Long-nosed mongoose
The long-nosed mongoose (Herpestes naso) is a mongoose native to Central African wetlands and rainforests. It has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List since 1996.[1]
| Long-nosed mongoose | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Herpestidae |
| Genus: | Herpestes |
| Species: | |
| Binomial name | |
| Herpestes naso[4][3] de Winton, 1901 | |
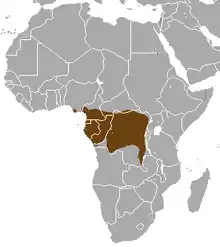 | |
| Long-nosed mongoose range | |
Distribution and habitat
The long-nosed mongoose is native to wetlands and rainforests from the Niger Delta in Nigeria, Cameroon to the Central African Republic, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Republic of the Congo and Democratic Republic of the Congo. It has been recorded from sea level up to an altitude of 640 m (2,100 ft).[1] It is one of the most water dependent species.[5]
Behaviour and ecology
The long-nose mongoose is usually solitary and lives in a home range of 41–46 ha (100–110 acres). It moves up to 4,600 m (15,100 ft) daily in this area foraging for food. It chooses different locations as night-time resting places.[6]
Threats
The long-nosed mongoose's habitat is fragmented because of logging, mining, and slash-and-burn agricultural practices.[1] In Gabon, it is hunted for sale in bushmeat markets.[7]
References
- Ray, J.; Bahaa-el-din, L.; Angelici, F. M. & Do Linh San, E. (2015). "Herpestes naso". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41615A45207915.
- de Winton, W. E. (1901). "Description of a New Mongoose from West Africa". Bulletin of the Liverpool Museums Under the City Council. 3 (2): 35–37.
- Wozencraft, W.C. (2005). "Species Herpestes naso". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 532–628. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- de Winton, W. E. (1901). "Description of a New Mongoose from West Africa". Bulletin of the Liverpool Museums Under the City Council. 3 (2): 35–37.
- Veron, G.; Patterson, B.; Reeves, R. (2008). "Global Diversity of Mammals (Mammalia) in Freshwater". In Balian, E. V.; Lévêque, C.; Segers, H.; Martens K. (eds.). Developments in Hydrobiology. Hydrobiologia. Volume 198. Freshwater Animal Diversity Assessment. Dordrecht: Springer. pp. 607–617. doi:10.1007/s10750-007-9122-1. S2CID 21156997.
- Ray, J. C. (1997). "Comparative ecology of two African forest mongooses, Herpestes naso and Atilax paludinosus". African Journal of Ecology. 35 (3): 237–253. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2028.1997.086-89086.x.
- Bahaa-el-din, L.; Henschel, P.; Aba’a, R.; Abernethy, K.; Bohm, T.; Bout, N.; Coad, L.; Head, J.; Inoue, E.; Lahm, S.; Lee, M. E.; Maisels, F.; Rabanal, L.; Starkey, M.; Taylor, G.; Vanthomme, A.; Nakashima, Y.; Hunter, L. (2013). "Notes on the distribution and status of small carnivores in Gabon". Small Carnivore Conservation (48): 19–29.
