Andean mountain cat
The Andean mountain cat (Leopardus jacobita) is a small wild cat native to the high Andes that has been listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List because fewer than 2,500 individuals are thought to exist in the wild.[1] It is traditionally considered a sacred animal by indigenous Aymara and Quechua people.[3]
| Andean mountain cat | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Felidae |
| Subfamily: | Felinae |
| Genus: | Leopardus |
| Species: | L. jacobita[2] |
| Binomial name | |
| Leopardus jacobita[2] (Cornalia, 1865) | |
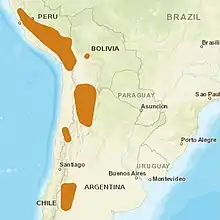 | |
| Distribution of the Andean cat, 2016[1] | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Oreailurus jacobita | |
It was first described by Emilio Cornalia who named it in honour of Jacobita Mantegazza.[4]
Characteristics
The Andean mountain cat has an ashy-gray fur, a gray head, ears and face. The areas around the lips and cheeks are white; two dark brown lines run from the corners of the eyes across the cheeks. There are some black spots on the forelegs, yellowish-brown blotches on the flanks, and up to two narrow, dark rings on the hind limbs. The long bushy tail has 6–9 rings, which are dark brown to black. The markings of juveniles are darker and smaller than those of adults. The skulls of adult specimens range in length from 100.4 to 114.8 mm (3.95 to 4.52 in) and are larger than those of the pampas cat and domestic cat.[5]
The Andean mountain cat has a black nose and lips, and rounded ears. On the back and on the tail, the hair is 40–45 mm (1.6–1.8 in) long. Its rounded footprints are 4 cm (1.6 in) long and 3.5 cm (1.4 in) wide. Its pads are covered with hair.[4]
Adult specimens range from 57.7 to 85 cm (22.7 to 33.5 in) in head-to-body length, with a 41.3 to 48.5 cm (16.3 to 19.1 in) long tail.[4][5] The shoulder height is about 36 cm (14 in) and body weight is up to 5.5 kilograms (12 lb).
The Andean mountain cat and pampas cat look similar. This makes it difficult to identify which cat is observed and makes correct estimations of populations problematic. This can be especially difficult when attempting to gain correct information from the observations of individuals that have seen one of these cats but are not aware to look for specific features to distinguish between the two.[6]
| Andean cat | Trait | Pampas Cat |
|---|---|---|
| 2⁄3 of the total body length. Thick and blunt with 6–9 wide rings. | Tail | 1⁄2 of the total body length. Thin and tapered with 9 thin rings. |
| Maximum width of rings: 60mm | Tail rings | Maximum width of rings: 20mm |
| Distinctive lines on sides of eyes. Rounded tips of ears. | Facial features | If lines are present, they are brown and less dramatic. Triangular-tipped ears are present for most of this species. |
| Very dark or black | Nose | Light colored, generally pink |
| Yellow– and rust-colored or gray and black | Overall color | Cream, red, rust, and black in color |
| One consistent coat pattern | Coat pattern | Three different coat patterns with different variations |
| Uniform coloration of the base color | Ear color | Patterned colored ears |
| Rings are not complete; stripes are spot-like in appearance | Front paws | Two or more well-defined, complete, black rings |
Distribution and habitat

The Andean mountain cat lives only at high elevations in the Andes.[7] Records in Argentina indicate that it lives at elevations from 1,800 m (5,900 ft) in the southern Andes to over 4,000 m (13,000 ft) in Chile, Bolivia and central Peru.[8][9][10][11] This terrain is arid, sparsely vegetated, rocky and steep. The population in the Salar de Surire Natural Monument was estimated at five individuals in an area of 250 km2 (97 sq mi).[9] Results of a survey in the Jujuy Province of northwestern Argentina indicates a density of seven to 12 individuals per 100 km2 (39 sq mi) at an elevation of about 4,200 m (13,800 ft).[12]
Its habitat in the Andes is fragmented by deep valleys, and its preferred prey, mountain viscachas (Lagidium) occur in patchy colonies.[1] Across this range, the level of genetic diversity is very low.[11]
It is also probable that mountain chinchillas were previously important prey of the Andean mountain cat before their populations were drastically reduced due to hunting for the fur trade.[10]
Ecology and behaviour
Six different species of carnivores live in the Andes Mountain range. Apart from the Andean cat, there are two other cat species: the pampas cat and the puma. The puma is a large predator, while the Andean and Pampas Cat are medium-sized predators. These two medium-sized predators are very much alike. They both hunt within the same territory. They hunt the same prey, the mountain viscacha (Lagidium viscacia), a rodent. The viscacha makes up 93.9% of the biomass consumed in the Andean cat's diet while the Pampas Cat depends on it for 74.8% of its biomass consumption.[9] Both of these cats depend on a specific prey to make up a large portion of their dietary needs. In some areas, the mountain viscacha will make up 53% of the Andean cat's prey items. This is because the other prey items are so significantly smaller that even though the Andean cat will successfully hunt, kill, and eat a mountain viscacha half the time, the mountain viscacha is so much larger than the other food items, it makes up more substance.[13] They also hunt frequently during the same periods. During one study, both the Andean cat and the Pampas Cat were seen most frequently during moonless nights; the second most sightings of these cats were during full moons.[14]
By using the residents' observations of Andean cats in coupled pairs with their litters, it is theorized that the mating season for the Andean cat is within the months of July and August. Because kittens have been seen in the months of April and October, this could mean that the mating season extends into November or even December. A litter will usually consist of one or two offspring born in the spring and summer months. This is common with many other species that also have their young when food resources are increasing.[15]
Threats
The following table lists the threat to the Andean cat and proposed interventions to mitigate them:[16]
| Priority | Direct threat | Indirect threat | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Habitat loss | Various forms of land use including mining, and water extraction, potentially increased by climate change. | Creation of protected areas and consolidation or improvement of existing ones; obeying with government and the industry sector; implementation of existing legislation; involvement of local communities on conservation and land use decisions; research on desertification processes affecting the Andean cat. |
| 2 | Habitat degradation | Inappropriate pastoralist and agricultural practices; unregulated tourism; mining, oil/gas extraction; unregulated use of water. | Working with communities to improve livestock management; lobbying with governments, industries and local communities to regulate tourist activities; implementation of existing legislation; implementation of water management plans when existing; research on the impacts of habitat degradation on Andean Cat population. |
| 3 | Hunting not for human use | Conflicting with small livestock breeding; lack of knowledge of the species by local community member; presence of dogs, incidental capture | Conflict mitigation, community education, implementation of existing legislation; research on the most effective methods to mitigate conflicts and improvement of perception of the species by local people. |
| 4 | Traditional hunting | Religious use of skins or taxidermy, hunting due to traditional beliefs | education; rekindling of traditional knowledge. |
| 5 | Reduction of prey populations | Hunting, presence of domestic dogs | Community education; implementation of existing legislation; research on predator-prey dynamics |
| 6 | Introduction of diseases | Dogs and cats as reservoirs and/or vectors | Research to determine the true extent of this threat |
| 7 | Hybridization | Sympatric with phylogenetically related species (L. colocolo) | Research to determine the true extent of this threat. |
Conservation
The Andean cat is listed on CITES Appendix I.[1] It is protected in all the countries of its range.[17]
The Andean Cat Alliance was formed in 2003 by representatives from Argentina, Bolivia, Peru and Chile with the aim of fostering research and conservation of the Andean cat.[16]
| Country | Law or policy | Protection offered | Year enacted | Number of protected areas | Sightings within protected areas | Unevaluated areas |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Argentina | National Law 22421 of Wildlife Conservation | Prohibits hunting and/or trade of the Andean cat | Unknown | 9 protected areas | Evidence found in 7 areas | 1 unevaluated, 1 partial |
| Statutory Decree 666/97 | ||||||
| Resolution No. 63/86 of the Secretary of Agriculture | ||||||
| Bolivia | Decree No. 22421 | General and undefined ban on hunting, capture, storage, and/or conditioning of wild animals and their by-products | 1990 | 8 protected areas | Evidence found in 6 areas | 2 areas unevaluated |
| Chile | Law No. 19473 | Ban on hunting all felids, with penalties of up to $6,000 fine and/or imprisonment up to 3 years | 1972 | 7 protected areas | Evidence found in 7 areas | All areas evaluated |
| Peru | Supreme Decree No. 013-99-AG | Ban on hunting, trading, and possession of living, dead, or body parts of the Andean cat | 1999 | 12 protected areas | Evidence found in 4 areas | 8 areas unevaluated |
References
- Villalba, L.; Lucherini, M.; Walker, S.; Lagos, N.; Cossios, D.; Bennett, M. & Huaranca, J. (2016). "Leopardus jacobita". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T15452A50657407. Retrieved 29 October 2018.
- Wozencraft, W.C. (2005). "Species Leopardus jacobitus". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 532–628. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- Macdonald, D.W.; Loveridge, A.J. & Nowell, K. (2010). "Dramatis personae: an introduction to the wild felids. Andean cat Leopardus jacobita (Cornalia, 1865)". In Macdonald, D.W. & Loveridge, A.J. (eds.). The Biology and Conservation of Wild Felids. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 35. ISBN 978-0-19-923444-8.
- Yensen, E.; Seymour, K. L. (2000). "Oreailurus jacobita" (PDF). Mammalian Species. 644 (644): 1–6. doi:10.1644/1545-1410(2000)644<0001:OJ>2.0.CO;2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 3 April 2015.
- Garcia-Perea, R. (2002). "Andean Mountain Cat, Oreailurus jacobita: Morphological Description and Comparison With Other Felines From The Altiplano". Journal of Mammalogy. 83 (1): 110–124. doi:10.1644/1545-1542(2002)083<0110:amcojm>2.0.co;2.
- Palacios, R. (2007). Manual para identificación de carnívoros andinos. Alianza Gato Andino, Córdoba, Argentina. 40 pp.
- Nowell, K. & Jackson, P. (1996). "Andean mountain cat, Oreailurus jacobitus (Cornalia, 1865)" (PDF). Wild Cats: status survey and conservation action plan. Gland, Switzerland: IUCN/SSC Cat Specialist Group. pp. 116–118.
- Sorli, L. E.; Martinez, F. D.; Lardelli, U. & Brandi, S. (2006). "Andean cat in Mendoza, Argentina – Further south and at lowest elevation ever recorded". Cat News (44): 24.
- Napolitano, C.; Bennett, M.; Johnson, W. E.; O'Brien, S. J.; Marquet, P. A.; Barría, I.; Poulin, E. & Iriarte, A. (2008). "Ecological and biogeographical inferences on two sympatric and enigmatic Andean cat species using genetic identification of faecal samples". Molecular Ecology. 17 (2): 678–690. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2007.03606.x. PMID 18205675. S2CID 8517958.
- Villalba, M. L.; Bernal, N.; Nowell, K. & MacDonald, D. W. (2008). "Distribution of two Andean small cats (Leopardus jacobita and pampas cat Leopardus colocolo) in Bolivia and the potential impacts of traditional beliefs on their conservation" (PDF). Endangered Species Research. 16 (1): 85–94. doi:10.3354/esr00389.
- Cossíos, D. E.; Madrid, A.; Condori, J. L. & Fajardo, U. (2007). "Update on the distribution of the Andean cat Oreailurus jacobita and the pampas cat Lynchailurus colocolo in Peru". Endangered Species Research. 3 (3): 313–320. doi:10.3354/esr00059.
- Reppucci, J.; Gardner, B. & Lucherini, M. (2011). "Estimating detection and density of the Andean cat in the high Andes". Journal of Mammalogy. 92 (1): 140–147. doi:10.1644/10-MAMM-A-053.1.
- Walker, R. S.; Novaro, A. J.; Perovic, P.; Palacios, R.; Donadio, E.; Lucherini, M.; Pia, M. & López, M. S. (2007). "Diets of three species of Andean Carnivores in High Altitude Deserts of Argentina". Journal of Mammalogy. 88 (2): 519–525. doi:10.1644/06-mamm-a-172r.1.
- Lucherini, M. (2009). "Activity Pattern Segregation of Carnivores in the High Andes". Journal of Mammalogy. 90 (6): 1404–1409. doi:10.1644/09-mamm-a-002r.1. S2CID 76656004.
- Cossíos D.; Beltrán Saavedra, F.; Bennet, M.; Bernal, N.; Fajardo, U.; Lucherini, M.; Merino, M. J.; Marino, J.; Napolitano, C.; Palacios, R.; Perovic, P.; Ramirez, Y.; Villalba, L.; Walker, S. & Sillero-Zubiri, C. (2007). Manual de metodologías para relevamientos de carnívoros alto andinos. Buenos Aires, Argentina: Alianza Gato Andino.
- Palacios, R.; Villalba, L., eds. (2011). Plan Estratégico para la Conservación del Gato Andino, 2011–2016 (PDF). La Paz, Bolivia: Alianza Gato Andino.
- Villalba, L.; Lucherini, M.; Walker, S.; Cossios, D.; Iriarte, A.; Sanderson, J.; Gallardo, G.; Alfaro, F.; Napolitano, C.; Sillero-Zubiri, C. (2004). The Andean Cat Conservation Action Plan (PDF). La Paz, Bolivia: Andean Cat Alliance.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
| Wikispecies has information related to Leopardus jacobita. |
- "Cat in Thin Air".
- "Alianza Gato Andino". Andean Cat Alliance.
- "Andean cat". IUCN/SSC Cat Specialist Group.
