Mount Fuji
Mount Fuji (富士山, Fujisan, IPA: [ɸɯꜜ(d)ʑisaɴ] (![]() listen)), located on the island of Honshū, is the highest mountain in Japan, standing 3,776.24 m (12,389.2 ft). It is the second-highest volcano located on an island in Asia (after Mount Kerinci on the island of Sumatra), and seventh-highest peak of an island on Earth.[1] Mount Fuji is an active stratovolcano that last erupted from 1707 to 1708.[4][5] The mountain stands about 100 km (62 mi) southwest of Tokyo and is visible from there on clear days. Mount Fuji's exceptionally symmetrical cone, which is snow-capped for about five months of the year, is commonly used as a cultural icon of Japan and it is frequently depicted in art and photography, as well as visited by sightseers and climbers.[6]
listen)), located on the island of Honshū, is the highest mountain in Japan, standing 3,776.24 m (12,389.2 ft). It is the second-highest volcano located on an island in Asia (after Mount Kerinci on the island of Sumatra), and seventh-highest peak of an island on Earth.[1] Mount Fuji is an active stratovolcano that last erupted from 1707 to 1708.[4][5] The mountain stands about 100 km (62 mi) southwest of Tokyo and is visible from there on clear days. Mount Fuji's exceptionally symmetrical cone, which is snow-capped for about five months of the year, is commonly used as a cultural icon of Japan and it is frequently depicted in art and photography, as well as visited by sightseers and climbers.[6]
| Mount Fuji | |
|---|---|
 Mount Fuji, Japan, seen from Oshino Hakkai | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 3,776.25 to 3,778.23 m (12,389.3 to 12,395.8 ft) |
| Prominence | 3,776 m (12,388 ft) [1] Ranked 35th |
| Isolation | 2,077 km (1,291 mi) |
| Listing | Highest peak in Japan Ultra-prominent peaks List of mountains in Japan 100 Famous Japanese Mountains |
| Coordinates | 35°21′29″N 138°43′52″E [2] |
| Naming | |
| Native name | 富士山 (Japanese) |
| Pronunciation | [ɸɯꜜ(d)ʑisaɴ] |
| Geography | |
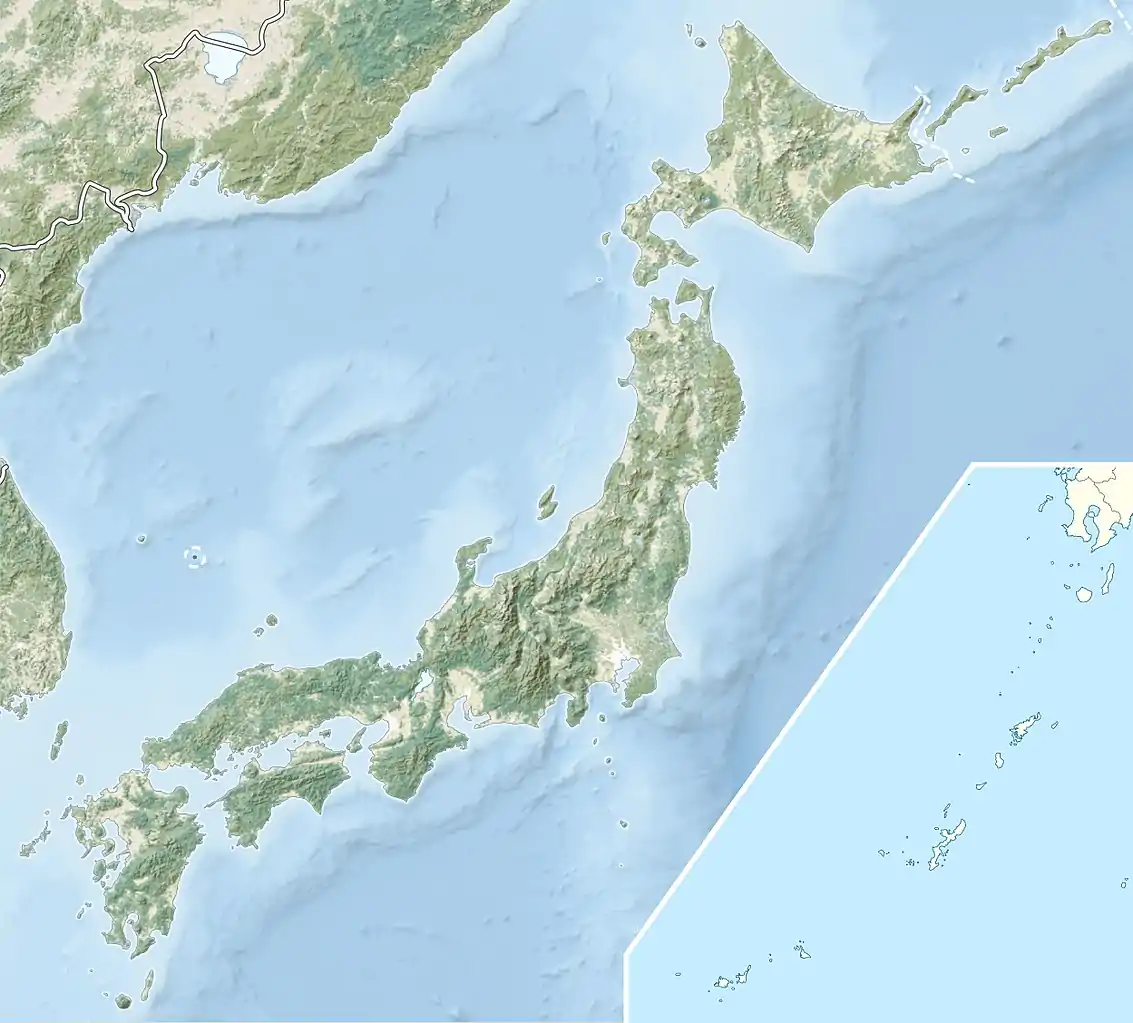 Mount Fuji Location of Mount Fuji in Japan  Mount Fuji Mount Fuji (Asia) | |
| Location | Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park |
| Country | Japan |
| Prefectures | Shizuoka and Yamanashi |
| Shikuchōson | Fuji, Fujinomiya, Fujiyoshida, Gotemba, Narusawa and Oyama |
| Topo map | Geospatial Information Authority 25000:1 富士山[3] 50000:1 富士山 |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | 100,000 years |
| Mountain type | Stratovolcano |
| Last eruption | 1707–08 |
| Climbing | |
| First ascent | 663 by En no Odzunu (役行者, En no gyoja, En no Odzuno) |
| Easiest route | Hiking |
| Official name | Fujisan, sacred place and source of artistic inspiration |
| Criteria | Cultural: iii, vi |
| Reference | 1418 |
| Inscription | 2013 (37th session) |
| Area | 20,702.1 ha |
| Buffer zone | 49,627.7 ha |
| Mount Fuji | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
"Mt. Fuji" in kanji | |||||
| Japanese name | |||||
| Kanji | 富士山 | ||||
| |||||
Mount Fuji is one of Japan's "Three Holy Mountains" (三霊山, Sanreizan) along with Mount Tate and Mount Haku. It is a Special Place of Scenic Beauty and one of Japan's Historic Sites.[7] It was added to the World Heritage List as a Cultural Site on June 22, 2013.[7] According to UNESCO, Mount Fuji has "inspired artists and poets and been the object of pilgrimage for centuries". UNESCO recognizes 25 sites of cultural interest within the Mount Fuji locality. These 25 locations include the mountain and the Shinto shrine, Fujisan Hongū Sengen Taisha, as well as the Buddhist Taisekiji Head Temple founded in 1290, later depicted by Japanese ukiyo-e artist Katsushika Hokusai.
Etymology
The current kanji for Mount Fuji, 富 and 士, mean "wealth" or "abundant" and "a man of status" respectively. However, the name predates kanji, and these characters are ateji, meaning that they were selected because their pronunciations match the syllables of the name but do not carry a meaning related to the mountain.
The origin of the name Fuji is unclear, having no recording of it being first called by this name. A text of the 9th century, Tale of the Bamboo Cutter, says that the name came from "immortal" (不死, fushi, fuji) and also from the image of abundant (富, fu) soldiers (士, shi, ji)[8] ascending the slopes of the mountain.[9] An early folk etymology claims that Fuji came from 不二 (not + two), meaning without equal or nonpareil. Another claims that it came from 不尽 (not + to exhaust), meaning never-ending.
Hirata Atsutane, a Japanese classical scholar in the Edo period, speculated that the name is from a word meaning, "a mountain standing up shapely as an ear (穂, ho) of a rice plant". British missionary John Batchelor (1854–1944) argued that the name is from the Ainu word for "fire" (fuchi) of the fire deity Kamui Fuchi, which was denied by a Japanese linguist Kyōsuke Kindaichi on the grounds of phonetic development (sound change). It is also pointed out that huchi means an "old woman" and ape is the word for "fire", ape huchi kamuy being the fire deity. Research on the distribution of place names that include fuji as a part also suggest the origin of the word fuji is in the Yamato language rather than Ainu. Japanese toponymist Kanji Kagami argued that the name has the same root as wisteria (藤, fuji) and rainbow (虹, niji, but with an alternative reading, fuji), and came from its "long well-shaped slope".[10][11][12][13]
Modern linguist Alexander Vovin proposes an alternative hypothesis based on Old Japanese reading */puⁿzi/: the word may have been borrowed from Eastern Old Japanese */pu nusi/ 火主 meaning 'fire master', see wikt:富士#Etymology 3.
Variations
In English, the mountain is known as Mount Fuji. Some sources refer to it as "Fuji-san", "Fujiyama" or, redundantly, "Mt. Fujiyama". Japanese speakers refer to the mountain as "Fuji-san". This "san" is not the honorific suffix used with people's names, such as Watanabe-san, but the Sino-Japanese reading of the character yama (山, "mountain") used in Sino-Japanese compounds. In Nihon-shiki and Kunrei-shiki romanization, the name is transliterated as Huzi.
Other Japanese names for Fuji Mount, which have become obsolete or poetic, include Fuji-no-Yama (ふじの山, "the Mountain of Fuji"), Fuji-no-Takane (ふじの高嶺, "the High Peak of Fuji"), Fuyō-hō (芙蓉峰, "the Lotus Peak"), and Fugaku (富岳/富嶽), created by combining the first character of 富士, Fuji, and 岳, mountain.[14]
History
%252C_also_known_as_Red_Fuji%252C_from_the_series_Thirty-six_Views_of_Mount_Fuji_(Fugaku_sanj%C5%ABrokkei)_MET_DP141062.jpg.webp)
Mount Fuji is an attractive volcanic cone and a frequent subject of Japanese art especially after 1600, when Edo (now Tokyo) became the capital and people saw the mountain while traveling on the Tōkaidō road. According to the historian H. Byron Earhart, "in medieval times it eventually came to be seen by Japanese as the “number one” mountain of the known world of the three countries of India, China, and Japan".[15] The mountain is mentioned in Japanese literature throughout the ages and is the subject of many poems.[16]
The summit has been thought of as sacred since ancient times and was forbidden to women until the Meiji era in the late 1860s. Ancient samurai used the base of the mountain as a remote training area, near the present-day town of Gotemba. The shōgun Minamoto no Yoritomo held yabusame in the area in the early Kamakura period.
The first ascent by a foreigner was by Sir Rutherford Alcock in September 1860, who ascended the mountain in 8 hours and descended in 3 hours.[17]:427 Alcock's brief narrative in The Capital of the Tycoon was the first widely disseminated description of the mountain in the West.[17]:421–27 Lady Fanny Parkes, the wife of British ambassador Sir Harry Parkes, was the first non-Japanese woman to ascend Mount Fuji in 1867.[18] Photographer Felix Beato climbed Mount Fuji two years later.[19]
On March 5, 1966, BOAC Flight 911, a Boeing 707, broke up in flight and crashed near the Mount Fuji Gotemba New fifth station, shortly after departure from Tokyo International Airport. All 113 passengers and 11 crew members died in the disaster, which was attributed to the extreme clear-air turbulence caused by lee waves downwind of the mountain. There is a memorial for the crash a short distance down from the Gotemba New fifth station.[20]
Today, Mount Fuji is an international destination for tourism and mountain climbing.[21][22] In the early 20th century, populist educator Frederick Starr's Chautauqua lectures about his several ascents of Mount Fuji—1913, 1919, and 1923—were widely known in America.[23] A well-known Japanese saying suggests that a wise person will climb Mt. Fuji once in their lifetime, but only a fool would climb it twice.[24][25] It remains a popular symbol in Japanese culture, including making numerous movie appearances,[26] inspiring the Infiniti logo,[27] and even appearing in medicine with the Mount Fuji sign.[28][29]
In September 2004, the manned weather station at the summit was closed after 72 years in operation. Observers monitored radar sweeps that detected typhoons and heavy rains. The station, which was the highest in Japan at 3,780 metres (12,402 ft), was replaced by a fully automated meteorological system.[30]
Mount Fuji was added to the World Heritage List as a Cultural Site on June 22, 2013.[7] However, the inscription became controversial after two professors at the Mt. Fuji World Heritage Centre, Shizuoka, were forced to quit their jobs because of academic and racial harassment by officials of Shizuoka prefecture government in March 2018.[31]
Geography
Mount Fuji is a very distinctive feature of the geography of Japan. It stands 3,776.24 m (12,389 ft) tall and is located near the Pacific coast of central Honshu, just southwest of Tokyo. It straddles the boundary of Shizuoka and Yamanashi Prefectures. Four small cities surround it: Gotemba to the east, Fujiyoshida to the north, Fujinomiya to the southwest, and Fuji to the south. It is surrounded by five lakes: Lake Kawaguchi, Lake Yamanaka, Lake Sai, Lake Motosu and Lake Shōji.[32] They, and nearby Lake Ashi, provide views of the mountain. The mountain is part of the Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park. It can be seen more distantly from Yokohama, Tokyo, and sometimes as far as Chiba, Saitama, Tochigi, Ibaraki and Lake Hamana when the sky is clear. It has been photographed from space during a space shuttle mission.[33]
 Fuji in early summer seen from the International Space Station (May 2001)
Fuji in early summer seen from the International Space Station (May 2001).jpg.webp) View from space from the ill-fated Space Shuttle Columbia mission (2003)
View from space from the ill-fated Space Shuttle Columbia mission (2003)_DSCF0017.jpg.webp) Fuji with persimmon-drying in autumn
Fuji with persimmon-drying in autumn
Climate
The summit of Mount Fuji has a tundra climate (Köppen climate classification ET). The temperature is very low at the high altitude, and the cone is covered by snow for several months of the year. The lowest recorded temperature is −38.0 °C (−36.4 °F) recorded in February 1981, and the highest temperature was 17.8 °C (64.0 °F) recorded in August 1942.
| Climate data for Mount Fuji Averages (1981–2010) Records (1932–2011) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | −1.7 (28.9) |
0.0 (32.0) |
1.0 (33.8) |
4.7 (40.5) |
12.2 (54.0) |
12.3 (54.1) |
17.4 (63.3) |
17.8 (64.0) |
16.3 (61.3) |
10.4 (50.7) |
6.9 (44.4) |
3.6 (38.5) |
17.8 (64.0) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −15.7 (3.7) |
−14.7 (5.5) |
−10.9 (12.4) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
−0.8 (30.6) |
3.6 (38.5) |
7.5 (45.5) |
9.3 (48.7) |
6.1 (43.0) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
−6.4 (20.5) |
−12.2 (10.0) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −18.4 (−1.1) |
−17.8 (0.0) |
−14.2 (6.4) |
−8.7 (16.3) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
1.1 (34.0) |
4.9 (40.8) |
6.2 (43.2) |
3.2 (37.8) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
−9.2 (15.4) |
−15.2 (4.6) |
−6.2 (20.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −21.7 (−7.1) |
−21.5 (−6.7) |
−17.8 (0.0) |
−12.1 (10.2) |
−6.5 (20.3) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
2.4 (36.3) |
3.6 (38.5) |
0.4 (32.7) |
−5.8 (21.6) |
−12.2 (10.0) |
−18.3 (−0.9) |
−9.3 (15.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −37.3 (−35.1) |
−38 (−36) |
−33.9 (−29.0) |
−27.8 (−18.0) |
−18.9 (−2.0) |
−13.1 (8.4) |
−6.9 (19.6) |
−4.3 (24.3) |
−10.8 (12.6) |
−19.5 (−3.1) |
−28.1 (−18.6) |
−33 (−27) |
−38 (−36) |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 35.0 | — | 58 | 60 | 61 | 70 | 79 | 73 | 67 | 53 | 50 | 47 | — |
| Source: JMA[34] | |||||||||||||
Geology
Mount Fuji is located at a triple junction trench where the Amurian Plate, Okhotsk Plate, and Philippine Sea Plate meet.[36][37] These three plates form the western part of Japan, the eastern part of Japan, and the Izu Peninsula respectively.[38] The Pacific Plate is being subducted beneath these plates, resulting in volcanic activity. Mount Fuji is also located near three island arcs: the Southwestern Japan Arc, the Northeastern Japan Arc, and the Izu-Bonin-Mariana Arc.[38]
Mt. Fuji's main crater is 780 metres (2,560 ft) in diameter and 240 metres (790 ft) in depth. The bottom of the crater is 100–130 metres (330–430 ft) in diameter. Slope angles from the crater to a distance of 1.5–2 kilometres (0.93–1.24 mi) are 31°–35°, the angle of repose for dry gravel. Beyond this distance, slope angles are about 27°, which is caused by an increase in scoria. Mid-flank slope angles decrease from 23° to less than 10° in the piedmont.[38]

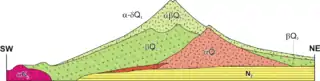
Scientists have identified four distinct phases of volcanic activity in the formation of Mount Fuji. The first phase, called Sen-komitake, is composed of an andesite core recently discovered deep within the mountain. Sen-komitake was followed by the "Komitake Fuji", a basalt layer believed to be formed several hundred thousand years ago. Approximately 100,000 years ago, "Old Fuji" was formed over the top of Komitake Fuji. The modern, "New Fuji" is believed to have formed over the top of Old Fuji around 10,000 years ago.[39]
Pre-Komitake started erupting in the Middle Pleistocene in an area 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) north of Mount Fuji. After a relatively short pause, eruptions began again which formed Komitake Volcano in the same location. These eruptions ended 100,000 years ago. Ashitake Volcano was active from 400,000 to 100,000 years ago, and is located 20 kilometres (12 mi) southeast of Mount Fuji. Mount Fuji started erupting 100,000 years ago, with Ko-Fuji (old-Fuji) forming 100,000 to 17,000 years ago, but which is now almost completely buried. A large landslide on the southwest flank occurred about 18,000 years ago. Shin-Fuji (new-Fuji) eruptions in the form of lava, lapilli and volcanic ash, have occurred between 17,000 and 8,000 years ago, between 7,000 and 3,500 years ago, and between 4,000 and 2,000 years ago. Flank eruptions, mostly in the form of parasitic cinder cones, ceased in 1707. The largest cone, Omuro-Yama, is one of more than 100 cones aligned NW-SE and NE-SW through the summit. Mt. Fuji also has more than 70 lava tunnels and extensive lava tree molds. Two large landslides are at the head of the Yoshida-Osawa and Osawa-Kuzure valleys.[38]
As of December 2002, the volcano is classified as active with a low risk of eruption. The last recorded eruption was the Hōei eruption which started on December 16, 1707 (Hōei 4, 23rd day of the 11th month), and ended about January 1, 1708 (Hōei 4, 9th day of the 12th month).[40] The eruption formed a new crater and a second peak, named Mount Hōei (after the Hōei era), halfway down its southeastern side. Fuji spewed cinders and ash which fell like rain in Izu, Kai, Sagami, and Musashi.[41] Since then, there have been no signs of an eruption. However on the evening of March 15, 2011, there was a magnitude 6.2 earthquake at shallow depth a few kilometres from Mount Fuji on its southern side. But according to the Japanese Meteorological Service there was no sign of any eruption.[42]
Current eruptive danger
Following the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake, there was speculation in the media that the shock may induce volcanic unrest at Mount Fuji. In September 2012, mathematical models created by the National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention (NRIESDP) suggested that the pressure in Mount Fuji's magma chamber could be 1.6 megapascals higher than it was before its last eruption in 1707. This was interpreted by some media outlets to mean that an eruption of Mount Fuji could be imminent.[43] However, since there is no known method of directly measuring the pressure of a volcano's magma chamber, indirect calculations of the type used by NRIESDP are speculative and unverifiable. Other indicators suggestive of heightened eruptive danger, such as active fumaroles and recently discovered faults, are typical occurrences at this type of volcano.[44]
Aokigahara forest

The forest at the northwest base of the mountain is named Aokigahara. Folk tales and legends tell of ghosts, demons, Yūrei and Yōkai haunting the forest, and in the 19th century, Aokigahara was one of many places poor families abandoned the very young and the very old.[45] Aokigahara is the world's third most popular suicide location after San Francisco's Golden Gate Bridge and the Nanjing Yangtze River Bridge .[46] Since the 1950s, more than 500 people have died in the forest, mostly suicides.[46] Approximately 30 suicides have been counted yearly, with a high of nearly 80 bodies in 2002.[47] The recent increase in suicides prompted local officials to erect signs that attempt to convince individuals experiencing suicidal intent to re-think their desperate plans, and sometimes these messages have proven effective.[48] The numbers of suicides in the past creates an allure that has persisted across the span of decades.[49][50]
Many of these hikers mark their travelled routes by leaving coloured plastic tapes behind as they pass, causing concerns from prefectural officials with regard to the forest's ecosystem.[51]
Adventuring
Transportation
The closest airport with scheduled international service is Mt. Fuji Shizuoka Airport. It opened in June 2009. It is about 80 kilometres (50 mi) from Mount Fuji.[52] The major international airports serving Tokyo, Tokyo International Airport (Haneda Airport) in Tokyo and Narita International Airport in Chiba, are hours from Mount Fuji.
Climbing routes



Approximately 300,000 people climbed Mount Fuji in 2009.[53] The most popular period for people to hike up Mount Fuji is from July to August, while huts and other facilities are operating and the weather is warmest.[53] Buses to the trail heads typically used by climbers start running on July 1.[54] Climbing from October to May is very strongly discouraged, after a number of high-profile deaths and severe cold weather.[55] Most Japanese climb the mountain at night in order to be in a position at or near the summit when the sun rises. The morning light is called 御来光 goraikō, "arrival of light".[56]
There are four major routes to the summit, each has numbered stations along the way. They are (clockwise, starting North): Kawaguchiko, Subashiri, Gotemba, and Fujinomiya routes.[57] Climbers usually start at the fifth stations, as these are reachable by car or by bus. The summit is the tenth station on each trail. The stations on different routes are at different elevations; the highest fifth station is located at Fujinomiya, followed by Yoshida, Subashiri, and Gotemba. There are four additional routes from the foot of the mountain: Shojiko, Yoshida, Suyama, and Murayama routes.
Even though it has only the second-highest fifth stations, the Yoshida route is the most-popular route because of its large parking area and many large mountain huts where a climber can rest or stay. During the summer season, most Mount Fuji climbing tour buses arrive there. The next-popular is the Fujinomiya route, which has the highest fifth station, followed by Subashiri and Gotemba. The ascent from the new fifth station can take anywhere between five and seven hours while the descent can take from three to four hours.[57]
Even though most climbers do not climb the Subashiri and Gotemba routes, many descend these because of their ash-covered paths. From the seventh station to near the fifth station, one could run down these ash-covered paths in approximately 30 minutes. Besides these routes, there are tractor routes along the climbing routes. These tractor routes are used to bring food and other materials to huts on the mountain. Because the tractors usually take up most of the width of these paths and they tend to push large rocks from the side of the path, the tractor paths are off-limits to the climbers on sections that are not merged with the climbing or descending paths. Nevertheless, one can sometimes see people riding mountain bikes along the tractor routes down from the summit. This is particularly risky, as it becomes difficult to control speed and may send some rocks rolling along the side of the path, which may hit other people.
The four routes from the foot of the mountain offer historical sites. The Murayama is the oldest Mount Fuji route and the Yoshida route still has many old shrines, teahouses, and huts along its path. These routes are gaining popularity recently and are being restored, but climbing from the foot of the mountain is still relatively uncommon. Also, bears have been sighted along the Yoshida route.
Huts at and above the fifth stations are usually manned during the climbing season, but huts below fifth stations are not usually manned for climbers. The number of open huts on routes are proportional to the number of climbers—Yoshida has the most while Gotemba has the fewest. The huts along the Gotemba route also tend to start later and close earlier than those along the Yoshida route. Also, because Mount Fuji is designated as a national park, it is illegal to camp above the fifth station.
There are eight peaks around the crater at the summit. The highest point in Japan, Ken-ga-mine, is where the Mount Fuji Radar System used to be (it was replaced by an automated system in 2004). Climbers are able to visit each of these peaks.
Paragliding
Paragliders take off in the vicinity of the fifth station Gotemba parking lot, between Subashiri and Hōei-zan peak on the south side of the mountain, in addition to several other locations, depending on wind direction. Several paragliding schools use the wide sandy/grassy slope between Gotemba and Subashiri parking lots as a training hill.
In culture
Shinto mythology
_-_panoramio.jpg.webp)
In Shinto mythology, Kuninotokotachi (国之常立神?, Kuninotokotachi-no-Kami, in Kojiki)(国常立尊?, Kuninotokotachi-no-Mikoto, in Nihon Shoki) is one of the two gods born from "something like a reed that arose from the soil" when the earth was chaotic. According to the Nihon Shoki, Konohanasakuya-hime, wife of Ninigi, is the goddess of Mount Fuji, where Fujisan Hongū Sengen Taisha is dedicated for her.
In ancient times the mountain was worshipped from afar. The Asama shrine was set up at the foothills to ward off eruptions. In the Heian period (794–1185) volcanic activity subsided and Fuji was used as a base for Shugendō, a syncretic religion combining mountain worship and Buddhism. Worshippers began to climb the slopes and by the early 12th century, Matsudai Shonin had founded a temple on the summit.[58]
Fuji-kō was an Edo period cult centred around the mountain founded by an ascetic named Hasegawa Kakugyō (1541–1646).[59] The cult venerated the mountain as a female deity, and encouraged its members to climb it. In doing so they would be reborn, "purified and... able to find happiness." The cult waned in the Meiji period and although it persists to this day it has been subsumed into Shintō sects.[60]
Popular culture
As a national symbol of the country, the mountain has been depicted in various art media such as paintings, woodblock prints (such as Hokusai's Thirty-six Views of Mount Fuji and 100 Views of Mount Fuji from the 1830s), poetry, music, theater, film, manga, anime, pottery[61] and even Kawaii subculture.
Before its explosive eruption in 1980, Mount St. Helens was once known as "The Fuji of America," for its striking resemblance to Mount Fuji. Mount Taranaki / Mount Egmont in New Zealand is also said to bear a resemblance to Mount Fuji, and for this reason has been used as a stand-in for the mountain in films and television.
Gallery
 Mount Fuji in the background of Taisekiji temple
Mount Fuji in the background of Taisekiji temple Mount Fuji from Lake Motosu which became the model of the thousand yen bill and the old five thousand yen bill
Mount Fuji from Lake Motosu which became the model of the thousand yen bill and the old five thousand yen bill
 View of Mount Fuji from the Fuji-Q Highland theme park
View of Mount Fuji from the Fuji-Q Highland theme park Mount Fuji seen from Jurigi Plateau in Susono, Shizuoka
Mount Fuji seen from Jurigi Plateau in Susono, Shizuoka Lenticular cloud over Mount Fuji seen from Mount Ogochi
Lenticular cloud over Mount Fuji seen from Mount Ogochi Silhouette of Mount Fuji seen from Mount Kita
Silhouette of Mount Fuji seen from Mount Kita Mount Fuji panorama
Mount Fuji panorama A view of Mount Fuji from Tenjoyama Park, overlooking Kawaguchiko
A view of Mount Fuji from Tenjoyama Park, overlooking Kawaguchiko
See also
- List of mountains and hills of Japan by height
- 100 Famous Japanese Mountains
- List of three-thousanders in Japan
- Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park
- List of World Heritage sites in Japan
- List of elevation extremes by country
- Mount Araido (阿頼度山, Araidosan), Araido Island (阿頼度島), Kuril Islands
- Mount St. Helens, nicknamed "Fuji-san of America" prior to its 1980 eruption
- Sacred mountains
References
- "富士山情報コ–ナ–". Sabo Works at Mt.Fuji.
- Triangulation station is 3775.63m. "Information inspection service of the Triangulation station" (in Japanese). Geospatial Information Authority of Japan, (甲府–富士山–富士山). Retrieved February 8, 2011.
- "Map inspection service" (in Japanese). Geospatial Information Authority of Japan, (甲府–富士山–富士山). Retrieved February 8, 2011.
- "Active Volcanoes of Japan". AIST. Geological Survey of Japan. Retrieved March 7, 2016.
- "Mount Fuji". Britannica Online. Retrieved October 17, 2009.
- Scheffel, Richard L.; Wernet, Susan J., eds. (1980). Natural Wonders of the World. United States: Reader's Digest Association. p. 153. ISBN 0-89577-087-3.
- Archived June 27, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- Although the word 士 can mean a soldier (兵士, heishi, heiji), or a samurai (武士, bushi), its original meaning is a man with a certain status.
- "Japanese Text Initiative theTaketori monogatari". Etext.lib.virginia.edu. August 31, 2004. Retrieved December 23, 2010.
- "富士山の名前の由来". May 31, 2008. Archived from the original on May 31, 2008. Retrieved December 23, 2010.
- "富士山 – 知泉Wiki". Tisen.jp. October 25, 2006. Retrieved December 23, 2010.
- "地名・富士山の意味". June 3, 2008. Archived from the original on June 3, 2008. Retrieved December 23, 2010.
- "富士山アイヌ語語源説について". Asahi-net.or.jp. Retrieved December 23, 2010.
- "Fuji-san" (in Japanese). Daijisen. Archived from the original on July 22, 2011.
- H. Byron Earhart (May 9, 2011). "Mount Fuji: Shield of War, Badge of Peace". The Asia-Pacific Journal.
- The Fujiyoshida City Board of Education (2003). "富士山吉田口登山道関連遺跡II". Comprehensive Database of Archaeological Site Reports in Japan. Retrieved September 1, 2016.
- Alcock, Rutherford (1863). The Capital of the Tycoon: A Narrative of Three Years Residence in Japan. I. London: Longman, Green, Longman, Roberts & Green.
- "Lilian Hope Parkes". The Cobbold Family History Trust. Retrieved February 1, 2020.
- Tucker, Anne Wilkes; et al. (2003). The History of Japanese Photography. p. 30. ISBN 978-0-300-09925-6.
- "ASN Aircraft accident Boeing 707-436 G-APFE Mount Fuji". Aviation Safety Network.
- "Climbing Mount Fuji? route maps" (PDF). pp. 4–5. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 27, 2009. Retrieved December 23, 2010.
- "Climbing Mt. Fuji travel log". ChristmasWhistler. June 30, 2002.
- "Starr Tells of Escape; American Scientist Found Refuge in a Tokio Temple". New York Times. New York. October 1, 1923.
- Tuckerman, Mike. "Climbing Mount Fuji". Japan Visitor. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Bremmer, Brian (September 15, 1997). "Mastering Mt. Fuji". Business Week.
- Uchida, Tomu (1955). Bloody Spear at Mount Fuji (血槍富士 Chiyari Fuji).
- "Launching Infiniti". Lippincott. Archived from the original on October 30, 2006.
- Sadeghian H (September 2000). "Mount Fuji sign in tension pneumocephalus". Archives of Neurology. 57 (9): 1366. doi:10.1001/archneur.57.9.1366. PMID 10987907.
- Heckmann JG, Ganslandt O; Ganslandt (April 2004). "Images in clinical medicine. The Mount Fuji sign". The New England Journal of Medicine. 350 (18): 1881. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm020479. PMID 15115834.
- "Weather Station on Mt. Fuji Closes". United Press International. September 30, 2004. Retrieved January 5, 2010.
- 「富士山世界遺産センター、2教授退職しピンチ」[Mt. Fuji World Heritage Centre in trouble after 2 Professors quit]『読売新聞』Yomiuri Newspaper 朝刊2018年4月3日 [April 3, 2018]
- "Fuji". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution.
- "STS-107 Shuttle Mission Imagery". NASA. January 26, 2003. Retrieved December 16, 2012.
- "JMA". Retrieved May 30, 2012.
- Miyaji, N. "Geology of Fuji Volcano". Fuji Volcano. Volcano Research Center, Earthquake Research Institute (ERI), University of Tokyo. Retrieved February 27, 2018.
- Moores, Eldridge M.; Twiss, Robert J. (1995). Tectonics. Waveland Press. p. 208. ISBN 978-1-4786-2199-7.
- "Mount Fuji". National Geographic Society. Retrieved May 18, 2018.
- Oguchi, Takashi; Oguchi, Chiaki (2010). Migon, Piotr (ed.). Mt. Fuji: The Beauty of a Symmetric Stratovolcano, in Geomorphological Landscapes of the World. Springer. pp. 303–309. ISBN 9789048130542.
- "Third ancient volcano discovered within Mount Fuji". Japan Times. April 4, 2004.
- Masato Oyama (March 2007). "宝永四年(1707)噴火 (1707 Eruption)". 富士山歴史噴火総解説 (Database of eruptions and other activities of Fuji Volcano, Japan, based on historical records since AD 781) (in Japanese). Shizuoka University. Retrieved September 25, 2008.
- Hayashi Gahō (1834) [1652]. "Siyun-sai Rin-siyo". Nipon o daï itsi ran or Annales des empereurs du Japon. Translated by Titsingh, Isaac. Paris: Oriental Translation Society of Great Britain and Ireland. p. 416.
- « 6.0 Earthquake east of Tokyo, signs of Mt. Fujiyama unrest is possible » Archived March 3, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, peoplestar.co.uk, Retrieved on March 16, 2011.
- Clark, Liat (September 6, 2012). "Pressure in Mount Fuji is now higher than last eruption, warn experts". Wired. Retrieved September 6, 2012.
- Klemeti, Erik (September 10, 2012). "Doooom! The Perception of Volcano Research by the Media". Wired. Retrieved September 10, 2012.
- "Japan's harvest of death". The Independent. London. September 17, 2011.
- Amazeen, no (December 21, 2005). "Book Review: Cliffs of Despair A Journey to Suicide's Edge". Monsters & Critics. Archived from the original on August 6, 2012. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Hadfield, Peter (June 16, 2001). "Japan struggles with soaring death toll in Suicide Forest". The Telegraph. London.
- "Sign saves lives of 29 suicidal people". Daily Yomuri Online. February 24, 2008. Archived from the original on March 2, 2008.
- Yoshitomo, Takahashi (Summer 1988). "Aokigahara-jukai: Suicide and Amnesia in Mt. Fuji's Black Forest". Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior. 18 (2): 164–75. doi:10.1111/j.1943-278X.1988.tb00150.x. PMID 3420643.
- Davisson, Jack. "The Suicide Woods of Mt. Fuji". Japazine. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Okado, Yuki (May 3, 2008). "Intruders tangle 'suicide forest' with tape". Asahi Shimbun. Archived from the original on May 6, 2008. Retrieved May 3, 2008.
- "Mt. Fuji Shiozuoka Airport Basic Information". Shizuoka Prefecture. Archived from the original on May 16, 2008.
- "(title in Japanese)" [The number of climbers of Mount. Fuji in 2009] (in Japanese). Ministry of the Environment.
- "Climbing Season". Official Website for Mt. Fuji Climbing.
- Video: Climbing Mount Fuji, Japan in May (closed season) at Youtube.com
- Glass, Kathy (August 26, 1990). "Climbing Mount Fuji By Night". New York Times.
- "Mountain Trails". Official Website for Mt. Fuji Climbing.
- "Mt. Fuji's selection as a cultural World Heritage site". Mt. Fuji World Heritage Div., Culture and Tourism Dept, Shizuoka Prefecture. Retrieved November 24, 2020.
- Melton, J. Gordon. Encyclopedia of Religious Phenomena. Canton, MI: Visible Ink Press, 2008, p 231
- Melton, J. Gordon. Encyclopedia of Religious Phenomena. Canton, MI: Visible Ink Press, 2008
- "収蔵品のご紹介 | サンリツ服部美術館". www.sunritz-hattori-museum.or.jp.
- Starr, Frederick (1924). Fujiyama, the Sacred Mountain of Japan. Chicago: Covici-McGee. OCLC 4249926.
External links
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Fuji. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mount Fuji. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Mount Fuji. |
- "Fujisan (Mount Fuji)" (PDF). Japan Meteorological Agency.
- Fujisan (Mount Fuji) – Smithsonian Institution: Global Volcanism Program
- Comprehensive Database of Archaeological Site Reports in Japan, Nara National Research Institute for Cultural Properties
- 3 dimensional model of Mount Fuji on sketchfab
- Official Web Site of Mt.Fuji Climbing