Tangier
Tangier, also Tangiers (/tænˈdʒɪər(z)/ tan-JEER(Z)) (Arabic: طنجة, romanized: ṭanja; Berber languages: ⵟⴰⵏⵊⴰ, romanized: ṭanja) is a city in northwestern Morocco. It is on the Maghreb coast at the western entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar, where the Mediterranean Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Spartel. The town is the capital of the Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceima region, as well as the Tangier-Assilah prefecture of Morocco.
Tangier
| |
|---|---|
 Tangier | |
 Flag | |
| Nickname(s): The blue and white city, Boughaz, North's bride | |
 Tangier Location of Tangier within Morocco  Tangier Tangier (Africa) | |
| Coordinates: 35°46′N 5°48′W | |
| Country | |
| Region | Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceima |
| Highest elevation | 230 m (750 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population (2014)[1] | |
| • Total | 947,952 |
| • Rank | 3rd in Morocco[1] |
| [lower-alpha 1] | |
| Demonym(s) | Tangierian |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| Postal code |
|
| Area code(s) | 0539 |
| Website | tanger |
| |
Many civilisations and cultures have influenced the history of Tangier, starting from before the 10th century BCE. Between the period of being a strategic Berber town and then a Phoenician trading centre to the independence era around the 1950s, Tangier was a nexus for many cultures. In 1923, it was considered as having international status by foreign colonial powers and became a destination for many European and American diplomats, spies, writers and businessmen.
The city is undergoing rapid development and modernisation. Projects include tourism projects along the bay, a modern business district called Tangier City Centre, an airport terminal, and a football stadium. Tangier's economy is set to benefit greatly from the Tanger-Med port.
Names
The Carthaginian name of the city is variously recorded as TNG (Punic: 𐤕𐤍𐤂), TNGʾ (𐤕𐤍𐤂𐤀), TYNGʾ (𐤕𐤉𐤍𐤂𐤀),[2] and TTGʾ (𐤕𐤕𐤂𐤀);[3] these appear in Greek and Roman sources as Tenga, Tinga, Titga, &c.[4] The old Berber name was Tingi (ⵜⵉⵏⴳⵉ), which Ruiz connects to Berber tingis, meaning "marsh".[5] The Greeks later claimed that Tingís (Greek: Τιγγίς) had been named for Tinjis, a daughter of the titan Atlas, who was supposed to support the vault of heaven nearby. Latin Tingis then developed into Portuguese Tânger, Spanish Tánger, and French Tanger, which entered English as Tangier and Tangiers. The Arabic and modern Berber name of the town is Ṭanja (طَنجة, ⵟⴰⵏⴵⴰ).[4]
Tangier was formally known as Colonia Julia Tingi ("The Julian Colony of Tingis") following its domination by colony status during the Roman Empire. The nicknames "Bride of the North" and "Door of Africa" reference its position in far northwestern Africa near the Strait of Gibraltar.
History
Ancient

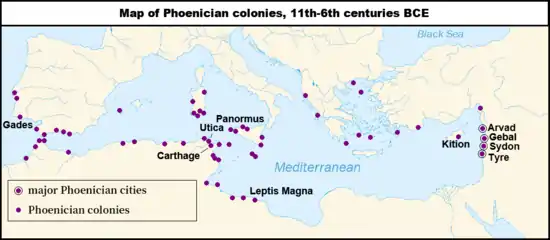
Tangier was founded as a Phoenician colony, possibly as early as the 10th century BC[6][7] and almost certainly by the 8th century BC.[8] The majority of Berber tombs around Tangier had Punic jewelry by the 6th century BC, speaking to abundant trade by that time.[9] The Carthaginians developed it as an important port of their empire by the 5th century BC.[6][7] It was probably involved with the expeditions of Hanno the Navigator along the West African coast.[6][8] The city long preserved its Phoenician traditions, issuing bronze coins under the Mauretanian kings with Punic script and others under the Romans bearing Augustus and Agrippa's heads and Latin script obverse but an image of the Canaanite god Baal reverse.[3] Some editions of Procopius place his Punic stelae in Tingis rather than Tigisis;[10] in either case, however, their existence is highly dubious.[11]
The Greeks knew this town as Tingis and, with some modification, record the Supposedly Tinjis, daughter of Atlas and widow of Antaeus, slept with Hercules and bore him the son Syphax. After Tinjis' death, Syphax then founded the port and named it in her honour.[12] The gigantic skeleton and tomb of Antaeus were tourist attractions for ancient visitors.[12] The Caves of Hercules, where he supposedly rested on Cape Spartel during his labors, remain one today.
Tingis came under the control of the Roman ally Mauretania during the Punic Wars. Q. Sertorius, in his war against Sulla's regime in Rome, took and held Tingis for a number of years in the 70s BC. It was subsequently returned to the Mauretanians but established as a republican free city during the reign of Bocchus III in 38 BC.[13]
Tingis received certain municipal privileges under Augustus and became a Roman colony under Claudius, who made it the provincial capital of Mauretania Tingitana.[14][4] Under Diocletian's 291 reforms, it became the seat of a count (comes) and Tingitana's governor (praeses).[13] At the same time, the province itself shrank to little more than the ports along the coast and, owing to the Great Persecution, Tingis was also the scene of the martyrdoms by beheading of Saints Marcellus and Cassian in 298.[6] Tingis remained the largest settlement in its province in the 4th century and was greatly developed.
Medieval


Probably invited by Count Boniface, who feared war with the empress dowager,[15] tens of thousands of Vandals under Gaiseric crossed into North Africa in 429 and occupied Tingis[16] and Mauretania as far east as Calama. When Boniface learned that he and the empress had been manipulated against each other by Aetius, he attempted to compel the Vandals to return to Spain but was instead defeated at Calama in 431.[15] The Vandals lost control of Tingis and the rest of Mauretania in various Berber uprisings.
Tingis was reconquered by Belisarius, the general of the Byzantine emperor Justinian I, in 533 as part of the Vandalic War.[16] The new provincial administration was moved, however, to the more defensible base at Septem (present-day Ceuta).[13] Byzantine control probably yielded to pressure from Visigoth Spain around 618.[17]
Count Julian of Ceuta supposedly led the last defences of Tangier against the Muslim invasion of North Africa.[18] Medieval romance made his betrayal of Christendom a personal vendetta against the Visigoth king Roderic over the honour of his daughter,[19] but Tangier at least fell to a siege[20] by the forces of the Arabian Musa bin Nusayr sometime between 707[21] and 711.[22][23] While he moved south through central Morocco, he had his deputy at Tangier Tariq ibn Zayid (usually said to be Musa's Berber general [19][24] launch the beginning of the Muslim invasion of Spain.[21] (Uqba ibn Nafi was frequently but erroneously credited with Tangier's conquest by medieval historians, but only owing to Musa's later disgrace at the hands of a jealous caliph.)[25]
Under the Umayyads, Tangier served as the capital of the Moroccan district (Maghreb al-Aqsa[26] or al-Udwa) of the province of Africa (Ifriqiya). The conquest of the Maghreb and Spain had, however, been undertaken principally as raids for slaves and plunder and the caliphate's leadership continued to treat all Berbers as pagans or slaves for tax purposes, even after their wholesale conversion to Islam.[27] In the area around Tangier, these hateful taxes were mostly paid in female slaves or in tender lambskins obtained by beating the ewes to induce premature birth.[27] Governor Yazid was murdered by Berber guards whom he had tattooed as slaves in c. 720,[27] and in the 730s similar treatment from Governor Ubayd Allah and al-Muradi, his deputy at Tangier, provoked the Berber Revolt. Inspired by the egalitarian Kharijite heresy, Barghawata and others under Maysara al-Matghari seized Tangier in the summer of 740.[28][29] In the Battle of the Nobles on the city's outskirts a few months later, Maysara's replacement Khalid ibn Hamid massacred the cream of Arab nobility in North Africa. An enraged Caliph Hisham ordered an attack from a second army "whose beginning is where they are and whose end is where I am" but this was defeated at Bagdoura the next year.[30] The Barghawata were concentrated further south on the Atlantic coast, and area around Tangier fell into chaos until 785.[31]
The Shia Arab refugee Idris arrived at Tangier[31] before moving further south, marrying into local tribes around Moulay Idriss and assembling an army that, among its other conquests, took Tangier c. 790. During the division of the sultanate that occurred on the death of Idris II, Tangier fell to his son Qasim in 829.[31] It was soon taken by Qasim's brother Umar, who ruled it until his death in 835.[31] Umar's son Ali became sultan (r. 874–883), as did Qasim's son Yahya after him (r. 880–904), but they governed from Fez.
The Fatimid caliph Abdullah al-Madhi began interfering in Morocco in the early 10th century, prompting the Umayyad emir of Cordova to proclaim himself caliph and to begin supporting proxies against his rivals. He helped the Maghrawa Berbers overrun Melilla in 927, Ceuta in 931, and Tangier in 949.[31] Tangier's governor was subsequently named chief over Cordova's Moroccan possessions and allies.[31] Ali ibn Hammud, named Cordova's governor for Ceuta in 1013, took advantage of the realm's civil wars to conquer Tangier and Málaga before overrunning Cordova itself and proclaiming himself caliph in 1016. His Barghawata ally Rizḳ Allāh was then permitted to rule from Tangier with general autonomy.[31]
Yusuf ibn Tashfin captured Tangier for the Almoravids in 1077.[31] It fell to Abd al-Mumin's Almohads in the 1147 and then flourished under his dynasty, with its port highly active.[31]
Like Ceuta, Tangier did not initially acknowledge the Marinids after the fall of the Almohads. Instead, the local chief Yusuf ibn Muhammad pledged himself to the Hafsids in Tunisia and then to the Abbasids in the east before being killed in AH 665 (late 1266 or early 1267 CE).[31] Abu Yusuf Yaqub compelled Tangier's allegiance with a three months' siege in 1274.[31]
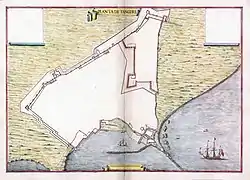
The next century was an obscure time of rebellions and difficulties for the city. During this time, the great Berber traveler Ibn Battuta was born in Tangier in 1304, leaving home at 20 for the hajj.[32] Piracy from Tangier and Salé began to harass shipping in the strait and North Atlantic in the late 14th century.[16] A partial plan of the late medieval kasbah was found in a Portuguese document now held by the Military Archives of Sweden in Stockholm.[33]
Modern
_(14780828702).jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)


When the Portuguese started their colonial expansion by taking Ceuta in retribution for its piracy[16] in 1415,[34] Tangier was always a major goal. They failed to capture it in 1437, 1458, and 1464,[31] but occupied it unopposed on 28 August 1471 after its garrison fled upon learning of the conquest of Asilah.[35] As in Ceuta, they converted its chief mosque into the town's cathedral church; it was further embellished by several restorations during the town's occupation.[13] In addition to the cathedral, the Portuguese raised European-style houses and Franciscan and Dominican chapels and monasteries.[16] The Wattasids assaulted Tangier in 1508, 1511, and 1515 but without success. In the 17th century, it passed with the rest of Portugal's domains into Spanish control as part of the personal union of the crowns[4] but maintained its Portuguese garrison and administration.[31]
Iberian rule lasted until 1661,[16] when it was given to England's King Charles II as part of the dowry of the Portuguese infanta Catherine of Braganza.[36] A squadron under the admiral and ambassador Edward Montagu arrived in November. English Tangier, fully occupied in January 1662,[37] was praised by Charles as "a jewell of immense value in the royal diadem"[16] despite the departing Portuguese taking away everything they could, even—according to the official report—"the very fflowers, the Windowes and the Dores".[38] Tangier received a garrison and a charter which made it equal to other English towns, but the religious orders were expropriated, the Portuguese residents nearly entirely left, and the town's Jews were driven out owing to fears concerning their loyalty.[39] Meanwhile, the Tangier Regiment were almost constantly under attack by locals who considered themselves mujahideen fighting a holy war.[31] Their principal leader was Khadir Ghaïlan (known to the English as "Gayland" or "Guyland") of the Banu Gurfat, whom the Earl of Peterborough attempted to buy off.[31] Ultimately, the truce only lasted for part of 1663 and 1664; on May 4 of the latter year, the Earl of Teviot and around 470 members of the garrison were killed in an ambush beside Jew's Hill.[31] Lord Belasyse happened to secure a longer-lasting treaty in 1666:[40] Khadir Ghaïlan hoped to support a pretender against the new Alawid sultan Al-Rashid and things subsequently went so badly for him that he was obliged to abide by its terms until his death in 1673.[31]
The English took advantage of the respite to improve greatly the Portuguese defences.[31] They also planned to improve the harbour by building a mole, which would have allowed it to play the same role that Gibraltar later played in British naval strategy. Incompetence, waste and outright fraud and embezzlement caused costs to swell; among those enriched was Samuel Pepys.[41] The mole cost £340,000 and reached 1,436 ft (438 m) long before its destruction.[42][43][44] Although funding was found for the fortifications, the garrison's pay was delayed until in December 1677 it was 21⁄4 years in arrears; Governor Fairborne dealt with the ensuing mutiny by seizing one of the soldier's muskets and killing him with it on the spot.
An attempt by Sultan Moulay Ismail of Morocco to seize the town in 1679 was unsuccessful; but longstanding exasperation with the colony's finances[45] and a crippling blockade by Jaysh al-Rifi pushed Parliament to write off the effort in 1680.[45] At the time, Tangier's population consisted of only about 700 apart from the thousand-man garrison; Governor Kirke estimated 400 of them had suffered gonorrhea from the same "mighty pretty" whore.[45] Forces under Lord Dartmouth (including Samuel Pepys) methodically destroyed the town and its port facilities for five months prior to Morocco's occupation of the city on 7 February 1684.[46]
Ali ibn Abdallah and his son Ahmed ibn Ali served in turn as the town's governors until 1743, repopulating it with Berbers from the surrounding countryside.[47] They were powerful enough to oppose Sultan Abdallah through his various reigns, giving support and asylum to his various rivals within and without the royal family.[48]
The Spanish attacked the city in 1790[14] but the city grew until, by 1810, its population reached 5,000.
From the 18th century, Tangier served as Morocco's diplomatic headquarters.[49] The United States dedicated its first consulate in Tangier during the George Washington administration.[50] In 1821, the Legation Building in Tangier became the first piece of property acquired abroad by the U.S. government—a gift to the U.S. from Sultan Moulay Suliman.
In 1828, Great Britain blockaded the port in retaliation for piracy.[51] As part of its ongoing conquest of neighboring Algeria, France declared war over Moroccan tolerance of Abd el-Kader; Tangier was bombarded by a French fleet under the Prince of Joinville on 6 August 1844.[48] What little of its fortifications were damaged[52] were later repaired by English engineers,[26] but French victory at Isly near the disputed border ended the conflict on French terms.
Italian revolutionary hero Giuseppe Garibaldi lived in exile at Tangier in late 1849 and the first half of 1850, following the fall of the revolutionary Roman Republic.
Tangier's geographic location made it a cockpit of European diplomatic and commercial rivalry in Morocco in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.[53] By the 1870s, it was the site of every foreign embassy and consul in Morocco but only held about 400 foreign residents out of a total population of around 20,000.[14] The city increasingly came under French influence, and it was here in 1905 that Kaiser Wilhelm II triggered an international crisis that almost led to war between his country and France by pronouncing himself in favour of Morocco's continued independence, with an eye to its future acquisition by the German Empire. The Algeciras Conference which ended the standoff left Tangier's police training and customs collections in international hands[49] but Britain's strong support of its "Entente Cordiale" with France ended German hopes concerning Morocco.
Improved harbour facilities were completed in 1907, with an inner and outer mole.[49] In the years leading up to the First World War, Tangier had a population of about 40,000, about half Muslim, a quarter Jewish, and a quarter European Christians. Of the Europeans, about three-quarters were Spanish artisans and labourers.[49][4] In 1912, Morocco was effectively partitioned between France and Spain; Spanish Morocco covered the country's far north and far south while the French protectorate covered the central remainder. The last Sultan of independent Morocco, Moulay Hafid, was exiled to the Sultanate Palace in the Tangier kasbah after his forced abdication in favour of his brother Moulay Yusef.
Tangier was made an international zone in 1923 under the joint administration of France, Spain and Britain under an international convention signed in Paris on 18 December 1923. Ratifications were exchanged in Paris on 14 May 1924. The convention was registered in League of Nations Treaty Series on 13 September 1924.[54] The convention was amended in 1928.[55] The governments of Italy, Portugal and Belgium adhered to the convention in 1928, and the government of the Netherlands in 1929. The standard-gauge Franco-Spanish Tangier–Fez Railway (French: Compagnie Franco-Espagnole du Tanger–Fès) was constructed from 1919 to 1927.
The international statute of Tangier promoted the formation of a cosmopolitan society where Muslims, Christians, and Jews lived together with reciprocal respect and tolerance. A town where men and women, with many different political and ideological tendencies, found refuge, including Spaniards from the right or from the left, Jews fleeing Nazi Germany and Moroccan nationalists. With very liberal economic and fiscal laws, Tangier became - in an international environment full of restrictions, prohibitions and monopolies - a tax haven with absolute freedom of trade.[56] The International Zone of Tangier had a 373 km2 (144 sq mi) area and, by the World War II, a population of about 50,000 inhabitants: 30,000 Muslims; 12,000 Jews; and 8,000-odd Europeans, with a decreasing proportion of working-class Spaniards.[13] However, Spanish troops occupied Tangier on 14 June 1940, the same day Paris fell to the Germans. Despite calls by Spanish nationalists to annex "Tánger español", the Franco regime publicly considered the occupation a temporary wartime measure.[57] A diplomatic dispute between Britain and Spain over the latter's abolition of the city's international institutions in November 1940 led to a further guarantee of British rights and a Spanish promise not to fortify the area.[58] The territory was restored to its pre-war status on October 11, 1945.[59]
In July 1952 the protecting powers met at Rabat to discuss the Zone's future, agreeing to abolish it. Tangier joined with the rest of Morocco following the restoration of full sovereignty in 1956.[60] At the time of the handover, Tangier had a population of around 40,000 Muslims; 31,000 Christians; and 15,000 Jews.[61]
Still basking in the Zone's countercultural glow and close by the kif-producing Rif Mountains, Tangier formed part of the hippie trail of the 1960s and '70s.[62] It became less popular and tourist attractions became run-down as cheap flights made central Moroccan cities like Marrakesh more accessible to European tourists; crime rose and a somewhat dangerous reputation drove more tourists away.[62] Since 2010, however, King Mohammed VI has made a point of restoring the city's shipping and tourist facilities and improving its industrial base. Among other improvements, the beach was cleaned and lined with new cafes and clubs; the new commercial port means cruise ships no longer unload beside cargo containers.[62]
Geography

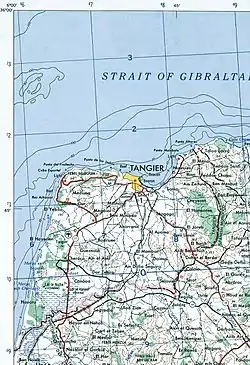
Central Tangier lies about 23 km (14 mi) east of Cape Spartel, the southern half of the Strait of Gibraltar.[49] It nestles between two hills at the northwest end of the Bay of Tangier, which historically formed the best natural harbour anywhere on the Moroccan coast before the increasing size of ships required anchorage to be made further and further from shore.[49] The shape of the gradually-rising underlying terrain creates the effect of the city as an amphitheatre, with the commercial district in the middle.[49] The western hill (French: La Montagne) is the site of the city's citadel or kasbah. The eastern hill forms Cape Malabata,[13] sometimes mooted as the point for a strait crossing.[63] (Years of studies have, however, made no real progress thus far.)[64]
The Marshan is a plateau about 1,189 metres (3,900 ft) long spreading west of downtown along the sea.[13]
Climate
Tangier has a mediterranean climate (Köppen Csa) with heavier rainfall than most parts of North Africa and nearby areas on the Iberian Peninsula owing to its exposed location.[65] The prevailing winds blow from the sea and have kept the site generally healthy even in earlier times with much poorer sanitation.[26] The summers are relatively hot and sunny and the winters are wet and mild. Frost is rare, although a new low of −4.2 °C (24.4 °F) was recorded in January 2005.[65]
| Climate data for Tangier (Tangier Airport) 1961–1990, extremes 1961–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.0 (71.6) |
27.0 (80.6) |
25.0 (77.0) |
27.0 (80.6) |
34.0 (93.2) |
36.0 (96.8) |
41.0 (105.8) |
39.0 (102.2) |
39.5 (103.1) |
30.0 (86.0) |
27.0 (80.6) |
24.5 (76.1) |
41.0 (105.8) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 16.2 (61.2) |
16.8 (62.2) |
17.9 (64.2) |
19.2 (66.6) |
21.9 (71.4) |
24.9 (76.8) |
28.3 (82.9) |
28.6 (83.5) |
27.3 (81.1) |
23.7 (74.7) |
19.6 (67.3) |
17.0 (62.6) |
21.8 (71.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 12.5 (54.5) |
13.1 (55.6) |
14.0 (57.2) |
15.2 (59.4) |
17.7 (63.9) |
20.6 (69.1) |
23.5 (74.3) |
23.9 (75.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
19.7 (67.5) |
15.9 (60.6) |
13.3 (55.9) |
17.7 (63.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 8.8 (47.8) |
9.4 (48.9) |
10.1 (50.2) |
11.2 (52.2) |
13.4 (56.1) |
16.2 (61.2) |
18.7 (65.7) |
19.1 (66.4) |
18.3 (64.9) |
15.6 (60.1) |
12.2 (54.0) |
9.7 (49.5) |
13.6 (56.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −4.2 (24.4) |
1.0 (33.8) |
3.5 (38.3) |
1.0 (33.8) |
7.0 (44.6) |
10.0 (50.0) |
11.0 (51.8) |
11.0 (51.8) |
10.0 (50.0) |
7.0 (44.6) |
3.0 (37.4) |
4.0 (39.2) |
−4.2 (24.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 103.5 (4.07) |
98.7 (3.89) |
71.8 (2.83) |
62.2 (2.45) |
37.3 (1.47) |
13.9 (0.55) |
2.1 (0.08) |
2.5 (0.10) |
14.9 (0.59) |
65.1 (2.56) |
134.6 (5.30) |
129.3 (5.09) |
735.9 (28.97) |
| Average precipitation days | 11.2 | 11.4 | 10.1 | 9.3 | 6.1 | 3.7 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 3.1 | 8.0 | 11.1 | 12.0 | 87.6 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 80 | 81 | 78 | 78 | 76 | 74 | 70 | 72 | 73 | 76 | 79 | 81 | 76 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 169.2 | 166.9 | 231.7 | 251.7 | 298.9 | 306.8 | 344.0 | 330.7 | 275.6 | 238.2 | 180.6 | 166.9 | 2,960.7 |
| Source 1: NOAA[66] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Deutscher Wetterdienst (humidity, 1973–1993)[67] Meteo Climat (record highs and lows)[68] | |||||||||||||
Subdivisions
Historically, the city proper within the medina ("Old Town") was divided into 14 districts based upon the Berber clans who resettled Tangier after the departure of the English.
The current prefecture is divided administratively into the following:[69]
| Name | Geographic code | Type | Households | Population (2004) | Foreign population | Moroccan population | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assilah | 511.01.01. | Municipality | 6,245 | 28,217 | 66 | 28,151 | |
| Bni Makada | 511.01.03. | Arrondissement | 47,384 | 238,382 | 74 | 238,308 | |
| Charf-Mghogha | 511.01.05. | Arrondissement | 30,036 | 141,987 | 342 | 141,645 | |
| Charf-Souani | 511.01.06. | Arrondissement | 25,948 | 115,839 | 273 | 115,566 | |
| Tanger-Medina | 511.01.07. | Arrondissement | 40,929 | 173,477 | 2,323 | 171,154 | |
| Al Manzla | 511.03.01. | Rural commune | 555 | 3,031 | 0 | 3,031 | |
| Aquouass Briech | 511.03.03. | Rural commune | 787 | 4,132 | 3 | 4,129 | |
| Azzinate | 511.03.05. | Rural commune | 920 | 4,895 | 0 | 4,895 | |
| Dar Chaoui | 511.03.07. | Rural commune | 877 | 4,495 | 0 | 4,495 | 1,424 residents live in the centre, called Dar Chaoui; 3,071 residents live in rural areas. |
| Lkhaloua | 511.03.09. | Rural commune | 2,405 | 12,946 | 1 | 12,945 | |
| Sahel Chamali | 511.03.11. | Rural commune | 1,087 | 5,588 | 2 | 5,586 | |
| Sidi Lyamani | 511.03.13. | Rural commune | 1,883 | 10,895 | 1 | 10,894 | 1,101 residents live in the centre, called Sidi Lyamani; 9,794 residents live in rural areas. |
| Boukhalef | 511.81.03. | Rural commune | 3,657 | 18,699 | 4 | 18,695 | 3,187 residents live in the centre, called Gueznaia; 15,512 residents live in rural areas. |
Economy


Tangier is Morocco's second most important industrial centre after Casablanca. The industrial sectors are diversified: textile, chemical, mechanical, metallurgical and naval. Currently, the city has four industrial parks of which two have the status of free economic zone (see Tangier Free Zone).
Tangier's economy relies heavily on tourism. Seaside resorts have been increasing with projects funded by foreign investments. Real estate and construction companies have been investing heavily in tourist infrastructures. A bay delimiting the city centre extends for more than 7 km (4 mi). The years 2007 and 2008 were particularly important for the city because of the completion of large construction projects; these include the Tangier-Mediterranean port ("Tanger-Med") and its industrial parks, a 45,000-seat sports stadium, an expanded business district, and a renovated tourist infrastructure.
Tanger-Med, a new port 40 km (25 mi) outside Tangier proper, began construction in 2004 and became functional in 2007. Its site plays a key role in connecting maritime regions, as it is in a very critical position on the Strait of Gibraltar, which passes between Europe and Africa. The makeup of the new port is 85% transhipment 15% for domestic import and export activities.[70] The port is distinguished by its size, infrastructure, and efficiency in managing the flow of ships. Tanger-Med has linked Morocco to Europe's freight industry. It has also helped connect Morocco to countries in the Mediterranean, Africa, and America. The port has allowed Tangier to become a more globalised city with new international opportunities that will help facilitate economic growth.[71] The construction and operation of the port aimed to create 120,000 new jobs, 20,000 at the port and 100,000 resulting from growing economic activity.
Agriculture in the area of Tangier is tertiary and mainly cereal. The city is chiefly famed for tangerines, a kind of mandarin orange hybrid first grown in the orchards then once south of the medina, but it was never commonly exported. As early as 1900, local consumption had already outstripped supply and required imports from Tetuan and elsewhere.[72] Mass farming of tangerines instead began in Florida in the United States, where the first tree was introduced at Palatka by a Major Atway sometime before 1843.[73]
Artisanal trade in the medina ("Old City") specialises mainly in leather working, handicrafts made from wood and silver, traditional clothing, and Moroccan-style shoes.
The city has grown quickly due to rural exodus from other smaller cities and villages. The 2014 population is more than three-times larger than 32 years ago (850.000 inhabitants in 2014 vs. 250,000 in 1982). This phenomenon has resulted in the appearance of peripheral suburban districts, mainly inhabited by poor people, that often lack sufficient infrastructure.
Notable landmarks



The old town is still surrounded by the remains of what was once more than 1,829 metres (6,000 ft) of stone rampart. Most of it dates to the town's Portuguese occupation, with restoration work later undertaken at different times. Three major bastions were the Irish Tower (Bordj al-Naʿam), York Castle (Bordj dar al-Barud), and the Bordj al-Salam.[13]
- Dar el Makhzen (Sultan's palace), built on the site of the former English Upper Castle[13]
- Ancien Palais du Mendoub
- Perdicaris Parc, for Jon Perdicaris
- Sidi Bou Abib Mosque
- Tangier Grand Mosque
- Church of the Immaculate Conception
- Anglican Church of St. Andrew
- Plaza de Toros (bullring arena) on Rue de Tetouan
- Gran Teatro Cervantes
- Tangier American Legation Museum
- Museum of Moroccan Arts and Antiquities
- Museum of Contemporary Art
- Fondation Lorin
- Musée de Carmen-Macein
- Grand Socco, the grand souk and square
- Petit Socco, the little souk
- Casabarata Souk, a giant flea market
- Hotel Continental
- Rue Es-Siaghine
- Rue de la Liberté
- Avenue Pasteur
- Avenue Mohammed VI beach
- Parc de la Mendoubia
- Marshan Quarter (Quartier du Marshan)
- Charf Hill (Colline du Charf)
- Café Hafa
Transport
Railway lines connect Tanger-Ville railway station with Rabat, Casablanca and Marrakesh in the south, and with Fes and Oujda in the east. The service is operated by ONCF. In November 2018 Africa's first high-speed train, the Kenitra–Tangier high-speed rail line, was inaugurated, linking Tangier to Casablanca in 2 hours, 10 minutes. By 2020 improvements between Casablanca and Kenitra are planned to further reduce the journey to 1 hour and 30 minutes.
The Rabat–Tangier expressway connects Tangier to Fès via Rabat 250 km (155 mi), and Settat via Casablanca 330 km (205 mi) and Tanger-Med port. The Ibn Batouta International Airport (formerly known as Tangier-Boukhalef) is 15 km (9 mi) south-west of the city centre.
The new Tanger-Med Port is managed by the Danish firm A. P. Moller–Maersk Group and will free up the old port for tourist and recreational development.
Tangier's Ibn Batouta International Airport and the rail tunnel will serve as the gateway to the Moroccan Riviera, the littoral area between Tangier and Oujda. Traditionally, the northern coast was a rural stronghold, with some of the best beaches on the Mediterranean. It is slated for rapid urban development. The Ibn Batouta International Airport has been modernised to accommodate more flights. The biggest airline at the airport is Royal Air Maroc.
Education

Tangier offers four types of education systems: Arabic, French, Spanish and English. Each offers classes starting from pre-Kindergarten up to the 12th grade, as for German in the three last years of high school. The Baccalaureat, or high school diploma are the diplomas offered after clearing the 12 grades.
Many universities are inside and outside the city. Universities like the Institut Superieur International de Tourisme (ISIT), which grants diplomas, offer courses ranging from business administration to hotel management. The institute is one of the most prestigious tourism schools in the country. Other colleges such as the École Nationale de Commerce et de Gestion (ENCG-T) is among the biggest business schools in the country as well as École Nationale des Sciences appliquées (ENSA-T), a rising engineering school for applied sciences. University known as Abdelmaled Essaadi holding many what they mainly known as faculties; Law, Economics and Social sciences (FSJEST) and the FST of Technical Sciences. and the most attended Institut of ISTA of the OFPPT.
Primary education
There are more than a hundred Moroccan primary schools, dispersed across the city. Private and public schools, they offer education in Arabic, French and some school English until the 5th grade. Mathematics, Arts, Science Activities and nonreligious modules are commonly taught in the primary school.
International primary institutions
- American School of Tangier
- École Adrien Berchet (French primary school)
- Groupe scolaire Le Détroit (French school)
- Colegio Ramón y Cajal (Spanish primary school)
- English College of Tangier
International high schools
- American School of Tangier
- Lycée Regnault de Tanger (French high school)
- Groupe scolaire Le Détroit (French school)
- Instituto Español Severo Ochoa (Spanish high school)
- English College of Tangier
- Mohammed Fatih Turkish School of Tangier
- Tangier Anglo Moroccan School
Culture



"Never in my life have I observed anything more bizarre than the first sight of Tangier. It is a tale out of the Thousand and One Nights... A prodigious mix of races and costumes...This whole world moves about with an activity that seems feverish."
When Count de Mornay traveled to Morocco in 1832 to establish a treaty supportive of the recent French annexation of Algeria, he took along the Romantic painter Eugène Delacroix. Delacroix not only reveled in the orientalism of the place; he also took it as a new and living model for his works on classical antiquity: "The Greeks and Romans are here at my door, in the Arabs who wrap themselves in a white blanket and look like Cato or Brutus..."[75] He sketched and painted watercolours continuously, writing at the time "I am like a man in a dream, seeing things he fears will vanish from him." He returned to his sketches and memories of North Africa for the rest of his career, with 80 oil paintings like The Fanatics of Tangier and Women of Algiers becoming legendary and influential on artists such as Van Gogh, Gauguin, and Picasso. They were particularly struck by the quality of the light: to Cézanne, "All this luminous colour... seems... that it enters the eye like a glass of wine running into your gullet and it makes you drunk straight away".[76] Tangier subsequently became an obligatory stop for artists seeking to experience the colours and light he spoke of for themselves—with varying results. Matisse made several sojourns in Tangier, always staying at the Grand Hotel Villa de France. "I have found landscapes in Morocco," he claimed, "exactly as they are described in Delacroix's paintings." His students in turn had their own; the Californian artist Richard Diebenkorn was directly influenced by the haunting colours and rhythmic patterns of Matisse's Morocco paintings.
The multicultural placement of Muslim, Christian and Jewish communities and the foreign immigrants attracted writer George Orwell, writer and composer Paul Bowles, playwright Tennessee Williams, the beat writers William S. Burroughs, Allen Ginsberg and Jack Kerouac, the painter Brion Gysin and the music group the Rolling Stones, who all lived in or visited Tangier during different periods of the 20th century.
In the 1940s and until 1956 when the city was an International Zone, the city served as a playground for eccentric millionaires, a meeting place for secret agents and a variety of crooks and a mecca for speculators and gamblers, an Eldorado for the fun-loving "Haute Volée". During the Second World War the Office of Strategic Services operated out of Tangier for various operations in North Africa.[77]
Around the same time, a circle of writers emerged which was to have a profound and lasting literary influence. This included Paul Bowles, who lived and wrote for over half a century in the city, Tennessee Williams and Jean Genet as well as Mohamed Choukri (one of North Africa's most controversial and widely read authors), Abdeslam Boulaich, Larbi Layachi, Mohammed Mrabet and Ahmed Yacoubi. Among the best known works from this period is Choukri's For Bread Alone. Originally written in Classical Arabic, the English edition was the result of close collaboration with Bowles (who worked with Choukri to provide the translation and supplied the introduction). Tennessee Williams described it as "a true document of human desperation, shattering in its impact." Independently, William S. Burroughs lived in Tangier for four years and wrote Naked Lunch, whose locale of Interzone is an allusion to the city.
After several years of gradual disentanglement from Spanish and French colonial control, Morocco reintegrated the city of Tangier at the signing of the Tangier Protocol on 29 October 1956. Tangier remains a very popular tourist destination for cruise ships and day visitors from Spain and Gibraltar.
Language
Most of the inhabitants of Tangier speak a very distinguished Moroccan Arabic that differs from other Darija counterparts. The difference resides in pronunciation, tempo, grammar and a unique vocabulary, heavily influenced by Spanish and Riffian.
Written Arabic is used in government documentation and on road signs together with French. French is taught in primary schools and high schools and used in universities and large businesses. Spanish is well understood (mainly by Tangierian locals exclusively) and spoken fluently. English, on the other hand, has been and still is used in tourist sectors, British accent is more common due to Gibraltar proximity.
The autochthonous population of Tangiers has been declining drastically since the mid 2000s, as the locals especially of young generation moved to the once governing entities of Spain and Gibraltar. While the industrial sector is expanding constantly, the internal immigration from the south to north is increasing rapidly. As a consequence, the Tangierian dialect is losing its distinctiveness or being altered (in a recent study, social media has been depicted as one of these factors).
Nowadays, the Tangierian dialect is less heard in public places and southern Darija dialect is more prominent in the area, to the extent that some observers question if Tangier retains its identity as it was before.
Religion
Due to its Christian past, it remains a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church.[4] Originally, the city was part of the larger Roman province of Mauretania Caesariensis, which included much of North Africa. Later the area was subdivided, with the eastern part keeping the former name and the newer part receiving the name of Mauretania Tingitana. It is not known exactly at what period there may have been an episcopal see at Tangier in ancient times, but in the Middle Ages Tangier was used as a titular see (i.e., an honorific fiction for the appointment of curial and auxiliary bishops), placing it in Mauretania Tingitana. For the historical reasons given above, one official list of the Roman Curia places the see in Mauretania Caesarea.
Towards the end of the 3rd century, Tangier was the scene of the martyrdoms of St. Marcellus, mentioned in the Roman Martyrology on 30 October, and of St. Cassian, mentioned on 3 December.[4]
Under the Portuguese, the diocese of Tangier was a suffragan of Lisbon but, in 1570, it was united with the diocese of Ceuta. Six Bishops of Tangier from this period are known, the first—who did not reside in his see—in 1468. During the era of the French and Spanish protectorates over Morocco, Tangier was the residence of the Prefect Apostolic of Morocco, the mission having been founded on 28 November 1630 and entrusted to the Friars Minor. At the time, it had a Catholic church, several chapels, schools and a hospital. The Prefecture Apostolic was raised to the status of Vicariate Apostolic of Marocco on 14 April 1908. On 14 November 1956, it became the Archdiocese of Tangier.[78]
The city also has the Anglican church of Saint Andrew. Since independence in 1956, the European population has decreased substantially. In the years leading up to the First World War, European Christians formed almost a quarter the population of Tangier.[49][4] The city also is still home to a small community of Moroccan Christians, as well as a small group of foreign Roman Catholic and Protestant residents.[79][80]
Jews have a long history in Tangier, in the years leading up to the First World War, Jewish formed almost a quarter the population of Tangier.[49][4] According to the World Jewish Congress there were only 150 Moroccan Jews remaining in Tangier.[81]
Sport
The indigenous Tangierians regard football as the primary entertainment when it comes to sport-material. There are several football fields around the city. Tangier would have been one of the host cities for the 2015 Africa Cup of Nations football tournament, which would be played at the new Ibn Batouta Stadium and in other cities across Morocco, until Morocco was banned from participating the Africa Cup of Nations due to their denial.[82] Basketball comes the second most practised sport in Tangier. The city is known for their local teams IRT, Ajax Tanger, Juventus Tangier and so on.
National Cricket Stadium is the only top-class cricket stadium in Morocco. Stadium hosted its first International Tournament from 12 to 21 August 2002. Pakistan, South Africa and Sri Lanka competed in a 50-overs one day triangular series. The International Cricket Council has granted international status to the Tangier Cricket Stadium, official approval that will allow it to become North Africa's first international cricket venue.
Museums
Museum of the American Legation, whose building was granted to the United States in 1821 by the Sultan Moulay Suliman served as a consulate of the United States and a later legation, as well as a high traffic post for the intelligence agents of the Second World War and a Peace Corps training facility. Today, its courtyards and narrow corridors serve as an elaborate museum that demonstrates relations between the United States and Morocco and the Moroccan heritage, including a wing dedicated to Paul Bowles, where you can see the documents and photographs of the writer donated to the museum by the gallerist and friend of the writer Gloria Kirby in 2010.[83]
In popular culture
Espionage

Tangier has been reputed as a safe house for international spying activities.[84] Its position during the Cold War and during other spying periods of the 19th and 20th centuries is legendary.
Tangier acquired the reputation of a spying and smuggling centre and attracted foreign capital due to political neutrality and commercial liberty at that time. It was via a British bank in Tangier that the Bank of England in 1943 for the first time obtained samples of the high-quality forged British currency produced by the Nazis in "Operation Bernhard".
The city has also been a subject for many spy fiction books and films (see Tangier in popular culture).
Notable people
- Ibn Battuta – Moroccan scholar and traveler who went on a worldwide quest.
- Yasser Harrak – Writer and human rights activist.
- Ralph Benmergui – Canadian TV and radio host at the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation
- Paul Bowles – American writer, composer and ethnomusicologist
- William S. Burroughs – Beat Generation writer, wrote Naked Lunch during the 1950s in Tangier.
- Alexandre Rey Colaço – Portuguese pianist
- Ion Perdicaris – Greek-American became the unofficial head of Tangier's foreign community
- Karim Debbagh – Moroccan film producer
- Roger Elliott – first British Governor of Gibraltar
- Antonio Fuentes – Painter described as the 'Picasso of Tangier'
- Abdullah al-Ghumari – Muslim cleric
- Sanaa Hamri – Moroccan music video director.
- Walter Harris - British writer
- Emmanuel Hocquard – French poet
- Jean-Luc Mélenchon – French politician, currently MEP
- Claude-Jean Philippe – French film critic
- Alexander Spotswood – American Lieutenant-Colonel and Lieutenant Governor of Virginia
- Heinz Tietjen – German music composer
- Abderrahmane Youssoufi – former Prime Minister of Morocco
- Ahmed Yacoubi – international painter extraordinaire
- Helena Maleno – human rights defender, journalist and writer
Twin towns – sister cities
Gallery
.jpg.webp) Panoramic view of Tangier
Panoramic view of Tangier The Palace of Justice, c. 1900
The Palace of Justice, c. 1900 The Palace of Justice, 2015
The Palace of Justice, 2015 Jewish Cemetery
Jewish Cemetery Souk
Souk City walls
City walls
See also
- History of Morocco
- List of cities in Morocco
- Tingis & Mauretania Tingitana
- List of Colonial Heads of Tangier
- English Tangier
- Tangier International Zone
References
Citations
- "Note de présentation des premiers résultats du Recensement Général de la Population et de l'Habitat 2014" (in French). High Commission for Planning. 20 March 2015. p. 8. Retrieved 9 October 2017.
- Ghaki (2015), p. 67.
- Head & al. (1911).
- Cath. Enc. (1913).
- Ruiz (2012), p. 208.
- Hartley (2007), p. 345.
- Davies (2009), p. 119.
- Roller (2006), p. 34.
- Gómez Bellard, Carlos; et al. (January 2008), "Rural Landscapes of the Punic World", Monographs in Mediterranean Archaeology, No. 11, London: Equinox, Ch. 5, p. 17.
- Meakin (1899), p. 10.
- Amitay (2011).
- L. Mestrius Plutarchus, "15: Sertorius", Parallel Lives, §9.
- Lévi-Provençal (1936), p. 650.
- Enc. Brit. (1878).
- Procopius, History of the Wars, Bk. III.
- Finlayson (1992), p. 26.
- Encyclopaedia Britannica, Vol. XVIII (11th ed.), s.v. "Morocco", p. 855.
- Akram (1980), p. 5.
- Collins (2003).
- Akram (1980), p. 9.
- Gerli (2003).
- Brett (2017).
- Ibn Abd al-Hakam (1922), Torrey, Charles Cutler (ed.), The History of the Conquest of Egypt, North Africa, and Spain..., New Haven: Yale University Press.
- Civantos (2017), p. 115.
- Benabbès, Ahmed (2005), "Les Premiers Raids Arabes en Numidie Byzantine: Questions Toponymiques", Identités et Cultures dans l'Algérie Antique, Rouen: University of Rouen. (in French)
- Baedeker (1901), p. 426.
- Brett (2017), p. 193.
- Ilahiane (2010), s.v. "Barghwata".
- Brett (2017), p. 194.
- Blankinship (1994), pp. 208–9.
- Lévi-Provençal (1936), p. 651.
- Ilahiane (2010), s.v. "Ibn Battuta Muhammad ibn ʿAbd Allah".
- Elbl (2012).
- B. W. Diffie, Prelude to Empire, Portugal Overseas before Henry the Navigator, University of Nebraska Press, Ann Arbor, 1960, pp. 83–90.
- Elbl (2013), p. 10.
- Winston S. Churchill, Marlborough: His Life and Times, Book I (University of Chicago Press: Chicago, 1933) p. 35.
- Elbl (2013), p. 12.
- Elbl (2013), pp. 12–13.
- Finlayson (1992), pp. 26–27.
- Articles of Peace Concluded and Agreed between His Excellency the Lord Bellasyse, His Majesties Governour of His City and Garrison of Tangier in Affrica, &c. and Cidi Hamlet Hader Ben Ali Gayland, Prince of VVest-Barbary, &c., London, 2 April 1666.
- Lincoln, Margarette (2014), "Samuel Pepys and Tangier, 1662–1684", Huntington Library Quarterly, 77, pp. 417–434, doi:10.1525/hlq.2014.77.4.417.
- Routh (1912).
- Elbl (2009).
- Elbl (2013), Ch. 8.
- Finlayson (1992), p. 28.
- Elbl (2013), pp. 13–14.
- Finlayson (1992), p. 31.
- Lévi-Provençal (1936), p. 652.
- Enc. Brit. (1911).
- Power, Faith and Fantasy: In the beginning, for America, was the Middle East Archived 2007-04-03 at the Wayback Machine, Matt Buckingham, week, February 14, 2007.
- "'Abd ar-Rasham". Encyclopædia Britannica. I: A-Ak – Bayes (15th ed.). Chicago, IL: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. 2010. pp. 17. ISBN 978-1-59339-837-8.
- Elbl (2013), p. 15.
- Bensoussan, David (2010). Il Était Une Fois Le Maroc: Témoignages Du Passé Judéo-Marocain (in French). Québec: Éditions Du Lys. ISBN 978-2-922505-21-4.
- League of Nations Treaty Series, vol. 28, pp. 542–631.
- Text in League on Nations Treaty Series, vol. 87, pp. 212–251.
- <Ceballos, Leopoldo, Historia de Tánger, Almuzara, 2009, pp. 10-11 and 23-24>
- Payne, S.G. The Franco Regime, 1936–1975. Madison: University of Wisconsin, 1987. 268.
- Payne 1987, p. 274, note 28.
- Benton, Assistant Secretary (October 21, 1945). "Reestablishment of the International Regime in Tangier". Department of State Bulletin. 330. XIII: 613–618.
- "Final Declaration of the International Conference in Tangier and annexed Protocol. Signed at Tangier, on 29 October 1956 [1957] UNTSer 130; 263 UNTS 165". 1956.
- "Tangier(s)", Jewish Virtual Library, archived from the original on 18 January 2012.
- Davies (2009), p. 120.
- Tremlett, Giles (15 December 2003), "Spain and Morocco Plan Tunnel Link", The Guardian.
- Leadbeater, Chris (31 May 2018), "Will a Tunnel from Spain to Africa Ever Be Built—And Who Would Use It?", The Telegraph.
- Valor, G. Ballester. "Synop report summary".
- "Tangier Climate Normals 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved October 14, 2016.
- "Klimatafel von Tanger / Marokko" (PDF). Baseline climate means (1961–1990) from stations all over the world (in German). Deutscher Wetterdienst. Retrieved October 14, 2016.
- "Station Tangier Airport" (in French). Météo Climat. Retrieved October 14, 2016.
- "Recensement général de la population et de l'habitat de 2004" (PDF). Haut-commissariat au Plan, Lavieeco.com. Retrieved 27 April 2012.
- César Ducruet, Fatima Mohamed-Chérif, Najib Cherfaoui. Maghreb Port Cities in Transition: The Case of Tangier (n.d.): n. pag. Web.
- Ouail El Im Rani Et Al., International Journal of Research in Management, Economics and Commerce, ISSN 2250-057X, Impact Factor: 6.384, Volume 06 Issue 07, July 2016, Page 73-81. Tangier Med Port: What Role for the Moroccan Economy and the International Trade? (n.d.): n. page. Web.
- Meakin (1901), p. 107.
- Hume (1913), p. 101.
- Noon, Patrick; et al. (2015), Delacroix and the Rise of Modern Art, New Haven: Yale University Press, p. 25, ISBN 978-1-85709-575-3.
- Wellington, Hubert, ed. (1980), The Journal of Eugène Delacroix, Cornell University Press, p. xv.
- Prodger, Michael (5 February 2016). "Damnation, Dante and Decadence: Why Eugene Delacroix is making a hero's return". The Guardian. Retrieved 30 April 2016.
- The American Legation at Tangier, Morocco Archived January 24, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- Annuario Pontificio 2010, p. 721
- MOROCCO 2018 INTERNATIONAL RELIGIOUS FREEDOM REPORT
- Pope Francis’ Visit to Morocco Raises Hopes for Its Christians
- Jewish in Morocco
- Morocco then South Africa to host Cups. FIFA.com (2011-01-29). Retrieved on 2011-06-04.
- "PAUL BOWLES WING: Tangier American Legation (TALIM)". www.paulbowles.org. Retrieved 2019-03-27.
- Pennell, C. R. (1999). "Wars: The Second World War in Morocco". Morocco since 1830: A History. New York University Press. p. 257. ISBN 978-1-85065-426-1.
- "Un jumelage Tanger - Phuket (Thaïlande) en projet". bladi.net (in French). Bladi.net. 2016-02-19. Retrieved 2020-10-19.
- "Algeciras y Tánger, hermanadas en políticas turísticas y culturales". lavozdigital.es (in Spanish). La Voz de Cádiz. 2018-09-24. Retrieved 2020-10-19.
- "Tanger et Da Nang liées par un accord de jumelage". lematin.ma (in French). Le Matin. 2019-03-29. Retrieved 2020-10-19.
- "Jumelage et Pactes d'amitié". puteaux.fr (in French). Puteaux. Retrieved 2020-10-22.
- "Decentralized international cooperation". saint-josse.irisnet.be. Saint-Josse-ten-Noode. 2019-05-21. Retrieved 2020-10-19.
Bibliography
- , 'Encyclopædia Britannica, 9th ed., Vol. XXIII, New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1878, p. 46.
- , 'Encyclopædia Britannica, 11th ed., Vol. XXVI, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1911, pp. 397–8.
- Akram, Agha Ibrahim (1980), The Muslim Conquest of Spain, Rawalpindi: Army Education Press.
- Amitay, Ory (2011), "Procopius of Caesarea and the Girgashite Diaspora", Journal for the Study of the Pseudoepigrapha, Vol. 20, No. 4, pp. 257–276, CiteSeerX 10.1.1.878.3222.
- Baedeker, Karl (1901), "Tangier", Spain and Portugal: Handbook for Travellers (2nd ed.), Leipzig: Karl Baedeker.
- Blankinship, Khalid Yahya (1994), The End of the Jihad State, Albany: SUNY Press, ISBN 978-0-7914-1827-7.
- Brett, Michael (2017), "Conversion of the Berbers to Islam", Islamisation: Comparative Perspectives from History, Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, pp. 189–198, ISBN 9781474417136.
- Civantos, Christina (2017), The Afterlife of al-Andalus: Muslim Iberia in Contemporary Arab and Hispanic Narratives, Albany: State University of New York Press, ISBN 9781438466712.
- Collins, Roger (2003), Count Julian, ISBN 9780415939188 & "Ṭarīq ibn Ziyād", Medieval Iberia, New York: Routledge, 2003, ISBN 9780415939188.
- Davies, Ethel (2009), "Tangier", North Africa: The Roman Coast, Chalfont St Peter: Bradt Travel Guides, pp. 119 ff, ISBN 9781841622873.
- Elbl, Martin Malcolm (2009), "(Re)claiming Walls: The Fortified Médina of Tangier under Portuguese Rule (1471–1661) and as a Modern Heritage Artefact", Portuguese Studies Review, No. 15, pp. 103–192.
- Elbl, Martin Malcolm (2012), "Tangier's Qasba Before the Trace Italienne Citadel of 1558–1566: The 'Virtual' Archaeology of a Vanished Islamic and Portuguese Fortress", Portuguese Studies Review, No. 17, pp. 1–44.
- Elbl, Martin Malcolm (2013), Portuguese Tangier (1471–1662): Colonial Urban Fabric as Cross-Cultural Skeleton, Peterborough: Baywolf Press, ISBN 9780921437505.
- Finlayson, Iain (1992), Tangier: City of the Dream, London: Tauris Parke, ISBN 9781780769264.
- Gerli, E. Michael (2003), "Mūsā ibn Nusayr", Medieval Iberia, New York: Routledge, ISBN 9780415939188.
- Ghaki, Mansour (2015), "Toponymie et Onomastique Libyques: L'Apport de l'Écriture Punique/Néopunique" (PDF), La Lingua nella Vita e la Vita della Lingua: Itinerari e Percorsi degli Studi Berberi, Studi Africanistici: Quaderni di Studi Berberi e Libico-Berberi, No. 4, Naples: Unior, pp. 65–71, ISBN 978-88-6719-125-3, ISSN 2283-5636. (in French)
- Hartley, James (2007), "Tangier", Cities of the Middle East and North Africa, Santa Barbara: ABC-CLIO, pp. 345–347, ISBN 9781576079195.
- Head, Barclay; et al. (1911), "Mauretania", Historia Numorum (2nd ed.), Oxford: Clarendon Press, pp. 887 ff.
- Hume, H. Harold (1913), Citrus Fruits and Their Culture, New York: O. Judd Co.
- Ilahiane, Hsain (2010), Historical Dictionary of the Berbers (2nd ed.), Lanham: Rowman & Littlefeld, ISBN 9781442281820.
- Lévi-Provençal, Évariste (1936), "Tangier", Encyclopaedia of Islam, Vol. IV (1st ed.), Leiden: E.J. Brill, pp. 650–652.
- Meakin, Budgett (1899), The Moorish Empire, London: Swan Sonnenschein & Co.
- Meakin, Budgett (1901), The Land of the Moors: A Comprehensive Description, London: Swan Sonnenschein & Co.
- Pétridés, Sophron (1913), "Tingis", Catholic Encyclopedia, XIV, New York: Encyclopedia Press.
- Roller, Duane W. (2006), Through the Pillars of Herakles: Greco-Roman Exploration of the Atlantic, Abington: Routledge, ISBN 9781134192328.
- Routh, Enid M.G. (1912), Tangier: England's Lost Atlantic Outpost, London: John Murray.
- Ruiz, Ana (2012), Medina Mayrit: The Origins of Madrid, New York: Algora Publishing, ISBN 9780875869254.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tangier. |
| Wikisource has the text of The New Student's Reference Work article "Tangier". |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Tangier. |
- Official site of The Tangier American Legation Institute for Moroccan Studies
- History, description, and images of Tangier on Archnet
- Tangier photo gallery
- Navigating Tangier's Labyrinth – slideshow by The New York Times
- "Tangier". Islamic Cultural Heritage Database. Istanbul: Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, Research Centre for Islamic History, Art and Culture. Archived from the original on 2013-04-27.
- Tangier on Archnet – History, sites, photos (historic and contemporary), and media
- Old maps of Tangier, Historic Cities site




%252C_Algeria_04966r.jpg.webp)