Trust Territory of Somaliland
The Trust Territory of Somaliland, officially the "Trust Territory of Somaliland under Italian administration"[1] (in Italian: Amministrazione fiduciaria italiana della Somalia) was a United Nations Trust Territory situated in present-day Somalia. Its capital was Mogadishu[2] and was administered by Italy from 1950 to 1960, following the dissolution of the former British Military Administration.
Trust Territory of Somaliland under Italian Administration Amministrazione fiduciaria italiana della Somalia "Dhulka Soomaaliyeed oo hoos yimaada Maamulka Talyaaniga" إقليم صوماليلاند تحت الوصاية للإدارة الإيطالية | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950–1960 | |||||||||
 Flag
 Coat of arms
| |||||||||
Anthem: National Anthem of Italy | |||||||||
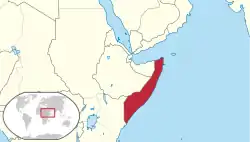 Location of the Trust Territory of Somaliland. | |||||||||
| Status | United Nations Trust Territory | ||||||||
| Capital | Mogadishu | ||||||||
| Common languages | Italian (official) · Somali · Arabic | ||||||||
| Religion | Islam | ||||||||
| Administrator | |||||||||
• 1950–1953 | Giovanni Fornari | ||||||||
• 1953–1957 | Enrico Martino | ||||||||
• 1957–1958 | Enrico Anzillotti | ||||||||
• 1958–1960 | Mario di Stefano | ||||||||
| Prime Minister | |||||||||
• 1956–1960 | Abdullahi Issa | ||||||||
| Historical era | Cold War | ||||||||
• Established | 1 April 1950 | ||||||||
• Independence | 1 July 1960 | ||||||||
| Currency | somalo | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Somalia |
|
|
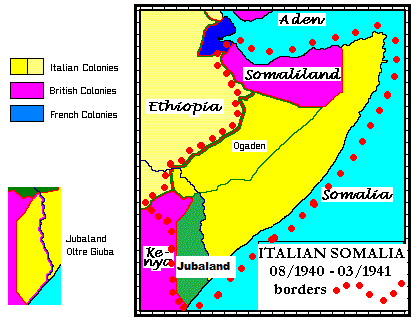
Italian Somaliland
In 1941, Italian Somaliland was occupied by British and South African troops as part of the East African Campaign of World War II. The British continued to administer the area until 1 April 1950. On that date Italian Somaliland was made a Trust Territory, as stipulated by United Nations General Assembly Resolution 289 of 21 November 1949.[3] This was the only case of a trusteeship being assigned to a defeated Second World War power.[4]
During the 1950s, with UN aid money pouring in and the presence of experienced Italian administrators who had come to see the region as their home, infrastructural and educational development blossomed in the region. The decade passed relatively without incident, and was marked by positive growth in virtually all aspects of local life.
Indro Montanelli, a defender of Italian colonial rule,[5] wrote in the late 1990s (when Somalia was devastated by civil war) that the ten years of Italian Trusteeship were the Golden age of Somalia: the population nearly doubled, illiteracy was reduced by 60%, malnutrition in the rural areas disappeared, the economy soared to the same level of the most developed African countries and there was complete integration in religious and social-political matters between all Somalia inhabitants.[6]
The conditional return of Italian administration to southern Somalia gave the new trust territory several unique advantages compared with other African colonies. To the extent that Italy held the territory by UN mandate, the trusteeship provisions gave the Somalis the opportunity to gain experience in political education and self-government. These were advantages that British Somaliland, which was to be incorporated into the new Somali state, did not have. Although in the 1950s British colonial officials attempted, through various development efforts, to make up for past neglect, the protectorate stagnated. The disparity between the two territories in economic development and political experience would cause serious difficulties when it came time to integrate the two parts.[7]
In 1954, the Italian government established post-secondary institutions of law, economics and social studies in Mogadishu, the territory's capital. These institutions were satellites of the University of Rome, which provided all the instruction material, faculty and administration.
In 1960, the Trust Territory of Somaliland (the former Italian Somaliland) became independent, following in the footsteps of the briefly extant State of Somaliland (the former British Somaliland) which had gained independence five days earlier, with Mohamed Haji Ibrahim Egal as Prime Minister on June 26, 1960.[8] On July 1, 1960, the two territories united as planned to form the Somali Republic.[9] A new government was formed with Haji Bashir Ismail Yusuf as the first President of the Somali National Assembly, Abdullahi Issa as Prime Minister, Aden Abdullah Osman Daar as President and Abdirashid Ali Shermarke as Prime Minister, later to become President (from 1967 to 1969). On June 20, 1961, through a popular referendum, the Somali people ratified a new constitution first drafted in 1960.[10]
Language
Italian was an official language in Italian Somaliland during the Fiduciary Mandate as well as during the first years of independence. Somali was also an official language. Arabic was also widely spoken. Somali was then written using an Arabic script, not adopting the Latin script until 1972.
Anthem, flag and coat of arms
The Somali national anthem from 1950 to 1960 was "Il Canto degli Italiani" ("The Song of the Italians"),[11] the same as the Italian metropole.
From 1 April 1950 to 21 October 1954, the Trusteeship used solely the flag of Italy. From 21 October until independence, the Italian flag was accompanied by that of the UN. On 1 July 1960, Independence Day of Somalia, the Italian and UN flags were lowered to the tune of Il Canto degli Italiani at the Governor's Palace in Mogadishu to symbolize the end of Italian control over the region.
The Italian coat of arms was solely used until 21 October 1954, when both the Italian and Somali coat of arms were used jointly. After independence, the Italian coat of arms ceased its official status.
Currency
The currency of the Trusteeship was the somalo. It was coined by the Bank of Italy for the Cassa per la Circolazione Monetaria della Somalia (the Trusteeship's central bank). The Somalo was replaced in 1962 with the Somali shilling.
Governors

- Giovanni Fornari (1 April 1950 to 23 February 1953)
- Enrico Martino (23 February 1953 to 1957)
- Enrico Anzillotti (1957 to 24 July 1958)
- Mario di Stefano (24 July 1958 to 1 July 1960)
Notes
- "(IX). Question of the frontier between the Trust Territory of Somaliland under Italian administration and Ethiopia" (PDF). UN General Assembly. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- "Italian Mogadiscio". Dadfeatured. May 19, 2018.
- "Question of the liquidation of the former Italian colonies - Resolution 289 (IV), UNGA, 21 November 1949". United Nations General Assembly. Retrieved 1 October 2020.
- Federico Senatore (2016). Dovunque mi trovi, parte del mondo. Storia di Augusto, da Montecassino al Protettorato somalo con Vademecum della Somalia (Edizioni Efesto ed.). p. 121. (in Italian)
- Avagliano, Mario; Palmieri, Marco (2013). Di pura razza italiana. L'Italia "ariana" di fronte alle leggi razziali. Milano: Baldini & Castoldi. ISBN 9788868656218.
- Indro Montanelli. "La Stanza di Montanelli" ("Montanelli’s Room"). He was Chief letters editor of newspaper Corriere della Sera
- Trusteeship and Protectorate: The Road to Independence of Somalia
- Encyclopædia Britannica, The New Encyclopædia Britannica, (Encyclopædia Britannica: 2002), p.835
- Britannica Concise Encyclopedia. Clarendon Press. 2008. p. 1783.
- Greystone Press Staff, The Illustrated Library of The World and Its Peoples: Africa, North and East, (Greystone Press: 1967), p.338
- Also called "Fratelli d'Italia" ("Brothers of Italy")
External links
- Video of the last day of Italian presence in Mogadishu, when was declared the Somali independence in July 1960 (in Italian)
- "L'Onu e l'Amministrazione fiduciaria italiana in Somalia" by Antonio Morone. (in Italian)
- Video on June 1950 of Somalia's visit by an Italian representative of the Thusteeship