Sexi (Phoenician colony)
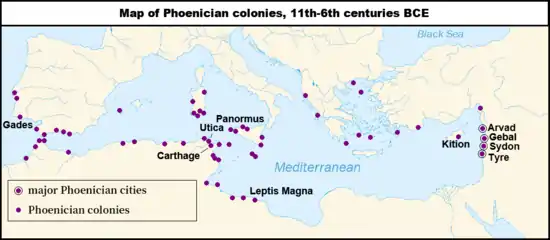
Sexi (Punic: 𐤑𐤊𐤑, ṢKṢ),[1] also known as Ex,[2] was a Phoenician colony at the present-day site of Almuñécar on southeastern Spain's Mediterranean coast.
._Piletas.jpg.webp) Basins of a garum factory (Firmun Lulium Sexi). | |
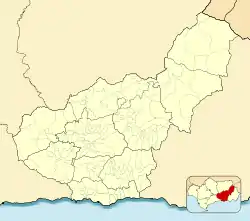 Location in the Province of Granada  Location in Andalusia  Location in Spain | |
| Location | Almuñécar, Spain |
|---|---|
| Region | Andalusia |
| Coordinates | 36°44′N 3°41′W |
| Part of | Phoenician colonies |
| History | |
| Founded | 3rd century BC |
| Abandoned | 2nd century BC |
The Roman name for the place was Sexi Firmum Iulium. Alternative transcriptions of the Phoenician name of the city in Latin include Seks, Sex, Seksi and Sexsi.[3]
History
The ancient Phoenician settlement, whose earliest phases are unclear, was located southwest of the Solorius Mons (the modern Sierra Nevada mountain range). From the 3rd-2nd centuries BC it issued a sizable corpus of coinage, with many coins depicting the Phoenico-Punic god Melqart on the obverse and one or two fish on the reverse, possibly alluding to the abundance of the sea and also a principal product of the area.[4] The Barrington atlas of the ancient world equates ancient Sexi with modern Almuñécar.[5]
References
Citations
- Huss (1985), p. 560.
- Aubet, María Eugenia (2005). Osborne, Robin; Cunliffe, Barry (eds.). Mediterranean Urbanization 800-600 BC. Oxford, UK: OUP. p. 194. ISBN 9780197263259.
- Ruiz Fernández, Antonio (1979). Almuñécar: en la antigüedad fenicia o 'Ex en el Ambito de Tartessos (in Spanish). Granada, Spain: Excma. Diputación Provincial, Instituto Provincial de Estudios y Promoción Cultural. p. 43. ISBN 9788450031171.
- Meadow, A.; Purefoy, P. (2002). SNG BM Spain-British Museum 2: Spain; London, The British Museum Press. No.'s 404-425.
- Richard J. A. Talbert et al (2000). Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World Princeton University Press. Map 27, B5.
Bibliography
- Huss, Werner (1985), Geschichte der Karthager, Munich: C.H. Beck, ISBN 9783406306549. (in German)