had both a shared and separate character,[10][11] and the sovereign's role as monarch of New Zealand has been distinct to his or her position as monarch of the United Kingdom.[12] As a result of this development, the monarchy has ceased to be an exclusively British institution, and in New Zealand has become a New Zealand establishment.[12] Nonetheless, the monarchy is often still inaccurately described as "British" in both legal and common language,[13][14] for reasons historical, political and of convenience; this conflicts with not only the New Zealand Government's recognition of a distinctly New Zealand Crown,[15][16] but also the sovereign's distinct New Zealand title.[17]
Effective with the Constitution Act 1986, no British government can advise the sovereign on any matters pertaining to New Zealand, meaning that on all matters of the New Zealand state, the monarch is advised solely by New Zealand ministers of the Crown.[8] As the monarch lives outside of New Zealand, one of the most important of these state duties carried out on the advice of the prime minister is the appointment of the governor-general, who represents the Queen and performs most of her domestic duties in her absence.[18][19] All royal powers in New Zealand may be carried out by both the monarch and governor-general and, in New Zealand law, the offices of monarch and governor-general are fully interchangeable, mention of one always simultaneously including the other.[20]
Title
One of the first post-Second World War examples of New Zealand's status as an independent monarchy was the alteration of the monarch's title by the Royal Titles Act 1953. For the first time, the official New Zealand title mentioned New Zealand separately from the United Kingdom and the other realms, to highlight the monarch's role specifically as Queen of New Zealand, as well as the shared aspect of the Crown throughout the realms; the title at that time was Elizabeth II, by the Grace of God of the United Kingdom, New Zealand and Her Other Realms and Territories Queen, Head of the Commonwealth, Defender of the Faith. Since the passage of the Royal Titles Act 1974, the monarch's title in New Zealand has been Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God Queen of New Zealand and Her Other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth, Defender of the Faith.[17]
Although the Queen's New Zealand title includes the phrase 'Defender of the Faith', neither the Queen nor the governor-general has any religious role in New Zealand; there has never been an established church in the country.[21] This is one of the key differences from the Queen's role in England, where she is Supreme Governor of the Church of England.[22][n 3]
Succession and regency

Succession is, for persons born before 28 October 2011, governed by male-preference cognatic primogeniture and, for those born after 28 October 2011, by absolute primogeniture—wherein succession passes to an individual's children according to birth order, regardless of gender.[24] The succession is governed by the Act of Settlement 1701, Bill of Rights 1689, and Royal Succession Act 2013,[25] legislation that also limits the succession to the biological, legitimate descendants of Sophia of Hanover, and stipulates that the monarch cannot be a Roman Catholic and must be in communion with the Church of England upon ascending the throne. Though, via adopting the Statute of Westminster (later repealed in New Zealand) and the Imperial Laws Application Act 1988, these constitutional documents as they apply to New Zealand now lie within the full control of the New Zealand Parliament,[26] New Zealand also agreed not to change its rules of succession without the unanimous consent of the other realms, unless explicitly leaving the shared monarchy relationship; a situation that applies symmetrically in all the other realms, including the United Kingdom, and has been likened to a treaty amongst these countries.[27] Thus, New Zealand's line of succession remains identical to that of the United Kingdom. As such, the rules for succession are not fixed, but may be changed by a constitutional amendment. The Constitution Act 1986 specifies that should a regent be installed in the United Kingdom, that individual will carry out the functions of the monarch of New Zealand.[28]
Upon a demise of the Crown (the death or abdication of a monarch), the late sovereign's heir immediately and automatically succeeds, without any need for confirmation or further ceremony—hence arises the phrase "The King is dead. Long live the King!" It is customary, though, for the accession of the new monarch to be publicly proclaimed by the governor-general on behalf of the Executive Council of New Zealand. Following an appropriate period of mourning, the monarch is also crowned in the United Kingdom in an ancient ritual, but one not necessary for a sovereign to reign.[n 4] Other than a transfer of all royal powers and functions to the new monarch from his or her predecessor, no other law or office is affected, as all references in legislation to previous monarchs, whether in the masculine (e.g. "His Majesty") or feminine (e.g. "the Queen"), continue to mean the reigning sovereign of New Zealand.[29] After an individual ascends the throne, he or she typically continues to reign until death, being unable to unilaterally abdicate.[n 5]
Finances
The sovereign only draws from New Zealand funds for support in the performance of her duties when in New Zealand or acting as Queen of New Zealand abroad; New Zealanders do not pay any money to the Queen or any other member of the royal family, either towards personal income or to support royal residences outside of New Zealand. Normally, tax dollars pay only for the costs associated with the governor-general as instruments of the Queen's authority, including travel, security, residences, offices, ceremonies, and the like. Supporters of the monarchy argue it costs New Zealand taxpayers only a small outlay for royal engagements and tours and the expenses of the governor-general's establishment. Monarchy New Zealand states "[t]his figure is about one dollar per person per year", about $4.3 million per annum.[30] An analysis by New Zealand Republic (a republican advocacy group) of the 2010 budget claimed the office of governor-general costs New Zealand taxpayers about $7.6 million in ongoing costs and $11 million for Government House upgrades,[31][32][33] figures Monarchy New Zealand claimed had been "arbitrarily inflated" by New Zealand Republic.[34]
Cook Islands, Niue and territories
The sovereign of New Zealand also serves as monarch to Cook Islands and Niue, territories in free association with New Zealand within the larger Realm of New Zealand.[35][36] The New Zealand monarchy, however, is unitary throughout all jurisdictions in the realm, with the headship of state being a part of all equally.[37] As such, the sovereignty of Cook Islands and Niue is passed on not by the governor-general or parliament of New Zealand but through the overreaching Crown itself as part of executive, legislative and judicial operations in all three areas.
The self-government provisions for the Cook Islands within the Realm of New Zealand allow the Queen to be directly represented as head of state in Cook Islands affairs by the Queen's representative, while the governor-general of New Zealand represents the monarch in matters pertaining to the entire realm.[35][38] The governor-general (themselves represented by state services commissioner[39]) represents the Queen in Niue,[36][40] carrying out all the monarch's constitutional and ceremonial duties of state on her behalf. The administrator of the territory of Tokelau is a government official appointed by New Zealand's minister of foreign affairs to represent the New Zealand Government—not the monarch personally.[41][42]
Representation of the state
As the living embodiment of the Crown, the sovereign is regarded as the personification, or legal personality, of the New Zealand state,[8] with the state therefore referred to as Her Majesty The Queen in Right of New Zealand,[n 6][43] or The Crown.[44] As such, the monarch is the employer of all government staff (including judges, members of the Defence Force, police officers, and parliamentarians), as well as the owner of all state lands (Crown land), buildings and equipment (Crown held property),[45] state-owned companies and agencies (Crown entities),[46] and the copyright for all government publications (Crown copyright).[47]
I, [name], swear that I will be faithful and bear true allegiance to Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth the Second, Her heirs and successors, according to law. So help me God.[48]
— Oath of Allegiance to the Queen
As the embodiment of the state, the monarch is the locus of Oaths of Allegiance,[49] required of many employees of the Crown,[50] as well as by new citizens, as per the Oath of Citizenship laid out in the Citizenship Act. This is done in reciprocation to the sovereign's Coronation Oath, wherein she promised "to govern the Peoples of... New Zealand... according to their respective laws and customs."[51]
Constitutional role
New Zealand's constitution is made up of a variety of statutes and conventions that are either British or New Zealand in origin,[2][26] and together give New Zealand a parliamentary system of government wherein the role of the Queen is both legal and practical. The Crown is regarded as a corporation sole,[52] with the sovereign, in the position of head of state,[3] as the centre of a construct in which the power of the whole is shared by multiple institutions of government acting under the sovereign's authority.[53]
The vast powers that belong to the Crown are collectively known as the Royal Prerogative,[19] the exercise of which does not require parliamentary approval, though it is not unlimited; for example, the monarch does not have the prerogative to impose and collect new taxes without the authorisation of an Act of Parliament.[2] The consent of the Crown must, however, be obtained before parliament may even debate a bill affecting the sovereign's prerogatives or interests, and no Act of Parliament binds the Queen or her rights unless the Act expressly provides that it does.[54]
Executive
The New Zealand Government (formally termed Her Majesty's Government[55]) is defined by the Constitution Act as the monarch acting on the advice of the Executive Council.[56] One of the main duties of the Crown is to ensure that a democratic government is always in place, which means appointing a prime minister to thereafter head the Cabinet, a committee of the Executive Council charged with advising the Crown on the exercise of the Royal Prerogative,[57] and legally required to keep the governor-general up to date on state affairs.[58][59]

In the construct of constitutional monarchy and responsible government, the ministerial advice tendered is typically binding, meaning the monarch reigns but does not rule.[60] However, the Royal Prerogative belongs to the Crown and not to any of the ministers,[53] and the royal and viceregal figures may unilaterally use these powers in exceptional constitutional crisis situations,[53][58][61] thereby allowing the monarch to make sure that the Government conducts itself in compliance with the constitution. There are also a few duties which must be specifically performed by, or bills that require assent by, the Queen; these include applying the royal sign-manual and Seal of New Zealand to the appointment papers of governors-general, the confirmation of awards of New Zealand royal honours,[4] and the approval of any change in her New Zealand title.
Foreign affairs
The Royal Prerogative also extends to foreign affairs: the sovereign or the governor-general conducts treaties, alliances and international agreements on the advice of the Cabinet.[62] The governor-general, on behalf of the Queen, also accredits New Zealand high commissioners and ambassadors, and receives similar diplomats from foreign states. The letters of credence and recall were formerly issued by the monarch, but now are issued in the name of the incumbent governor-general (instead of following the usual international process of the letters being from one head of state to another). The issuance of passports falls under the Royal Prerogative, and, as such, all New Zealand passports are issued in the monarch's name and remain her property.[63]
Parliament
| External video | |
|---|---|
 Queen Elizabeth II opening a session of the New Zealand Parliament, 12 January 1954 | |
The sovereign is one of the two components of the New Zealand Parliament.[61] The monarch and governor-general do not, however, participate in the legislative process save for the granting of Royal Assent, which is necessary for a bill to be enacted as law; either figure or a delegate may perform this task; this is now a matter of convention. The Crown is further responsible for summoning and dissolving the House of Representatives,[65] after which the governor-general usually calls for a general election. The new parliamentary session is marked by either the monarch or the governor-general reading the Speech from the Throne;[66] as the both are traditionally barred from the House of Representatives, this ceremony takes place in the Legislative Council Chamber;[67] the monarch has personally opened parliament on six occasions: January 1954, February 1963, March 1970, February 1974, February 1986, and February 1990.[68]
Despite the sovereign's exclusion, members of parliament must still express their loyalty to her and defer to her authority, as the Oath of Allegiance must be recited by all new parliamentarians before they may take their seat.[49] Further, the official opposition is traditionally dubbed as Her Majesty's Loyal Opposition,[69] illustrating that, while its members are opposed to the incumbent government, they remain loyal to the sovereign (as personification of the state and its authority).[70][71]
Courts
The sovereign is responsible for rendering justice for all her subjects, and is thus traditionally deemed the fount of justice.[72] However, she does not personally rule in judicial cases; instead the judicial functions of the Royal Prerogative are performed in trust and in the Queen's name by judges and justices of the peace. The monarch is immune from criminal prosecution, the notion in common law being that the sovereign "can do no wrong";[73] the monarch cannot be prosecuted in her own courts for criminal offences. The monarch, and by extension the governor-general, also grants immunity from prosecution, exercises the royal prerogative of mercy,[19] and may pardon offences against the Crown, either before, during, or after a trial.
The Crown and the Defence Force

The Crown also sits at the pinnacle of the New Zealand Defence Force. The governor-general is commander-in-chief and under the Defence Act 1990 is authorised to "raise and maintain armed forces",[74] consisting of the New Zealand Army, Royal New Zealand Navy, and Royal New Zealand Air Force. The sovereign's position as head of the Defence Force[75] is reflected in New Zealand's naval vessels bearing the prefix Her Majesty's New Zealand Ship (His Majesty's New Zealand Ship in the reign of a male monarch), and in the requirement that all members of the armed forces swear their allegiance to the sovereign and his or her heirs and successors.[76] The governor-general commissions officers to command the forces.[61]
Allegiance [by Defence Force personnel is to] the Sovereign, [however] loyalty [is] to the Government of the day... The Defence Force and the disposition of those Forces are at the decision... of Her Majesty's Ministers for the time being.[77]
— State Services Commission, December 2001
Though the monarch and members of her family also act as colonels-in-chief of various regiments in the military, these posts are only ceremonial in nature, reflecting the Crown's relationship with the military through participation in military ceremonies both at home and abroad.[n 7] The country's only currently ranked admiral of the fleet is Prince Philip, the Queen's consort;[79] this title is held in conjunction with those of Field Marshal and Marshal of the Royal New Zealand Air Force.[79] Various regiments have also received a royal prefix, such as the Corps of Royal New Zealand Engineers, the Royal New Zealand Infantry Regiment, and the Royal New Zealand Army Logistic Regiment.
The Crown and Māori

Māori interaction with the Crown dates back to 1832, when King William IV of the United Kingdom appointed James Busby as British Resident, to address concerns on the part of Māori in the Bay of Islands over expanding European settlements in that area. On 28 October 1835, Busby oversaw a hui (forum) held at Waitangi, at which a flag was selected for New Zealand and a declaration of independence written by Busby was signed by 36 Māori chiefs; both were acknowledged the following year by the King in a letter from Lord Glenelg.[80]
As a result, the declaration's ratification by the British Parliament in 1836, officials in the Colonial Office determined in 1839 that a treaty of cessation would need to be signed with Māori for the British Crown to acquire sovereignty over New Zealand.[81] The Treaty of Waitangi was signed in 1840 by representatives of the British Crown and over 500 Māori chiefs,[82] and is considered the founding document of the nation.[83] The Treaty identifies the Crown's right to kawanatanga, or "governorship", leading one Māori academic to argue that kawanatanga, or Her Majesty's Government in New Zealand, is party to the treaty.[84]
Since the treaty's implementation, a number of petitions have been made by Māori directly to the sovereign in London, whom they felt they had a special relationship, the first coming from northern chiefs in 1852. This and all subsequent appeals were directed back to the sovereign's New Zealand ministers for advice on how to proceed.[85] The results were not always favourable to Māori, who have communicated their discontent to the monarch or other royals; in response to a refusal by the Executive Council in 1981 to allow Mana Motuhake direct access to the Queen, Māori activist Dun Mihaka offered a traditional rebuke by baring his buttocks at the Prince and Princess of Wales. In a later incident Mihaka attempted to crash into the Queen's motorcade; he was intercepted by police before this happened.[86]
In the Māori language, the Queen is sometimes referred to as te kōtuku-rerenga-tahi, meaning "the white heron of a single flight"; in Māori proverb, the rare white heron is a significant bird seen only once in a lifetime.[8] In 1953, for her coronation, Elizabeth was given a kiwi feather korowai cloak,[87] which she wears when attending a pōwhiri, or Māori welcoming ceremony, also speaking partly in Māori.[9]
Cultural role
Royal presence and duties
Members of the royal family have been present in New Zealand since the late 1800s, their reasons including participating in military manoeuvres or undertaking official royal tours.[88][89] Usually important milestones, anniversaries, or celebrations of New Zealand culture will warrant the presence of the monarch, while other royals will be asked to participate in lesser occasions. Official duties involve the sovereign representing the New Zealand state at home or abroad, or her relations as members of the royal family participating in government organised ceremonies either in New Zealand or elsewhere.[n 8] The advice of the New Zealand Cabinet is the impetus for royal participation in any New Zealand event. Such events have included centennials and bicentennials; Waitangi Day; the openings of Commonwealth and other games; anniversaries of Māori treaty signings; awards ceremonies; anniversaries of the monarch's accession; and the like. Conversely, unofficial duties are performed by royal family members on behalf of New Zealand organisations of which they may be patrons, through their attendance at charity events, visiting with members of the New Zealand Defence Force as colonel-in-chief, or marking certain key anniversaries.
_(crop).jpg.webp)
Since 1869, when Prince Alfred, one of Queen Victoria's sons, arrived on New Zealand's shores,[92] dozens of tours of New Zealand by a member of the royal family have taken place, though only five of those occurred before 1953.[89] After Alfred came the Duke and Duchess of Cornwall and York (later King George V and Queen Mary) in 1901;[93] The Prince of Wales (later King Edward VIII), in 1920;[94] the Duke and Duchess of York (later King George VI and Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother) in 1927;[95] and Prince Henry, Duke of Gloucester, from 1934 to 1935.[96] Queen Elizabeth II was the first reigning monarch of New Zealand to tour the country, becoming such when she arrived during her 1953–1954 global tour; she broadcast from Government House in Auckland her annual Royal Christmas Message.[97]
Queen Elizabeth also toured New Zealand on a number of other occasions: between 6 and 18 February 1963, she attended celebrations at Waitangi and the Queen Elizabeth II Arts Council was founded as the nation's gift to the monarch;[98] from 12 to 30 March 1970, the Queen, accompanied by Prince Charles and Princess Anne, participated in the James Cook bicentenary celebrations;[99] between 30 January and 8 February 1974, and she attended and closed that year's Commonwealth Games in Christchurch and participated in New Zealand Day events at Waitangi.[100] As part of a Commonwealth-wide tour for her Silver Jubilee, Elizabeth was in New Zealand from 22 February to 7 March 1977; she made a brief visit, between 12 and 20 October 1981, following a Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting (CHOGM) in Melbourne; marked the centennial of the New Zealand Police during a tour from 22 February to 2 March 1986; the Queen closed the Commonwealth Games in Auckland and, with her son, Prince Edward, took part in events marking the sesquicentennial of the Treaty of Waitangi between 1 and 16 February 1990; between 1 and 10 November 1995, she attended the CHOGM in Auckland and opened the newly refurbished parliament buildings; and, as part of her global tour for her Golden Jubilee, Elizabeth was in New Zealand from 22 to 27 February 2002.[99][101]
Some of the royal tours undertaken by more junior members of the royal family include the 1990 visit of Princess Anne to commemorate the 75th anniversary of the Gallipoli landings on Anzac Day,[102] and when Prince William represented the Queen of New Zealand at VE and VJ Day commemorations in 2005, as part of an 11-day tour,[103] and opened the new Supreme Court of New Zealand building in early 2010.[104] Prince Edward spent two terms of the 1982 academic year as a house tutor and junior master at the Wanganui Collegiate School.[9]
I want to show you that the Crown is not merely an abstract symbol of our unity but a personal and living bond between you and me.
— Queen Elizabeth II, Christmas Message, New Zealand, 1953[105]
Apart from New Zealand, the Queen and her family regularly perform public duties in the other 15 nations of the Commonwealth of which she is head of state.[106] This situation, however, can mean members of the royal family will be promoting one nation and not another. On some occasions the Queen has represented the United Kingdom while her governor-general represented New Zealand, with both in attendance at the same event.[107]
Symbols
References to the monarchy are commonplace in public life in New Zealand and represent one of the most recognisable ways the head of state is incorporated into New Zealand's national identity. Royal symbols may specifically distinguish institutions that derive their authority from the Crown (such as parliament), establishments with royal associations, or merely be ways of expressing loyal or patriotic sentiment.
The main symbol of the monarchy is the sovereign herself—her portrait, for instance, currently appears on all coins, the twenty-dollar banknote,[108][109] and postage stamps such as the Queen Elizabeth II definitive stamp.[110] There are references to St Edward's Crown, on New Zealand's coat of arms,[111] on various medals, and awards.[112] These latter cases reflect the monarch's place as the formal head of the New Zealand royal honours system. As such, only she can approve the creation of an honour, which she does as requested by the New Zealand Government.[113][114] Though the monarch themselves formally appoints members to the various orders,[115] the governor-general administers most other responsibilities relating to New Zealand honours on the sovereign's behalf (such as investitures).[113]

Similar to coats of arms, flags are utilised to represent royal authority. A personal flag for use by the Queen in New Zealand was adopted in 1962.[116] It features the shield design of the New Zealand coat of arms in the form of an oblong or square. Superimposed in the centre is a dark blue roundel bearing an initial 'E' surmounted by a crown, all within a gold chaplet of roses.[116]
Music and song are utilised in various ways as reminders and identifiers of the sovereign. New Zealand inherited the anthem "God Save the Queen" (or, alternatively, "God Save the King") from Britain.[117] It remains one of the two national anthems, along with "God Defend New Zealand", but has been generally restricted to Anzac Day services and official occasions where the monarch, a member of the royal family, or the governor-general is being either honoured or in attendance for a particular purpose.[117]
As in other Commonwealth realms, the Queen's Official Birthday is a public holiday and, in New Zealand, is observed on the first Monday in June.[118] Celebrations are mainly official, including the Birthday Honours list and military ceremonies.[119][120]
Organisations with royal patronage
To receive patronage, an organisation must prove to be long lasting, and to be of the highest standard in their field. These organisations, such as the Royal New Zealand Returned and Services' Association, signified by the prefix royal, have received patronage from various monarchs and their families. Royal patronage is the royal individual's decision to make, though the Ministry for Culture and Heritage will help organisations to seek patronage.[121]
Debate
Despite a similar level of political involvement by the monarchy in both countries, there is less agitation for ending the monarchy of New Zealand and creating a New Zealand republic than in neighbouring Australia, where the republicanism movement is stronger. Past public opinion polls have shown that while the majority of Australians are in favour of a republic, New Zealanders on average favour retaining the monarchy.[122] Supporters of the monarchy claim that for New Zealand, "...monarchy summarises the inheritance of a thousand years of constitutional government and our links with a glorious past".[123]
Neither National nor Labour, the two major political parties currently in parliament, have a stated policy of creating a republic, though some members of parliament have publicly expressed their personal support for a republic. Some members have also expressed support for the monarchy. Former Deputy Prime Minister Michael Cullen declared that he supported the monarchy, stating in 2004 he was "a sort of token monarchist in the Cabinet these days."[124] However, in 2010 he repudiated that stance, taking the view that New Zealand should move towards a republic once the Queen's reign ends.[125] In 2008, former Prime Minister John Key, then Leader of the Opposition, said he is "not convinced [a republic] will be a big issue in the short term,"[126] but does believe that a republic is "inevitable."[127][128] There are two special-interest groups representing both sides of the debate in New Zealand and arguing the issue in the media from time to time: Monarchy New Zealand and New Zealand Republic.[129]
There are a number of legal issues to be addressed in order to abolish the monarchy,[130] though individuals on both sides of the argument take a different view of the level of difficulty faced.[131] Much of the unsurety involves the reserve powers of the sovereign; the relationship between the various regions of the Realm of New Zealand sharing the same sovereign (the absence of these matters from republican arguments having been criticised as a "self-centredness of republican discussions in New Zealand"[36]); and effects on the relationship between the Crown and Māori, specifically, the continued legal status of the Treaty of Waitangi and its claims and settlements.[132][133][134] Some academics expressed concern that governments could use republicanism to evade treaty responsibilities,[135] while others, such as Professor Noel Cox, Chairman-Emeritus of Monarchy New Zealand, have argued a republic would not absolve the Government of its obligations under the treaty.[136]
.jpg.webp)
The institution enjoys the support of most New Zealanders, particularly those born before the Second World War.[137] With the approval of the current monarch, and the position of the Treaty of Waitangi under a republic remaining a concern to Māori and other New Zealanders alike, as well as the question of what constitutional form a republic might take unresolved, support for a republic remains no higher than one third to 40 per cent of the population.[137][138] However, polls indicate that many New Zealanders see the monarchy as being of little day-to-day relevance; a One News/Colmar Brunton poll in 2002 found that 58 per cent of the population believed the monarchy has little or no relevance to their lives.[139] National Business Review poll in 2004 found 57 per cent of respondents believed New Zealand would become a republic "in the future".[140] On 21 April 2008, New Zealand Republic released a poll of New Zealanders showing 43 per cent support the monarchy should Prince Charles become king of New Zealand, and 41 per cent support a republic under the same scenario.[141] A poll by The New Zealand Herald in January 2010, before a visit by Prince William to the country, found 33.3 per cent wanted Prince Charles to be the next monarch, with 30.2 per cent favouring Prince William. 29.4 per cent of respondents preferred a republic in the event Queen Elizabeth died or abdicated.[142]
On 14 October 2009, a bill put forward in parliament by Keith Locke to bring about a referendum on the monarchy was drawn from the ballot of members' bills and introduced into the legislative chamber.[143] It had been presumed that this bill would have been binding in New Zealand only, having no effect in the Cook Islands or Niue.[36] On 21 April 2010 the bill was defeated at its first reading 68–53,[127] and did not continue through to select committee.
On the eve of a royal tour by Prince Charles and Camilla, Duchess of Cornwall, 10 November 2012, a One News/Colmar Brunton poll reported 70 per cent of people questioned responded they wanted to "keep The Queen as head of state", while only 19 per cent supported a republic.[144][145] Following the tour, a poll by Curia Market Research commissioned by New Zealand Republic found 51 per cent of respondents wanted Charles as King once the Queen's reign ends, while 41 per cent supported a republic.[146]
Support for the monarchy in New Zealand tends to increase during times where there is considerable focus on the royal family, whether this be due to royal tours or significant events such as a royal wedding.[147]
History

Lieutenant James Cook first sailed to New Zealand in 1769. There he mapped the entire coastline and tentatively claimed the land for King George III of the United Kingdom.[148] Beginning in 1790, an increasing number of European settlers came to New Zealand.[148] In 1833, with growing lawlessness amongst traders and settlers, the British government appointed James Busby as British Resident to protect British trading interests. Despite Busby's presence, trouble increased. In 1840, the British government sent Captain William Hobson to New Zealand as lieutenant governor; he was instructed to negotiate a voluntary transfer of sovereignty from the Māori to the British Crown.[82] The resultant Treaty of Waitangi was signed on 6 February 1840, at Waitangi in the Bay of Islands.[82] Following the Treaty, the islands of New Zealand became a Crown colony and Queen Victoria became the monarch over New Zealand.[82][149]
In the early 19th century, some Māori who visited London were introduced to royalty. The first, Moehanga (or Te Mahanga) met King George III and Queen Charlotte in 1806.[150] Other rangatira (chiefs) to meet the monarch include Hongi Hika, who met King George IV in 1820.[151]
In 1852, the New Zealand Constitution Act 1852 was passed, establishing responsible government in New Zealand. The Act reserved significant constitutional powers for the monarch, including the right to refuse assent.[152]
Queen Victoria's second son, Prince Alfred, Duke of Edinburgh, became the first British royal to visit New Zealand. He landed in Wellington on April 11, 1869, aboard his ship HMS Galatea.
In 1907, New Zealand achieved the status of 'Dominion', which denoted that it was a country of the British Empire (and later the Commonwealth of Nations) with autonomy in domestic and foreign affairs.[153] In 1917, letters patent of King George V set out the powers, duties and responsibilities of the governor-general and the Executive Council.[154] The governor-general remained an appointee of the British Crown on the advice of the British Cabinet.[155]
The concept of a fully independent New Zealand sharing the person of the sovereign with the United Kingdom and other countries only emerged gradually over time through constitutional convention. A series of Imperial Conferences held in London, from 1917 on, resulted in the Balfour Declaration of 1926, which provided that the United Kingdom and the Dominions were to considered as "autonomous communities within the British Empire, equal in status, in no way subordinate to one another in any aspect of their domestic or external affairs, though united by a common allegiance to the Crown".[156] The governor-general of New Zealand, as with all the other governors-general of the empire, became the direct representative of the monarch in person, rather than a diplomatic channel between the New Zealand and British governments.[157]
The Crown was further separated amongst its Dominions by the Statute of Westminster in 1931, an Act of the British parliament, which gave New Zealand and other Dominions the authority to make their own laws in all matters, while requiring them all to seek each other's assent for changes to monarchical titles and the common line of succession.[158] The British Parliament specifically gave up any claim to legislate for a Dominion, save at its own request.[159] New Zealand ratified the Statute in 1947, after the passing of the Statute of Westminster Adoption Act 1947.[160] A convention persisted that New Zealand prime ministers consulted the British government on the appointment of governors-general until 1967.[161]
Recent developments
I look forward to continuing to serve to the best of my ability in the years to come. It fills me with great pride to stand before you here today to express my lasting respect and deep affection for this country and for New Zealanders everywhere.[162]
— Queen Elizabeth II, 25 February 2002
The sovereign did not possess a title unique to New Zealand until the New Zealand Parliament enacted the Royal Titles Act in 1953,[17] altering the style borne by Queen Elizabeth II and giving her the title of Queen of the United Kingdom, New Zealand and Her Other Realms and Territories.[17] Accordingly, the name of the country in official usage was also changed to the Realm of New Zealand.[153]
More recently, the Constitution Act 1986 has become the principal formal statement of New Zealand's constitution. This law formally establishes that the sovereign (in Right of New Zealand) is the head of state of New Zealand and that the governor-general is her representative; each can, in general, exercise all the powers of the other.[19][n 9]
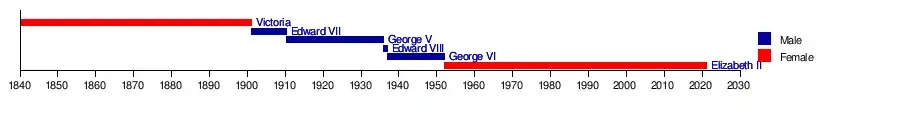
List of monarchs
Listed are the Kings and Queens regnant who have reigned over New Zealand—the British colony of New Zealand, from 1840; followed by the Dominion of New Zealand, beginning in 1907; and finally the present-day sovereign state of New Zealand. Originally, these monarchs reigned in their right as British sovereigns.
Timeline of monarchs
See also
Notes
- The monarchy is also referred to as the Crown, the Crown in Right of New Zealand, Her Majesty the Queen in Right of New Zealand or the Sovereign in Right of New Zealand, especially in regard to the entire government of New Zealand.[1][2]
- The Statute of Westminster was initiated by the British parliament. Although it was not adopted in New Zealand until 1947, the statute's validity in the United Kingdom meant that British ministers of the Crown would no longer intervene in New Zealand affairs without the consent of New Zealand politicians. See § History
- When in New Zealand, the Queen has attended Anglican church services,[23] but she has no official role in the Anglican Church in New Zealand.
- For example, Edward VIII was never crowned, yet was undoubtedly king during his short time on the throne.
- The only New Zealand monarch to abdicate, Edward VIII, did so with the authorisation of the New Zealand government granted in His Majesty's Declaration of Abdication Act 1936 (UK).
- For example, if a lawsuit is filed against the government, the respondent is formally described as Her Majesty the Queen in Queen in Right of New Zealand, or simply Regina.
- Such events include inspections of the troops, and anniversaries of key battles; the governor-general represents the sovereign at military commemorations in New Zealand and sometimes at ceremonies abroad; for example, Sir Anand Satyanand in 2007 attended commemorations of the Battle of Passchendaele in Belgium,[78] whenever the sovereign or a member of her family is in Auckland, they lay a wreath at the War Memorial, or at the National War Memorial in Wellington.
- Though the royal family represents other countries abroad, as directed by their respective cabinets, and typically the governor-general will undertake state visits and other foreign duties on behalf of the monarch of New Zealand,[90] members of the royal family will also take part in New Zealand events overseas. For example, on 11 November 2006, the Queen – accompanied by the Duke of Edinburgh, the Prince of Wales, the Duchess of Cornwall, Prince William, the Duke of York, and the Princess Royal – dedicated the New Zealand war memorial in London's Hyde Park, reviewing a royal Guard of honour formed by the largest contingent of New Zealand forces seen in the UK since her coronation in 1953.[91]
- The Constitution Act also repealed and replaced the Statute of Westminster, and removed the remaining ability of the British parliament to intervene in New Zealand constitutional affairs.[10]
Citations
- Shore & Kawharu 2014, p. 17
- Office of the Governor-General of New Zealand. "On the Constitution of New Zealand". Retrieved 29 June 2017.
- Elizabeth II (13 December 1986), Constitution Act 1986, 2.1, Wellington: Parliamentary Counsel Office (New Zealand), retrieved 30 December 2009
- Cabinet Office 2017, p. 3
- Cabinet Office 2017, p. 7
- "Changing attitudes to monarchy". NZ History. Ministry for Culture and Heritage. Retrieved 24 February 2018.
- Cook, Megan (20 June 2012). "Royal family". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 7 August 2019.
- The Royal Household. "The Queen and the Commonwealth > Queen and New Zealand > The Queen's role in New Zealand". Queen's Printer. Archived from the original on 21 March 2015. Retrieved 1 January 2010.
- Royal Household. "The Queen and the Commonwealth > Queen and New Zealand > Royal visits". Queen's Printer. Archived from the original on 24 December 2010. Retrieved 2 January 2010.
- A.E. Currie (1944). New Zealand and the Statute of Westminster, 1931. Butterworth.
- Trepanier, Peter (2004). "Some Visual Aspects of the Monarchical Tradition" (PDF). Canadian Parliamentary Review. Ottawa: Commonwealth Parliamentary Association. 27 (2): 28. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 March 2010. Retrieved 8 October 2009.
- Kisch, Conrad (2009). Destination. New Zealand. Gyldendal Uddannelse. p. 43. ISBN 9788702075847.
- "Royal family – Royal tours". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
Many New Zealanders are content to have the British monarch as head of state
- Copley, Gregory R. (1999). Defense & Foreign Affairs Handbook. Perth Corporation. p. 1056. Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- McLean, Gavin. "The Queen's constitutional and public ceremonial roles". Government House.
She reigns as Queen of New Zealand independently of her position as Queen of the United Kingdom.
- Boyce 2008, p. 172
- Peaslee, Amos J. (1985). Constitutions of Nations (Rev. 4th ed.). Dordrecht: Nijhoff. p. 882. ISBN 9789024729050. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- Office of the Governor-General of New Zealand. "Role & Functions > The Role of the Governor-General". Government House. Retrieved 26 March 2019.
- Cabinet Office 2017, p. 8
- Elizabeth II 1986, 3.2
- Ahdar, Rex (2014). Religion and the State in New Zealand (PDF). pp. 569–571. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
New Zealand has never had an established church.
- "The Queen, the Church and other faiths". The Royal Household. 7 January 2016. Retrieved 18 January 2019.
- "Picture Gallery: Queen tours New Zealand". BBC News. 24 February 2002. Retrieved 21 January 2019.
- "Girls equal in British throne succession". BBC News. 28 October 2011.
- "Royal Succession Act 2013". New Zealand Legislation. Parliamentary Counsel Office (New Zealand). Retrieved 12 July 2014.
- Cabinet Office 2017, p. 2
- Tony O'Donohue v. Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, 41404 (ON S.C.), S.33 (Ontario Superior Court of Justice 2003).
- Elizabeth II 1986, 4.1
- Elizabeth II 1986, 5.1–2
- "Cost of the Monarchy". Monarchy New Zealand. 2009. Archived from the original on 4 December 2010. Retrieved 2 October 2010.
- "Vote Prime Minister and Cabinet" (PDF). New Zealand Treasury. May 2010. pp. 269–270. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 May 2010. Retrieved 2 October 2010.
- "Defending the monarchy – the cost". New Zealand Republic. 2010. Archived from the original on 1 May 2010. Retrieved 26 September 2010.
- New Zealand Republic (20 May 2010). "Governor-General more expensive". Scoop.co.nz.
- "Monarchy New Zealand Calls for the Resignation of Republican Chair" (PDF). 28 October 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 15 November 2010.
- "Government of the Cook Islands". Jarvy Web. Retrieved 2 January 2010.
- Townend, Andrew (2003). "The Strange Death of the Realm of New Zealand: The Implications of a New Zealand Republic for the Cook Islands and Niue". Victoria University of Wellington Law Review. Wellington: Victoria University of Wellington. 34 (3): 571. doi:10.26686/vuwlr.v34i3.5768. Archived from the original on 26 April 2009. Retrieved 2 January 2010.
- "Tokelau: A History of Government" (PDF). Wellington: Council for the Ongoing Government of Tokelau. 2008. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- Elizabeth II (1981), Constitution of the Cook Islands, 3.1, Avarua: Pacific Islands Legal Information Institute, retrieved 2 January 2010
- Elizabeth II (30 March 1988), State Sector Act 1988, 3, Wellington: Parliamentary Counsel Office (New Zealand), retrieved 2 January 2010
- Elizabeth II (29 August 1974), Niue Constitution Act 1974, Schedule 2.I.1, Wellington: Parliamentary Counsel Office (New Zealand), retrieved 2 January 2010
- "Administrator of Tokelau announced". Beehive.govt.nz. New Zealand Government. 15 December 2017. Retrieved 18 October 2019.
- "Administration". www.tokelau.org.nz. Government of Tokelau. Retrieved 18 October 2019.
- Elizabeth II (21 May 2004), Guarantee Eligibility Certificate (PDF), Wellington: New Zealand Treasury, p. 1, archived from the original (PDF) on 22 May 2010, retrieved 16 May 2009
- Zines, Leslie (2008). The High Court and the Constitution. Federation Press. p. 14. ISBN 9781862876910. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
- "Types of Crown property". Land Information New Zealand. Retrieved 24 October 2018.
- Cabinet Office 2017, p. 41
- Elizabeth II (1994), Copyright Act 1994, 26.1, Parliamentary Counsel Office (New Zealand) (published 15 December 1994), retrieved 24 October 2018
- Elizabeth II 1957
- Elizabeth II (24 October 1957), Oaths and Declarations Act 1957, 17, Wellington: Parliamentary Counsel Office (New Zealand), retrieved 1 January 2010
- Elizabeth II 1957, 22–25
- "The Form and Order of Service that is to be performed and the Ceremonies that are to be observed in the Coronation of Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II in the Abbey Church of St. Peter, Westminster, on Tuesday, the second day of June 1953". Anglican Liturgical Library. Retrieved 16 May 2009.
- George V (9 April 1925), "s. 180", Law of Property Act 1925, London: Queen's Printer
- Cox, Noel (September 2002). "Black v Chrétien: Suing a Minister of the Crown for Abuse of Power, Misfeasance in Public Office and Negligence". Murdoch University Electronic Journal of Law. Perth: Murdoch University. 9 (3): 12. Retrieved 17 May 2009.
- Joseph, Philip A. (2014). Constitutional and Administrative Law in New Zealand (4th ed.). Thomson Reuters. pp. 669–674.
- Elizabeth II. "Seal of New Zealand Act 1977". Parliamentary Counsel Office. Retrieved 1 November 2018.
- Elizabeth II 1986, 3A.1
- Elizabeth II 1983, VII
- Cabinet Office 2017, p. 9
- Elizabeth II 1983, XVI
- Cabinet Office 2017, p. 14
- Office of the Governor-General of New Zealand. "Role & Functions > The Constitutional Role of the Head of State". Government House. Retrieved 26 March 2019.
- Barnett 2017, p. 103
- Barnett 2017, p. 106
- British Pathe (12 January 1954). Queen Opens New Zealand Parliament (1954) (Newsreel). 138.09. Retrieved 11 November 2018.
- Cabinet Office 2017, p. 75
- Cabinet Office 2017, p. 87
- "Roles and regalia at the Opening of Parliament". New Zealand Parliament. 13 October 2014. Retrieved 11 November 2018.
- "Display of royal memorabilia". New Zealand Parliament. 29 April 2011. Retrieved 12 November 2018.
During her first eagerly awaited tour over the summer of 1953-4 Parliament was summoned for a special short session in January to allow her to open Parliament and deliver the Speech from the Throne. She again opened a special session of Parliament in February 1963. She also opened Parliament in March 1970 and February 1974. In February 1977 she opened another special session at the same time as formally opening the Beehive (the Executive Wing). More recently she has opened Parliament in February 1986 and February 1990.
- "The relevance of Parliament". New Zealand Parliament. 11 May 2005. Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- Schmitz, Gerald (December 1988), The Opposition in a Parliamentary System, Ottawa: Queen's Printer for Canada, archived from the original on 21 March 2015, retrieved 28 October 2009
- Mulgan, R. G.; Aimer, Peter (2004). Politics in New Zealand. Auckland University Press. p. 110. ISBN 9781869403188.
- "Fount of Justice". British Monarchist League. Retrieved 31 August 2016.
- The New Zealand Law Journal. Butterworths of New Zealand. 1994. p. 53.
- Elizabeth II (1 April 1990), Defence Act 1990, 5, 6.1, Wellington: Parliamentary Counsel Office, retrieved 1 January 2010
- The Queens Role in New Zealand, archived from the original on 26 September 2013, retrieved 24 January 2011
- Elizabeth II 1990, 34
- State Services Commission. "Review of the Performance of the Defence Force in Relation to Expected Standards of Behaviour, and in Particular the Leaking and Inappropriate Use of Information by Defence Force Personnel". State Services Commission. Retrieved 1 January 2010.
- "Governor-General visits Belgium for Passchendaele Commemoration". Government House. 6 July 2007.
- Heald, Tim (1991). The Duke: A Portrait of Prince Philip. London: Hodder and Stoughton. pp. 264–267. ISBN 978-0-340-54607-9.
- The Lord Glenelg (25 May 1836), "EXTRACT of a DESPATCH from Lord GLENELG to Major-General Sir RICHARD BOURKE, New South Wales", written at London, Documents > Declaration of Independence, Christchurch: Waitangi Associates, retrieved 11 January 2010
- Orange, Claudia (2004). An Illustrated History of the Treaty of Waitangi. Wellington: Bridget Williams Books. p. 42. ISBN 978-1-877242-16-8.
- Mallenby, Patricia E.A.; Mallenby, Jeremy T.T. (2002). Essays in World History: An Undergraduate Perspective. Victoria, B.C.: First Choice Books. pp. 314–215. ISBN 9780978059316.
- Cabinet Office 2017, p. 1
- Jackson, Moana (1996), Trainor, Luke (ed.), Republicanism in New Zealand, Palmerston North: Dunmore Press, p. 119, ISBN 978-0-86469-256-6
- History Group of the New Zealand Ministry for Culture and Heritage. "Politics and government > Maori leadership > Maori King movement – 1860–94 > Normalising relations". Ministry for Culture and Heritage (New Zealand). Retrieved 2 January 2010.
- "Top 10 Odd Protests – Down (Under) And Dirty". Time. 15 December 2008. Retrieved 8 January 2010.
- Royal Household. "The Queen and the Commonwealth > Queen and New Zealand > Symbols and ceremonies". Queen's Printer. Retrieved 2 January 2010.
- "The Duke of Edinburgh, 1869–71". An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand. 1966. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
- Cook, Megan (20 June 2012). "Royal family - Royal tours". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- Office of the Governor-General of New Zealand. "Role & Functions " The Governor-General's Three Roles". Government House. Retrieved 26 March 2019.
- "Queen honours New Zealand's dead". BBC. 11 November 2006. Retrieved 17 November 2006.
- "The Duke of Edinburgh, 1869–71". An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand. 1966. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- "The Duke and Duchess of Cornwall, 1901". An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand. 1966. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- "The Prince of Wales, 1920". An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand. 1966.
- "The Duke and Duchess of York, 1927". An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand. 1966. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- "The Duke of Gloucester, 1934–35". An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand. 1966.
- "The Queen and Duke of Edinburgh, 1953–54". An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand. 1966. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- "The 1963 Tour". An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand. 1966. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- "Later visits by Queen Elizabeth and Prince Philip". NZ History. Ministry for Culture and Heritage. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- "Royal family at Waitangi, 1974". NZ History. Ministry for Culture and Heritage. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- The Department of Internal Affairs, Visits to New Zealand by The Queen and Duke of Edinburgh, Department of Internal Affairs (New Zealand)
- "Untitled". National Library of New Zealand. 26 April 1990.
Gallipoli veterans received 1990 Commemoration medals from Princess Anne at the Beehive yesterday.
- Associated Press (3 July 2005), "Prince William charms crowds in New Zealand", USA Today, retrieved 16 January 2010
- Key, John; John Key (2 November 2009). "Prime Minister announces visit of Prince William". Scoop. Retrieved 20 January 2010.
- Longford, Elizabeth (1984). The Queen: The Life of Elizabeth II. Ballantine Books. p. 185. ISBN 9780345320049.
- "The Queen and the Commonwealth". royal.uk. The Royal Household. Retrieved 11 November 2018.
- "Gov-Gen visits Belgium for Passchendaele Commemoration". Scoop.co.nz (Press release). Government House. 6 July 2007. Retrieved 21 January 2019.
- Wilson, John (16 September 2016). "Nation and government - System of government". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 29 October 2018.
The Queen’s portrait appears on New Zealand’s banknotes and coins (though no longer on most issues of postage stamps).
- Pollock, Kerryn (20 June 2012). "Coins and banknotes - Decimal currency, 1960s to 2000s". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 29 October 2018.
- "Queen Elizabeth II". New Zealand Post. Retrieved 30 October 2018.
- "Coat of Arms". Ministry for Culture and Heritage. Retrieved 29 October 2018.
St Edward's Crown, shown above the shield, was used in the Coronation ceremony of Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II. The crown symbolises Her Majesty as Queen of New Zealand under the New Zealand Royal Titles Act 1953.
- For instance: The Queen's Service Order, Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet, retrieved 29 October 2018.
- "New Zealand Royal Honours". The Governor-General. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- "Honours Unit - DPMC". Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- Macauley, G.A. (1994). "Honours and Arms: Legal and Constitutional Aspects of Practice Concerning Heraldry and Royal Honours in New Zealand". Canterbury Law Review. 5 (3).
- Pollock, Kerryn (20 April 2016). "Flags". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- Swarbrick, Nancy (20 June 2012). "National anthems". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- "Queen's Birthday". Public Holidays Global Pty Ltd. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- Rudman, Brian. "Clear signal from Her at the Palace". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- "New Zealand Honours Lists". www.dpmc.govt.nz. New Zealand Department of Prime Minister and Cabinet. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- "Use of the word "Royal" guidelines | Ministry for Culture and Heritage". Ministry for Culture and Heritage. Retrieved 7 September 2016.
- Kullmann, Claudio (November 2008). "Attitudes towards the Monarchy in Australia and New Zealand Compared". Commonwealth & Comparative Politics. 46 (4): 442–463. doi:10.1080/14662040802461125. S2CID 144715921.
- "What the New Zealand press said about ...... Prince Charles". The Guardian. 9 March 2005. Retrieved 23 September 2011.
- Daily Hansard: Clerk of the House of Representatives. Clerk of the House of Representatives. 16 December 2004.
- "Cullen: New Zealand should be republic". Herald on Sunday. 29 August 2010. Retrieved 29 August 2010.
- "Strong backing for MMP referendum". TVNZ. 23 June 2008. Archived from the original on 18 May 2011. Retrieved 13 July 2008.
- Holden, Lewis J. (2009). The New Zealand Republic Handbook: A Guide to Creating the New Zealand Republic. Republican Movement. p. 71.
- Smith, Peter (1 September 2008), "Key knocking on door of government", Financial Times, retrieved 4 September 2008
- "New Zealand has voted to get rid of the Queen". The Independent. 6 September 2016. Retrieved 29 June 2017.
- Stockley, Andrew P. (1996), "Becoming a Republic? Issues of Law", in Trainor, Luke (ed.), Republicanism in New Zealand, Palmerston North: Dunmore Press, p. 81, ISBN 978-0-86469-256-6
- Stockley, Andrew (1998). "Of Conventions and Constitutional Change: Lessons for New Zealand". University of New South Wales Law Journal. Sydney: University of New South Wales. 21 (3). Archived from the original on 5 November 2012. Retrieved 25 January 2010.
- Ladley, Andrew (2000), "Who should be Head of State?", in James, Colin (ed.), Building the Constitution, Wellington: Institute of Policy Studies, pp. 267, 273
- Milne, Johnathan (30 May 2004), "The People vs the Crown", Sunday Star-Times, p. 7
- Brookfield, F.M. (Jock) (1995). Republican New Zealand: Legal Aspects and Consequences. New Zealand Law Review. p. 310.
- Tunks, Andrea (1996), Trainor, Luke (ed.), Republicanism in New Zealand, Palmerston North: Dunmore Press, p. 117, ISBN 978-0-86469-256-6
- Cox, Noel (2002). "The Treaty of Waitangi and the Relationship Between Crown and Maori in New Zealand". Brooklyn Journal of International Law. Brooklyn: University of Brooklyn. 28. SSRN 420020.
- Kiwis Divided Over Monarchy (PDF), Research NZ, 23 December 2008, archived from the original (PDF) on 13 May 2010, retrieved 31 January 2010
- D, Michael (26 November 2013). "Republicanism 'recipe for disaster'". Stuff.co.nz. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
- "NZ premier denies royal snub". BBC. 23 February 2002. Retrieved 16 June 2008.
- "New Zealanders Resigned to Their Fate". National Business Review. 17 August 2004.
- "Opinion divided on NZ becoming republic". TV3. 21 April 2008. Retrieved 21 April 2008.
- Kara Segedin (19 January 2010). "Charles and William evens for throne". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 31 January 2010.
- House of Representatives (15 October 2009), Order Paper, 71, Parliamentary Counsel Office (New Zealand)
- "Prince Charles and Camilla arrive in New Zealand". 1 News. TVNZ. 10 November 2012. Retrieved 12 November 2012.
- "One News 10 November 2012". 10 November 2012.
- "Poll finds Prince Charles' popularity unchanged by visit". 1 News. TVNZ. 19 December 2012.
- Hubbard, Anthony (January 2018). "Monarchy or republic? The debate for NZ's head of state rages on". Stuff.co.nz.
- DeRouen, Karl R. (2005). Defense and Security: A Compendium of National Armed Forces and Security Policies. ABC-CLIO. p. 496. ISBN 9781851097814. Retrieved 29 June 2017.
- Orange, Claudia (20 June 2012). "Treaty of Waitangi - Interpretations of the Treaty of Waitangi". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- "Moehanga becomes first Māori to visit England". NZHistory. Ministry for Culture and Heritage. Retrieved 1 November 2018.
- Cook, Megan (20 June 2012). "Royal family - Māori and the royal family". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 21 August 2016.
- Constitution Act 1852, Section 56.
- "What changed? - Dominion status". Ministry for Culture and Heritage. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
- Boyce 2008, p. 173
- "New Zealand Sovereignty: 1857, 1907, 1947, or 1987?". Governor-General of New Zealand. 28 August 2007. Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- "Dominion status and legislation". The National Archives. Retrieved 31 August 2016.
- "History of the Governor-General – Regalised". NZHistory. Ministry for Culture and Heritage. 17 July 2014. Retrieved 24 October 2018.
- "Statute of Westminster 1931". legislation.gov.uk. Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- McIntyre, W. David (20 June 2012). "Self-government and independence - Statute of Westminster". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 24 October 2018.
- "Dominion Day - From colony to dominion". NZHistory. Ministry for Culture and Heritage. 20 December 2012. Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- Joseph, Philip A (2014), Constitutional and Administrative Law in New Zealand, Wellington: Brookers, p. 140, ISBN 978-0-864-72843-2
- "State dinner in Wellington, New Zealand, 25 February 2002". royal.uk. The Royal Household. 25 February 2002. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
References
- "New Zealand Constitution Act 1852". Victoria University of Wellington - New Zealand Electronic Text Collection. 30 June 1852. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
- Barnett, Hilaire (2017). Constitutional & Administrative Law (12th ed.). Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-315-45836-6.
- Boyce, Peter John (2008). The Queen's Other Realms: The Crown and Its Legacy in Australia, Canada and New Zealand. Sydney: Federation Press. ISBN 978-1-862-87700-9. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- Cabinet Office (2017). "Cabinet Manual" (PDF). Wellington: Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet. Retrieved 29 June 2017.
- Cox, Noel (2008). A Constitutional History of the New Zealand Monarchy: The Evolution of the New Zealand Monarchy and the Recognition of an Autochthonous Polity. Saarbrücken, Germany: V.D.M. Verlag Dr. Müller Aktiengesellschaft & Co. K.G. ISBN 978-3-639-00877-7.
- Shore, Cris; Kawharu, Margaret (17 June 2014). "The Crown in Right of New Zealand: Anthropological Perspectives on an Imagined Sovereign". Sites: A Journal of Social Anthropology and Cultural Studies. 11 (1): 17–37. doi:10.11157/sites-vol11iss1id267. ISSN 1179-0237. Retrieved 28 June 2017.
Further reading
- Ashley, Mike (1999). The mammoth book of British kings and queens. London: Robinson Publishers. ISBN 978-1-84119-096-9.
- Gimpel, Diane Marczely (2011). Monarchies. Edina, Minn.: ABDO Pub. Co. ISBN 978-1-617-58950-8.
- Mulgan, Richard (2004). Politics in New Zealand (3rd ed.). Auckland: Auckland University Press. ISBN 978-1-869-40318-8.
- Quentin-Baxter, Alison; McLean, Janet (2017). This Realm of New Zealand: The Sovereign, the Governor-General, the Crown. Auckland University Press. ISBN 978-1-869-40875-6.
External links
- New Zealand press releases at The Royal Household website
- Monarchy New Zealand
- Royal visit to NZ in 1953–54
.jpg.webp)







