Prime Minister of Malaysia
The prime minister of Malaysia (Malay: Perdana Menteri Malaysia) is the head of government of Malaysia. The prime minister directs the executive branch of the federal government. The Yang di-Pertuan Agong appoints a member of Parliament (MP) who, in his opinion, is most likely to command the confidence of a majority of MPs, the prime minister, usually the leader of the party winning the most seats in a general election.
| Prime Minister of Malaysia
Perdana Menteri Malaysia | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Official emblem of the Office of the Prime Minister | |
| Government of Malaysia Prime Minister's Department | |
| Style | Yang Amat Berhormat (The Right Honourable) unless otherwise specified |
| Status | Head of Government |
| Member of | Cabinet National Finance Council National Security Council House of Representatives |
| Reports to | Parliament |
| Residence | Seri Perdana, Putrajaya |
| Seat | Perdana Putra, Putrajaya |
| Appointer | Yang di-Pertuan Agong |
| Term length | 5 years or less, renewable (while commanding the confidence of the lower house of Parliament with General Elections held no more than five years apart) |
| Constituting instrument | Federal Constitution of Malaysia |
| Inaugural holder | Tunku Abdul Rahman |
| Formation | 31 August 1957 |
| Salary | MYR 22,826.65 per month[1] |
| Website | www |
After the formation of Malaysia on 16 September 1963, Tunku Abdul Rahman, the chief minister of the Federation of Malaya, became the first prime minister of Malaysia.
Appointment

According to the Federal Constitution, the Yang di-Pertuan Agong shall first appoint a prime minister to preside over the Cabinet. The prime minister is to be a member of the Dewan Rakyat (House of Representatives), and who in his majesty's judgment is likely to command the confidence of the majority of the members of that House. This person must be a Malaysian citizen, but cannot have obtained their citizenship by means of naturalisation or registration. The Yang di-Pertuan Agong shall appoint other ministers from either the Dewan Rakyat or Dewan Negara (Senate) with the prime minister's advice.
The prime minister and his cabinet ministers must take and subscribe to the oath of office and allegiance as well as the oath of secrecy in the presence of the Yang di-Pertuan Agong before they can exercise functions of office. The Cabinet is collectively accountable to the Parliament of Malaysia. The members of the Cabinet shall not hold any office of profit and engage in any trade, business or profession that will cause a conflict of interest. The Prime Minister's Department (sometimes referred to as the Prime Minister's Office) is the body and ministry in which the prime minister exercises his/her functions and powers.
In the case where a government cannot get its appropriation (budget) legislation passed by the House of Representatives, or when the House passes a vote of "no confidence" in the government, the prime minister is bound by convention to resign immediately. The Yang di-Pertuan Agong's choice of replacement prime minister will be dictated by the circumstances. All other ministers shall continue to hold office by the pleasure of the Yang di-Pertuan Agong, unless if the appointment of any minister is revoked by his majesty upon the advice of the prime minister. Any minister may resign his office.
Following a resignation in other circumstances, defeat in an election, or the death of a prime minister, the Yang di-Pertuan Agong would generally appoint as the new leader of the governing party or coalition as new Prime Minister.
Powers
The power of the prime minister is subject to a number of limitations. Prime ministers removed as leader of his or her party, or whose government loses a vote of no confidence in the House of Representatives, must advise a new election of the lower house or resign the office. The defeat of a supply bill (one that concerns the spending of money) or unable to pass important policy-related legislation is seen to require the resignation of the government or dissolution of Parliament, much like a non-confidence vote, since a government that cannot spend money is hamstrung, also called loss of supply.
The prime minister's party will normally have a majority in the House of Representatives and party discipline is exceptionally strong in Malaysian politics, so passage of the government's legislation through the House of Representatives is mostly a formality.
Under the Constitution, the prime minister’s role includes advising the Yang di-Pertuan Agong on:
- the appointment of the federal ministers (full members of cabinet);
- the appointment of the federal deputy ministers, parliamentary secretaries (non-full members of cabinet);
- the appointment of 44 out of 70 Senators in the Dewan Negara;
- the summoning and adjournment of sittings of the Dewan Rakyat;
- the appointment of judges of the superior courts (which are the High Courts, the Court of Appeal, and the Federal Court);
- the appointment of the attorney-general and the auditor-general; and
- the appointment of the chairmen and members of the Judicial and Legal Service Commission, Election Commission, Police Force Commission, Education Service Commission, National Finance Council, and Armed Forces Council;
Under Article 39 of the Constitution, executive authority is vested in the Yang di-Pertuan Agong. However, Article 40(1) states that in most cases, the Yang di-Pertuan Agong is bound to exercise his powers on the advice of the Cabinet or a minister acting under the Cabinet's general authority. Thus, most of the day-to-day work of governing is actually done by the prime minister and the Cabinet.
Caretaker prime minister
Under Article 55(3) of Constitution of Malaysia, the lower house of Parliament, unless sooner dissolved by the Yang di-Pertuan Agong with his own discretion on the advice of the prime minister, shall continue for five years from the date of its first meeting. Article 55(4) of the Constitution permits a delay of 60 days of general election to be held from the date of dissolution and Parliament shall be summoned to meet on a date not later than 120 days from the date of dissolution. Conventionally, between the dissolution of one Parliament and the convening of the next, the prime minister and the cabinet remain in office in a caretaker capacity.
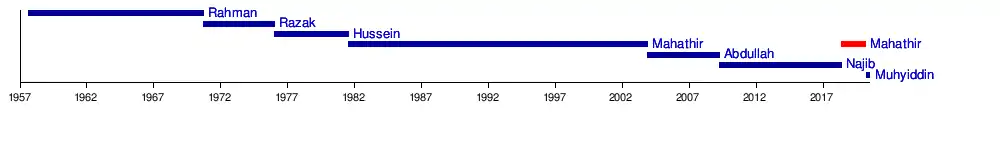
List of prime ministers of Malaysia
Colour key (for political coalitions/parties):
Alliance Party
Barisan Nasional
Pakatan Harapan
Perikatan Nasional
Timeline
List of acting prime ministers of Malaysia
From time to time, prime ministers are required to leave the country on business and a deputy is appointed to take their place during that time. In the days before jet aeroplanes, such absences could be for extended periods. However, the position can be fully decided by the Yang Di-pertuan Agong, The King of Malaysia when the position remains empty following the sudden resignation or death of the prime minister.
- Abdul Razak Hussein was the acting prime minister after the first prime minister, Tunku Abdul Rahman, stepped down as prime minister for three months in 1959 to strengthen his party, the Alliance for the 1959 federal elections after it had lost two states, Kelantan and Terengganu, in the state elections which at that time were held before the federal contest.
- Ismail Abdul Rahman occasionally acted as acting prime minister when Tunku Abdul Rahman and Abdul Razak Hussein were on leave for going abroad.
- V. T. Sambanthan was called to serve as acting prime minister and chair the cabinet meeting for a day when the former prime minister Abdul Razak Hussein was overseas and his deputy Ismail Abdul Rahman had died.
- In 1988, when UMNO as the founding member of the Barisan Nasional coalition was declared unlawful and illegal political party, Mahathir Mohamad was disqualified as the Barisan Nasional chairman. Ling Liong Sik became the new chairman of the Barisan Nasional and served as an acting prime minister for a couple of days until the new party, UMNO Baru, was legalised by the Registrar of Societies (ROS).
- Anwar Ibrahim acted as an acting prime minister for two months started from 19 May 1997 as Mahathir Mohamad was on vacation.
Colour key (for political parties):
| Portrait | Name
(Birth–Death) |
Term of office | Political Party | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
.jpg.webp) |
Abdul Razak Hussein (1922–1976) |
19 August 1959 | 19 November 1959 | Alliance (UMNO) | |
 |
Ismail Abdul Rahman (1915–1973) |
22 September 1970 | 22 September 1970 | ||
 |
V. T. Sambanthan (1919 - 1979) |
3 August 1973 | 13 August 1973 | Alliance (MIC) | |
| Ling Liong Sik (b. 1943) |
4 February 1988 | 16 February 1988 | Barisan Nasional (MCA) | ||
 |
Anwar Ibrahim (b. 1947) |
19 May 1997 | 19 July 1997 | Barisan Nasional (UMNO) | |
List of interim prime ministers of Malaysia
During the 2020 Malaysian political crisis, Mahathir Mohamad had been appointed as the interim prime minister by the Yang di-Pertuan Agong following the abrupt resignation of he himself as the 7th Prime Minister of Malaysia since he won the 14th General Election massively in 2018 while the King himself decided the appointment of Muhyiddin Yassin as the new 8th Prime Minister of Malaysia few days later. This position does not exist in any part of the laws of Malaysia, however, the Yang di-Pertuan Agong created the position to handle the situation during the crisis, based on his powers provided by the Federal Constitution.[2]
Colour key (for political parties):
| Portrait | Name
(Birth–Death) |
Term of office | Political Party | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
_(cropped).jpg.webp) |
Mahathir Mohamad (b. 1925) |
24 February 2020 | 1 March 2020 | PH (PPBM) | |
Living former prime ministers
Prime ministers are usually granted certain privileges after leaving office at government expense. Former prime ministers continue to be important national figures.
| Portrait | Name | Term(s) of office | Date of birth |
|---|---|---|---|
.jpg.webp) | Mahathir Mohamad | 1981–2003, 2018–2020 | 10 July 1925 (age 95) |
 | Abdullah Ahmad Badawi | 2003–2009 | 26 November 1939 (age 81) |
 | Mohd Najib Abdul Razak | 2009–2018 | 23 July 1953 (age 67) |
The most recently deceased prime minister was Tunku Abdul Rahman (1903–1990), who died on 6 December 1990.
See also
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Prime ministers of Malaysia. |
- "CPPS Policy Factsheet: Remuneration of Elected Officials in Malaysia" (PDF). Centre for Public Policy Studies. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 May 2016. Retrieved 11 May 2016.
- Yusof, Dr Muhammad Fathi (25 February 2020). "Kuasa Perdana Menteri Interim ditentukan Agong". BH Online (in Malay). Retrieved 15 April 2020.



.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)

.jpg.webp)