Nilgiri marten
The Nilgiri marten (Martes gwatkinsii) is the only marten species native to southern India. It lives in the hills of the Nilgiris and parts of the Western Ghats. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List.[1]
| Nilgiri marten | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Mustelidae |
| Genus: | Martes |
| Species: | M. gwatkinsii |
| Binomial name | |
| Martes gwatkinsii (Horsfield, 1851) | |
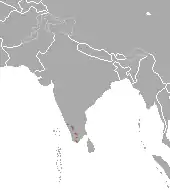 | |
| Nilgiri marten range | |
Description
.jpg.webp)
The Nilgiri marten is deep brown from head to rump, with the forequarters being almost reddish, with a bright throat ranging in colour from yellow to orange. It has a prominent frontal concavity and is larger than the yellow-throated marten.[2] It is about 55–65 cm (22–26 in) long from head to vent and has a tail of 40–45 cm (16–18 in). It weighs about 2.1 kg (4.6 lb).[3]:6
Distribution and habitat
The Nilgiri marten mainly inhabits the shola grassland and high altitude evergreen forests, and occasionally the adjacent mid-altitude moist deciduous forests and commercial plantations, that span the Western Ghats in the South Indian states of Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu. The marten's English common name is derived from the Nilgiri Hills that form the center of its range, but sightings have been reported as far north as Charmadi Ghat and as far south as the Neyyar and Peppara Wildlife Sanctuaries.[4][5][6][7][8][9]

Ecology and behaviour

The Nilgiri marten is diurnal. It is mainly arboreal, but descends to the ground occasionally. It is omnivorous and preys on birds, small mammals and insects such as cicadas.[10][2] It has also been observed feeding on a variety of fruits and seeds.[11]
References
- Mudappa, D.; Jathana, D. & Raman, T. R. S. (2015). "Martes gwatkinsii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T12847A86161239.
- Prater, S. H. (2005) [1971]. The Book of Indian Animals (3rd ed.). Mumbai: Bombay Natural History Society, Oxford University Press.
- Hussain, S. A. (1999). "Mustelids, Viverrids and Herpestids of India: Species Profile and Conservation Status". ENVIS Bulletin: Wildlife and Protected Areas. Dehradun: Wildlife Institute of India. 2 (2): 1–38. ISSN 0972-088X.
- Christopher, G. & Jayson, E. A. (1996). "Sightings of Nilgiri marten (Martes gwatkinsii Horsfield) at Peppara Wildlife Sanctuary and Silent Valley National Park, Kerala, India" (PDF). Small Carnivore Conservation. 15: 3–4. ISSN 1019-5041. Archived from the original on 19 April 2020.
- Madhusudan, M. D. (1995). "Sighting of the Nilgiri marten (Martes gwatkinsii) at Eravikulam National Park, Kerala, India" (PDF). Small Carnivore Conservation. 13: 6–7. ISSN 1019-5041. Archived from the original on 19 April 2020.
- Gokula, V. & Ramachandran, N. K. (1996). "A record of the Nilgiri marten (Martes gwatkinsii Horsfield) in Upper Bhavani". Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society. 93 (1): 82. ISSN 0006-6982.
- Mudappa, D. (1999). "Lesser Known Carnivores of the Western Ghats". ENVIS Bulletin: Wildlife and Protected Areas. Dehradun: Wildlife Institute of India. 2 (2): 65–70. ISSN 0972-088X.
- Balakrishnan, P. (2005). "Recent sightings and habitat characteristics of the endemic Nilgiri Marten Martes gwatkinsii in Western Ghats, India" (PDF). Small Carnivore Conservation. 33: 14–16. ISSN 1019-5041. Archived from the original on 19 April 2020.
- Krishna, K. & Karnad, D. (2010). "New records of the Nilgiri marten Martes gwatkinsii in the Western Ghats, India" (PDF). Small Carnivore Conservation. 43: 23–27. ISSN 1019-5041. Archived from the original on 19 April 2020.
- Hutton, A. F. (1948). "Feeding habits of the Nilgiri marten [Charronia gwatkinsii (Horsfield)]". Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society. 48 (2): 355–356. ISSN 0006-6982.
- Anil, G.; Kishor, N.; Gafoor, N.; Ommer, N. & Nameer, P. O. (2018). "Observations on the Nilgiri Marten Martes gwatkinsii (Mammalia: Carnivora: Mustelidae) from Pampadum Shola National Park, the southern Western Ghats, India". Journal of Threatened Taxa. 10 (1): 11226–11230. doi:10.11609/jott.3446.10.1.11226-11230.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Martes gwatkinsii. |
