Prostaglandin G2
Prostaglandin G2 is an organic peroxide belonging to the family of prostaglandins.[1] The compound has been isolated as a solid, although it is usually used in vivo. It quickly converts into prostaglandin H2, a process catalyzed by the enzyme COX.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
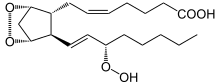
| IUPAC name
(5Z)-7-{(1R,4S,5R,6R)-6-[(1E,3S)-3-Hydroperoxy-1-octen-1-yl]-2,3-dioxabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-yl}-5-heptenoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H32O6 | |
| Molar mass | 368.464 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Prostaglandin G2 is produced from the fatty acid arachidonic acid. The reaction, an oxygenation, requires the enzyme cyclooxygenase, which inserts two molecules of O2 into the C-H bonds of the substrate acid.[1][2]
References
- van der Donk, Wilfred A.; Tsai Ah-Lim; Kulmacz Richard J. (2002). "The cyclooxygenase reaction mechanism". Biochemistry. 41: 15451–8. doi:10.1021/bi026938h.
- "Prostaglandin G2". Santa cruz biotechnology, inc. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.