President of Indonesia
The president of the Republic of Indonesia (Indonesian: Presiden Republik Indonesia) is the head of state and also head of government of the Republic of Indonesia. The president leads the executive branch of the Indonesian government and is the commander-in-chief of the Indonesian National Armed Forces. Since 2004, the president and vice president are directly elected to a five-year term.
| President of the Republic of Indonesia
Presiden Republik Indonesia | |
|---|---|
 Presidential Seal | |
| Style | Mr./Madam President (Bapak/Ibu Presiden) (informal) The Honourable (formal) His/Her Excellency (international correspondence) |
| Status | Head of State Head of Government |
| Member of | Cabinet |
| Residence | Merdeka Palace (Official) State Palace Bogor Palace Tampaksiring Palace Gedung Agung Cipanas Palace |
| Seat | Jakarta |
| Appointer | Direct popular election |
| Term length | Five years, renewable once |
| Constituting instrument | Constitution of Indonesia |
| Precursor | Governor-General of Indonesia |
| Inaugural holder | Sukarno |
| Formation | 18 August 1945 |
| Deputy | Vice President of Indonesia |
| Salary | Rp 62,740,030 (US$ 4,392) per month[1] |
| Website | www |
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Indonesia |
|
|




Joko Widodo is the 7th and current president of Indonesia. He assumed office on 20 October 2014.
History
Sukarno era
The Indonesian presidency was established during the formulation of the 1945 Constitution by the Investigating Committee for Preparatory Work for Independence (BPUPK). The office was first filled on 18 August 1945 when Sukarno was elected by acclamation by the Preparatory Committee for Indonesian Independence (PPKI) because according to the Transitional Provisions of the Constitution, "the President and the Vice President for the first time shall be elected by the PPKI." Also, the body responsible for the presidential elections, the People's Consultative Assembly (MPR), had not yet been formed.[3] On 16 October 1945, Vice President Mohammad Hatta announced a vice-presidential decree which gave the Central National Committee of Indonesia (KNIP) legislative powers.[4] On 11 November 1945, the KNIP made the decision to separate the role of Head of State from that of Head of Government. Although a new constitution had not been set up yet, Indonesia was now a de facto parliamentary democracy with the president as a ceremonial Head of State whose function was to ask the prime minister as the Head of the Government to form a new Cabinet.
During the Indonesian National Revolution, both Sukarno and Hatta were captured by the Dutch in Yogyakarta on 18 December 1948. Sukarno then gave a mandate for Sjafruddin Prawiranegara to form an emergency Government.[5] This was done and the Emergency Government of the Republic of Indonesia (PDRI) was formed in Sumatra with Prawiranegara as its chairman. Prawiranegara handed back his mandate to Sukarno on 13 July 1949.[6] On 17 December 1949, Sukarno was elected president of the Republic of the United States of Indonesia (RIS) and presidential mandate passed to Assaat.[7] When it became clear that RIS was going to be replaced by a unitary state, Asaat stepped down from the presidency and Sukarno once again became president on 15 August 1950.
Indonesia now adopted the constitution that had been intended for RIS. Officially known as the Provisional Constitution, the document confirmed the president's role as the head of state, but limited him to a mostly ceremonial role. He appointed a prime minister on the advice of formateurs.[8]
Despite his limited constitutional role, Sukarno commanded great moral authority. Nonetheless, he was never content with the role of ceremonial head of State, and grew increasingly disenchanted with western-style parliamentary democracy. In the early 1950s, he began calling for the implementation of "Guided Democracy," in which decisions would be made after lengthy deliberation with a view toward achieving a consensus under presidential "guidance."
The rest of the decade saw a series of unstable governments. Taking advantage of the situation, Sukarno made a speech in April 1959 and suggested that Indonesia return to the 1945 Constitution.[9] The People reacted enthusiastically and there was strong pressure on the Constitutional Assembly, the body responsible for formulating a new constitution, to adopt the 1945 Constitution. When the assembly did not budge, Sukarno issued a presidential decree on 5 July 1959 declaring that Indonesia was returning to the 1945 Constitution.[9] That document made the president head of government as well as head of state. In May 1963, the People's Consultative Assembly appointed Sukarno president for Life.[10]
Although Indonesia had re-adopted the 1945 Constitution, it did not mean that it was strictly adhered to. The MPR, which at this stage was still on a provisional basis (MPRS), was subservient to the president despite its status of the Nation's highest Governing Body. It was only in 1966, when the political tide began to turn against Sukarno that the MPRS nominally regained its rightful constitutional status. In 1967, Sukarno was forced to resign as president, and army chief of staff Suharto was appointed as acting president.
Suharto era
Suharto was appointed president in his own right in 1968. During his rise to power, Suharto seemed determined to observe at least the forms of the constitution, and this continued when he became president. Suharto allowed the MPR to execute its constitutional duty of formulating the Outlines of State Policy (GBHN); as president, he was responsible for implementing them. Suharto also made it a presidential obligation to deliver accountability speeches near the end of his terms. During the speech, Suharto outlined the achievements that his administration had made and how those achievements had adhered to the GBHN set by the MPR. Despite the constitutional and democratic façade, Suharto made sure that the MPR was also subservient to him. In 1969, a law was passed that required appointments to the MPR to be made official by the president.[11] He also took measures that largely emasculated the opposition parties. For example, he had the power to issue governmental regulations in lieu of law, which nominally had to be approved by the House of People's Representatives (DPR, the pre-2004 legislative branch). However, given the DPR's infrequent sessions and the near-total dominance of the pro-government political grouping, Golkar, such approval was a mere formality. Thus, for all intents and purposes, Suharto ruled by decree for most of his tenure. For the better part of Suharto's rule, he effectively held all governing power in the nation.
Reform era
Suharto fell from power in May 1998 and the presidency experienced changes as a result of the reform movement. Compared to Suharto, who had all of his accountability speeches accepted, B. J. Habibie had his only accountability speech rejected.[12] Abdurrahman Wahid then became the first president who had to beat another candidate to be elected, as Sukarno and Suharto had been sole candidates. As a result of this, Wahid was also the first president to be elected through counting votes instead of by acclamation. However, Wahid was impeached and removed from office by the MPR. This was a clear sign that while the presidency is the key institution, the MPR was now truly a check on the president's power. Wahid was replaced by his Vice President, Megawati Sukarnoputri, daughter of Sukarno and former opposition leader during Suharto's presidency. Megawati is the first and, so far, only female ever to become President of Indonesia.[13]
During the 2001 MPR Annual Session, it was finally decided that from 2004 onwards, the president will directly be elected by the people.[14] In 2004 Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono became Indonesia's first directly elected president, beating incumbent Megawati Sukarnoputri in the runoff election. In 2014, Yudhoyono finished his second presidential term and was barred from seeking re-election.
The 3rd Indonesian presidential election was held on 9 July 2014 and matched former general and Suharto's ex-son in law Prabowo Subianto against the governor of Jakarta, Joko Widodo. On 22 July the General Elections Commission announced Joko Widodo's victory. He and his vice president, Jusuf Kalla, were sworn-in on 20 October 2014, for a 5-year term.
The presidency
Requirements to run for office
The 1945 Constitution: The presidential candidate has to be of Indonesian origin.
The Provisional Constitution: The presidential candidate has to be an Indonesian citizen aged at least 30 years old. He cannot be someone who is deemed to be undesirable or has had his right to take part in elections stripped. He is also required to not be involved with any private corporations.
The Amended 1945 Constitution: The presidential candidate has to be an Indonesian citizen since his/her birth, who has not willingly become a citizen in another nation, has not betrayed the nation, and is physically and mentally capable of performing the duties. Amended Constitution also states that further criteria will be determined by laws. The president is also required to be nominated by a Political Party or a coalition of Political Parties.
2008 Law No. 42 Regarding Presidential and Vice-Presidential Elections
The presidential candidate must:
- Mindful of God;[15]
- have been an Indonesian citizen since his/her birth, who has not willingly become a citizen of another nation;
- have not betrayed the nation, and has not been involved in any corruption or other criminal activity;
- be physically and mentally capable of performing the duties;
- be a permanent resident in the territory of the Republic of Indonesia;
- have reported his/her wealth to the Corruption Eradication Commission;
- have no debt individually or collectively that can create a loss for the state;
- have not been declared bankrupt by a court decision;
- never been involved in any despicable act;
- be registered as a voter;
- be registered as a tax payer and have paid taxes for at least the last five years;
- have never previously served as president for two terms;
- faithful to Pancasila, the 1945 Constitution, and the vision of the Proclamation of Indonesian Independence;
- have never been sentenced to jail for more than five years;
- not be less than 35 years of age;
- have graduated at least from the senior high school or its equivalent.
Election, oath/promise/statement of office, term of office, Constitutional requirement
The 1945 Constitution: Together with the vice president, the president is elected by the MPR with the largest number of votes. The president-elect is also required to read either an oath or a promise of office before officially becoming president. The term of office is five years and after that the president can be re-elected again.
The Provisional Constitution: Together with the vice president, the president is elected according to rules specified by laws. The president-elect is required to read either an oath or a promise or a statement of office before officially becoming president. The president is constitutionally required to live where the seat of Government is.
The Amended 1945 Constitution: Together with the vice president, the president is elected directly by the people on a ticket. Further election rules are determined by laws passed by the DPR. The president-elect is required to read either an oath or a promise of office before officially becoming president. The term of office is five years and after that the president can be re-elected for only one more term.
Distribution of Votes: Winners must receive over half the votes total, including at least 20% of the votes in at least half the 34 provinces.[16]
Oath of Office of the President of the Republic of Indonesia: "I swear by God to fulfill the duties of president (vice president) of the Republic of Indonesia to the best of my capabilities and in the fairest way possible, to uphold the Constitution by all means and to execute all laws and regulations as straightforwardly as possible as well as to dedicate myself to the service of the Nation and the People."
Pledge of Office of the President of the Republic of Indonesia: "I solemnly pledge to fulfill the duties of president (vice president) of the Republic of Indonesia to the best of my capabilities and in the fairest way possible, to uphold the Constitution by all means and to execute all laws and regulations as straightforwardly as possible as well as to dedicate myself to the service of the Nation and the People."
Powers
The 1945 Constitution: The president has constitutional authority over the Government and has the power to name and remove ministers. He has the power to create laws with the agreement of the People's Representative Council (DPR), to make Government regulations in accordance with laws, and in the case of emergencies has the power to make Government regulations in lieu of law. Militarily, the president holds supreme authority over the Army, Navy, and Air Force whilst security-wise, the president has the power to declare a State of Emergency. Diplomatically, the president, with the agreement of the DPR, has the power to declare war, peace, and to sign treaties. In addition, he or she appoints ambassadors and consuls as well as accepting ambassadors from other countries. Finally, the president has power to give amnesties and pardons as well as awarding titles and honours.
The Provisional Constitution: The president has the power to name cabinets and appoint the prime minister with the advice of formateurs. The president is able to remove ministers from office and has the right to be informed of important matters by the Council of Ministers. As the head of state, the president has the power to dissolve the DPR and order for an election to be held within 30 days. Militarily, the president holds supreme authority over the Armed Forces although any decision on this matter needs to be countersigned by the appropriate ministers and wartime control of troops has to be placed under an Armed Forces Commander. The president requires permission from the DPR to declare war and sign treaties although he or she has independent power to appoint ambassadors and to accept them. The president also has the power to grant pardons.
The Amended 1945 Constitution: The president has constitutional authority over the government and has the power to name and remove ministers. He or she has the right to propose bills to DPR, to discuss bills with the DPR to reach an agreement, make government regulations in accordance with laws, and in the case of emergencies has the power to make Government regulations in lieu of law. Militarily, the president holds supreme authority over the Indonesian National Armed Forces. Diplomatically, the president can only sign treaties, appoint ambassadors, accept ambassadors from other countries, rehabilitate prisoners, and appoint Judicial Committee members with the DPR's agreement. The president has the power to grant pardons but must consider the advice of the Supreme Court. The president also has the final say over chief justice candidates.
Assistance in performing duties
The 1945 Constitution: The president is assisted by the vice president and his or her ministers. The president is also able to seek advice from the Supreme Advisory Council (DPA).
The Provisional Constitution: The president is assisted by the vice president.
The Amended 1945 Constitution: The president is assisted by the vice president and his ministers. The president is also allowed to form his own advisory teams which will further be regulated by laws passed by DPR.
Line of succession and impeachment
The 1945 Constitution: If the president dies, resigns, or is unable to perform his/her duties for any reason, he/she is replaced by the vice president.
The Provisional Constitution: If the president dies, resigns, or is unable to perform his/her duties for any reason, he/she is replaced by the vice president.
The Amended 1945 Constitution: If the president dies, resigns, or is unable to perform his/her duties for any reason, he/she is replaced by the vice president. If the president and the vice president dies, resigns, or is unable to perform his/her duties for any reason, the government will be taken over together by the minister of foreign affairs, minister of home affairs and minister of defence. Then the MPR will elect a new president from the two candidates nominated by the political parties whose candidates were the winner and the runner-up in the previous presidential election.[17] Under the amended constitution, the president can now be impeached and removed from office. If the president is viewed to be unfit to perform his duties and has committed crimes such as corruption or betraying the nation, the DPR can appeal to the Supreme Court to try the president. Furthermore, the DPR can ask the Constitutional Court to look into the matter, during which it has 90 days to make a decision. With the decision made, the DPR can motion for the MPR to convene. The president would then be given one last chance to defend himself before the MPR makes the decision whether or not the president should be impeached.
Post-Presidency
Law 7 of 1978[18] stipulates that former presidents are entitled to a pension. Former presidents are also entitled to a house with electricity, water, and telephone bills covered by the government. In addition to that former presidents will have free healthcare for their families and a car with chauffeur.
Decorations

A president of Indonesia, as the issuer of decorations and the primary owner of Star Decorations (Indonesian: Tanda Kehormatan Bintang) is automatically awarded the highest class of all civilian and military Star Decorations. Currently there are 14 decorations which will be bestowed upon him/her soon after taking office, namely:[19]
 Star of the Republic of Indonesia, 1st Class (Indonesian: Bintang Republik Indonesia Adipurna)
Star of the Republic of Indonesia, 1st Class (Indonesian: Bintang Republik Indonesia Adipurna) Star of Mahaputera, 1st Class (Indonesian: Bintang Mahaputera Adipurna)
Star of Mahaputera, 1st Class (Indonesian: Bintang Mahaputera Adipurna) Star of Merit, 1st Class (Indonesian: Bintang Jasa Utama)
Star of Merit, 1st Class (Indonesian: Bintang Jasa Utama) Star of Humanity (Indonesian: Bintang Kemanusiaan)
Star of Humanity (Indonesian: Bintang Kemanusiaan) Star of Democracy Upholder, 1st Class (Indonesian: Bintang Penegak Demokrasi Utama)
Star of Democracy Upholder, 1st Class (Indonesian: Bintang Penegak Demokrasi Utama).png.webp) Star of Culture Parama Dharma (Indonesian: Bintang Budaya Parama Dharma)
Star of Culture Parama Dharma (Indonesian: Bintang Budaya Parama Dharma) Star of Bhayangkara (Indonesian: Bintang Bhayangkara Utama)
Star of Bhayangkara (Indonesian: Bintang Bhayangkara Utama) Guerilla Star (Indonesian: Bintang Gerilya)
Guerilla Star (Indonesian: Bintang Gerilya) Sacred Star (Indonesian: Bintang Sakti)
Sacred Star (Indonesian: Bintang Sakti) Star of Dharma (Indonesian: Bintang Dharma)
Star of Dharma (Indonesian: Bintang Dharma) Star of Yudha Dharma, 1st Class (Indonesian: Bintang Yudha Dharma Utama)
Star of Yudha Dharma, 1st Class (Indonesian: Bintang Yudha Dharma Utama) Star of Kartika Eka Paksi, 1st Class (Indonesian: Bintang Kartika Eka Paksi Utama)
Star of Kartika Eka Paksi, 1st Class (Indonesian: Bintang Kartika Eka Paksi Utama)_-_ribbon_bar.png.webp) Star of Jalasena, 1st Class (Indonesian: Bintang Jalasena Utama)
Star of Jalasena, 1st Class (Indonesian: Bintang Jalasena Utama) Star of Swa Bhuwana Paksa, 1st Class (Indonesian: Bintang Swa Bhuwana Paksa Utama)
Star of Swa Bhuwana Paksa, 1st Class (Indonesian: Bintang Swa Bhuwana Paksa Utama)
List of presidents
Timeline
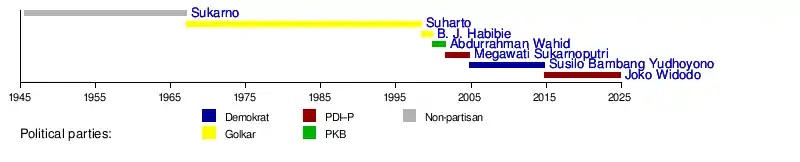
During the Indonesian National Revolution
- Sukarno (18 August 1945 – 18 December 1948)
- Sjafruddin Prawiranegara (19 December 1948 – 13 July 1949) – Head of Emergency Government
- Sukarno (14 July 1949 – 17 December 1949)
- Assaat (17 December 1949 – 15 August 1950) – during the United States of Indonesia, Sukarno became the president of the United States of Indonesia. The Republic merely a component of the union.
- Sukarno (from 15 August 1950) – upon (re)-establishment of the unitary Republic of Indonesia.
Living former presidents
As of 3 February 2021, there are two living former Indonesian presidents. The most recent former president to die was Bacharuddin Jusuf Habibie, on 11 September 2019. The living former presidents, in order of service, are:
| Photo | Name | Term of office | Date of birth |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Megawati Sukarnoputri | 23 January 1947 | |
 |
Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono | 9 September 1949 | |
Notes
- "Megawati Digaji Rp 112 Juta, Lebih Besar dari Gaji Presiden" (in Indonesian). Kompas.com. 28 May 2018. Retrieved 17 July 2018.
- "Bendera Kepresidenan Bung Karno". Rakyat Merdeka (in Indonesian). 11 April 2017. Archived from the original on 8 February 2018. Retrieved 7 February 2018.
- Kahin, George McTurnan (1952) Nationalism and Revolution in Indonesia, Cornell University Press, ISBN 0-8014-9108-8 p138
- Kahin, George McTurnan (1952) Nationalism and Revolution in Indonesia, Cornell University Press, ISBN 0-8014-9108-8 p152
- "[Urangawak] Peran PDRI Akhirnya Diakui" (in Indonesian). Archived from the original on 11 October 2007. Retrieved 12 March 2007.
- Djalal, Hasjim (16 August 2002). "Mengenang Dubes Palar dan Diplomasi Indonesia". Kompas (in Indonesian). Archived from the original on 16 March 2005. Retrieved 12 March 2007.
- 991128 Archived 13 April 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- "Temporal Constitution of Indonesia 1950". Ministry of Finance of Indonesia. 15 August 1950. Retrieved 12 May 2015.
- "Republika Online". Republika Online.
- Ricklefs, M.C. (2008) [1981]. A History of Modern Indonesia Since c.1300 (4th ed.). London: MacMillan. p. 454. ISBN 978-0-230-54685-1.
- "Law of Indonesia Number 6 Year 1969 (UU No.6/1969) about The composition and rating of People's Consultative Assembly, People's Representative Council and Regional People's Representative Council". Hukum Online. 17 December 1969. Retrieved 12 May 2015.
- Friend, Theodore (2003) Indonesian Destinies, The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press 2003 ISBN 0-674-01834-6, p461
- John Aglionby (July 2001). "Special report: Indonesia and East Timor". Retrieved 12 May 2015.
- "MPR dan Pemilihan Presiden Langsung". VOA Indonesia. 6 November 2001. Archived from the original on 25 August 2006. Retrieved 20 July 2004.
- Ropi I. (2017) Ketuhanan Yang Maha Esa: Contests of Meaning and Interpretation. In: Religion and Regulation in Indonesia. Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore
- NEHRU, VIKRAM; BULKIN, NADIA (24 October 2013). "How Indonesia's 2014 Elections Will Work". Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. Retrieved 23 March 2017.
- Laurencius Simanjuntak (22 January 2010). "Wapres Bisa Jadi Presiden, Kemudian Memilih Wakilnya". Detik.com. Retrieved 12 May 2015.
- "Law of Indonesia No. 7 Year 1978 (UU No.7/1978) about Rights of Finance/Administrative President and Vice President, and Former President and Vice President of the Republic of Indonesia" (PDF). National Library of the Republic of Indonesia. 18 December 1978. Retrieved 12 May 2015.
- "Tanda Kehormatan yang dimiliki Presiden" (in Indonesian). Direktorat Jenderal Kebudayaan Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan Republik Indonesia. 10 May 2019. Retrieved 23 August 2019.
External links
- (in Indonesian) Republic of Indonesia Presidential Documents, from the National Library of Indonesia
- (in Indonesian) 1945 Constitution
- (in Indonesian) Provisional Constitution

