Solar eclipse of March 4, 1802
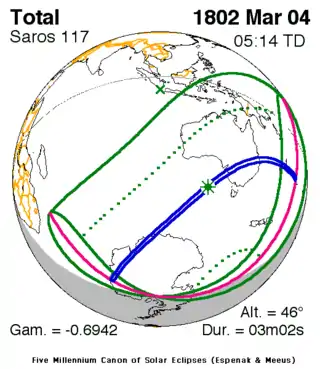
A total solar eclipse occurred on March 4, 1802. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The eclipse was visible in Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, Australia, New Zealand and Antarctica, while the totality was seen in Australia and Antarctica.[1]
| Solar eclipse of March 4, 1802 | |
|---|---|
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | -0.6943 |
| Magnitude | 1.0428 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 182 sec (3 m 2 s) |
| Coordinates | 44°S 131.5°E |
| Max. width of band | 196 km (122 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 5:14:29 |
| References | |
| Saros | 117 (57 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9045 |
References
- "Solar eclipse of March 4, 1802". NASA. Retrieved June 15, 2012.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
.jpg.webp)


