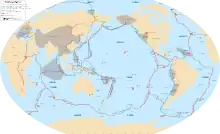
Outline of plate tectonics
This is a list of articles related to plate بيغسل ززرنعtectonics and tectonic plates.
What is plate tectonics?
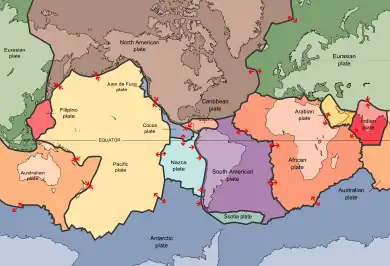
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin: tectonicus, from the Ancient Greek: τεκτονικός, lit. 'pertaining to building') is a scientific theory describing the large-scale motion of seven large plates and the movements of a larger number of smaller plates of Earth's lithosphere, since tectonic processes began on Earth between 3.3 and 3.5 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of continental drift, an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted plate-tectonic theory after seafloor spreading was validated in the late 1950s and early 1960s.
The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (the crust and upper mantle), is broken into tectonic plates. The Earth's lithosphere is composed of seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where the plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary: convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries (or faults). The relative movement of the plates typically ranges from zero to 100 mm annually.
Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction, or one plate moving under another, carries the edge of the lower one down into the mantle; the area of material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total geoid surface area of the lithosphere remains constant. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories, since disproven, proposed gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.
Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater mechanical strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection; that is, the slow creeping motion of Earth's solid mantle. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from spreading ridges due to variations in topography (the ridge is a topographic high) and density changes in the crust (density increases as newly formed crust cools and moves away from the ridge). At subduction zones the relatively cold, dense oceanic crust is "pulled" or sinks down into the mantle over the downward convecting limb of a mantle cell. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate. (Full article...)
General concepts
- Asthenosphere – The highly viscous, mechanically weak and ductile region of Earth's mantle
- Aulacogen – A failed arm of a triple junction, an inactive rift zone
- Back-arc basin – Submarine features associated with island arcs and subduction zones
- Bimodal volcanism – The eruption of both mafic and felsic lavas from a single volcanic centre
- Continent – Very large landmass identified by convention
- Crust – The outermost solid shell of a rocky planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite
- Epeirogenic movement – Upheavals or depressions of land exhibiting long wavelengths and little folding
- Fault (geology) – Fracture or discontinuity in rock across which there has been displacement
- Fault mechanics – A field of study that investigates the behavior of geologic faults
- Active fault – A geological fault likely to be the source of an earthquake sometime in the future
- Flux melting – The process by which the melting point is reduced by the admixture of a material known as a flux
- Geodynamics – Study of dynamics of the Earth
- Island arc – Arc-shaped archipelago formed by intense seismic activity of long chains of active volcanoes
- Mantle – Part of the interior of the planet Earth
- Mohorovičić discontinuity – Boundary between the Earth's crust and the mantle
- Mountain – A large landform that rises fairly steeply above the surrounding land over a limited area
- Mid-ocean ridge, also known as Oceanic ridge – Basaltic underwater mountain system formed by plate tectonic spreading
- Oceanic trench – Long and narrow depressions of the sea floor
- Paleoclimatology – Study of changes in ancient climate
- Paleomap – Map of continents and mountain ranges in the past based on plate reconstructions
- Seamount – A mountain rising from the ocean seafloor that does not reach to the water's surface
- Slab (geology) – The portion of a tectonic plate that is being subducted
- Slab gap hypothesis – Explanation for several instances of crustal extension that occur inland near former subduction zones
- Slab window – A gap that forms in a subducted oceanic plate when a mid-ocean ridge meets with a subduction zone and the ridge is subducted
- Supercontinent – Landmass comprising more than one continental core, or craton
- Terrane – Fragment of crustal material formed on, or broken off from, one tectonic plate and accreted or "sutured" to crust lying on another plate
- Volcano – Rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface
Tectonic plate interactions
Tectonic plate interactions – Definitions and examples of the interactions between the relatively mobile sections of the lithosphere
- Continental drift – The movement of the Earth's continents relative to each other
- Convergent boundary – Region of active deformation between colliding tectonic plates
- Divergent boundary – Linear feature that exists between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other
- Extensional tectonics – Study of the structures formed by, and the processes associated with, the stretching of a planetary body's crust
- Isostasy – State of gravitational equilibrium between Earth's crust and mantle
- Leaky transform fault – A transform fault with volcanic activity along a significant portion of its length producing new crust.
- Mantle convection – The slow moving motion of Earth's solid mantle caused by convection currents carrying heat from the planet's interior to its surface
- Obduction – The overthrusting of oceanic lithosphere onto continental lithosphere at a convergent plate boundary
- Orogeny – The formation of mountain ranges
- Passive margin – The transition between oceanic and continental lithosphere that is not an active plate margin
- Plume tectonics – Geophysical theory of movement of mantle plumes under tectonic plates
- Ridge push – A proposed driving force for tectonic plate motion as the result of the lithosphere sliding down the raised asthenosphere below mid-ocean ridges
- Seafloor spreading – Process at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge
- Strike-slip tectonics – Structure and processes associated with zones of lateral displacement in the Earth's crust
- Subduction – A geological process at convergent tectonic plate boundaries where one plate moves under the other
- Tectonic uplift – The portion of the total geologic uplift of the mean earth surface that is not attributable to an isostatic response to unloading
- Thrust tectonics – Study of the structures formed by, and the tectonic processes associated with, the shortening and thickening of the crust
- Transform fault, also known as Transform boundary – Plate boundary where the motion is predominantly horizontal
- Triple junction – The point where the boundaries of three tectonic plates meet
Back arc basins
Back-arc basin – Submarine features associated with island arcs and subduction zones
Continents
Continent – Very large landmass identified by convention
- Africa – Continent
- Antarctica – Continent
- Asia – Continent
- Australia (continent) – Continental landmass on the Australian Plate
- Europe – Continent
- North America – Continent
- South America – Continent mostly in the Southern Hemisphere of Planet Earth
Supercontinent – Landmass comprising more than one continental core, or craton
- Eurasia – The combined continental landmass of Europe and Asia
Paleocontinents
Paleocontinent – A distinct area of continental crust that existed as a major landmass in the geological past
- Asiamerica – Large island formed from Laurasia, separated by shallow continental seas from Eurasia to the West and eastern North America to the East
- Amazonian Craton – A geologic province in South America
- Appalachia (Mesozoic)
- Arctica – An ancient continent in the Neoarchean era
- Armorican terrane – A microcontinent or group of continental fragments rifted away from Gondwana
- Asiamerica – Large island formed from Laurasia, separated by shallow continental seas from Eurasia to the West and eastern North America to the East
- Atlantica – An ancient continent formed during the Proterozoic about 2 billion years ago
- Australia (continent) – Continental landmass on the Australian Plate (Also known as Sahul)
- Avalonia – Microcontinent in the Paleozoic era named for the Avalon Peninsula in Newfoundland
- Baltica – Late-Proterozoic to early-Palaeozoic continent
- Cathaysia – A microcontinent or group of terranes that rifted off Gondwana during the Late Paleozoic
- Chilenia – Ancient microcontinent, containing central Chile and western Argentina
- Chiloé Block – An ancient microcontinent or terrane that collided with the South American Plate during the Proterozoic
- Cimmeria (continent) – An ancient string of microcontinents that rifted from Gondwana
- Congo Craton – Precambrian craton that with four others makes up the modern continent of Africa
- Chilenia – Ancient microcontinent, containing central Chile and western Argentina
- Cuyania – An ancient microcontinent now part of Argentina
- Laramidia – An island continent that existed during the Late Cretaceous period
- Iberian Plate – Small tectonic plate now part of the Eurasian plate
- Insular India – The isolated land mass which became the Indian subcontinent
- Kalahari Craton – old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, that occupies large portions of South Africa, Botswana, Namibia and Zimbabwe
- Kazakhstania – A geological region in Central Asia which consists of the area roughly centered on Lake Balkhash, north and east of the Aral Sea, south of the Siberian craton and west of the Altai Mountains
- Kerguelen Plateau – Oceanic plateau in the southern Indian Ocean
- Laramidia – An island continent that existed during the Late Cretaceous period
- Laurentia – A large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of the North American continent
- Mauritia (microcontinent) – A Precambrian microcontinent that broke away as India and Madagascar separated
- North China Craton – continental crustal block in northeast China, Inner Mongolia, the Yellow Sea, and North Korea
- Pampia – An ancient microcontinent or terrane that collided with Río de la Plata Craton and Río Apas Craton during the late Proterozoic and early Cambrian
- Río de la Plata Craton – A medium-sized continental block in Uruguay, eastern Argentina and southern Brazil
- São Francisco Craton – An ancient craton in the eastern part of South America with outcrops in Minas Gerais and Bahia, Brazil
- Siberia (continent) – An ancient craton forming the Central Siberian Plateau
- South China (continent)
- Sunda (continent)
- Supercontinent – Landmass comprising more than one continental core, or craton
- Columbia (supercontinent) – Ancient supercontinent of approximately 2,500 to 1,500 million years ago
- Euramerica
- Gondwana – Neoproterozoic to Carboniferous supercontinent
- Kenorland – Hypothetical Neoarchaean supercontinent from about 2.8 billion years ago
- Laurasia – Northern supercontinent that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent
- Nena (supercontinent) – Early Proterozoic supercontinent
- Pangaea – Supercontinent from the late Paleozoic to early Mesozoic eras
- Pannotia – Hypothesized Neoproterozoic supercontinent from the end of the Precambrian
- Rodinia – Hypothetical neoproterozoic supercontinent from between about a billion to about three quarters of a billion years ago
- Ur (continent) – Proposed archaean supercontinent from about 3.1 billion years ago
- Vaalbara – Archaean supercontinent from about 3.6 to 2.7 billion years ago
Earthquakes
Earthquake – Shaking of the surface of the earth caused by a sudden release of energy in the crust
- Blind thrust earthquake – Movement along a thrust fault that is not visible at the surface
- Intraplate earthquake – Earthquake that occurs within the interior of a tectonic plate
- Interplate earthquake – Earthquake that occurs at the boundary between two tectonic plates
- Megathrust earthquake – Type of earthquake that occurs at subduction zones at destructive convergent plate boundaries
Oceans
Ocean – A body of water that composes much of a planet's hydrosphere
Ancient oceans
List of ancient oceans – A list of former oceans that disappeared due to tectonic movements and other geographical and climatic changes
- Adamastor Ocean – A Precambrian "proto-Atlantic" ocean in the Southern Hemisphere
- Boreal Sea – A Mesozoic-era seaway that lay along the northern border of Laurasia
- Bridge River Ocean – An ancient ocean between North America and the Insular Islands during the Paleozoic
- Iapetus Ocean – ocean that existed in the late Neoproterozoic and early Paleozoic eras
- Central American Seaway – A body of water that once separated North America from South America
- Goianides Ocean – An ocean in South America in Neoproterozoic
- Goiás Ocean
- Hudson Seaway – A major seaway of North America during the Cretaceous Period
- Iapetus Ocean – ocean that existed in the late Neoproterozoic and early Paleozoic eras
- Khanty Ocean – A small Precambrian ocean between Baltica and the Siberian continent
- Lapland-Kola Ocean
- Mirovia – A hypothesized superocean surrounding the supercontinent Rodinia in the Neoproterozoic Era
- Paleo-Tethys Ocean – An ocean on the margin of Gondwana between the Middle Cambrian and Late Triassic
- Pan-African Ocean – A hypothesized paleo-ocean whose closure created the supercontinent of Pannotia
- Pannonian Sea – Shallow ancient sea where the Pannonian Basin in Central Europe is today
- Panthalassa – Prehistoric superocean that surrounded Pangaea
- Paratethys – A large shallow sea that stretched from the region north of the Alps over Central Europe to the Aral Sea in Central Asia
- Pharusian Ocean – An ancient ocean that existed from 800 to 635 million years ago
- Piemont-Liguria Ocean – A former piece of oceanic crust that is seen as part of the Tethys Ocean
- Poseidon Ocean – Supposed ocean that existed in the Mesoproterozoic period
- Pre-Svecofennian Ocean
- Proto-Tethys Ocean – An ancient ocean that existed from the latest Ediacaran to the Carboniferous
- Rheic Ocean – ancient ocean which separated two major palaeocontinents, Gondwana and Laurussia
- Slide Mountain Ocean – An ancient ocean that existed between the Intermontane Islands and North America
- Sundance Sea – An inland sea that existed in North America during the mid-to-late Jurassic Period of the Mesozoic Era
- Tethys Ocean – Mesozoic ocean between Gondwana and Laurasia
- Tornquist Sea – A sea between the palaeocontinents Avalonia and Baltica about 600 to 450 million years ago
- Turgai Sea – A large shallow body of salt water of the Mesozoic and Cenozoic Eras
- Ural Ocean – A small, ancient ocean between Siberia and Baltica
- Valais Ocean – Subducted ocean basin. Remnants found in the Alps in the North Penninic nappes.
- Western Interior Seaway – Large prehistoric inland sea that split the continent of North America
Superoceans
Superocean – An ocean that surrounds a supercontinent
- Mirovia – A hypothesized superocean surrounding the supercontinent Rodinia in the Neoproterozoic Era
- Pan-African Ocean – A hypothesized paleo-ocean whose closure created the supercontinent of Pannotia
- Panthalassa – Prehistoric superocean that surrounded Pangaea
Orogenies
Orogeny – The formation of mountain ranges
- List of orogenies – Known mountain building events of the Earth's history
- Mountain formation – The geological processes that underlie the formation of mountains
- Fold mountains – Mountains formed by compressive crumpling of the layers of rock
- Algoman orogeny – Late Archaean episode of mountain building in what is now North America
Rifts
Rift – A linear zone where the Earth's crust is being pulled apart, and is an example of extensional tectonics
- Mid-ocean ridge – Basaltic underwater mountain system formed by plate tectonic spreading
- Saint Lawrence rift system – A seismically active zone paralleling the Saint Lawrence River
Active rifts
- Propagating rift – A seafloor feature associated with spreading centers at mid-ocean ridges and back-arc basins
Continental rifts
- East African Rift – An active continental rift zone in East Africa
- Laptev Sea Rift – A divergent tectonic plate boundary between the North American Plate and the Eurasian Plate
- Afar Triangle – A geological depression caused by the Afar Triple Junction
Oceanic ridges
- Aden Ridge – Part of an active oblique rift system in the Gulf of Aden, between Somalia and the Arabian Peninsula
- Cocos Ridge
- Explorer Ridge – mid-ocean ridge west of British Columbia, Canada
- Gorda Ridge – tectonic spreading center off the northern coast of California and southern Oregon
- Juan de Fuca Ridge – A divergent plate boundary off the coast of the Pacific Northwest region of North America.
- South American–Antarctic Ridge – Mid-ocean ridge in the South Atlantic between the South American Plate and the Antarctic Plate
- Chile Rise – An oceanic ridge at the tectonic divergent plate boundary between the Nazca and Antarctic plates
- East Pacific Rise – A mid-oceanic ridge at a divergent tectonic plate boundary on the floor of the Pacific Ocean
- East Scotia Ridge
- Gakkel Ridge – A mid-oceanic ridge under the Arctic Ocean between the North American Plate and the Eurasian Plate(Mid-Arctic Ridge)
- Nazca Ridge – A submarine ridge on the Nazca Plate off the west coast of South America
- Pacific-Antarctic Ridge – Tectonic plate boundary in the South Pacific Ocean
- Central Indian Ridge – A north-south-trending mid-ocean ridge in the western Indian Ocean
- Carlsberg Ridge – The northern section of the Central Indian Ridge between the African Plate and the Indo-Australian Plate
- Southeast Indian Ridge – A mid-ocean ridge in the southern Indian Ocean
- Southwest Indian Ridge – A mid-ocean ridge on the bed of the south-west Indian Ocean and south-east Atlantic Ocean
- Mid-Atlantic Ridge – A divergent tectonic plate boundary that in the North Atlantic separates the Eurasian and North American plates, and in the South Atlantic separates the African and South American plates
- Kolbeinsey Ridge (North of Iceland)
- Mohns Ridge
- Knipovich Ridge (between Greenland and Spitsbergen)
- Reykjanes Ridge (South of Iceland)
Aulacogens
Aulacogen – A failed arm of a triple junction, an inactive rift zone
- Adelaide Rift Complex
- Alpha Ridge – A major volcanic ridge under the Arctic Ocean
- Aegir Ridge – An extinct mid-ocean ridge in the far-northern Atlantic Ocean
- Anza trough – A rift in Kenya that was formed in the Jurassic Period
- Bahr el Arab rift – A major geological feature in the southwest Sudan
- Benue Trough – A major geological structure underlying a large part of Nigeria and extending from the Bight of Benin to Lake Chad
- Central Lowlands – A geologically defined area of relatively low-lying land in southern Scotland
- Eastern North America Rift Basins – A series of sediment-filled aborted rifts created by large-scale continental extension
- Fundy Basin – A sediment-filled rift basin on the Atlantic coast of southeastern Canada
- Gulf of Suez Rift – A continental rift zone that was active between the Late Oligocene and the end of the Miocene
- Gulf St Vincent – A large inlet of water on the southern coast of South Australia between the Yorke Peninsula and the Fleurieu Peninsula
- Kula-Farallon Ridge – An ancient mid-ocean ridge that existed between the Kula and Farallon plates in the Pacific Ocean during the Jurassic period
- Melut Basin – A rift basin in South Sudan
- Midcontinent Rift System – Geological rift in the center of the North American continent
- Mississippi embayment – Low-lying basin filled with Cretaceous to recent sediments
- Muglad Basin – A large rift basin in southern Sudan and South Sudan
- Narmada River – A river of central India in a rift valley
- New Madrid Seismic Zone – Major seismic zone in the southern and midwestern United States
- Newark Basin – A sediment-filled rift basin in northern New Jersey, south-eastern Pennsylvania and southern New York
- Nipigon Embayment – An inactive continental rift zone in Northwestern Ontario, Canada
- Oslo Graben – An inactive Permian geological rift in Norway
- Ottawa-Bonnechere Graben – A rift valley extending from near Montréal through Ottawa in Canada
- Pacific-Farallon Ridge – A spreading ridge during the late Cretaceous that separated the Pacific Plate to the west and the Farallon Plate to the east
- Pacific-Kula Ridge – A mid-ocean ridge between the Pacific and Kula plates in the Pacific Ocean during the Paleogene period
- Phoenix Ridge
- Saguenay Graben – A rift valley in the geological Grenville Province of southern Quebec, Canada.
- Southern Oklahoma Aulacogen – A failed rift in the western and southern US of the triple junction that became the Iapetus Ocean
- Spencer Gulf – A large inlet in South Australia between the Eyre Peninsula and the Yorke Peninsula
- Timiskaming Graben – A northwesterly extension of the Ottawa-Bonnechere Graben
- Wichita Mountains – Mountains in the US state Oklahoma
Subduction zones
Subduction zone – A geological process at convergent tectonic plate boundaries where one plate moves under the other
- Middle America Trench – A subduction zone in the eastern Pacific off the southwestern coast of Middle America
Suture zones
Suture (geology) – Joining together of separate terranes along a major fault zone
- Great Falls Tectonic Zone – A major intracontinental shear zone between the Hearne craton and Wyoming craton
- Huincul Fault – An east-west oriented continental-scale fault that extends from the Neuquén Basin eastwards into the Argentine Shelf
- Iapetus Suture – One of several major geological faults caused by the collision of several ancient land masses forming a suture
- Indus-Yarlung suture zone – A tectonic suture in southern Tibet and across the north margin of the Himalayas where the Indian and Eurasian plates meet
- Jormua Ophiolite – A remnant of ancient oceanic lithosphere near Jormua, Finland
- Magallanes-Fagnano Fault – A continental transform fault between the Scotia Plate and the South American Plate
- Morais ophiolite complex – A metamorphic complex of oceanic and continental crust terranes in Portugal
- Periadriatic Seam – The border between the Adriatic and European plates
- Pieniny Klippen Belt – Zone in the Western Carpathians, with a very complex geological structure
- Trans-European Suture Zone – Boundary between the East European Craton and the orogens of South-Western Europe
- Vulcan structure – Convergent tectonic boundary between the Medicine Hat and Loverna Blocks in North America
Tectonic plates
Tectonic plate – Continuous section of the lithosphere of the Earth which is moving relative to adjacent plates
- List of tectonic plates – A list of the relatively moving sections of the lithosphere of Earth
- African Plate – A major tectonic plate underlying Africa west of the East African Rift
- Anatolian Plate – A continental tectonic plate comprising most of the Anatolia (Asia Minor) peninsula
- Antarctic Plate – A tectonic plate containing the continent of Antarctica and extending outward under the surrounding oceans
- Arabian Plate – A minor tectonic plate consisting mostly of the Arabian Peninsula, extending northward to Mesopotamia and the Levant
- Burma Plate – A minor tectonic plate in Southeast Asia
- Cocos Plate – young oceanic tectonic plate beneath the Pacific Ocean off the west coast of Central America
- Eurasian Plate – A tectonic plate which includes most of the continent of Eurasia
- Explorer Plate – oceanic tectonic plate beneath the Pacific Ocean off the west coast of Vancouver Island, Canada
- Farallon Plate – An ancient oceanic plate that has mostly subducted under the west coast of the North American Plate
- Gorda Plate – One of the northern remnants of the Farallon Plate
- Indian Plate – A minor tectonic plate that got separated from Gondwana
- Juan de Fuca Plate – A small tectonic plate in the eastern North Pacific
- Halmahera Plate – A small tectonic plate in the Molucca Sea
- Indo-Australian Plate – A major tectonic plate formed by the fusion of the Indian and Australian plates
- Pacific Plate – An oceanic tectonic plate under the Pacific Ocean
- Molucca Sea Plate – small fully subducted tectonic plate near Indonesia
- Nazca Plate – Oceanic tectonic plate in the eastern Pacific Ocean basin
- North American Plate – Large tectonic plate including most of North America, Greenland and part of Siberia.
- Philippine Sea Plate – oceanic tectonic plate to the east of the Philippines
- South American Plate – Major tectonic plate which includes most of South America and a large part of the south Atlantic
- Sunda Plate – A minor tectonic plate including most of Southeast Asia
Terranes
Terrane – Fragment of crustal material formed on, or broken off from, one tectonic plate and accreted or "sutured" to crust lying on another plate
- Arctic Alaska-Chukotka terrane – A terrane that includes parts of Alaska, Siberia and the continental shelf between them
- Arequipa-Antofalla – A basement unit underlying the central Andes in northwestern Argentina, western Bolivia, northern Chile and southern Peru
- Armorican Massif – A geologic massif that covers a large area in the northwest of France
- Armorican terrane – A microcontinent or group of continental fragments rifted away from Gondwana
- Avalonia – Microcontinent in the Paleozoic era named for the Avalon Peninsula in Newfoundland
- Briançonnais zone – A piece of continental crust in the Penninic nappes of the Alps
- Bronson Hill Arc – A bimodal volcanic arc and associated Ordovician sediments
- Buffalo Head Terrane – A terrane in the western Canadian Shield in northern Alberta
- Cache Creek Terrane – A geologic terrane in British Columbia and southern Yukon, Canada
- Carolina terrane – exotic terrane from central Georgia to central Virginia in the United States
- Cassiar Terrane – Cretaceous terrane located in the Northern Interior of British Columbia and southern Yukon
- Chilenia – Ancient microcontinent, containing central Chile and western Argentina
- Chiloé Block – An ancient microcontinent or terrane that collided with the South American Plate during the Proterozoic
- Cuyania – An ancient microcontinent now part of Argentina
- Cymru Terrane – An inferred fault bounded terrane of the basement rocks of the southern United Kingdom
- Florida Platform – A flat geological feature with the emergent portion forming the Florida peninsula
- Franciscan Assemblage
- Ganderia – A terrane in the northern Appalachians which broke off the supercontinent Gondwana
- Gascoyne Complex – A terrane of Proterozoic granite and metamorphic rock in Western Australia
- Great Lakes tectonic zone
- Great Valley Sequence – group of late Mesozoic formations in the Cental Valley of California
- Hebridean Terrane – Part of the Caledonian orogenic belt in northwest Scotland
- Hottah terrane – A Paleoproterozoic terrane in the northwestern end of the Canadian Shield
- Irumide Belt – a Mesoproterozoic terrane on the southern margin of the Bangweulu Block in Zambia
- Ivrea zone – A tectonic terrane in the Italian Alps
- Lhasa terrane – A fragment of crustal material, sutured to the Eurasian Plate during the Cretaceous that forms present-day southern Tibet
- Madre de Dios Terrane – A distinct fragment of Earth's crust in southwestern Patagonia
- Meguma terrane – A terrane exposed in southern Nova Scotia
- Narooma Terrane – A geological structural region on the south coast of New South Wales, Australia
- Narryer Gneiss Terrane – A geological complex of ancient rocks in Western Australia
- Omineca Arc – A volcanic arc terrane in western North America
- Pampia – An ancient microcontinent or terrane that collided with Río de la Plata Craton and Río Apas Craton during the late Proterozoic and early Cambrian
- Pelso Plate – A small tectonic unit in the Pannonian Basin in Europe
- Salinian Block – A terrane west of the main trace of the San Andreas Fault system in California
- Shan–Thai Terrane – A mass of continental crust extending from Tibet into Southeast Asia
- Slide Mountain Terrane – A late Paleozoic terrane in British Columbia, Canada
- Smartville Block – A volcanic arc accreted onto the North American Plate
- Sonoma Volcanics – A geologic formation of volcanic origin in California
- Sonomia Terrane – A crustal block accreted onto the North American Plate in Northwest Nevada
- Spavinaw terrane – Intrusive and volcanic rocks in the mid-continent region of the United States
- Stikinia – A terrane in British Columbia, Canada
- Tuareg Shield – geological formation between the West African craton and the Saharan Metacraton in West Africa
- Western Gneiss Region – A large geological unit in Norway, part of the Baltic shield
- Wrangellia Terrane – Geological area in northwestern North America
- Wrekin Terrane – An inferred basement rock terrane of the southern United Kingdom
- Yakutat Block – Terrane in the process of accreting to the North American continent along the south central coast of Alaska
- Yukon–Tanana Terrane – largest tectonostratigraphic terrane in the northern North American Cordillera
Triple junctions
Triple junction – The point where the boundaries of three tectonic plates meet
- Aden-Owen-Carlsberg Triple Junction – The junction of three tectonic plate boundaries in the northwest Indian Ocean
- Afar Triple Junction – Place where three tectonic rifts meet in East Africa
- Azores Triple Junction – Place where the boundaries of the North American, the Eurasian and the African tectonic plates intersect
- Banda Sea Triple Junction – Point where the boundaries of the Indo-Australian Plate, the Pacific Plate and the Eurasian Plate meet
- Boso Triple Junction – The meeting point of the Okhotsk Plate, the Pacific Plate, and the Philippine Sea Plate
- Bouvet Triple Junction – Meeting point of the boundaries of the South American Plate, the African Plate, and the Antarctic Plate
- Chile Triple Junction – The place where the South American, Nazca and Antarctic tectonic plates meet
- Fifteen-Twenty Fracture Zone – A fracture zone on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge at the migrating triple junction between the North American, South American, and Nubian plates
- Mount Fuji – Volcano in Yamanashi and Shizuoka Prefectures, Japan
- Galapagos Triple Junction – Place where the boundaries of the Cocos Plate, the Nazca Plate, and the Pacific Plate meet
- Iapetus Suture – One of several major geological faults caused by the collision of several ancient land masses forming a suture
- Kamchatka-Aleutian Triple Junction – Place where the Pacific Plate, the Okhotsk Plate, and the North American Plate meet
- Karlıova Triple Junction – Place where the Anatolian Plate, the Eurasian Plate and the Arabian Plate meet
- Macquarie Triple Junction – Place where the Indo-Australian Plate, Pacific Plate, and Antarctic Plate meet
- Mendocino Triple Junction – The point where the Gorda plate, the North American plate, and the Pacific plate meet
- Queen Charlotte Triple Junction – Point where the Pacific Plate, the North American Plate, and the Explorer Plate meet
- Rivera Triple Junction – Place where the North American Plate, the Rivera Plate, and the Pacific Plate meet
- Rodrigues Triple Junction – Place where the African Plate, the Indo-Australian Plate, and the Antarctic Plate meet
- Tongareva triple junction – Defunct triple junction of the Pacific Plate, the Farallon Plate, and the Phoenix Plate
Other plate tectonics topics
- Computational Infrastructure for Geodynamics – Organization that advances Earth science
- Paleoclimatology – Study of changes in ancient climate
- Paleomap – Map of continents and mountain ranges in the past based on plate reconstructions
- Plate reconstruction – The process of reconstructing the positions of tectonic plates in the geological past
- Timeline of the development of tectonophysics (after 1952) – Chronological listing of significant events in the history of tectonophysics
- Timeline of the development of tectonophysics (before 1954) – Chronological listing of significant events in the history of tectonophysics
- Vine–Matthews–Morley hypothesis – The first key scientific test of the seafloor spreading theory of continental drift and plate tectonics.
- Eclogitization – The tectonic process in which the dense, high-pressure, metamorphic rock, eclogite, is formed
Specific areas
(to be reallocated)
- Alpine Fault – A right-lateral strike-slip fault, that runs almost the entire length of New Zealand's South Island.
- Benham Rise, also known as Benham Plateau
- Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain – A mostly undersea mountain range in the Pacific Ocean that reaches above sea level in Hawaii.
- Geology of the Alps – The formation and structure of the European Alps
- Indian subcontinent – Peninsular region in south-central Asia south of the Himalayas
- Mariana Trench – The deepest part of Earth's oceans, where the Pacific Plate is subducted under the Mariana Plate
- Mid-Atlantic Ridge – A divergent tectonic plate boundary that in the North Atlantic separates the Eurasian and North American plates, and in the South Atlantic separates the African and South American plates
- Mohorovičić discontinuity – Boundary between the Earth's crust and the mantle
- Molucca Sea Collision Zone – region of complex tectonic activity in Indonesia
- Pacific-Antarctic Ridge – Tectonic plate boundary in the South Pacific Ocean
- Philippine Mobile Belt – Complex portion of the tectonic boundary between the Eurasian Plate and the Philippine Sea Plate, comprising most of the country of the Philippines
- Ring of Fire – Area of high earthquake and volcanic activity, also the circum-Pacific belt
- San Andreas Fault – A continental transform fault through California between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate
- Tethys Ocean, also known as Tethys Sea – Mesozoic ocean between Gondwana and Laurasia