Spanish missions in Baja California
The Spanish missions in Baja California were a large number of religious outposts established by Catholic religious orders, the Jesuits, the Franciscans and the Dominicans, between 1683 and 1834 to spread the Christian doctrine among the Native Americans or Indians living on the Baja California peninsula. The missions gave Spain a valuable toehold in the frontier land, and introduced European livestock, fruits, vegetables, and industry into the region. The Indians were severely impacted by the introduction of European diseases such as smallpox and measles and by 1800 their numbers were a fraction of what they had been before the arrival of the Spanish.
Part of a series on |
| Spanish missions in the Americas of the Catholic Church |
|---|
 |
| Missions in North America |
| Missions in South America |
| Related topics |
|
|


Mexico secularized all missions in its territory in 1834 and the last of the missionaries departed in 1840. Some of the mission churches survive and are still in use.[1]
Background
As early as the voyages of Christopher Columbus, the Kingdom of Spain sought to establish missions to convert pagans to Catholicism in Nueva España (New Spain). New Spain consisted of the Caribbean, Mexico, and portions of what is now the Southwestern United States. To facilitate colonization, the Catholic Church awarded these lands to Spain.
In addition to the presidio (royal fort) and pueblo (town), the misión was one of three major agencies employed by the Spanish crown to extend its borders and consolidate its colonial territories. Asistencias ("sub-missions" or "contributing chapels") were small-scale missions that regularly conducted Catholic religious services on days of obligation, but lacked a resident priest. Smaller sites called visitas ("visiting chapels") also lacked a resident priest, and were often attended only sporadically. Since 1493, the Crown of Spain had maintained missions throughout Nueva España.
Each frontier station was forced to be self-supporting, as existing means of supply were inadequate to maintain a colony of any size. To sustain a mission, the padres needed colonists or converted Indigenous Americans, called neophytes, to cultivate crops and tend livestock in the volume needed to support a fair-sized establishment. Scarcity of imported materials and lack of skilled laborers compelled the Fathers to employ simple building materials and methods. Although the Spanish hierarchy considered the missions temporary ventures, individual settlement development was not based simply on "priestly whim." The founding of a mission followed longstanding rules and procedures. The paperwork involved required months, sometimes years of correspondence, and demanded the attention of virtually every level of the bureaucracy. Once empowered to erect a mission in a given area, the men assigned to it chose a specific site that featured a good water supply, proximity to a population of indigenous peoples, and arable land. The padres, their military escort and often converted mainland indigenous people or mestizos initially fashioned defendable shelters, from which a base was established and the mission could grow.
Construction of the iglesia (church) constituted the focus of the settlement, and created the center of the community. The majority of mission sanctuaries were oriented on a roughly east–west axis to take the best advantage of the sun's position for interior illumination. The workshops, kitchens, living quarters, storerooms, and other ancillary chambers were usually grouped in the form of a quadrangle, inside which religious celebrations and other events often took place.
The Native Americans
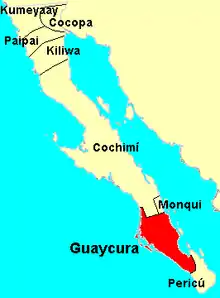
Indian peoples encountered by the Spanish missionaries in Baja California (from north to south) were the Kumeyaay, Cocopah, Pai Pai,[2] Kiliwa,[3] Cochimi, Monqui, Guaycura, and Pericu.[4] The Kumeyaay and Cocapah practiced limited agriculture, but the majority of the Baja Californians were nomadic or semi-nomadic hunter-gatherers who eked out a living under difficult desert conditions and scarcity of fresh water.
In a policy followed throughout much of Latin America called reductions, the missionaries concentrated the Indians at or near the mission for religious instruction and training to become sedentary farmers and stock herders. Their goal was to create a self-sufficient theocracy in which the missionary, usually supported by Spanish soldiers and laymen, attempted to rule over every facet of the Indian's religious and secular lives.[5] The Indigenous peoples were housed often by gender, forcibly converted to Catholicism and acculturated to the Spanish Empire within the confines of the mission. Recalcitrant indigenous peoples often ran away or revolted, and many missions maintained a precarious existence during the colonial era. Use of firearms, corporal punishment in the form of whippings and religious ritual and psychological punishments were all methods employed by the missionaries to maintain and expand control.[6] There were instances of armed resistance by the Indians against the missions, notably the Pericue revolt of 1734-1737, and Indians at the missions frequently ran away to escape the religious and labor regime forced on them by the missionaries or sabotaged the missionary's efforts by passive resistance.[7]
At the time of first contact with the Spanish, the Native Americans living in Baja California may have numbered as many as 60,000. By 1762, their numbers had fallen to 21,000 and by 1800 to 5,900. The primary reason for the decline was recurrent epidemics of European diseases, primarily smallpox, measles, and typhus. The spread of disease was facilitated by the missionary's practice of congregating the population near the mission. Endemic Syphilis resulted in higher child mortality and a reduced birth rate. By the early 19th century, the tribes of Baja California were culturally extinct, except for the Kumeyaay, Cocopah, and Pai Pai.[8]
Missions in Baja California
.jpg.webp)
Fortún Jiménez de Bertadoña discovered the Baja California Peninsula in early 1534. However, it was Hernán Cortés who recognized the peninsula as the "Island of California" in May 1535, and is therefore officially credited with the discovery. In January 1683, the Spanish government chartered an expedition consisting of three ships to transport a contingent of 200 men to the southern tip of Baja California. Under the command of the governor of Sinaloa, Isidoro de Atondo y Antillón, and accompanied by Jesuit priest Eusebio Francisco Kino, the ships made landfall in La Paz. The landing party was eventually forced to abandon its initial settlement due to the hostile response on the part of the natives. The missionaries attempted to establish a settlement near present-day Loreto, which they named Misión San Bruno but failed for lack of supplies.[9] Kino went on to establish a number of missions in the Pimería Alta, now located in southern Arizona, USA and Sonora, Mexico.
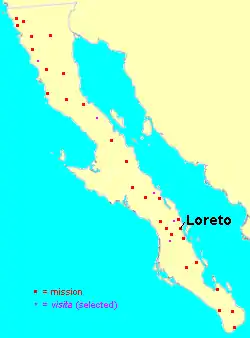
The Jesuit priest Juan María de Salvatierra eventually managed to establish the first permanent Spanish settlement in Baja California, the Misión Nuestra Señora de Loreto Conchó. Founded on October 19, 1697, the mission become the religious center of the peninsula and administrative capital of Las Californias. From there, other Jesuits went out to establish other settlements throughout the lower two-thirds of the peninsula, founding 17 missions and several visitas (sub-missions) between 1697 and 1767.[10]
Unlike the mainland settlements that were designed to be self-sustaining enterprises, the remote and harsh conditions on the peninsula made it all but impossible to build and maintain these missions without ongoing assistance from the mainland. Supply lines from across the Gulf of California, including from the missions and ranches of Padre Eusebio Kino on the mainland to the Port of Guaymas, played a crucial role in keeping the Baja California mission system intact.
During the sixty years that the Jesuits were permitted to work among the natives of California, 56 members of the Society of Jesus came to the Baja California peninsula, of whom 16 died at their posts (two as martyrs). Fifteen priests and one lay brother survived the hardships, only to be subjected to enforcement of the decree launched against the Society by King Carlos III of Spain.[11] It was rumored that the Jesuit priests had amassed a fortune on the peninsula and were becoming very powerful. On February 3, 1768 the King ordered the Jesuits forcibly expelled from the Americas and returned to the home country. Gaspar de Portolà was appointed Governor of Las Californias, with orders to supervise the Jesuit expulsion and oversee the installation of replacement Franciscan priests.[12]
The Franciscans, under the leadership of Fray Junípero Serra, took charge of the missions and closed or consolidated several of the existing installations. A total of 39 Friars Minor toiled on the peninsula during the five years and five months of Franciscan rule. Four of them died, 10 were transferred to new northern missions, and the remainder returned to Europe.[13]
Governor Portolà was put in command of an expedition to travel north and establish new settlements at San Diego and Monterey. Serra went along as leader of the missionaries, to establish missions in those places.[14] On the way north, Serra founded Misión San Fernando Rey de España de Velicatá. Francisco Palóu was left in charge of the existing missions, and founded the Visita de la Presentación in 1769.
Representatives of the Dominican order arrived in 1772, and by 1800, had established nine more missions in northern Baja, all the while continuing with the administration of the former Jesuit missions. The peninsula was divided into two separate entities in 1804, with the southern one having the seat of government established in the Port of Loreto. In 1810, Mexico sought to end Spanish colonial rule, gaining her independence in 1821, after which Mexican President Guadalupe Victoria named Lt. Col. José María Echeandía governor of Baja California Sur and divided it into four separate municipios (municipalities). The capital was moved to La Paz in 1830, after Loreto was partially destroyed by heavy rains. In 1833, after Baja California was designated as a federal territory, the governor formally put an end to the mission system by converting the missions into parish churches.
In Geographical Order, North to South
Baja California (state)
- Misión El Descanso (Misión San Miguel la Nueva), in Rosarito 32°12′18.65″N 116°54′19.61″W
- Misión de Nuestra Señora de Guadalupe del Norte, in Guadalupe 32°5′42.65″N 116°34′29.18″W
- Misión San Miguel Arcángel de la Frontera, in Ensenada 32°5′38.07″N 116°51′15.72″W
- Misión Santa Catarina Virgen y Mártir, in Ensenada 31°49′38.00″N 115°49′16.00″W
- Misión Santo Tomás de Aquino 31°33′2.93″N 116°24′34.92″W
- Misión San Vicente Ferrer 31°16′12.83″N 116°11′7.83″W
- Misión Santo Domingo de la Frontera, near Colonia Vicente Guerrero 30°46′18.62″N 115°56′14.61″W
- Misión San Pedro Mártir de Verona 30°44′55.27″N 115°15′58.07″W
- Misión Nuestra Señora del Santísimo Rosario de Viñadaco, near El Rosario 30°2′28.38″N 115°44′20.31″W
- Misión San Fernando Rey de España de Velicatá 29°58′16.19″N 115°14′12.02″W
- Visita de Calamajué (Intended mission, visiting station) 29°25′16.30″N 114°11′42.40″W
- Misión Santa María de los Ángeles, near Cataviña (extremely isolated) 30°43′55.50″N 114°32′50.20″W
- Misión San Francisco Borja (restored chapel) 28°44′39.85″N 113°45′14.56″W
- Misión Santa Gertrudis 28°3′4.05″N 113°5′7.20″W
Baja California Sur
- Misión San Ignacio Kadakaamán, in San Ignacio 27°17′1.66″N 112°53′54.94″W
- Misión Nuestra Señora de Guadalupe de Huasinapi, in Guadalupe 26°55′9.50″N 112°24′20.60″W[15]
- Visita de San José de Magdalena, near San José Magdalena 27°3′40.33″N 112°13′24.87″W
- Misión Santa Rosalía de Mulegé, in Mulegé 26°53′7.29″N 111°59′9.00″W
- Visita de San Juan Bautista Londó founded in 1699
- Misión San Bruno 26°13′57″N 111°23′53″W
- Misión La Purísima Concepción de Cadegomó, (final location) in La Purísima 26°11′25.87″N 112°4′22.95″W[16]
- Misión San Jose de Comondú, near San José de Comondú 26°03′34.59″N 111°49′20.41″W (final location)[17]
- Misión de Nuestra Señora de Loreto Conchó, in Loreto 26°00′37″N 111°20′36″W
- Misión San Francisco Javier de Viggé-Biaundó 25°51′38″N 111°32′37″W in San Javier
- Misión San Juan Bautista Malibat (Misión Liguí), in Liguí 25°44′22″N 111°15′51″W
- Misión Nuestra Señora de los Dolores del Sur Chillá, near La Presa 24°53′14.02″N 111°1′49.81″W[18]
- Misión San Luis Gonzaga Chiriyaqui, 10 miles (16 km) south then east of Ciudad Constitución 24°54′28.50″N 111°17′27.77″W[19]
- Misión de Nuestra Señora del Pilar de La Paz Airapí, in La Paz 24°9′42.02″N 110°18′46.87″W[20]
- Misión Santa Rosa de las Palmas (the first mission site, also known as Misión Todos Santos), in Todos Santos 23°27′37.30″N 110°13′8.31″W[21]
- Misión Santiago de Los Coras, in Santiago 23°28′32.25″N 109°43′2.75″W[22]
- Misión Estero de las Palmas de San José del Cabo Añuití, in San José del Cabo 23°3′43.56″N 109°41′44.17″W[23]
Jesuit Establishments (1684–1767)
- Misión San Bruno founded in 1684, closed 1685.
- Misión de Nuestra Señora de Loreto Conchó founded in 1697
- Visita de San Juan Bautista Londó founded in 1699
- Misión San Francisco Javier de Viggé-Biaundó founded in 1699
- Misión San Juan Bautista Malibat (Misión Liguí) founded in 1705
- Misión Santa Rosalía de Mulegé founded in 1705
- Misión San Jose de Comondú founded in 1708
- Misión La Purísima Concepción de Cadegomó founded in 1720
- Misión de Nuestra Señora del Pilar de La Paz Airapí founded in 1720
- Misión Nuestra Señora de Guadalupe de Huasinapi founded in 1720
- Misión Santiago de Los Coras founded in 1721
- Misión Nuestra Señora de los Dolores del Sur Chillá founded in 1721
- Misión San Ignacio Kadakaamán founded in 1728
- Misión Estero de las Palmas de San José del Cabo Añuití founded in 1730
- Misión Santa Rosa de las Palmas (Misión Todos Santos) founded in 1733
- Misión San Luis Gonzaga Chiriyaqui founded in 1740
- Misión Santa Gertrudis founded in 1752
- Misión San Francisco Borja founded in 1762
- Visita de Calamajué (Visita de Calamyget) founded in 1766
- Misión Santa María de los Ángeles founded in 1767
Franciscan Establishments (1768–1773)
- Misión San Fernando Rey de España de Velicatá founded in 1769
- Visita de la Presentación founded in 1769
Dominican Establishments (1774–1834)
- Misión Nuestra Señora del Santísimo Rosario de Viñadaco founded in 1774
- Visita de San José de Magdalena founded in 1774
- Misión Santo Domingo de la Frontera founded in 1775
- Misión San Vicente Ferrer founded in 1780
- Misión San Miguel Arcángel de la Frontera founded in 1787
- Misión Santo Tomás de Aquino founded in 1791
- Misión San Pedro Mártir de Verona founded in 1794
- Misión Santa Catarina Virgen y Mártir founded in 1797
- Visita de San Telmo founded in 1798
- Misión El Descanso (Misión San Miguel la Nueva) founded in 1817
- Misión de Nuestra Señora de Guadalupe del Norte founded in 1834
Father-Presidents of the Baja California Mission System
- Father Junípero Serra (1769–1784)
- Father Francisco Palóu (acting) (1784–1785)
- Father Fermín Francisco de Lasuén (1785–1803)
- Father Pedro Estévan Tápis (1803–1812)
- Father José Francisco de Paula Señan (1812–1815)
- Father Mariano Payeras (1815–1820)
- Father José Francisco de Paula Señan (1820–1823)
- Father Vicente Francisco de Sarría (1823–1824)
- Father Narciso Durán (1824–1827)
- Father José Bernardo Sánchez (1827–1830)
- Father García Diego (1831–1835)
- Father José María González Rubio (1835–1843)
- Father José Anzar (1843–?)
The "Father-Presidente" was the head of the Catholic missions in Alta and Baja California. He was appointed by the apostolic college in Mexico City until 1812, when the position became known as the "Commissary Prefect" who was appointed by the Commissary General of the Indies (a Franciscan residing in Spain). Beginning in 1831, separate individuals were elected to oversee Upper and Lower California.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Missions in Baja California. |
References
- Burckhalter, David, Sedgwick, Mina, and Fontana, Bernard L. (2013), Baja California Missions, Tucson: University of Arizona Press, p.27. Downloaded from Project Muse.
- Winter, Werner. 1967. "The Identity of the Paipai (Akwa'ala)." In Studies in Southwestern Ethnolinguistics: Meaning and History in the Language of the American Southwest, edited by Dell H. Hymes and William E. Bittle, pp. 371–378. Mouton, The Hague.
- Meigs, Peveril, "The Kiliwa Indians of Lower California". Iberoamerica No. 15. University of California, Berkeley.
- Schmal, John P., Indigenous Baja, http://www.houstonculture.org/mexico/baja.html, accessed 1 Apr 2016
- Burckhalter, David, Sedgwick, Mina, and Fontana, Bernard L. (2013), Baja California Missions, Tucson: University of Arizona Press, p. 7. Downloaded from Project Muse.
- Jackson, Robert H., 1981, Epidemic Disease and Population Decline in the Baja California Missions, 1697-1834. Southern California Quarterly 63:308-346. Downloaded from JSTOR.
- Jackson, Robert H. (1986), "Patterns of Demographic Change in the Missions of Southern Baja California", Journal of California and Great Basin Anthropology, Vol. 8, NO. 2, pp. 173-279. Downloaded from JSTOR.
- Jackson, Robert H. (1981), "Epidemic Disease and Population Decline in the Baja California Missions, 1697-1834", Southern California Quarterly, Vol. 63, No. 4, pp 308-341. Downloaded from JSTOR.
- Burckhalter et al, p. 17; Bolton, 1936
- Crosby, Harry W. (1994), Antigua California, Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press, pp. 20-26, p.179
- Robert Michael Van Handel, "The Jesuit and Franciscan Missions in Baja California." M.A. thesis. University of California, Santa Barbara, 1991.
- Engelhardt, pp. 275-77
- Robert Michael Van Handel, "The Jesuit and Franciscan Missions in Baja California." M.A. thesis. University of California, Santa Barbara, 1991.
- Engelhardt, pp. 3-18
- http://vivabaja.com/missions4/ (Guadalupe) accessed Jan 2017
- http://vivabaja.com/missions4/ (La Purísima) accessed Jan 2017
- http://vivabaja.com/missions4/ (Comondú) accessed Jan 2017
- http://vivabaja.com/missions4/ (Los Dolores Chilla) accessed Jan 2017
- http://vivabaja.com/missions4/ (San Luis Gonzaga) accessed Jan 2017)
- http://www.visitmexico.com/es/cultura-e-historia-en-el-corazon-de-la-paz (Cathedral built on Jesuit mission site) accessed Jan 2017
- http://vivabaja.com/missions4/ (Santa Rosa de las Palmas) accessed Jan 2017
- http://vivabaja.com/missions4/ (Santiago) and https://www.google.com/maps/search/maps/@23.4754437,-109.7184842,284m/data=!3m1!1e3 (map label) accessed Jan 2017
- http://vivabaja.com/missions4/ (San José del Cabo) and Google Earth (map label at GPS coordinates) accessed Jan 2017
Further reading
- Bolton, Herbert Eugene. 1936. Rim of Christendom. Macmillan, New York.
- Burrus, Ernest J. 1954. Kino Reports to Headquarters: Correspondence of Eusebio F. Kino, S.J., from New Spain with Rome. Instituto Historicum S.J., Rome.
- Burrus, Ernest J. 1965. Kino Writes to the Duchess. Jesuit Historical Institute, Rome.
- Mathes, W. Michael. 1969. First from the Gulf to the Pacific: The Diary of the Kino-Atondo Peninsular Expedition, December 14, 1684-January 13, 1685. Dawson's Book Shop, Los Angeles.
- Engelhardt, Zephyrin, O.F.M. Missions and Missionaries, Volume One|San Francisco: The James H. Barry Co., 1908.
- Jackson, Robert H. "Epidemic Disease and Population Decline in the Baja California Missions, 1697-1834" Southern California Quarterly 63:308-346|
- Mathes, W. Michael. 1974. Californiana III: documentos para la historia de la transformación colonizadora de California, 1679-1686. José Porrúa Turanzas, Madrid.
- Van Handel, Robert Michael. "The Jesuit and Franciscan Missions in Baja California." M.A. thesis. University of California, Santa Barbara, 1991.
- Vernon, Edward W. 2002. Las Misiones Antiguas: The Spanish Missions of Baja California, 1683-1855. Viejo Press, Santa Barbara, California.
External links
- www.ca-missions.org — The official website of the California Mission Studies Association, a good source of accurate, peer-reviewed information on Mission Era history with an extensive links page.
- California Missions article at The Catholic Encyclopedia
- Missions of Baja California and Baja California Sur
- Google earth map of the Baja missions
- Reseña histórica de las misiones de Baja California by Dr. W. Michael Mathes (in Spanish)